Urine amylase (Amylasuria), Amylase/Creatinine clearance ratio
Urine amylase (Amylasuria)
What sample is needed for Urine amylase?
- The sample is urine.
- Can obtain random 2 hours urine sample.
- Amylase is unstable in acidic urine, so adjust pH to the alkaline range.
- Store urine at 4 °C.
- You can also collect 24-hour samples. Discard the first sample and then collect the rest of the 24-hour samples in the container, including the last sample.
- Also, venous blood is collected to make the serum amylase level.
- Don’t eat or drink for at least 2 hours for blood tests.
What are the precautions for Urine amylase?
- Urine amylase is unstable in acidic urine. Acid urine decreases amylase levels.
- Adjust the pH to 7.0.
- Refrigerate the urine.
- Avoid urine contamination by stool.
- Dexamethasone, furosemide, methanol, ethanol, thiazide, salicylates, chloride salts, and meperidine are medications that increase the result.
- Medication that will decrease the level is citrate.
What are the Indications for urine Amylase?
- This test tells about pancreatic dysfunction.
- It differentiates acute pancreatitis from other:
- Abdominal pain.
- Epigastric discomfort.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- It diagnoses pancreatitis in the late stages when the blood amylase is normal.
- Raised in acute pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, and peptic ulcer.
How will you define amylase?
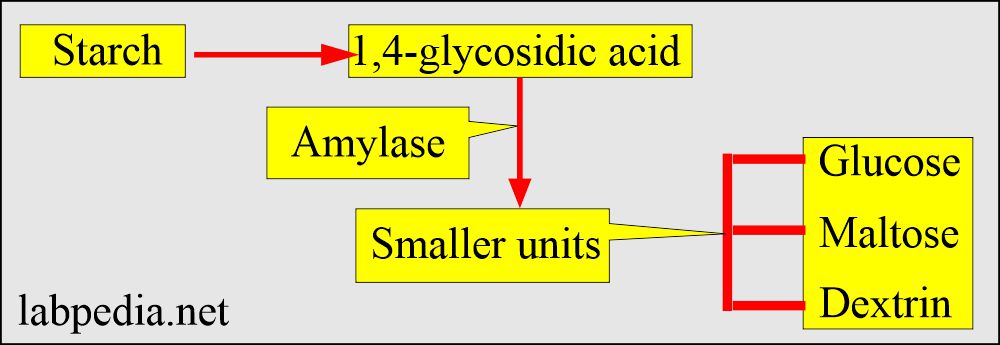
- The amylase enzyme changes starch to sugar.
- Amylase is described into two forms:
- α-Amylase found in humans.
- β-Amylase is found in plants and bacteria.
What is the action of the amylase?
- Amylase enzymes change starch into sugars.
- Large polysaccharide molecules are broken into smaller dextrin, maltose, and glucose units.
- Salivary glands have the greatest concentration, and they will convert starch into sugars (Hydrolysis of starch) while food is in the mouth and esophagus.
- Normally, a low level of amylase is found in the blood and excreted in a small amount in the urine.
- When the pancreas and salivary glands are inflamed, more enzymes enter the blood, and more amylase is excreted in the urine.
- In the case of pancreatitis, the amylase level in the blood is raised for a short time, while the urine level remains for several days.
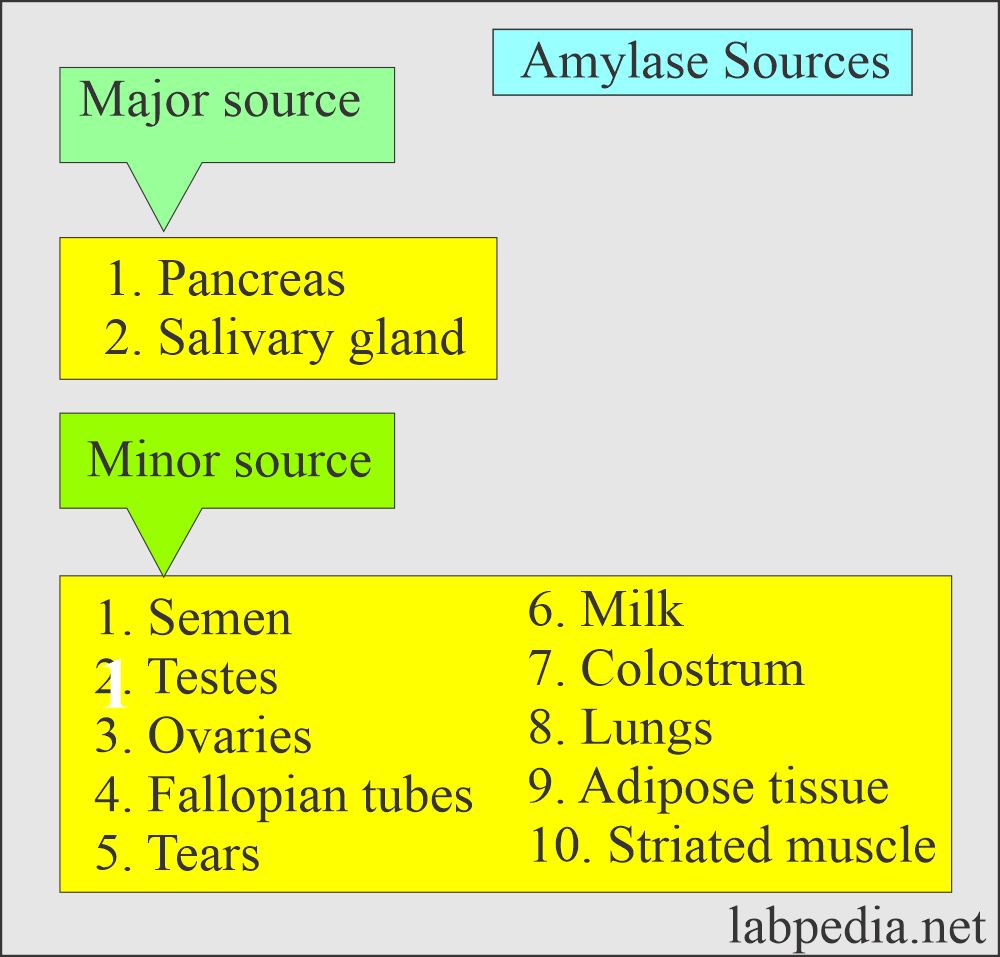
What are the sites where amylase is formed?
- Following are the sites where amylase is formed:
- Salivary glands. These glands have the greatest concentration.
- Pancreas.
- Liver (little or no amylase activity).
- Fallopian tubes.
What are the sites where Amylase activity is found?
- Semen, testes.
- Ovaries, fallopian tubes.
- Striated muscles.
- Lungs.
- Adipose tissue.
- Colostrum and milk.
- The tears.
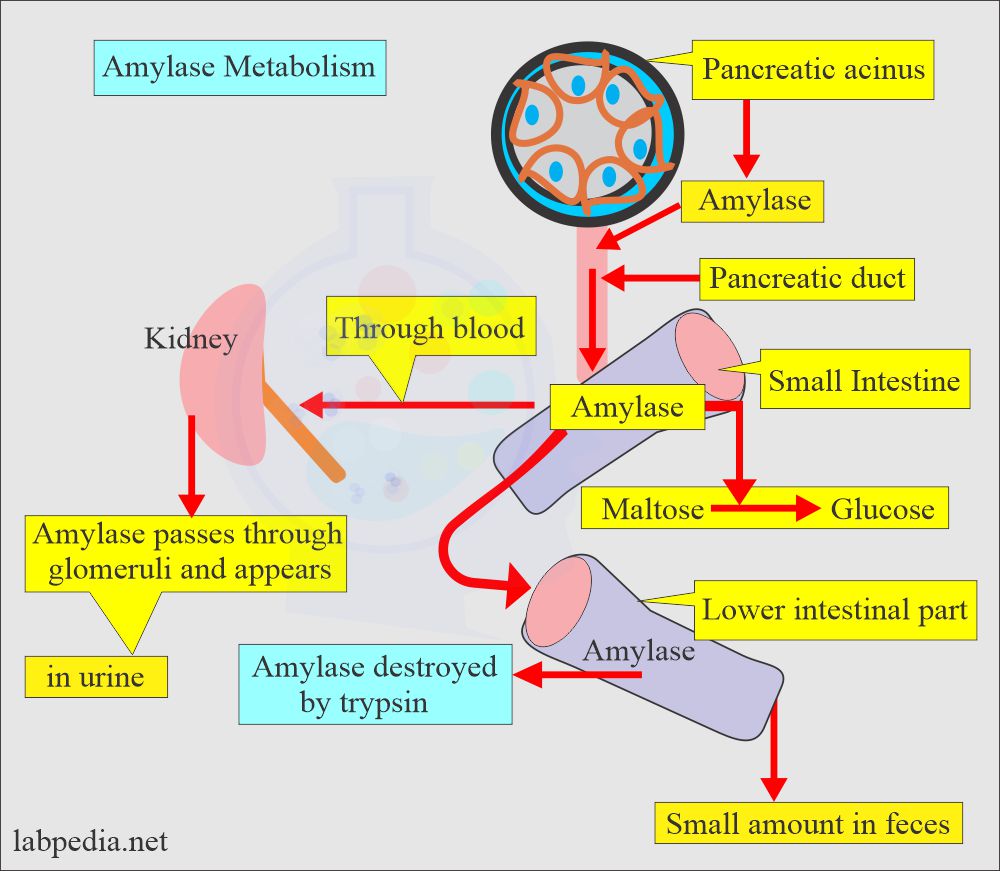
How will be the secretion of amylase?
- Amylase from pancreatic acini goes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum.
- Once in the intestine, it converts carbohydrates into simple sugars.
- Amylase activity in the serum and urine originates from pancreatic and salivary glands.
How will be the excretion of amylase?
- An Amylase is a small unit that can pass through the glomeruli and is found in the urine.
- Urinary amylase clearance is increased in acute pancreatitis from normal to 3 folds.
- A value of >550 U/L has a sensitivity of 62% and 97%, specific for acute pancreatitis.
- In damage to the salivary glands or pancreas, more enzyme in the blood is excreted in the urine.
What are the changes in pancreatitis?
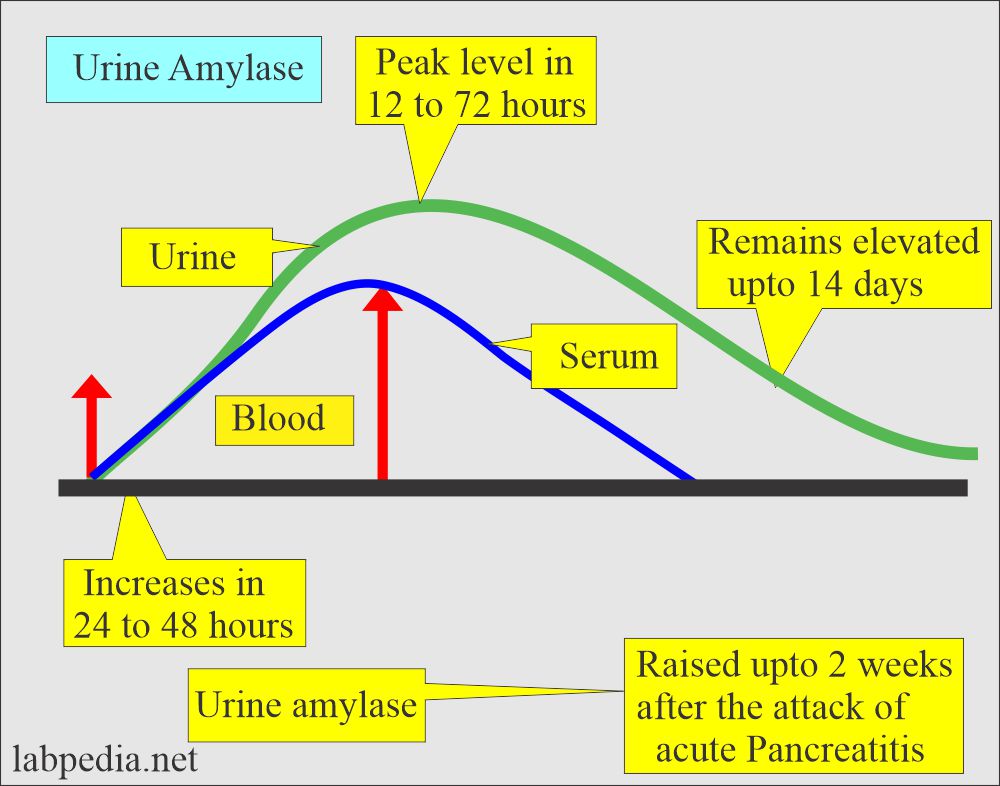
- A prolonged amylase level in urine may be raised until 5 to 7 days.
- The short-lived peak in blood, maybe 1 to 2 days, and return to normal.
- In acute pancreatitis, the Amylase picture is as follows:
- The initial rise of 2 to 12 hours.
- The peak level is 12 to 72 hours.
- The normal level reaches 3 to 4 days (short-lived peak).
- Urine amylase may remain elevated up to 2 weeks after the acute episode of acute pancreatitis.
How will you perform the urine amylase test?
- Urine amylase rises within 24 hours after serum amylase and generally remains elevated for 7 to 10 days.
- Various labs have used 1, 2, and 24-hour collections and have roughly equal success.
- The short period should be collected accurately.
What is the normal Urine Amylase level?
Source 1
- 1 to 17 U/hour
- 170 to 2000 U/L
- Abbott TDX = 5 to 27 U/h.
Source 2
- Up to 5000 Somogyi units /24 hours Or
- 6.5 to 48.1 units/hour.
Sources 4
- 2 hours sample = 2 to 34 U.
- 24-hour sample = 24 to 408 U.
- Another reference gives a normal range = 1 to 17 U/h.
- So, different kits have different ranges.
Another source
- <400 IU/L
Another source
- 0 to 275 units/L
Another source
- All ages = 10 to 80 amylase units/hour or 0 to 17 U/hour.
-
- 3 to 35 IU/hour
- 6 to 30 Wohlegemuth units/mL
- up to 6000 Somogy units/hour
- In pregnancy, it is raised.
-
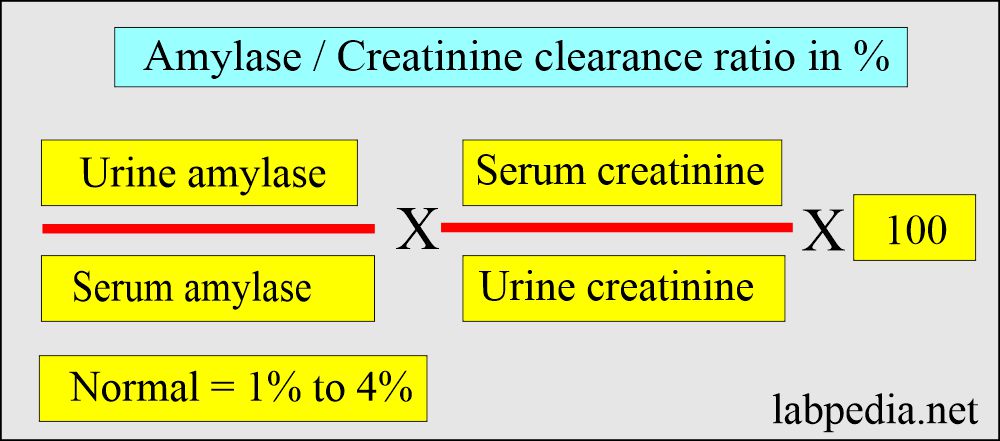
Amylase/creatinine clearance ratio:
What is the principle of amylase/creatinine clearance ratio?
- Amylase excretion in the urine depends upon renal function, so urinary amylase excretion correlates with creatinine clearance.
- In acute pancreatitis, amylase clearance is increased compared to creatinine in the urine.
- The amylase/creatinine clearance ratio depends upon this function of the kidneys.
What are the advantages of the amylase/creatinine clearance ratio?
- This is done on a random urine and serum sample instead of 2 or 24 hours.
- One urine and one serum sample were collected.
- The calculation of the amylase/creatine clearance ratio normally is 1% to 4%.
- The amylase/creatinine clearance ratio becomes abnormal after 1 to 2 days of the serum amylase level, and it will remain abnormal as long as urine amylase is present.
- The amylase/creatinine clearance ratio is more accurate than the serum amylase.
What are the disadvantages of the amylase/creatinine clearance ratio?
- The exact degree of specificity is still not established.
- This may be raised in some cases of diabetic ketoacidosis and burns.
- This may be normal in mild azotemia, but in severe azotemia, it is raised.
- Some authors believe that this has little value.
- The amylase/creatinine clearance ratio is decreased in macroamylasia.
- >5% amylase/creatinine ratio is diagnostic of pancreatitis.
What are the causes of increased urine Amylase levels?
- Acute Pancreatitis.
- Chronic relapsing pancreatitis.
- Penetrating peptic ulcer to the pancreas.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Parotitis (mumps) is called sialadenitis.
- Ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
- Pulmonary infarction.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Pancreatic cyst.
- Peritonitis.
- Biliary tract disease.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Few lung or ovarian tumors.
- Alcoholic intoxication.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Acute respiratory insufficiency.
What are the causes of decreased urine Amylase?
- Pancreatic Insufficiency.
- Advanced chronic pancreatitis.
- Renal failure.
- Liver disease (severe).
- Liver cancer.
- Advanced cystic fibrosis.
- Hyperglycemia.
What are the causes of the increased Amylase/creatinine clearance ratio?
- Pancreatitis.
- Toxemia of pregnancy.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Renal insufficiency.
Normal urine picture:
| Physical features | Chemical features | Microscopic findings |
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Does urine amylase disappear like serum amylase?
Question 2: What is the effect of diabetic ketoacidosis on amylase/creatinine clearance ratio?