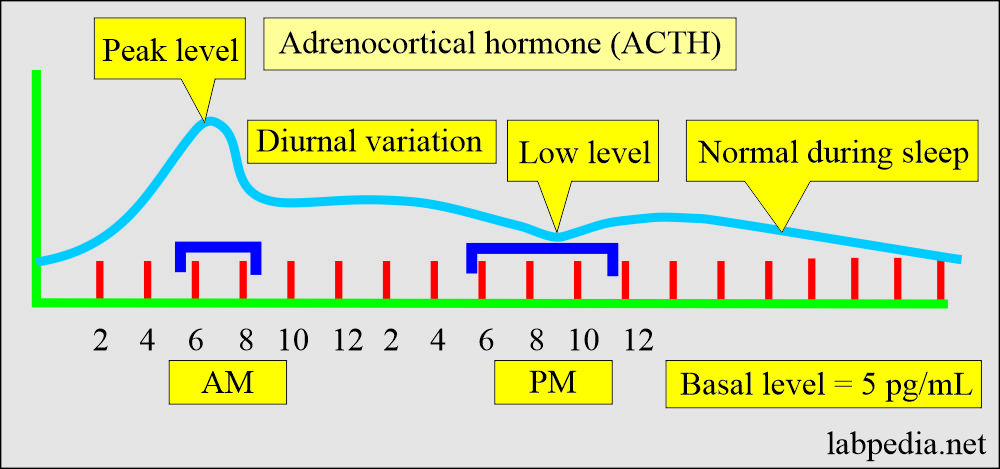
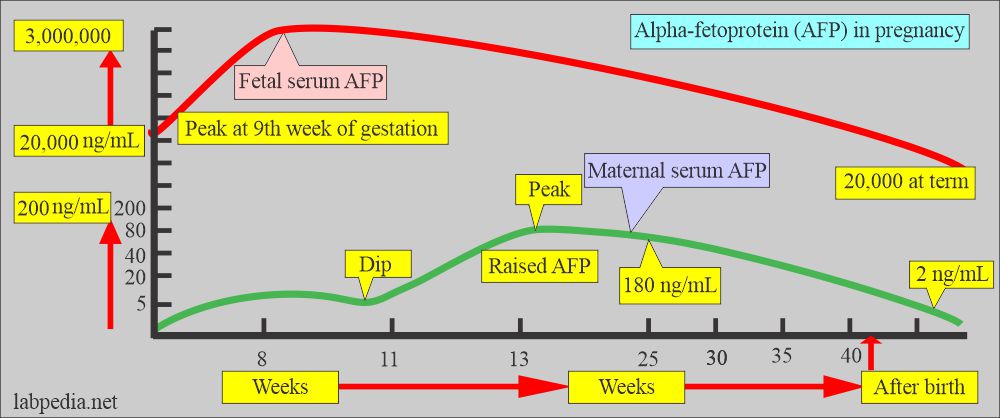
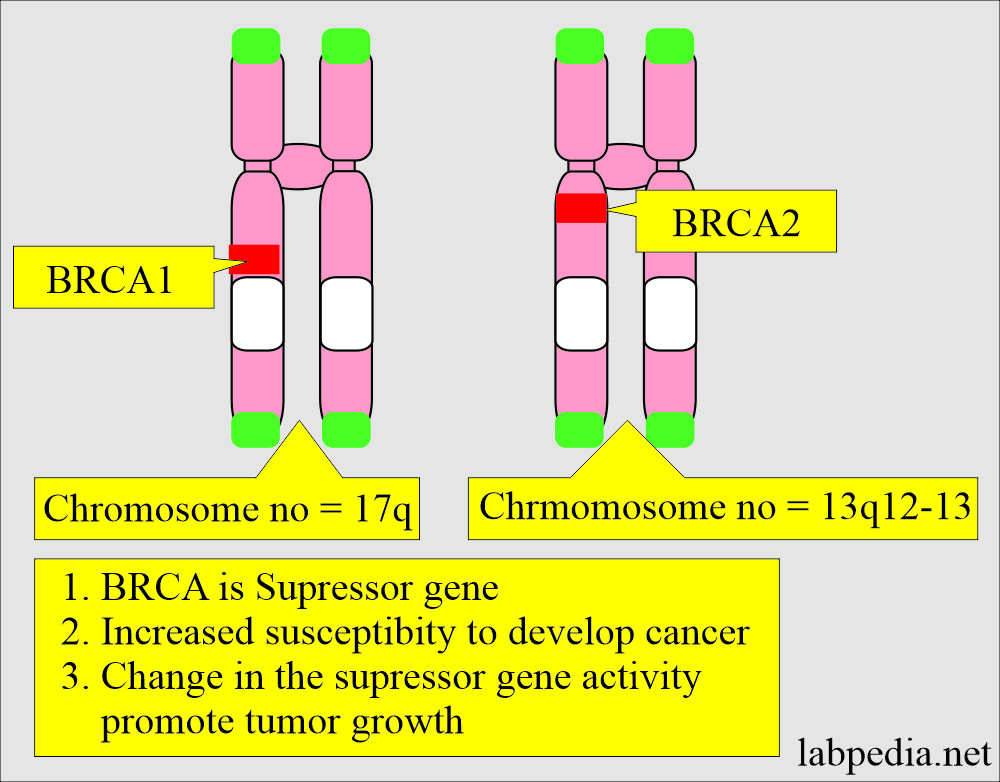
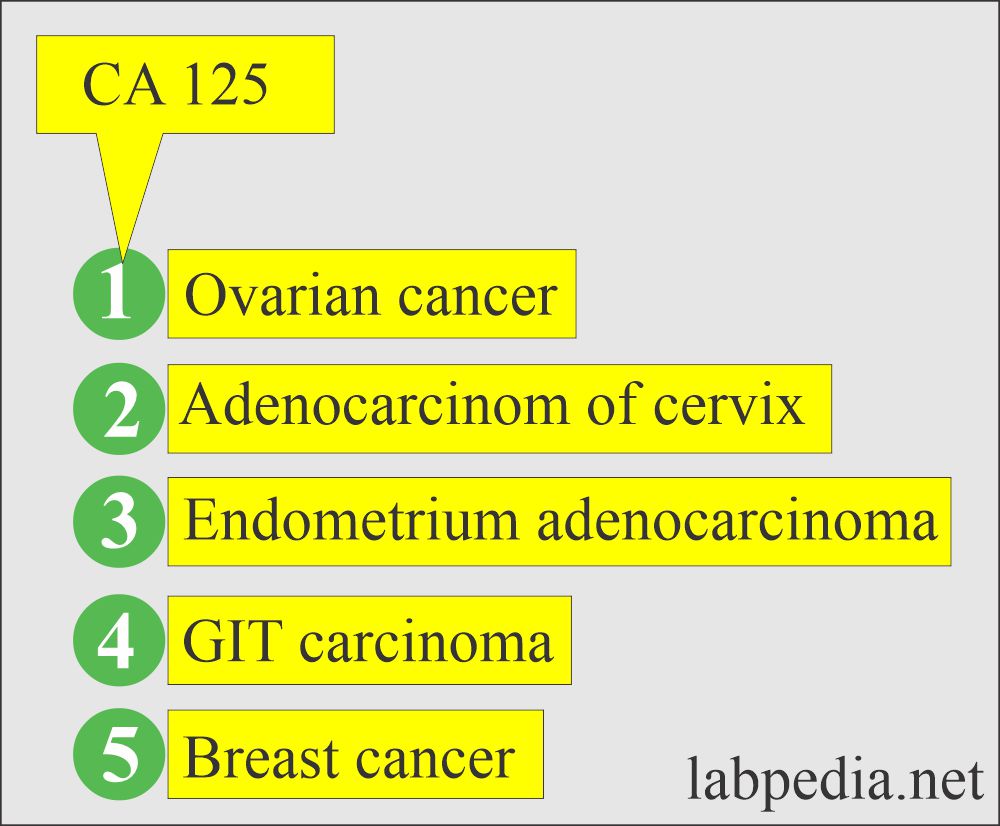
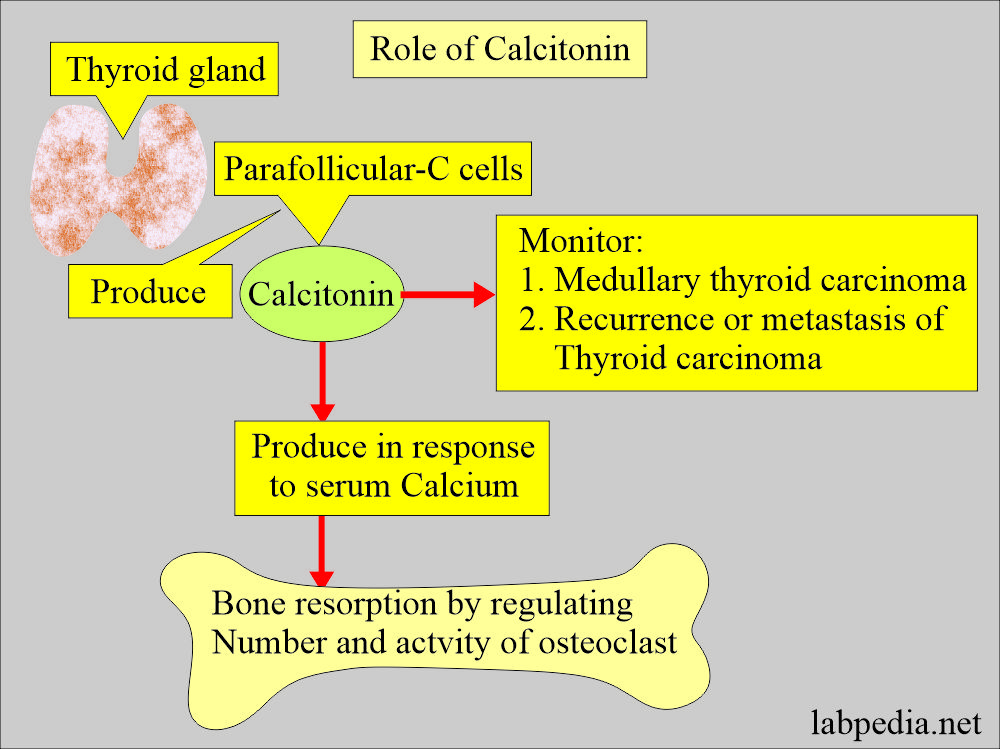
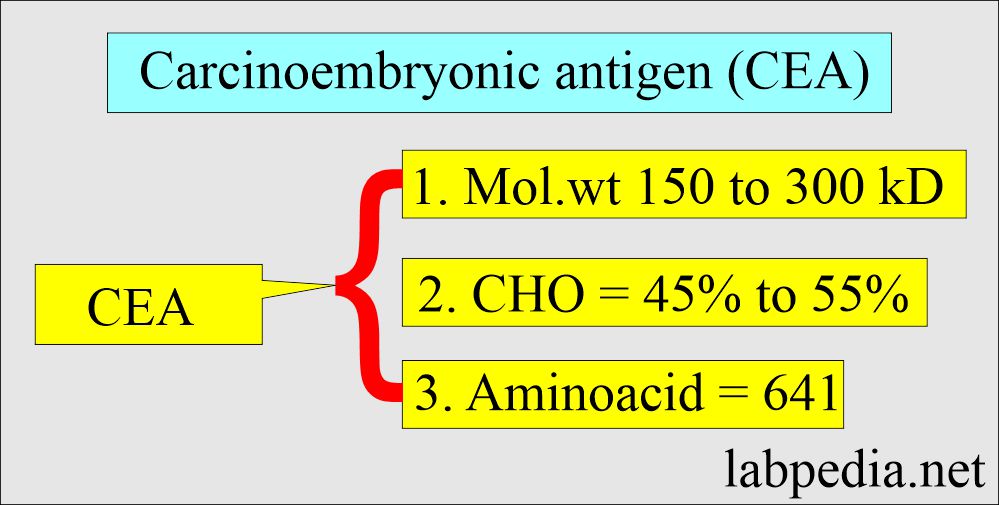
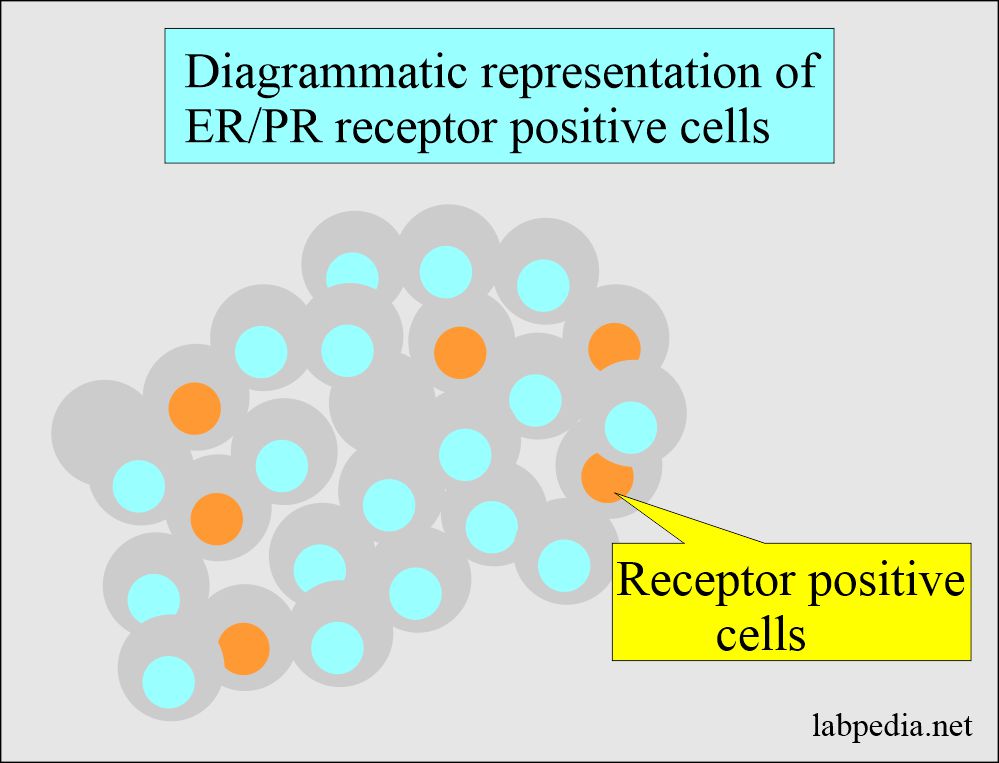
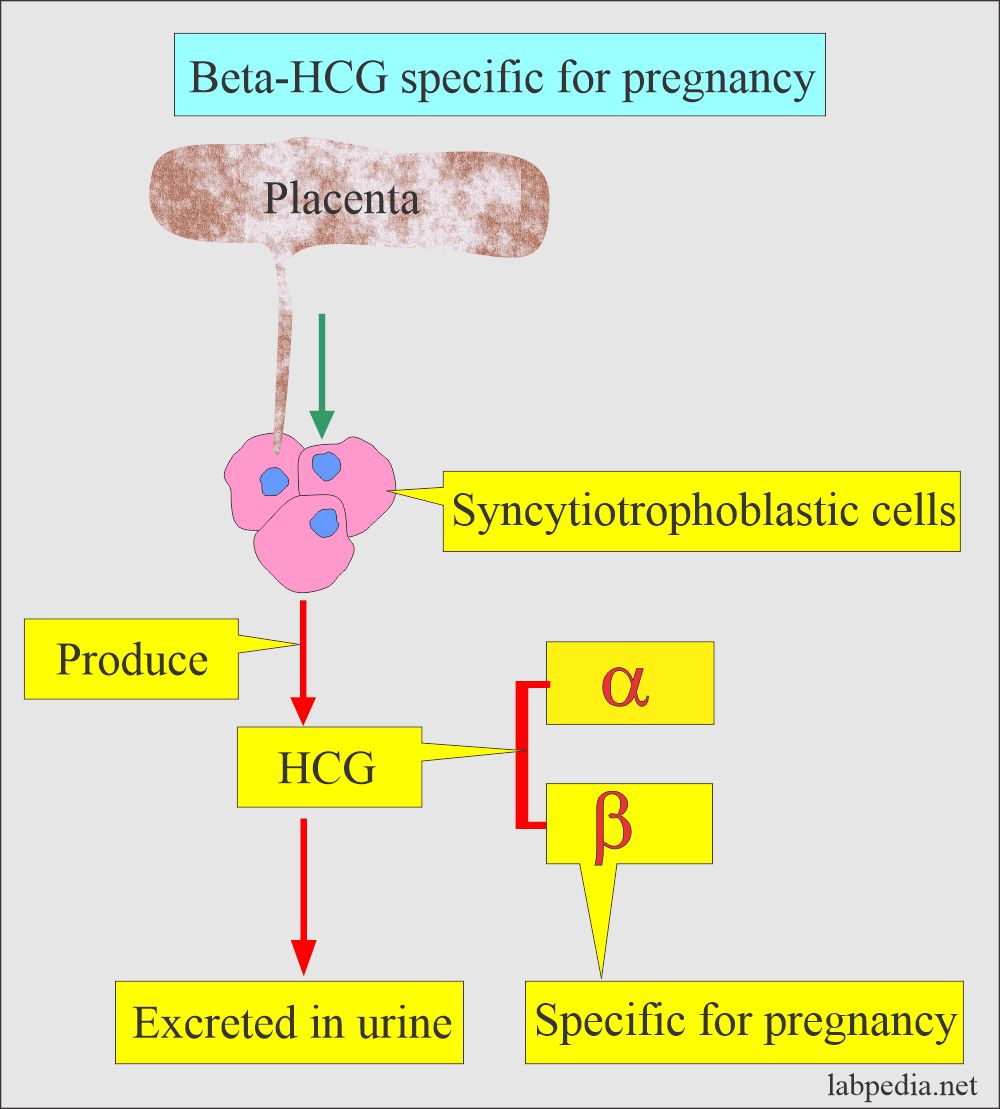
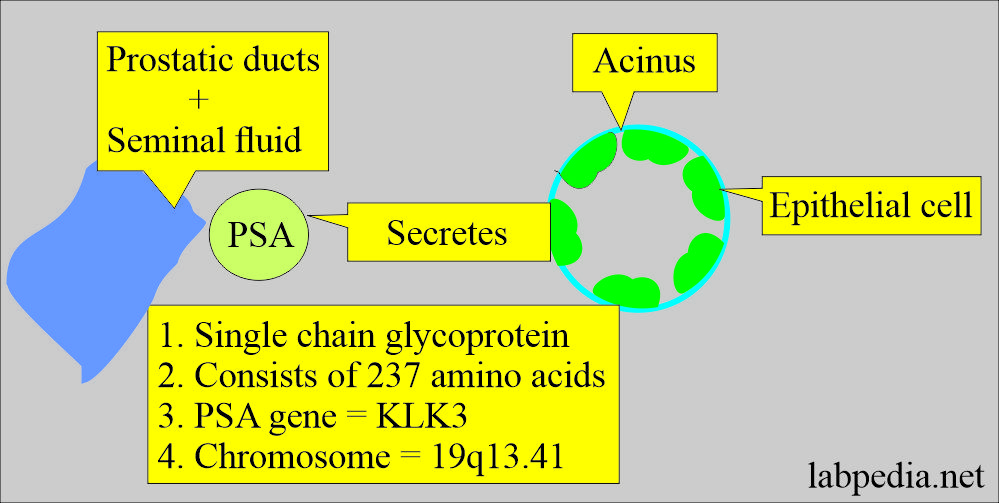
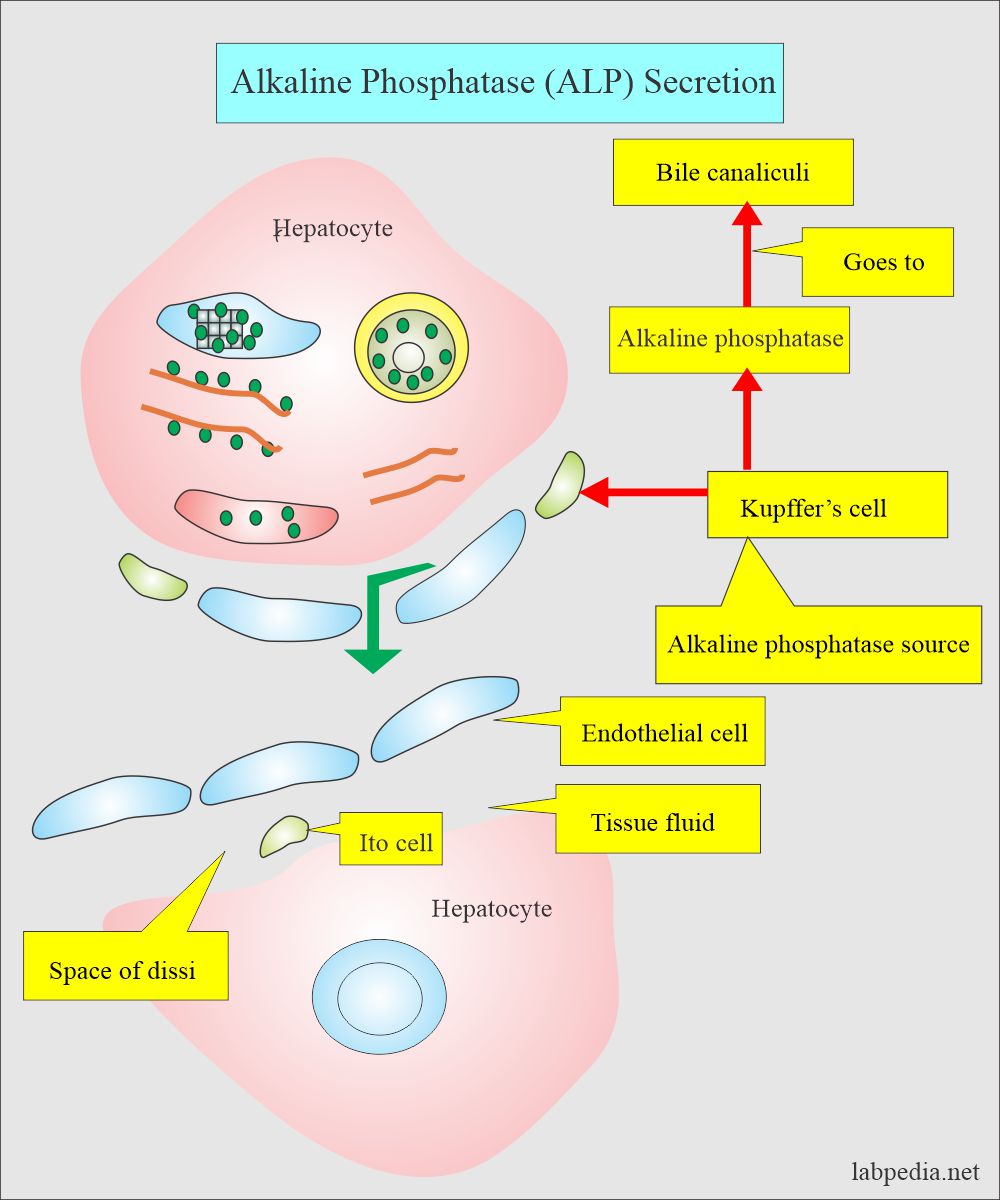
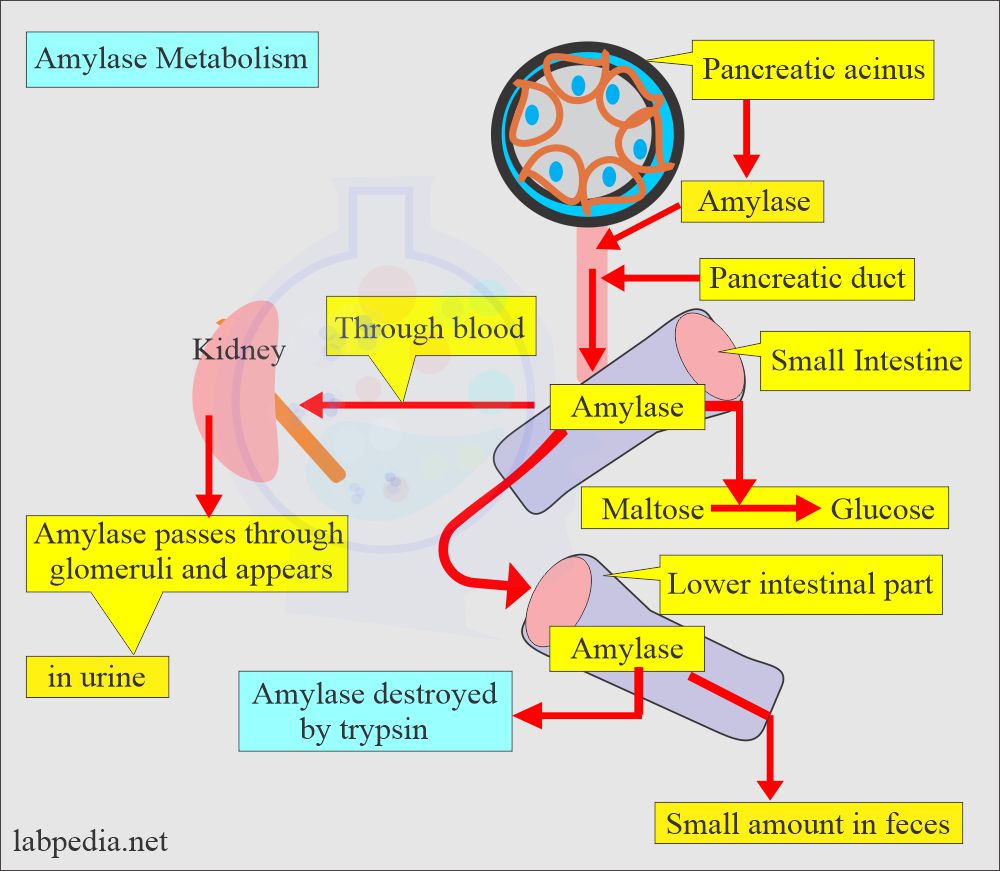
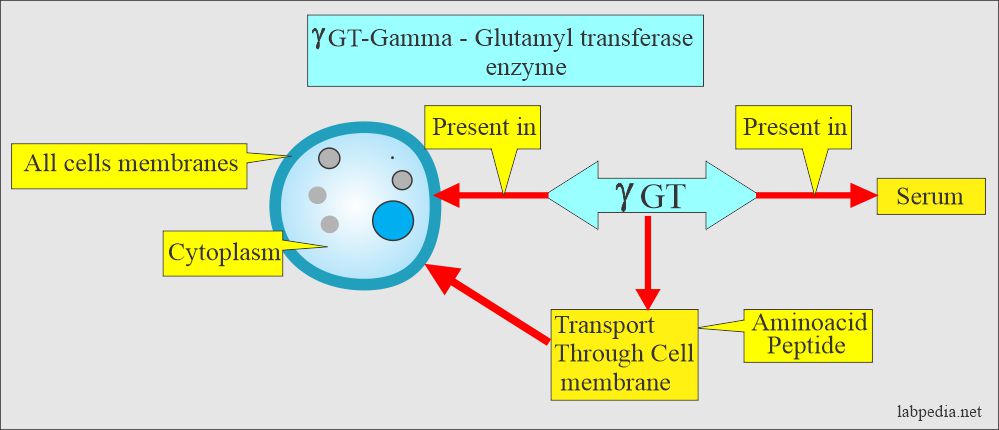
Tumor markers:- Part 14 – Summary of Tumor markers
Summary of Tumor markers
Tumor markers are summarised:
| Tumor marker | Tumor diagnosis or association (origin of tumors) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
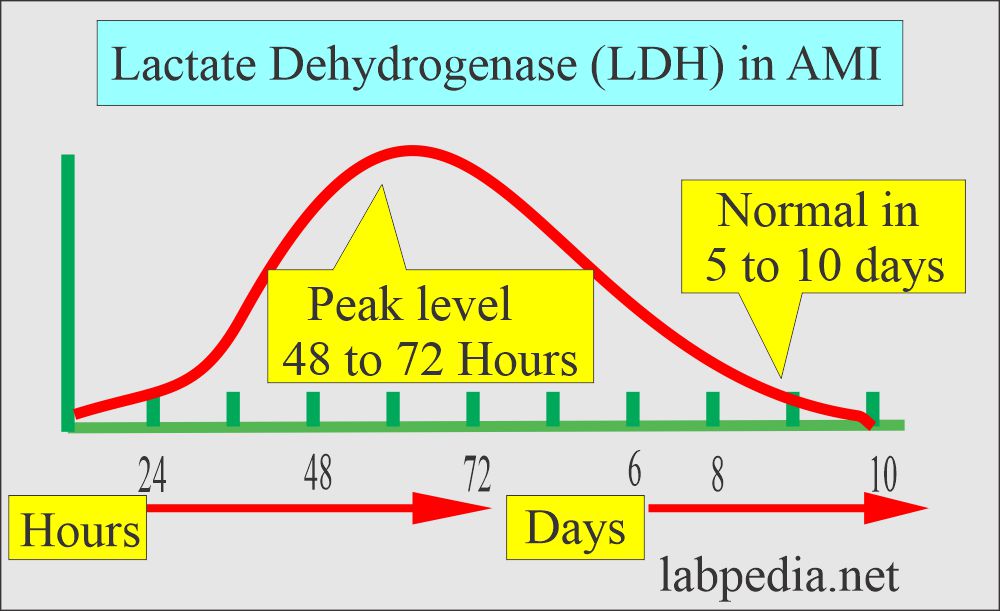
| Enzymes | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
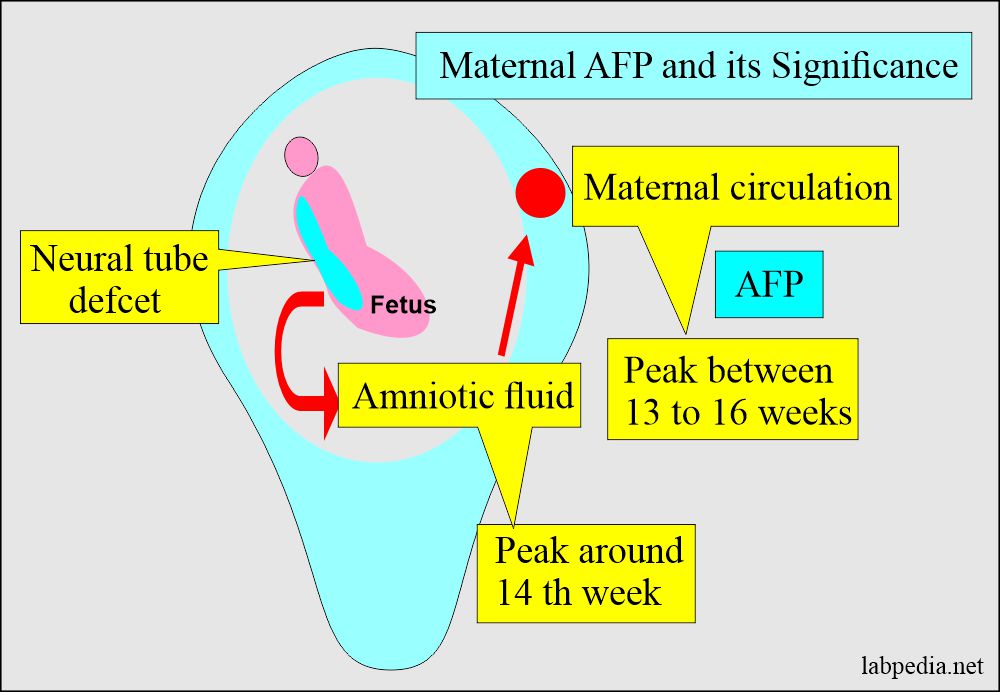
| Oncofetal antigens | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Proteins as a tumor marker | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|