Tumor Markers:- Part 10 – Thyroglobulin (Tg) as Tumor marker
Thyroglobulin (Tg)
What sample is needed for Thyroglobulin (Tg)?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
What are the Indications for Thyroglobulin (Tg)?
- Thyroglobulin is advised after the treatment of thyroid cancer.
- It is advised to assess the presence and possibly extent of residual, recurrent, or metastatic follicular or papillary carcinoma.
- This is done to diagnose hyperthyroidism.
- This is the tumor marker for well-differentiated thyroid cancer (follicular and papillary).
- Thyroglobulin is not elaborated by medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer.
- This can also help to monitor thyroid cancer or metastatic cancer.
- It predicts the outcome of therapy for hyperthyroidism.
- The presence of pleural effusion indicates metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
What precautions are needed to estimate thyroglobulin (Tg)?
- Make sure that patients are off the thyroid medication for 6 weeks.
- Evaluate the TSH level before testing the Tg.
- Anti-Tg antibodies are present in 15% to 35% of patients with thyroid cancer. These will interfere with the Tg results.
- It is not recommended for initial diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma.
- Do not use in patients with preexisting thyroid diseases.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Thyroglobulin (Tg)?
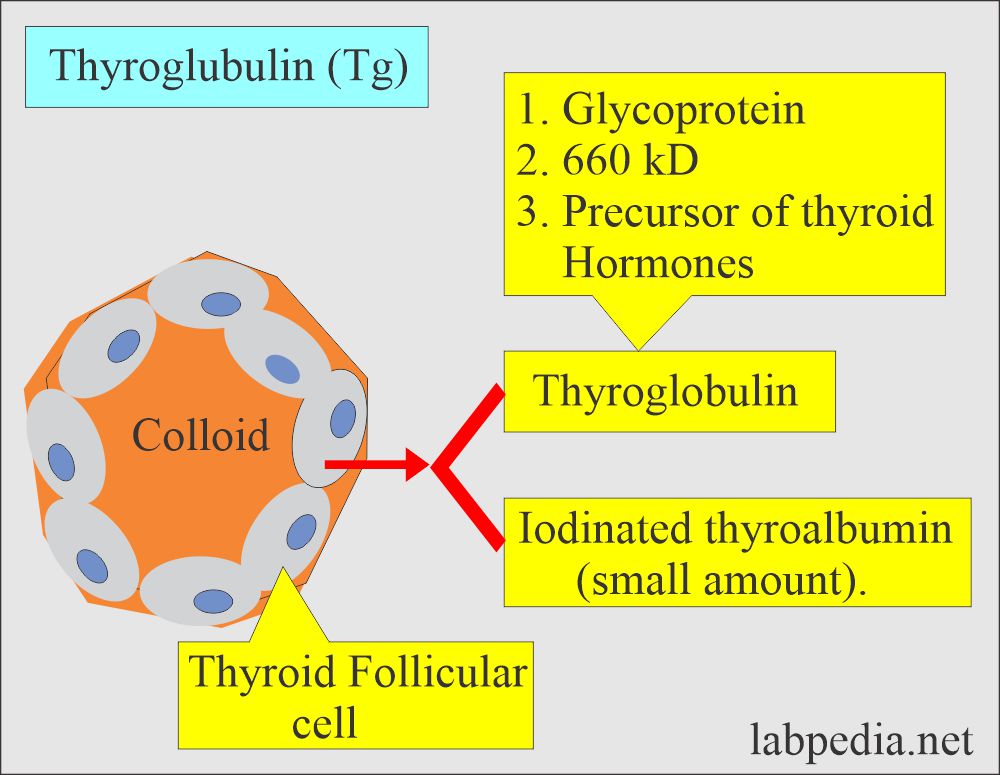
- Definition of thyroglobulin:
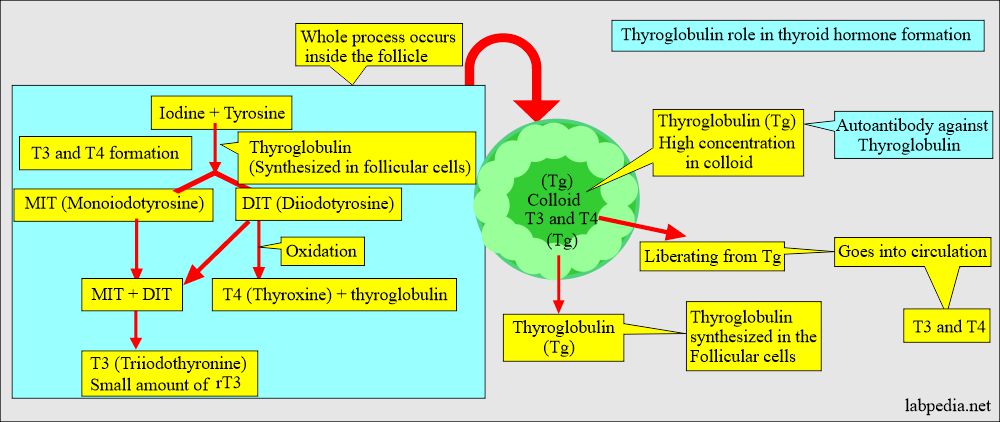
- It is an iodine-containing glycoprotein of high molecular weight (660 kD) that is present in the colloid of the thyroid follicles.
- It is synthesized and secreted by the thyroid follicles. Up to 30 ng/mL (45 pmol/L) of it is present in the serum of normal people.
- Thyroglobulin (Tg) represents the thyroid mass.
- Thyroglobulin is a glycoprotein, 660 kD, and iodinated secretion of epithelial cells of the thyroid gland.
- It is synthesized and secreted by the thyroid follicular cells.
- Thyroglobulin is a precursor of the thyroid hormone.
- This may be made by normal epithelial cells and cancer cells.
- Raised values of thyroglobulin (Tg) are found in the following:
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Thyroiditis.
- Iodine deficiency.
- Benign thyroid adenomas.
- Differentiated thyroid carcinomas (follicular and papillary carcinoma and papillary-follicular carcinoma).
- Medullary carcinoma does not produce thyroglobulin (Tg).
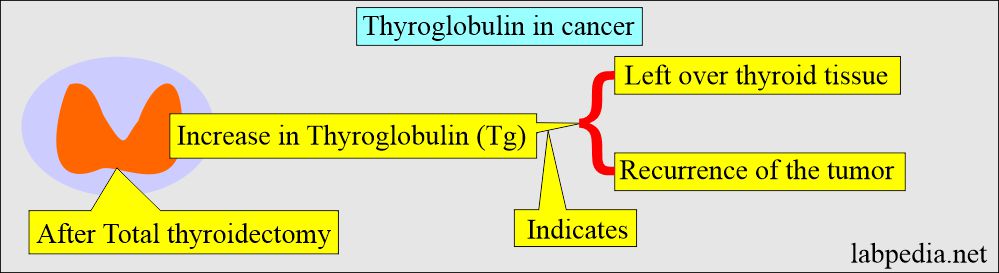
- A very low level of Tg after thyroid surgery indicates that there is little left in the thyroid tissues.
- In the case of functional carcinoma, thyroglobulin should not be detected after thyroidectomy or radioiodine uptake.
- Thyroglobulin is detected in case of incomplete surgery.
- The iodinated secretion also contains T3, T4, and hormones.
What is the difference between thyroglobulin and thyroxine-binding globulin?
| Clinical parameter | Thyroglobulin (Tg) | Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Both proteins are essential for proper thyroid function, but their roles are distinct—one is involved in hormone production (Tg), and the other in hormone transport (TBG).
Does Thyroglobulin call a tumor marker?
- Half-life is about 65 hours (another reference days 8 to 22 hours).
- It takes nearly a month before thyroglobulin becomes undetectable following total thyroidectomy.
- In cancer cases operated on, Thyroglobulin (Tg) is measured postoperatively to determine the disease’s activity and the volume of thyroid tissue left behind.
- The rising level of Thyroglobulin (Tg) indicates tumor recurrence and progression.
- Thyroglobulin (Tg) is also raised in benign conditions, so it is not specific or sensitive enough to diagnose thyroid cancer.
- After thyroidectomy, thyroid hormone replacement is needed for normal body metabolism.
- Because of thyroid hormone replacement, TSH levels are low, so there is minimal stimulation of thyroid cells.
- To stimulate Thyroglobulin (Tg) in thyroid cancer cases after thyroidectomy, stop the hormone replacement for at least 6 weeks.
- Now, TSH will be stimulated, stimulating Thyroglobulin (Tg) production from the epithelial cells.
- If there are any leftover thyroid cancer cells, the Thyroglobulin (Tg) level will increase.
- After surgery and radiation in cancer patients, the Thyroglobulin (Tg) level is undetectable.
What are the advantages of thyroglobulin in cancer patients?
- A thyroid tumor scan with I131 is required to differentiate begin and cancer cells.
- Thyroglobulin estimation advantage is less exposure to radiation in the form of I131.
- With thyroglobulin estimation, I131 is not needed.
- Patients with metastasis are not detected by the I131 scan, where thyroglobulin (Tg) is raised.
How will you discuss the Thyrogen-stimulation test?
- Thyrogen is a synthetic purified recombinant source like a human thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
- Thyrogen is synthetic TSH and is called thyrotropin alpha.
- Keep the patient off the hormone replacement therapy.
- Two injections of thyrogen are given on two consecutive days.
- Take a blood sample of the patient for thyroid hormones and thyroglobulin.
- Normal thyroid tissue and thyroid cancer cells raise >10 times Tg level by TSH stimulation.
- Thyrogen stimulates the thyroid gland and raises the thyroglobulin (Tg) level.
- What are the advantages of the thyrogen test?
- It monitors patients who have undergone thyroid surgery.
- It can detect residual tumors.
- It helps to determine the proper dosage of hormone replacement therapy.
What is the importance of the presence of antithyroglobulin antibodies?
- Anti-thyroglobulin antibodies are present in 10% of the normal population and 20% of those with thyroid cancer and are a major issue in thyroglobulin testing.
What are the normal Thyroglobulin (Tg) values?
Source 1
| Age | ng/mL |
| Cord blood | 24.4 ± 3.7 |
| One hour | 29.7 ± 4.2 |
| 48 hours | 41.9 ± 5.8 |
| Adult | 3 to 42 |
| Thyroid patient | <5 |
- To convert into SI unit x 1.0 = µg/L
Male Thyroglobulin (Tg)
- 0 to 11 months = 0.6 to 5.5 ng/mL.
- 1 to 11 years = 0.6 to 50.1 ng/mL.
- Adult = 0.5 to 53 ng/mL.
Female Thyroglobulin (Tg)
- 1 to 11 months = 0.5 to 5.5 ng/mL.
- 1 to 11 years = 0.5 to 52.1 ng/mL.
- Adult = 0.5 to 43 ng/mL.
- Another source gives normal values as follows:
- Adult = 3 to 42 ng/mL.
- Newborn = 36 to 48 ng/mL.
- 87% of normal adults have a serum value of <10 ng/mL.
What are the causes of increased Thyroglobulin (Tg) levels?
- Thyroid follicular and papillary carcinoma.
- Thyroid adenoma.
- Untreated and metastatic thyroid cancer.
- Subacute thyroiditis, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and Grave’s disease.
- Benign thyroid adenoma.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Recurrence of the metastatic tumor after the treatment.
- Some patients with endemic goiter.
- Silent, painless thyroiditis.
- Marked liver insufficiency.
What are the causes of decreased Thyroglobulin (Tg) levels?
- Infants with goiter (Hypothyroidism).
- Thyrotoxicosis factitia.
- Thyroid agenesis in infants.
- Total thyroidectomy with radiation.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is thyrogen test?
Question 2: What is the site of formation of thyroglobulin?