Tumor Markers:- Part 3 – Alk. phosphatase, CK, LDH, Acid phosphatase, and PSA
Tumor Markers
- There are various specific tumor markers for various types of malignancies.
- Following is the list of tumor markers.
- Alkaline phosphatase.
- Creatinine Kinase.
- Lactate dehydrogenase.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase.
- Prostatic specific antigen.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone.
- Calcitonin.
- HCG
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
- AFP
- CA 15-3
- CA 19-9
- CA 50
- CA 72-4
- CA 125
- CA 549
Alkaline Phosphatase
What sample is needed for Alkaline phosphatase?
- We need venous blood to prepare the serum.
What are the precautions for Alkaline phosphatase?
- Avoid hemolyzed samples; it will give the wrong results.
- Some drugs increased the value, such as vitamin D, barbiturates, allopurinol, chlorpropamide, colchicine, indomethacin, isoniazid, and methotrexate.
- A fasting sample is needed; a fast of 10 to 12 hours before collection is important.
- If the sample is left at room temperature, it will lead to false and increased results.
What are the indications for Alkaline phosphatase?
- It is advised for bone and liver diseases.
- It is advised in the metastatic bone tumors.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Alkaline phosphatase?
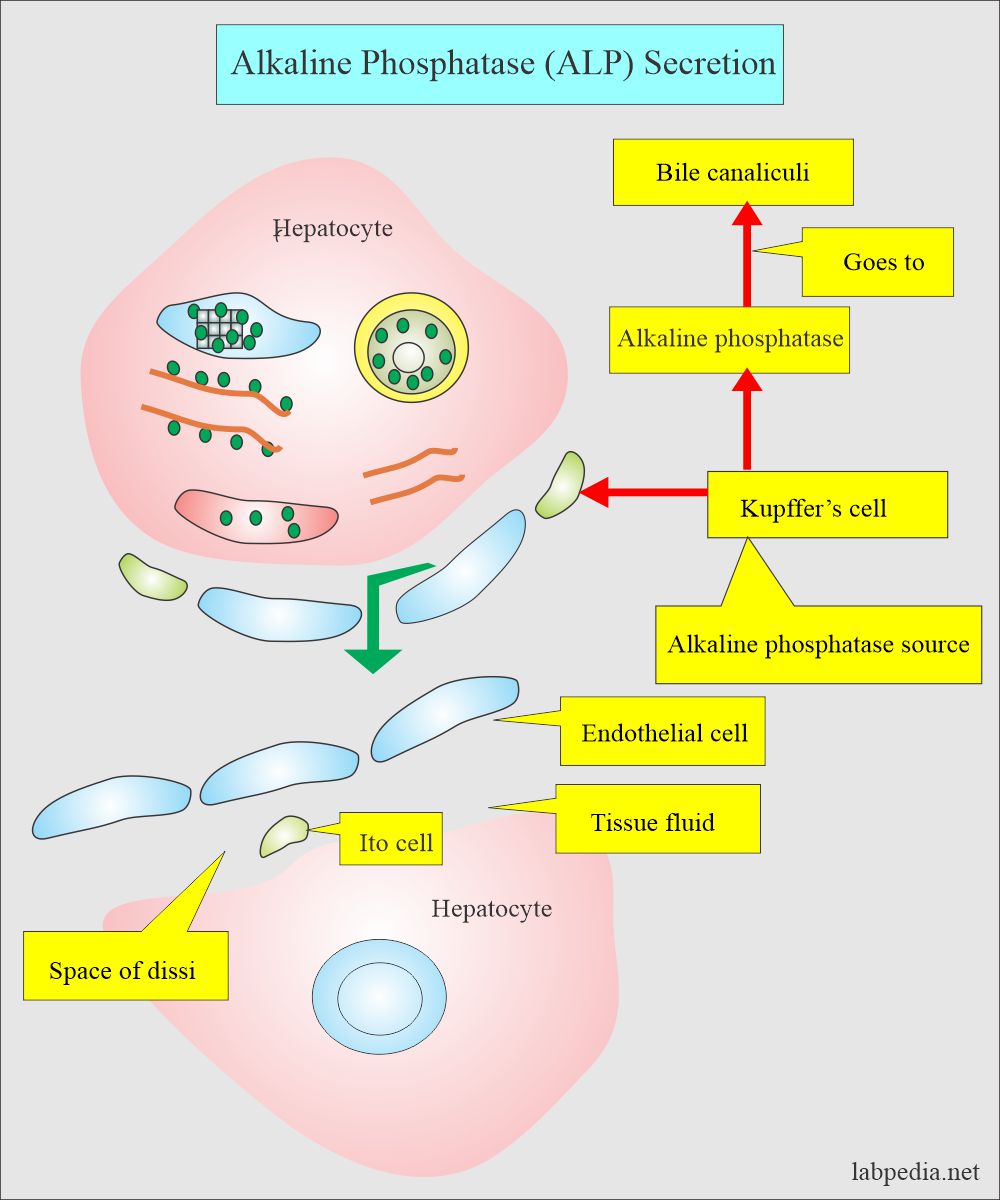
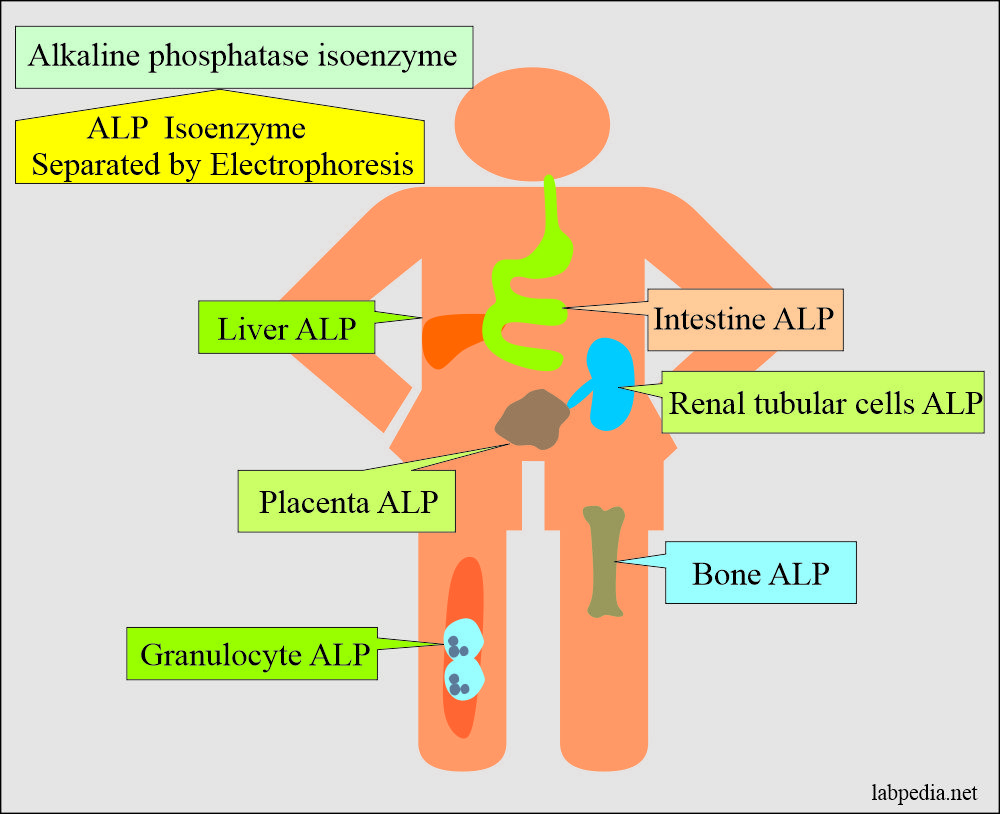
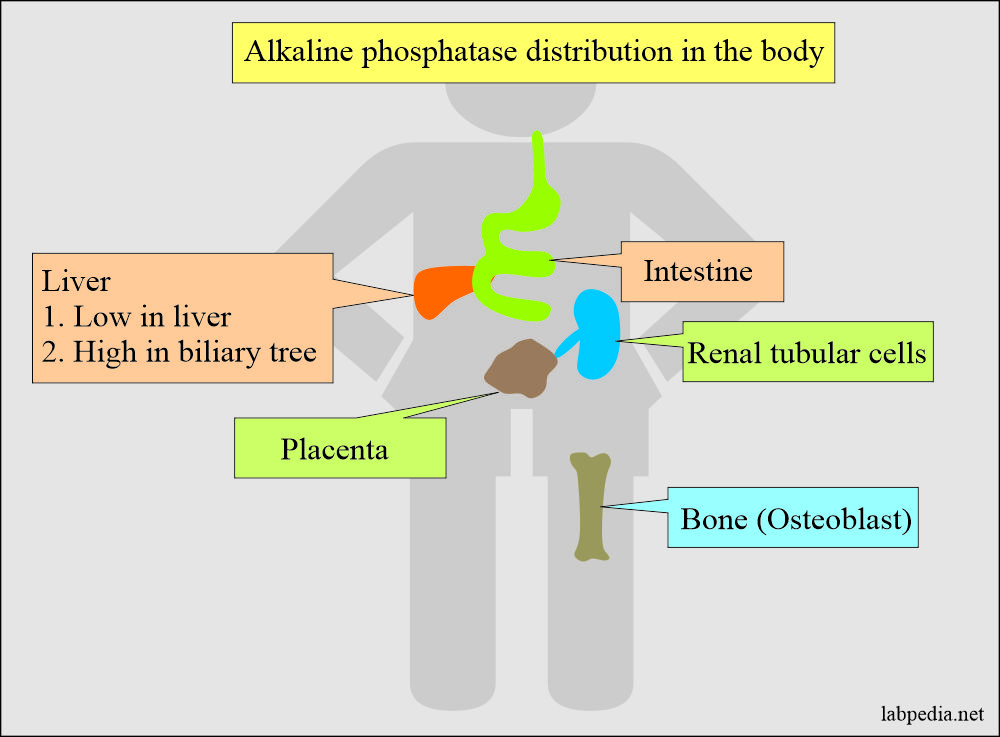
- Alkaline phosphatase is present in all the tissue, but the maximum amount is found in the liver, bone, and placenta.
- Alkaline phosphatase originates in osteoblasts, the lining of the hepatobiliary tree, intestinal tract, and placenta.
- Alkaline phosphatase is used as an index of liver and bone diseases.
What are the isoenzymes of Alkaline phosphatase?
- Liver isoenzyme = 20 to 130 U/L.
- Bone isoenzyme = 20 to 120 U/L.
- Intestinal isoenzyme = 0 to 18 U/L.
- Placental isoenzyme = 50% of the total in the third trimester.
- The liver isoenzyme is more stable than the bone isoenzyme.
- Placental isoenzyme is produced by the trophoblastic cells.
- Placental isoenzyme is also raised in pregnant women.
- This was discovered by Fishman in 1968.
- This was the first tumor marker, along with AFP and CEA.
- The alkaline phosphatase marker is raised in the following ways:
- Metastatic tumors of bone or liver.
- Prostatic cancer with bone metastasis. There is osteoblastic activity and a markedly raised level.
- Breast cancer metastasis to the bone with osteolytic activity and mildly raised level.
- Leukemia, Lymphoma, and sarcoma with metastases to the liver.
- This may be raised in other malignancies like ovarian, lung, trophoblastic, gestation tumors, seminoma, Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and GIT tumors.
What is the normal Alkaline phosphatase?
Source 2
- Adult = 30 to 120 units/L
- Old people = Higher than the adult’s value.
- Children/adolescents:
- <2 years = 85 to 235 units/L.
- 2 to 8 years = 65 to 210 units/L.
- 9 to 15 years = 60 to 300 units/L.
- 16 to 21 years = 30 to 300 units/L.
What are the causes of increased Alkaline phosphatase?
- Osteosarcoma.
- Liver cell carcinoma.
- Metastasis to the liver.
- Primary or secondary bone tumors.
- Liver and bone lymphoma and leukemia.
Creatine Kinase (CK)
What sample is needed for Creatine kinase (CK)?
- We need venous blood to prepare the serum.
What are the indications for Creatine kinase?
- It is advised for the diagnosis of Myocardial infarction.
- It is advised in the metastatic bone tumors.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Creatine Kinase?
- Creatine kinase is also called creatine phosphokinase (CPK), and CK isoenzymes.
- Creatine kinase is the enzyme that activates creatine in the muscles by transferring a high-energy phosphate group in the reaction. This reaction is reversible.
- Creatine + ATP ↔ Creatine phosphate + ADP
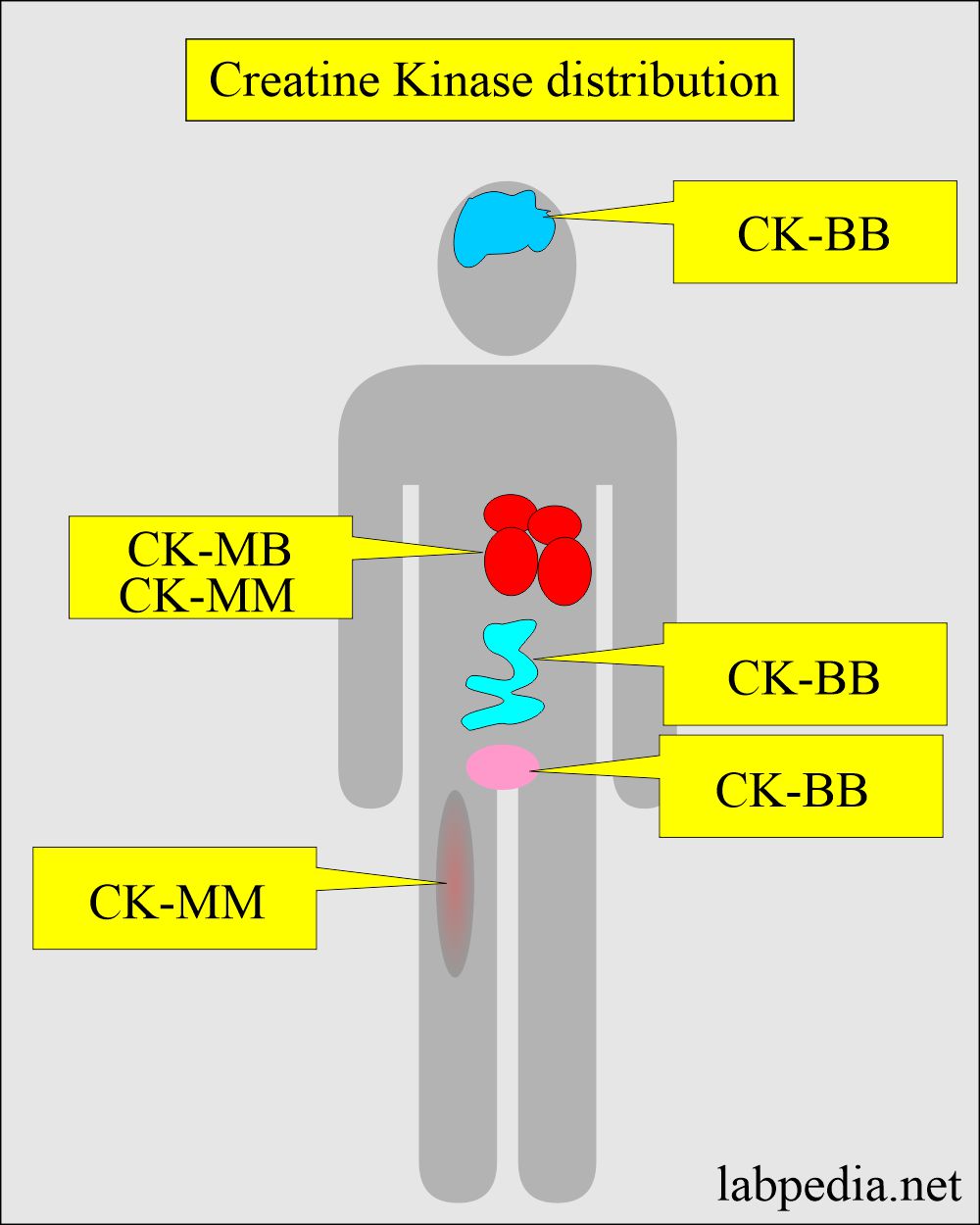
- CK is high concentrations in the heart, skeletal muscles, and brain.
- Creatine kinase is a dimer consisting of two subunits (polypeptide chains):
- CK – M
- CK – B
- There are three isoenzymes:
- CK-1 (BB). is present in the brain, prostate, GIT, bladder, lungs, uterus, and placenta.
- CK-2 (MB) is present in high concentrations in the cardiac muscles.
- CK-3 (MM) is present in the cardiac and skeletal muscles.
What are the causes of raised Creatine Kinase in malignancies?
- This is raised in:
- Prostatic cancer.
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung.
- Maybe elevated in breast, ovary, stomach, and colon cancers.
What is the normal value of total CPK (Source 2):
- Adult/elderly
- Male = 55 to 170 units/L
- Female = 30 to 135 units/L
- Values are higher after the exercise.
- Newborn = 68 to 580 units/L
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
What sample is needed for Lactate dehydrogenase?
- Venous blood is taken to prepare the serum.
What are the indications for lactate dehydrogenase?
- It is advised to see cell necrosis in conditions like acute myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, and hemolytic anemia.
- It is advised for liver diseases, renal infarction, pancreatitis, muscular dystrophy, and acute pulmonary infarction.
- It is advised in cancers.
What is the normal LDH level?
Source 2
- Adult/elderly = 100 to 190 units/L at 37 °C.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)?
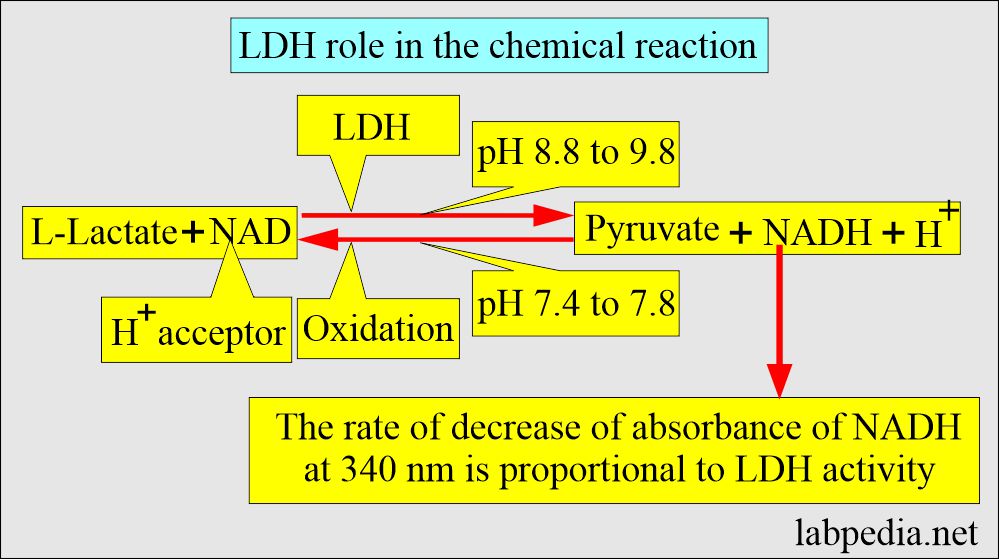
- This is an enzyme in the glycolytic pathway’s action, and it is released when cell membrane damage occurs.
- LDH is found in the cells of Herat, RBCs, kidneys, liver, brain, lungs, and skeletal muscles.
- When there is an injury to cells then, LDH enters the blood.
- This is not a good indicator of cell injury because of its presence in most of the tissue.
- Its level correlates with the tumor mass and gives a prognostic indicator of the progress of the disease.
LDH isoenzymes are:
| LDH isoenzyme | Tumor Markers: | Organ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is present in:
|
- Isoenzyme LD-5 is associated with liver metastasis.
- LDH is a nonspecific tumor marker and is raised in:
- Liver cell carcinoma.
- Lymphomas.
- Acute leukemias.
- Germ cell testicular tumors.
- Breast cancer.
- Colon cancer.
- Stomach cancer.
- Lung cancer.
- An elevated level of LDH in the urine indicates neoplasm or injury to the urogenital system.
- LD-5 positive in the spinal fluid indicates metastasis to the central nervous system.
Neuron-specific Enolase (NSE)
What are the Indications for Neuron-specific enolase (NSE)?
- It monitors treatment and predicts relapse in small-cell lung cancer.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of NSE?
- Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) is the isoenzyme in the glycolytic pathway identified by the immunoassay and found mostly in neuron and neuroendocrine cells.
- This is a glycolytic pathway.
What is the normal value of Neuron-speicfic Enolase (NSE)?
- NSE = < 12.5 µg/mL.
What are the causes of increased NSE?
- It is raised in neuroendocrine tumors:
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung.
- It is found in 68% of limited diseases.
- 87% is found in the extensive disease.
- What is the purpose of Neuron-specific enolase (NSE)?
- It monitors the following tumors:
- Neuroblastoma.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Carcinoid.
- Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.
- Melanoma.
- Pancreatic endocrine tumors.
Prostatic acid phosphatase
What sample is needed for Prostatic acid phosphatase?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
What are the indications for Prostatic acid phosphatase?
- It is advised to diagnose prostatic cancer.
- It is also advised to see the response to the treatment and monitor the cancer.
- Advised in case of metastasis of the prostatic cancer.
What are the precautions for prostatic acid phosphatase?
- Avoid rectal examination or prostatic massage before testing the blood sample at least 2 days before this test.
- Avoid urinary catheterization or instrumentation before taking a blood sample.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of the prostatic acid phosphatase?
- Acid phosphatase is found in many tissues, including the liver, blood vessels, red blood cells, platelets, and bone marrow.
- The maximum concentration is found in the prostate gland.
- The estimation of acid phosphatase is advised for:
- The diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma.
- Staging of the prostatic carcinoma.
- To monitor the efficacy of the treatment of prostatic carcinoma.
- The level is raised when the prostatic carcinoma has metastasized beyond the capsules to the other parts of the body, especially to the bone.
- After complete curative surgery for prostatic cancer, the acid phosphatase decreases to normal in several days.
- When the patient is treated with estrogen therapy, it returns to normal in several weeks.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is a better indicator and most clinically significant.
- PAP is more accurate than total acid phosphatase.
- This is produced primarily by the prostate and raised in:
- Prostatic cancer.
- Osteogenic sarcoma.
- Multiple myelomas.
- Metastasis to the bone.
Prostatic specific antigen (PSA)
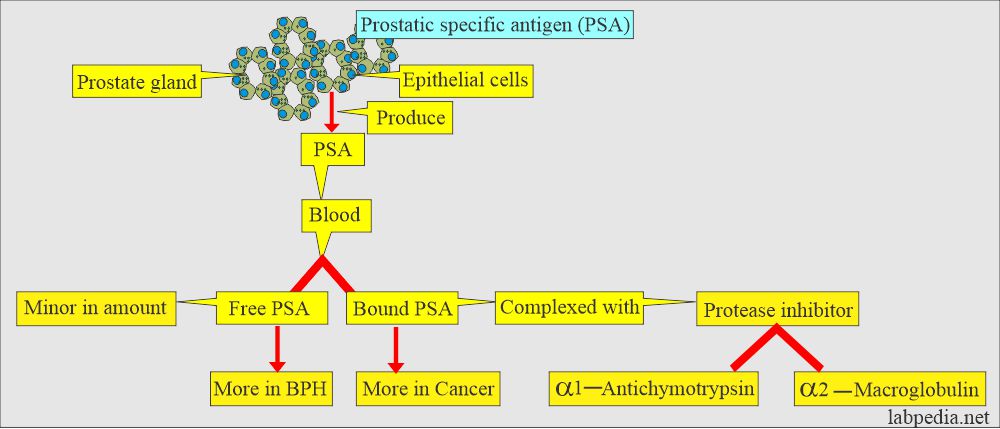
- PSA is a glycoprotein normally found in the cytoplasm of the prostatic epithelial cells.
- This antigen is detected in all males, but its level is markedly increased in prostatic carcinoma.
- Its level is related to the size of the tumor.
What is the use of PSA?
- This is specific for the diagnosis of prostatic cancer.
- It is used to detect, stage, and monitor the treatment of prostatic carcinoma.
- Its use is more specific for monitoring the treatment.
- The sensitivity of PSA is 70% at the cut-off value of 4.0 µg/L.
- Specificity is more than 90% if the cut-off value is raised to 8 µg/L.
- The level of PSA correlates with the stage of the disease.
When should PSA be measured for the follow-up of prostatic carcinoma?
- Every 3 months after the surgery during the first year.
- After 4 months in the second year.
- After 6 months every year.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How to treat prostatic carcinoma with follow-up by PSA?
Question 2: What is the role of Neuron-specific enolase?

Excellent bookmarks.
Thanks.
My son had cancer (Burkitts Lymphoma) when he was ten. He is now 31. His lab work showed that his Alkaline phosphatase is low (44-121. Should he be concern or do further testing?
Please see this link:
https://labpedia.net/alkaline-phosphatase-alp/
This link will help you to treat low alkaline phosphatase.