Uric acid, Blood Uric Acid
Uric acid
What sample is needed for Uric acid?
- Get the venous blood and prepare the serum.
- The serum is preferred, but this test can be done on the plasma.
- A random sample can be used.
- Serum/plasma is stable for 3 to 5 days at 4 °C.
What precautions are needed for estimating uric acid?
- EDTA and fluoride cause positive interference with the uricase method.
- Severe exercise increases the level of uric acid.
What are the indications for Uric acid?
- This is advised to diagnose gout.
- This test is advised to monitor the treatment of gout.
- This test is also helpful in assessing recurrent urinary stone formation.
- This test is done in leukemic patients and renal failure patients. Urate deposition may lead to renal failure.
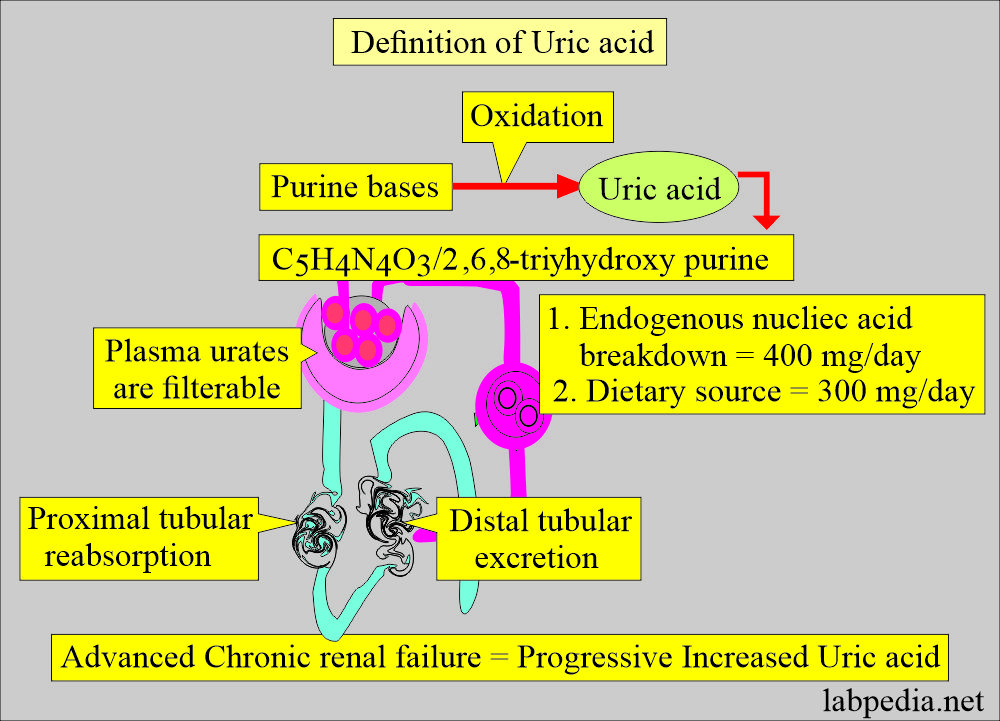
How will you define uric acid?
- Uric acid is a waste product formed in the body due to purine metabolism.
- Uric acid is a nitrogenous compound. Its chemical formula is C5H4N4O3.
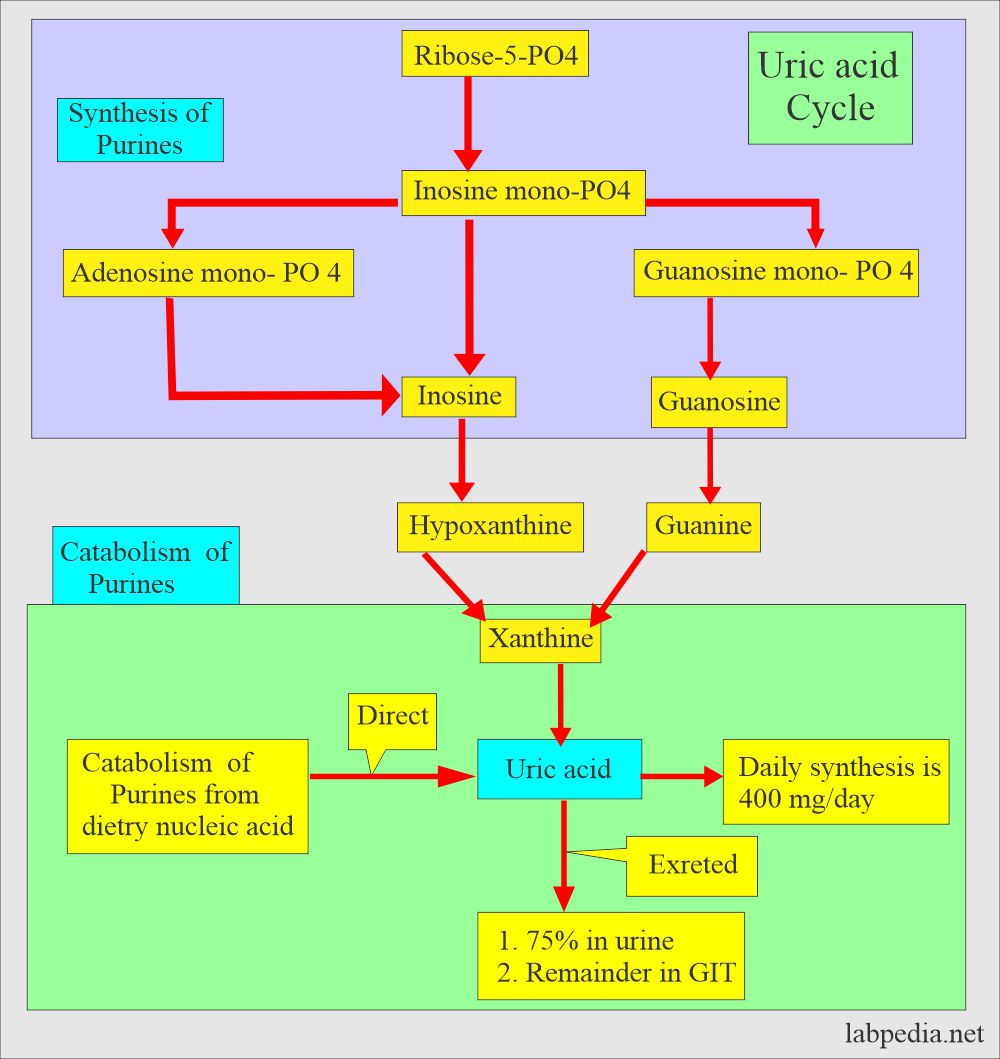
- In humans, uric acid is the end product of the catabolism of purine nucleosides adenosine and guanosine.
- Purine from the catabolism of dietary nucleic acid is directly converted to uric acid.
How will you discuss the biochemistry of uric acid?
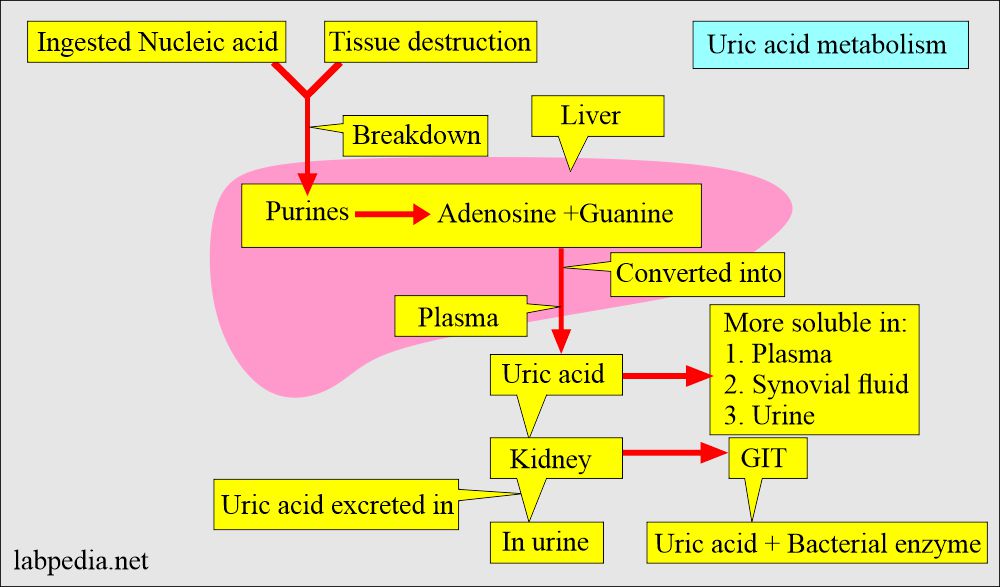
- Uric acid is synthesized in the liver and intestinal mucosa.
- The kidneys excrete 2/3 and 1/3 via the GI tract.
- The breakdown of nucleic acid forms uric acid.
- Uric acid is the end product of purine nucleoside, adenosine, and guanosine catabolism.
- Purine sources:
- Present in many diets.
- It may be produced by the body’s breakdown of adenosine and guanosine catabolism.
- Purine from dietary nucleic acid is directly converted to uric acid.
- The uric acid synthesis in the body is 400 mg/day.
- The diet source is 300 mg/day in addition.
- Most of the body’s purines are excreted as uric acid into the urine.
- Uric acid in the plasma is found as monosodium urates.
- Uric acid is more soluble in plasma, synovial fluid, and urine than in an aqueous solution.
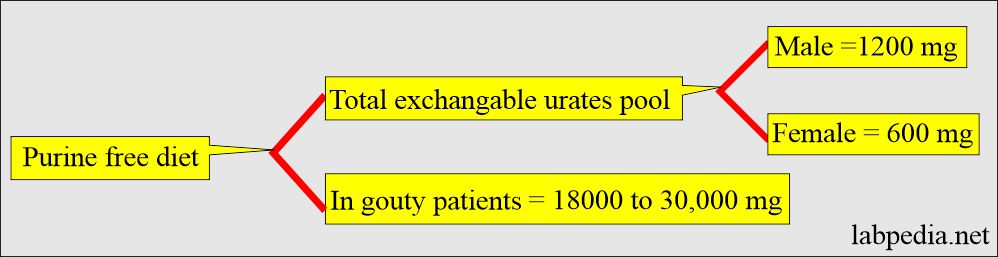
- A patient with gout has a urates pool of 18,000 to 30,000 mg. This overproduction is due to the increased synthesis of purine precursors.
- Mainly, uric acid forms in the liver.
- The blood level of the uric acid depends upon the following:
- The rate of synthesis in the liver.
- The rate of excretion by the kidneys.
- Uric acid is transported from the liver to the kidney through the blood.
- Uric acid removal:
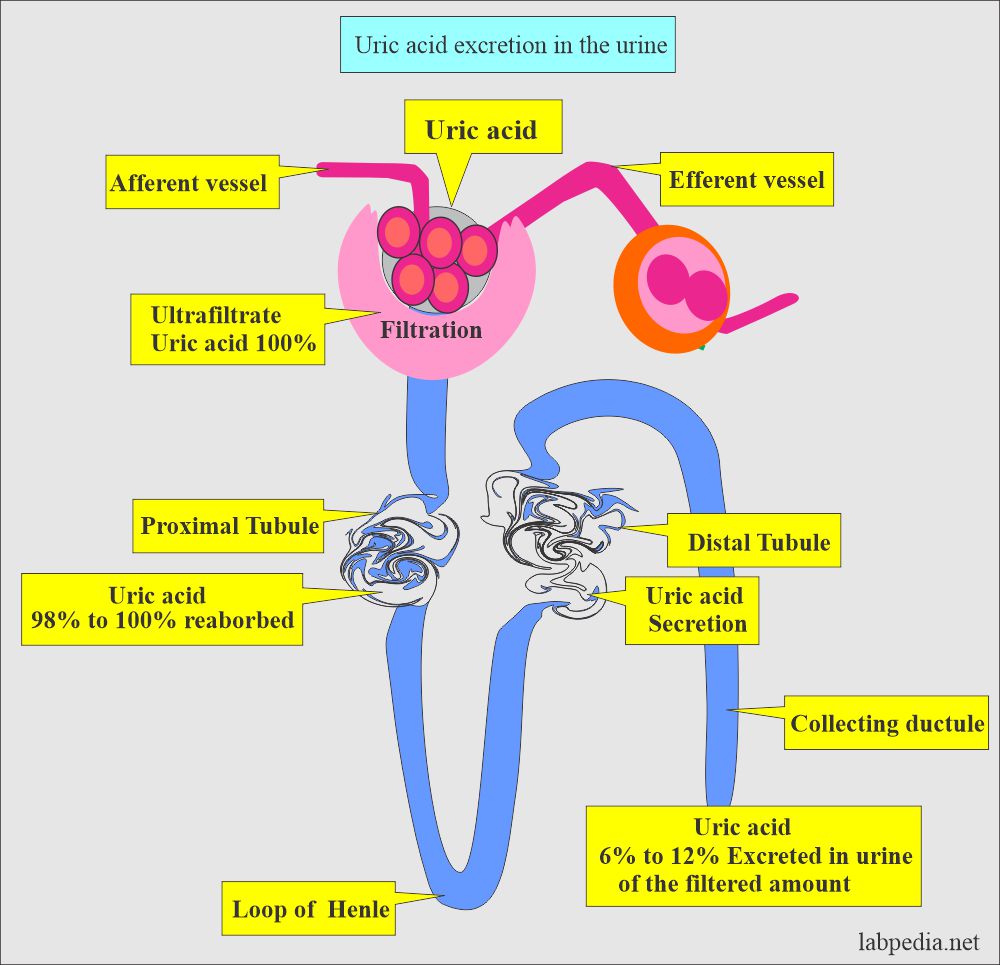
- From the kidney, 75% is filtered.
- The rest 25% is excreted in the GI tract and degraded there.
- AT pH >5.57, most uric acid is in the urates form; this chemical form is soluble in the urine.
- Uricase enzyme deficiency accumulates uric acid in the body.
- Why is there an increased level of uric acid? That is due to the following:
- Excessive cell breakdown.
- Catabolism of nucleic acid.
- Failure to excrete, as in renal failure.
- Uric acid levels are very labile and show day-to-day variation.
- Increased by emotional stress, fasting, and increased body weight.
What are the complications of uric acid?
- Kidney failure or stones in a child or adolescent.
- Unexplained neurological problems in infants or children.
- The appearance of gout in a young man or woman under the age of 30 years.
What is the normal uric acid?
Source 1
| Age | mg/dL | |
| Child <12 years | 2.0 to 5.5 | |
| Male | Female | |
| Adult | 4.4 to 7.6 | 2.3 to 6.6 |
| 60 to 90 years | 4.2 to 8.0 | 3.5 to 7.3 |
| >90 years | 3.5 to 8.3 | 2.2 to 7.7 |
Source 2
- Male = 4.0 to 8.5 mg/dL
- Female = 2.7 to 7.3 mg/dL
- Old people = Values may be slightly increased.
- Child = 2.5 to 5.5 mg/dL
- Newborn = 2.0 to 6.2 mg/dL
Another source
- Male = 3.4 to 7.0 mg/dL.
- Female = 2.4 to 6.0 mg/dL.
- Children = 2.0 to 5.5 mg/dL.
- Hyperuricemia: most books define the uric acid level:
- Men = > 7 mg/dL (0.42 mmol/L)
- Women = > 6 mg/dL. (0.36 mmol/L)
- (Some of the books give higher values)
GOUT
How will you define gout?
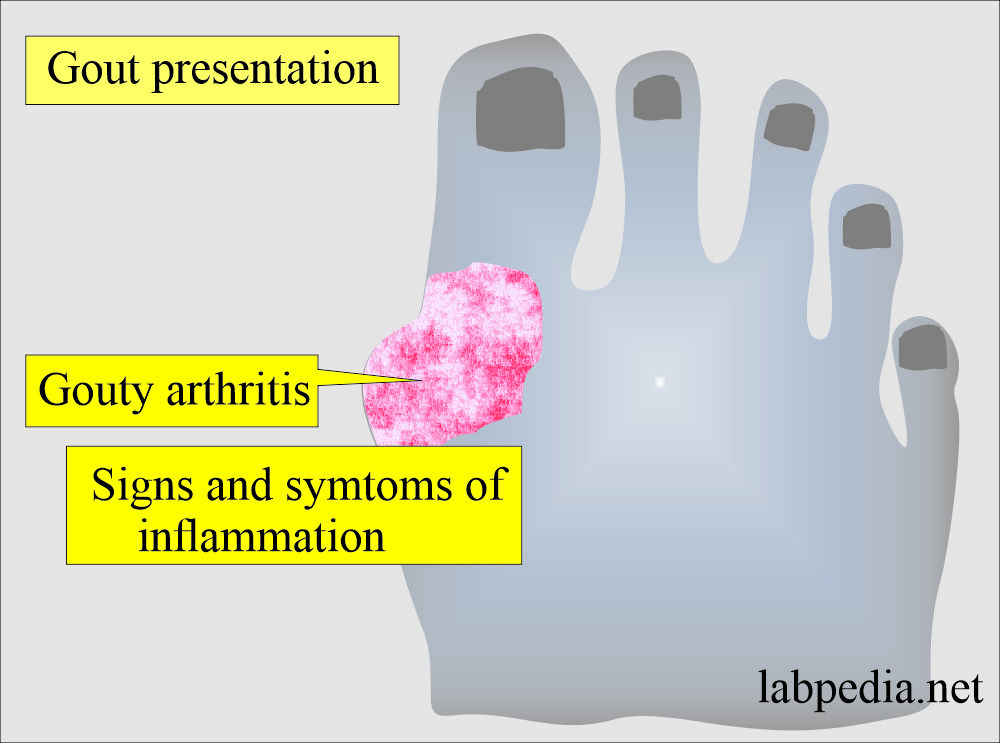
- Gout usually involves a single specific joint, usually small joints of the extremities.
- The most common site is the metatarsal-phalangeal joint of the great toe, which is involved in 75% of the cases.
- The knee and ankle are involved in 50% of the cases.
- There is precipitation of monosodium urates from super-saturated body fluids.
What are the characteristic features of gout?
- Gout is 7 times more common in males than females.
- Acute attacks are usually accompanied by fever and leucocytosis.
- It leads to arthritis.
- The patient may have more than one joint involvement in the first attack.
- There is the deposition of uric acid crystals in the periarticular joint tissue.
- The plasma is saturated with>6.4 mg/dL of uric acid, and the urate crystals precipitate in the tissue.
- They initiate acute inflammation with the presence of polys and macrophagic cells.
- The deposit of uric acid in soft tissue is called Tophi.
- When urine is supersaturated with uric acid, it leads to stone formation.
What are the clinical presentations of the gout?
- Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia is asymptomatic, which is diagnosed by a lab test.
- These patients are at more risk of developing renal stones.
- Symptomatic patients may develop Gout (acute gouty arthritis).
- The deposits of urates are responsible for the signs and symptoms of inflammation.
- Gouty arthritis may be associated with deposits of urates in the joint fluids.
- The patient may develop gouty nephropathy.
- May have urate nephrolithiasis.
- The deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals causes pseudogout.
- Gout is uncommon in children, menopausal women, and males under the age of 30 years.
- Peak age is 40 to 50 years of age in males and later age group in females.
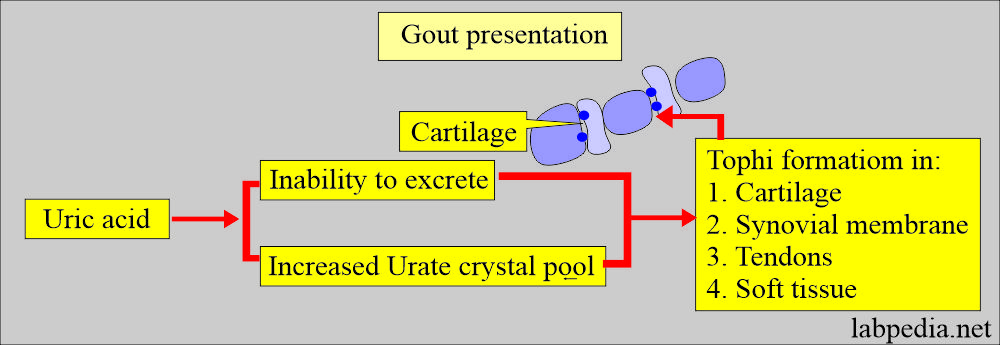
- Gout with the formation of Tophi: This is the third presentation mode. It may begin at an early or late age.
- Progressive inability to excrete uric acid and increase in the urate crystal pool, which appears Tophi in the cartilage, synovial membrane, tendons, and soft tissue.
How will you treat the Gout?
- Prevent the acute attack.
- Prevent stone formation.
- The acute attack needs anti-inflammatory, non-steroidal drugs, and allopurinol.
- Colchicine is used in patients who can tolerate NSAIDs.
- Cortisone can be injected into the joints.
- Ice -packs may be applied to relieve the pain.
- The patient has been advised to have a low-purine diet.
- Intake of fluid is encouraged to increase urinary output.
- Antihyperuricemic drugs like Zyloric are given.
What causes increased Uric acid levels (Hyperuricemia >7 mg/dL in males and >6 mg/dL in females)?
- Gout.
- Renal diseases and Renal failure, prerenal Azotemia.
- Alcoholism.
- Lead poisoning.
- Leukemia, Multiple Myeloma, Lymphoma.
- Starvation, weight-loss diets.
- Metabolic acidosis. and Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Toxemia of pregnancy.
- Liver diseases.
- Hemolytic Anaemia.
- Following excessive cell destruction, as in chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- Lead poisoning.
- Alcoholism.
- Hereditary gout.
- Hyperlipidemia and obesity.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Hypoparathyroidism.
- Hemolytic anemias.
- Psoriasis.
- Glycogen storage disease.
- Increased ingestion of purines in diet, e.g., liver, sweetbreads, kidneys, and anchovies.
- An inborn genetic error in purine metabolism.
- Metastatic cancers.
- Rhabdomyolysis, e.g., Heavy Exercise, Crush injury, burns, epileptic seizure, and myocardial infarction.
What are the causes of Hyperuricemia due to decreased excretion?
- Primary:
- Idiopathic.
- Secondary:
- Acidosis in diabetes and starvation.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Toxemia of pregnancy.
- Shock or chronic blood loss.
- Alcoholism.
- Hyperlipoproteinemia.
- Acute and Chronic renal failure.
- Lead poisoning.
- Salicylate due to low doses.
- Thiazide diuretics.
What causes decreased Uric acid levels (Hypouricemia <2 mg/dL)?
- Fanconi’s syndrome
- Wilson’s disease
- Some malignancies like Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Myeloma.
- Deficiency of xanthine oxidase.
- Lead poisoning.
- Yellow atrophy of the liver.
- Salicylates in low doses.
- Thiazide diuretics.
- Increased renal reabsorption.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: In which sex is gout more common?
Question 2: What is the role of purines in the body?

thank you