Workup of Lymphoma case
Workup of Lymphoma case
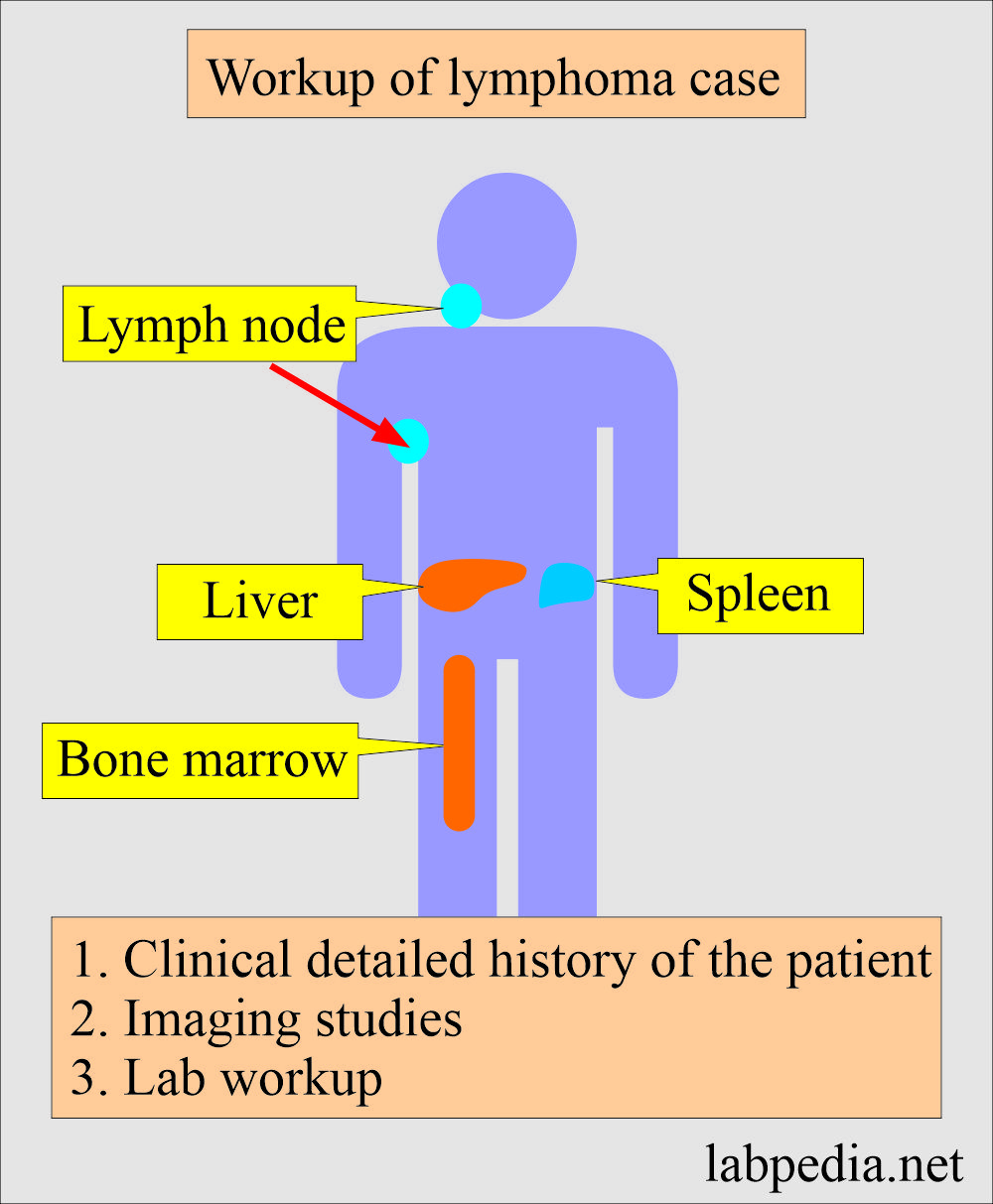
- Lymphoma cases, either non-Hodgkins or Hodgkin’s, need the following workup.
How will you do the clinical Examination?
- Carefully examine the lymph node, spleen, liver, etc.
- Lymph nodes are painless and persistently increasing in size.
- Fever >38 C.
- Night sweating.
- Weight loss over the last 6 months.
- Fatigue, pruritus, alcohol-induced pain in lymph nodes (Hodgkin’s lymphoma).
- Extranodal symptoms and involvement of CNS, bone marrow, and GITract.
- How will you perform a physical examination?
- Examine the lymph nodes.
- Check for liver and spleen.
- Check for signs of anemia.
- Check for CNS involvement.
What will you order for a blood workup?
- Total leukocytes (TLC).
- Differential leukocyte count (DLC). Peripheral blood smears may show abnormal lymphocytes.
- Hemoglobin.
- Advise the Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and CRP. They are raised in Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Platelet count.
What is the purpose of a Bipedal lymphangiogram.?
- This is done for iliac and para-aortic lymph nodes.
What is the purpose of staging laparotomy?
- Laparoscopy can be done for splenectomy, liver biopsy, abdominal lymph nodes, and bone marrow biopsy.
- Nowadays, it is not done because of improved imaging.
What Biochemical tests are needed?
- Liver function test (LFT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are needed.
- Advise comprehensive metabolic panel.
- Advise uric acid.
- Advise calcium that is raised in bone involvement.
What is the purpose of ultrasonography?
- CT scan and MRI are advised for further workup.
What is the purpose of liver and spleen scans?
- 25% positive in the nonpalpable spleen by the pathologist.
- 50% negative in the palpable spleen by the pathologist.
What is the purpose of Bone Marrow in lymphoma cases?
- 9% to 29% may show as aggregates or diffuse infiltrates of lymphoma cells.
- 25% positive in the nonpalpable spleen by the pathologist.
- 50% negative in the palpable spleen by the pathologist.
- Now, because of modern advances in medical science, staging laparotomy is not needed.
How will you summarize the Lymphoma case workup?
- Clinical evaluation of the patient:
- A thorough physical examination is needed.
- Take the detailed history of the patient.
- Ask for any other disease present in these patients.
- Imaging studies:
- Imaging is very important in finding the spread of diseases.
- Imaging studies avoid staging laparotomy.
- Various imaging techniques are:
- CT scan (Computed tomography). It will evaluate the lymphadenopathy and any other organs involved.
- PET scan (positron emission tomography): This study involved injecting radioactive material. It detects the involvement of the lymph nodes throughout the body.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) helps detect brain and spinal cord lymphoma.
- X-rays are done on specific areas of the body, especially the chest, for nodal and pulmonary disease.
- Lab workup:
- Advise complete blood count.
- Advise liver and kidney function tests.
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) helps as a marker and gives a prognosis.
- Advise the tumor marker for patient follow-up.
- Bone marrow examination for the infiltrate of the lymphoma.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of LDH?
Question 2: What is the significance of ESR and CRP?