Urine Bilirubin, Bilirubinuria
Urine Bilirubin (Bilirubinuria)
What sample is needed for urine bilirubin?
- The sample is urine.
- A random sample can be taken.
What are the precautions for urine bilirubin?
- A fresh urine sample is needed.
- Store at 2 to 8 °C for no longer than 24 hours.
- Even at room temperature, it converts into biliverdin.
- Avoid urine to light. Avoid daylight or fluorescent light.
- Light converts bilirubin to biliverdin, which is not detected by routine methodology.
- Exposure to light urine will decrease bilirubin.
What are the reasons for false positives?
- A false positive result is seen in the metabolites of drugs like phenazopyridine.
- The substances that color the urine red or turn red in the acid medium are:
- Chlorpromazine.
- Phenothiazine.
- Indol.
- Pyridium
- The substances that color the urine red or turn red in the acid medium are:
What are the reasons for a negative urine bilirubin?
- False-negative results are seen:
- With the ascorbic acid intake.
- Oxidation of bilirubin to biliverdin.
- Increased nitrite concentration.
- Hydrolyzation of bilirubin diglucuronide to free bilirubin.
What are the Indications for urine bilirubin?
- Diagnose hepatitis.
- Diagnose any liver damage.
- Monitor the treatment of hepatitis.
How will you define urine bilirubin?
- The conjugated bilirubin is excreted from the kidneys and appears in the urine.
- Unconjugated bilirubin can not pass the glomerular filtration, so it is not in the urine.
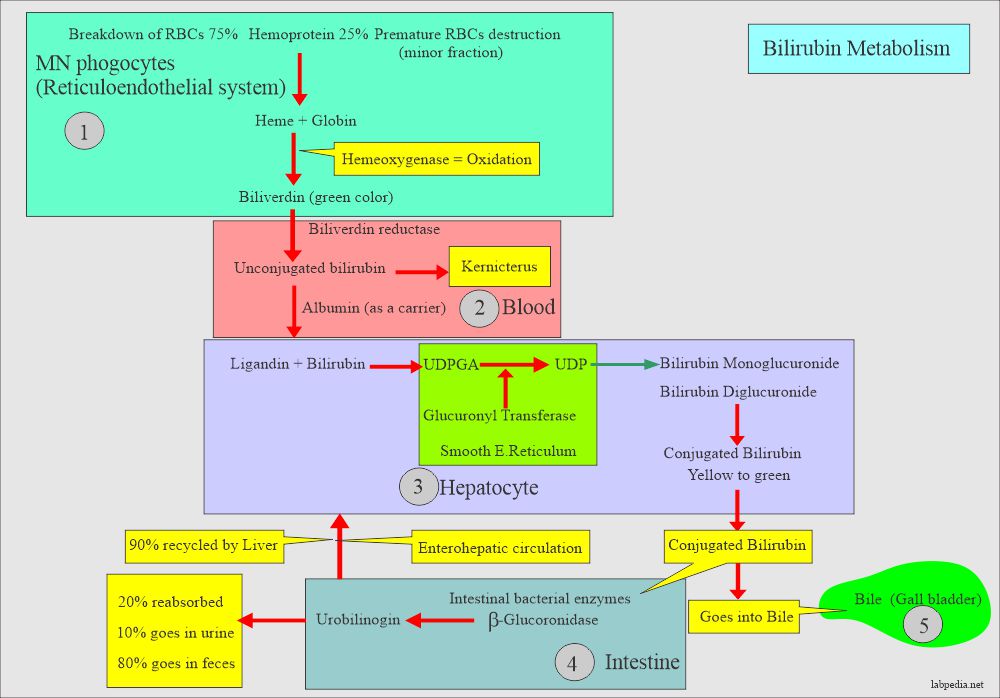
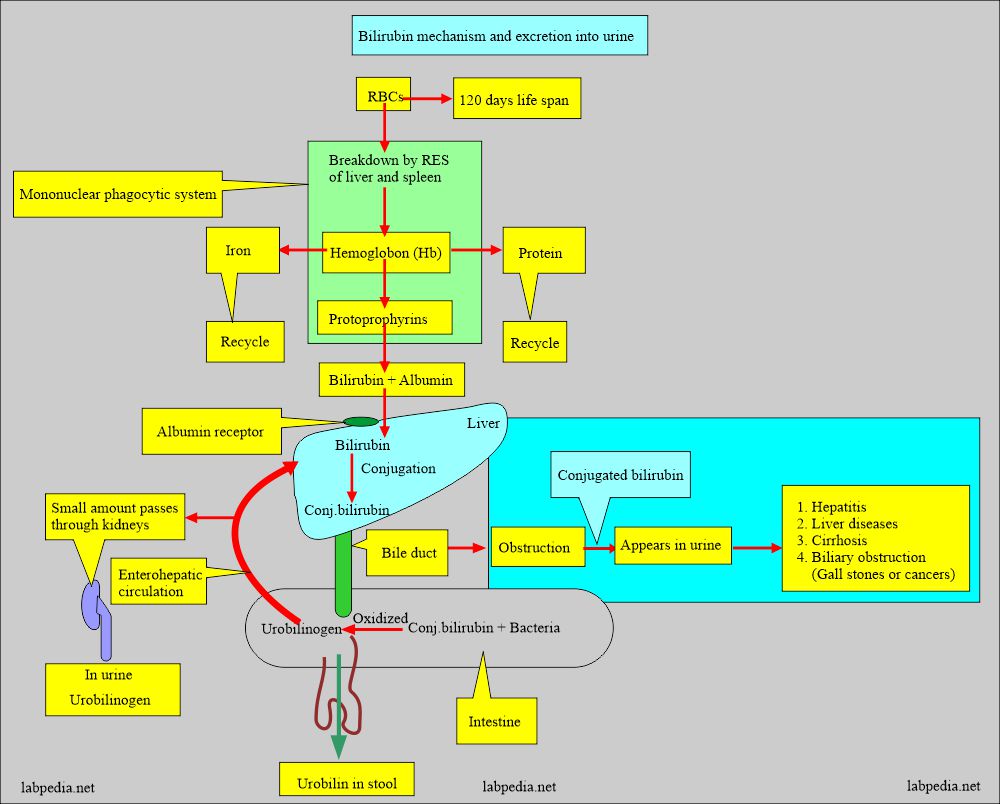
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of bilirubin metabolism?
- A detectable amount of bilirubin is not found in the urine.
- The breakdown of hemoglobin leads to bilirubin formation, which goes to the liver.
- From the liver, it is excreted into the bile.
- Excretion of bilirubin is seen in obstructive jaundice and not in hemolytic jaundice unless there is liver damage.
- The diagram explains bilirubin metabolism and excretion of bilirubin in the urine.
What is the Clinical significance of urine bilirubin?
- Urine bilirubin is the early sign of:
- Hepatocellular disease.
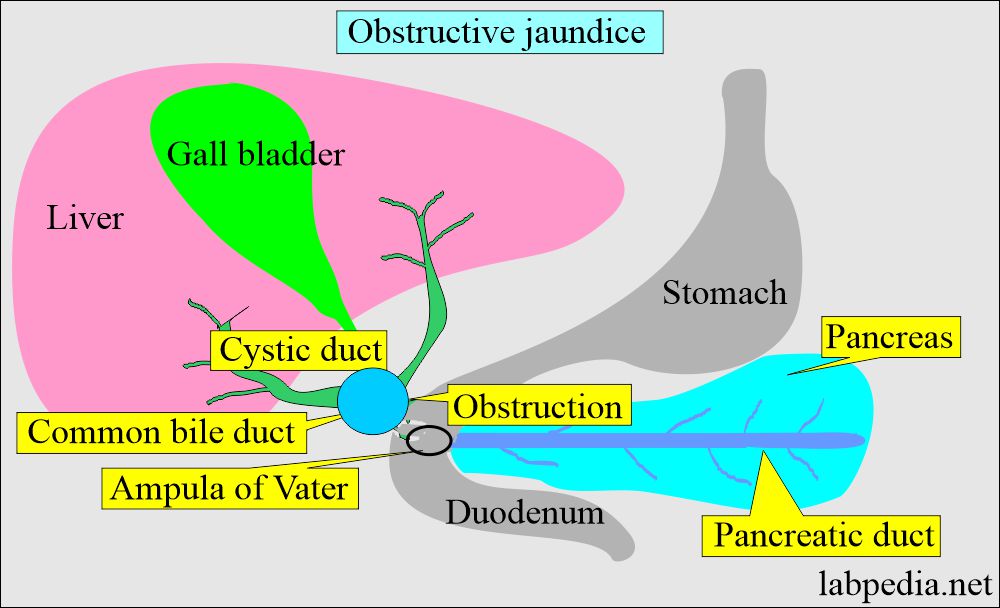
- Intra or extrahepatic biliary obstruction.
- Bilirubin appears in the urine before other signs of hepatitis appear.
- Bilirubin’s presence or absence in the urine is helpful for clinical jaundice.
- Bilirubin is the major component of bile.
- If there is an obstruction to the bile, that will lead to conjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- Conjugated bilirubin is water-soluble, so it will appear in the urine.
- The presence of bilirubin in urine indicates defects after conjugation and defects in excretion.
- Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment in the bile produced by the liver.
- Bilirubin in urine color = dark yellow or orange.
- This test measures the amount of bilirubin excreted in the urine.
- The presence of bilirubin in the urine indicates jaundice.
What is the normal urine bilirubin?
- Normally, bilirubin is absent in the urine (0 to 0.02 mg/dL or 0 to 0.34 µmol/L).
- Even traces indicate liver disease like hepatitis.
How will you check urine bilirubin?
The following tests are used to check bilirubin in the urine:
- Fouchet’s test.
- Strip method.
- Tablet method.
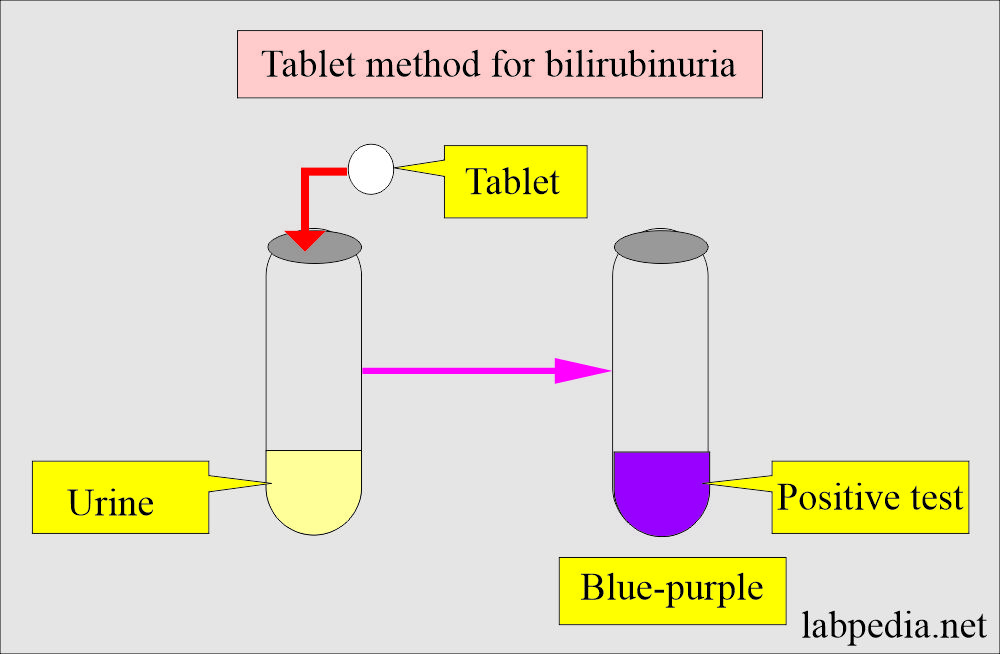
How will you perform the tablet method?
- In this test, bilirubin forms stable diazonium salt that produces blue-purple azobilirubin.
- This reaction is specific to bilirubin.
- Read the result after 60 seconds.
- Moisture will deteriorate the reagents.
- Always use a white dry tablet.
- It detects the urine bilirubin level as low as 0.5 mg/dL.
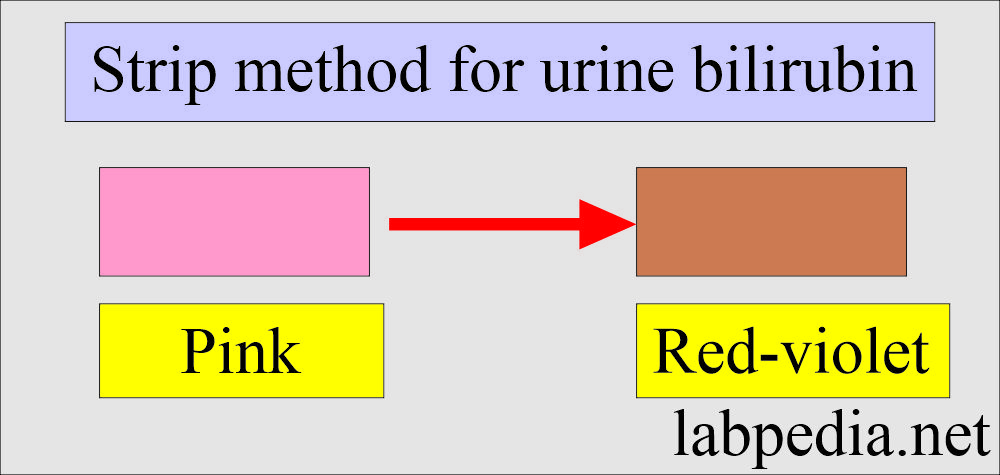
How will you perform the Strip method?
- These are mostly available as multiple test strips.
- This reaction depends upon the diazo reaction. These strips are impregnated with the diazo reagent.
- This method detects a concentration of 0.5 mg/dL or greater.
- Insert the strip in the urine no longer than one second.
- After 60 seconds, the Diazo reagent reacts with bilirubin at an acidic pH.
- A pink to red-violet color is produced.
- The intensity of the color depends upon the concentration of the bilirubin in the urine.
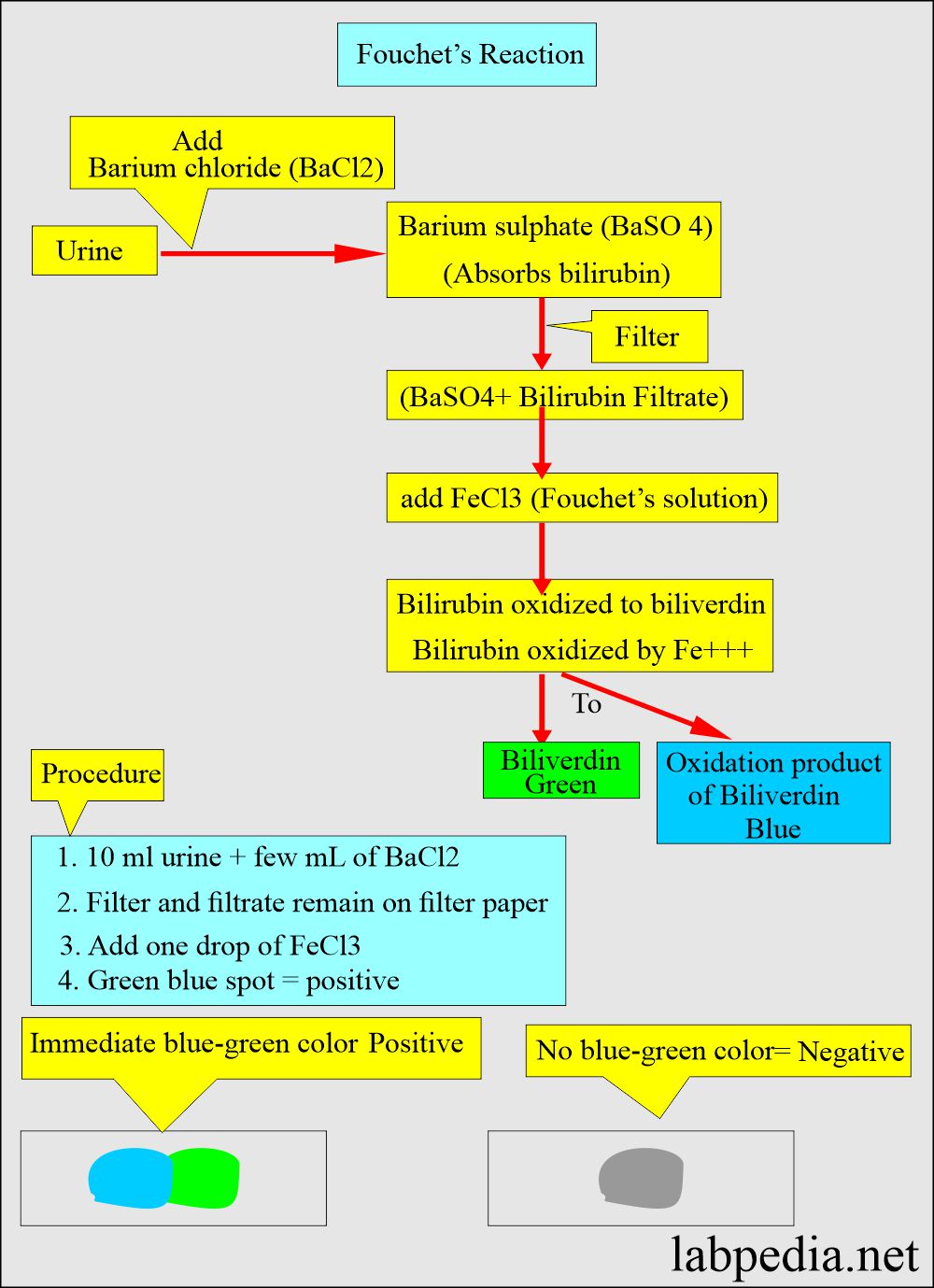
How will you perform the Fouchet’s or Ferric chloride reaction?
- Add urine to barium chloride, forming a barium sulfate precipitate containing bilirubin.
- Barium sulfate + bilirubin filter and get the precipitate.
- Add ferric chloride (Fouchet’s solution) to the above precipitate.
- Bilirubin oxidized to biliverdin, which gives a green-blue color.
How will you compare Fouchet’s and Diazo’s reaction?
| Characteristics | Fouchet’s reaction (FeCl3) | Diazo reaction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the positivity of various strip detection levels?
| Type of the strip | The detection level of bilirubin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of increased urine bilirubin?
- Hepatitis and liver diseases are caused by infection or exposure to toxic agents ( cirrhosis ).
- Obstructive biliary tract disease.
- Liver or biliary tract tumor.
- Septicemia.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Gallstones.
- Metastatic tumor in the liver.
- Drugs
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Rotor syndrome.
What is the differential diagnosis of Urine Bilirubin/urobilinogen?
| Etiology | Urine bilirubin | Urine urobilinogen |
| Normal | Negative | Positive/Negative (<1 Ehrlich unit) |
| Obstruction | Positive (Increased) | Usually absent |
| Hemolysis | Absent | Positive (Increased) |
| Hepatitis (liver injury) | Positive (or increased) | Increased |
- Urine bilirubin is negative in hemolytic disease.
Bilirubin (urine and blood) in various types of jaundice:
| Type of the jaundice | Etiology | Urine bilirubin | Urine urobilinogen | Blood bilirubin | Fecal appearance |
| Hemolytic or prehepatic |
|
Negative (Usually absent) | Increased | Raised | Dark brown |
| Hepatic or hepatocellular |
|
Increased (variable) (+ or -) |
Increased (++) |
An increased, variable amount | Normal or pale |
| Post-hepatic or obstructive |
|
Increased (+++) | Absent (or very low) |
|
Clay-colored, acholic |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can unconjugated bilirubin pass through the kidneys?
Question 2: When urine bilirubin appears in the urine in jaundice?

I think there is a mistake in the table comparing bilirubin and urobilinogen in the urine.
in obstructive jaundice, the urobilinogen should be absent/reduced, not increased. Whereas in hemolytic anemia, the urobilinogen is increased, not negative
Table corrected, thanks for the comment.
1) I know that conjugated bilirubin is excreted in the urine, resulting in bilirubinuria, but why is the color of bilirubin urine dark amber or cola-colored while conjugated bilirubin is yellow in color?
2) Urobilinogen is oxidized in the kidney and changed to urobilin, but does conjugated bilirubin undergo a similar change and change color?
3) In the figure, conjugated bilirubin is shown from yellow to green, but the color of the reagent is yellow. Bile is also yellow if there is no infection, but is it correct that conjugated bilirubin is green?
4) Babies with elevated direct bilirubin appear greenish-yellow. If conjugated bilirubin is yellow, please also tell me the reason for the greenish-yellow color, such as whether biliverdin in the blood increases and is deposited on the skin, or whether biliverdin is produced in the skin.
I am sending you some google search material.
Biliverdin (from the Latin for green bile) is a green tetrapyrrolic bile pigment and is a product of heme catabolism. It is the pigment responsible for a greenish color sometimes seen in bruises.
However, biliverdin deposition in the skin is relatively uncommon compared to bilirubin.
1) I know that conjugated bilirubin is excreted in the urine, resulting in bilirubinuria, but why is the color of bilirubin urine dark amber or cola-colored while conjugated bilirubin is yellow in color?
2) Urobilinogen is oxidized in the kidney and changed to urobilin, but does conjugated bilirubin undergo a similar change and change color?
3) In the figure, conjugated bilirubin is shown from yellow to green, but the color of the reagent is yellow. Bile is also yellow if there is no infection, but is it correct that conjugated bilirubin is green?
4) Babies with elevated direct bilirubin appear greenish-yellow. If conjugated bilirubin is yellow, please also tell me the reason for the greenish-yellow color, such as whether biliverdin in the blood increases and is deposited on the skin, or whether biliverdin is produced in the skin.
No doubt biliverdin deposition in the skin is relatively uncommon in the skin. But there are reports that that biliverdin can deposit
in the skin.