Uric acid Quantitative (24-Hours Urine), Uricosuria
Uric acid Quantitative (24-hours urine)
What sample is needed for Uric acid Quantitative (24-hour urine)
- This test is done in the urine.
- Collect urine for 24 hours.
- Discard the first sample (empty the urinary bladder), and then collect all urine samples until 24 hours have passed.
- Also, add the last sample (empty the urinary bladder) to the container.
- Do not refrigerate the urine; add NaOH (10 mL) to keep the urine alkaline.
- If there is no bacterial growth, the urine will be stable at 22 °C to 24 °C for three days.
What are the indications for Uric acid Quantitative (24-hour urine)
- To find if kidney stones are due to high uric acid levels in the body.
- Evaluates uric acid metabolism in gout.
It helps to evaluate the effect of uricosuric drugs.
What are the Precautions for Uric acid Quantitative (24-hour urine)?
- Some drugs increase the uric acid level like:
- Salicylates.
- Diuretics.
- Vitamin C.
- Cytotoxic drugs are used to treat cancers (leukemias and lymphomas).
- Strenuous exercise.
- A diet high in purines.
- Allopurinol decreases the uric acid level.
How would you discuss the pathophysiology of Uric Acid?
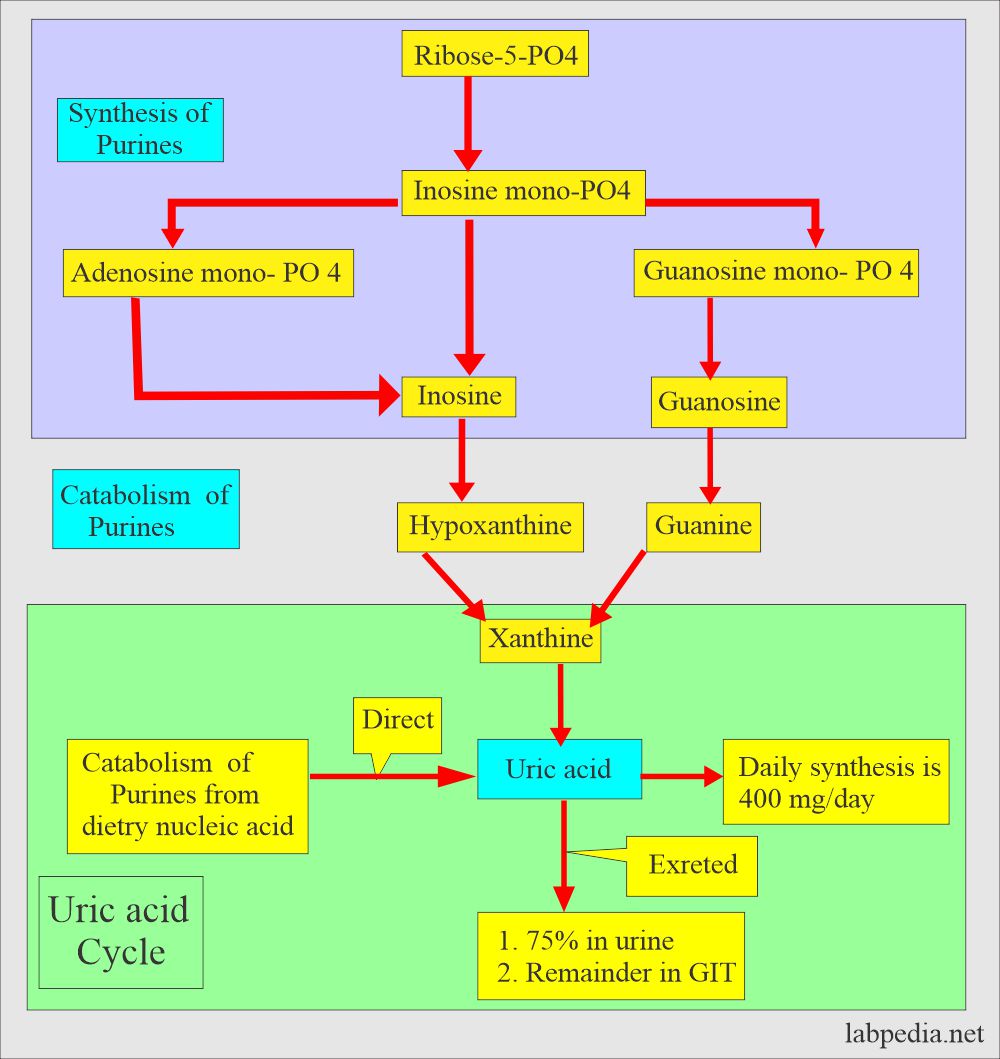
- Uric acid is the major product of catabolism of:
- Purine Nucleosides.
- Adenosine.
- Guanosine.
- Nucleic acid precursors are purines, adenosine, and guanosine.
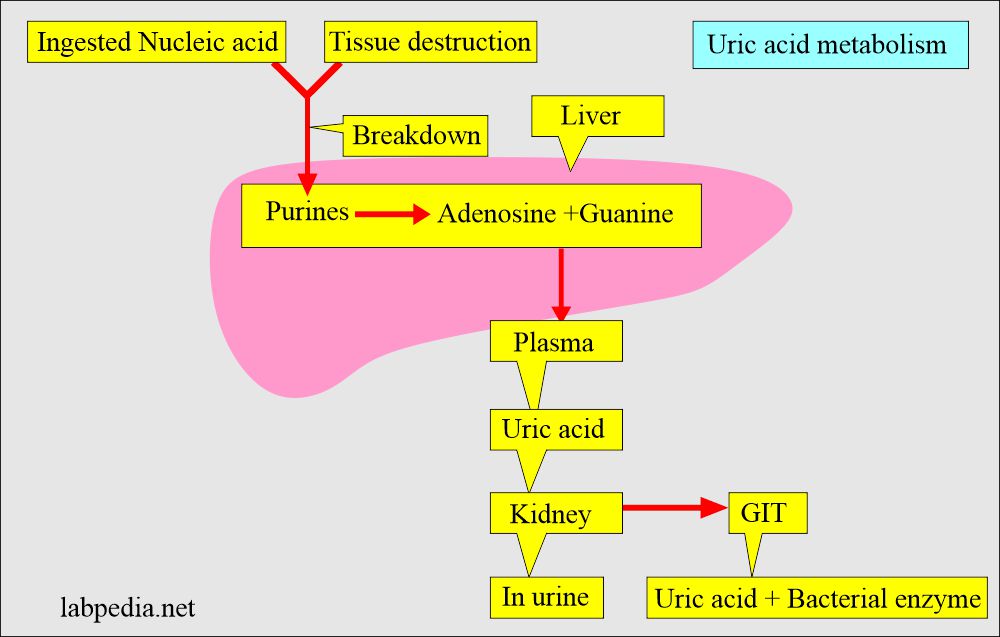
- Dietary nucleic acid forms purines, directly converted to uric acid.
- Endogenous nucleic acid forms purines; these are excreted as uric acid into the urine.
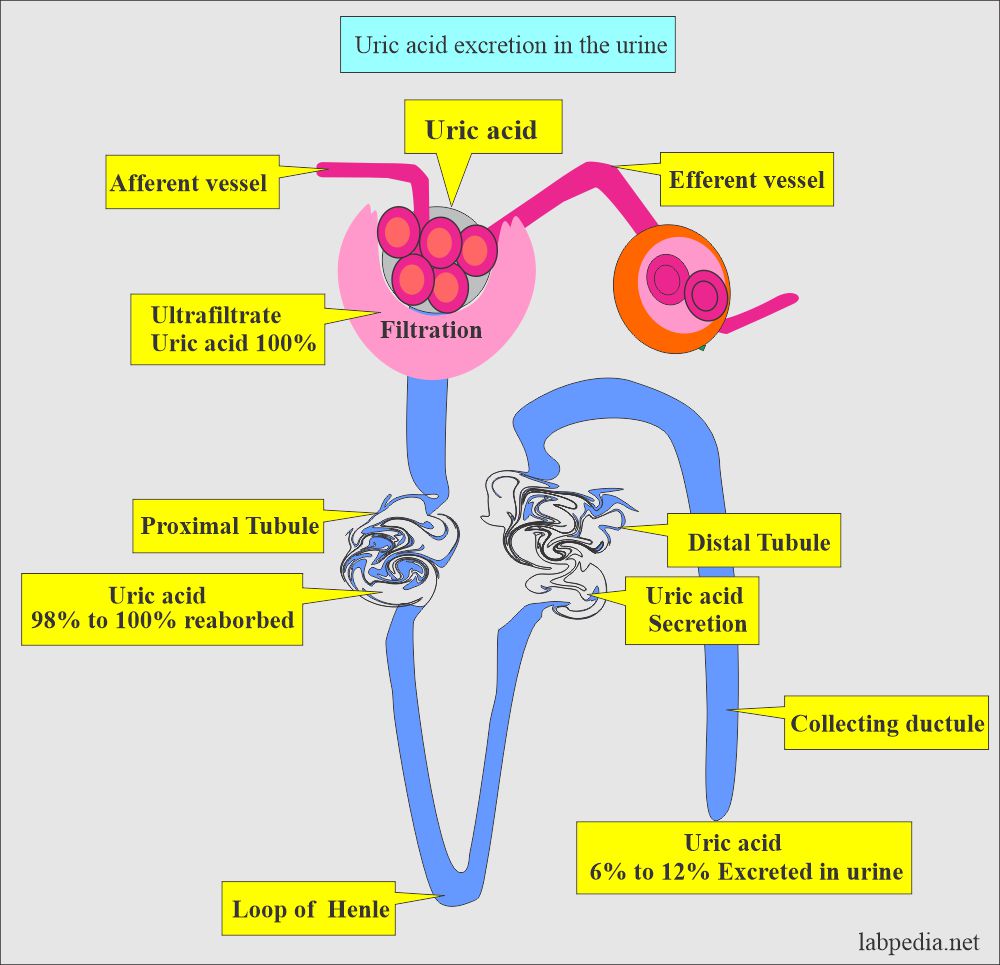
- Uric acid is readily filtered through the glomerulus.
- Uric acid is absorbed + excreted by the kidney; only 6% to 12% of filtrate is uric acid in urine.
- Most of the uric acid is excreted by the kidney and a small amount by the intestinal tract.
- Normally, bacteria degrade 1/3 of the uric acid formed in the intestine.
- Excess of uric acid is related to dietary intake of purines or endogenous uric acid production.
- Uric acid is more soluble at a pH of >5.75.
- Uric acid is undissociated at a pH of <5.75.
- Most uric acid is excreted in the urine, and the rest passes out in the stool.
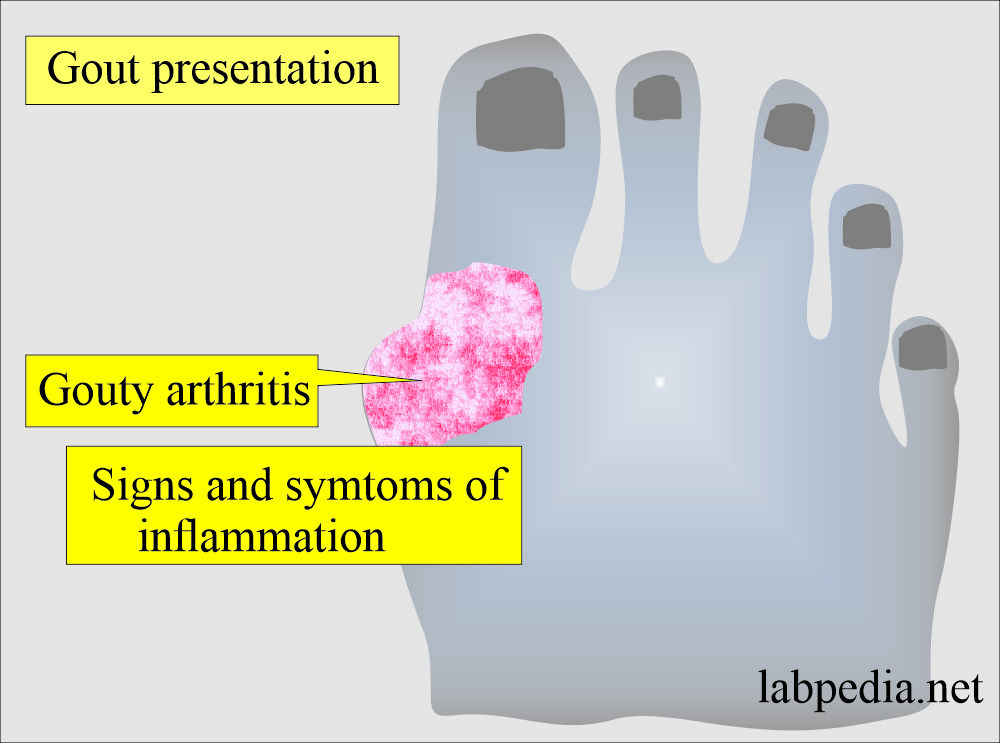
Does clinically, hyperuricemia may lead to gout?
- This is also called gouty arthritis.
- It appears in common sites in large toes, feet, ankles, knees, and elbows.
- There is severe pain in the joints.
- There is stiffness in the joints.
- There are limited movements of the joints.
- Joints are deformed.
- There are redness and swelling of the joints.
- There may be uric acid deposits called gouty tophi.
- There is a higher chance of the formation of uric renal stones.
What is the normal Uric acid in urine for 24 hours?
Source 1
| Diet | mg/day Uric acid (24 hours) |
The average on a
|
|
| Purine free diet | |
|
|
|
|
| Low purine | |
|
|
|
|
| High purine diet | |
|
|
Source 2
- Urine = 250 to 750 mg/24 hours or
- 1.48 to 4.43 mmol/24 hours
Another source
- Men = 250 to 800 mg /24 hours
- Women = 250 to 750 mg /24 hours
- With a purine-free diet = <400 mg / 24 hours.
- With a high purine diet = <1000 mg / 24 hours.
What are the causes of raised urine uric acid levels (Uricosuria)?
- Gout.
- Renal calculi.
- Cancers (widespread disease).
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia.
- Multiple myelomas.
- Viral hepatitis.
- High–purine diet.
- Wilson’s disease.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Polycythemia vera.
What are the causes of decreased urine uric acid levels?
- Long-term alcohol abuse.
- Chronic glomerulonephritis (chronic kidney disease).
- Lead poisoning.
- Xanthinuria.
- Folic acid deficiency.
- Cytotoxic drugs.
- Eclampsia.
Acidosis (ketotic or lactic).
Normal urine picture:
| Physical features | Chemical features | Microscopic findings |
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: At what pH of urine is uric acid soluble?
Question 2: What is the uric acid major product of catabolism?

there is no way how the calculation done or no guidance for that
There is a slight increase in the SGPT. Please check your viral profile. If negative, take more fruits and check SGPT/SGOT after one month. Oral contraceptives may be the cause.
I have not written the methodology because it varies from different kits.
I have upgraded the topic; now, please see it.
https://labpedia.net/urine-uric-acid-quantitative-24-hrs-urine-sample-uricosuria/