Thyroid:- Part 7 – Triiodothyronine Total, T3 Total
Triiodothyronine Total (T3)
What sample is needed for Triiodothyronine Total (T3)?
- This test is done on the patient’s serum.
What are the precautions for triiodothyronine total (T3)?
- Ask about the history of radioisotopes if given before the test because it will alter the result.
- In pregnancy, T3 values are increased.
- Some of the drugs increased the T3 level, like estrogens, oral contraceptives, and methadone.
- Some of the drugs decreased the T3 level, like anabolic steroids, phenytoin (Dilantin), androgens, Inderal, salicylates, and reserpine.
- It is not advised for the diagnosis of hypothyroidism because the decreased value has minimal significance.
- It decreases in healthy older persons when Free T4 is normal.
What are the indications for Triiodothyronine total (T3)?
- T3 evaluates the thyroid function.
- T3 is used to diagnose hyperthyroidism.
- T3 is used to monitor the therapy in case of hyperthyroidism.
- Diagnosis of T3 thyrotoxicosis (TSH is suppressed, and T4 is normal).
- It is advised when Free T4 is borderline raised.
- In the cases of unexplained atrial fibrillation.
- It is advised that T4 replacement therapy be monitored. It is better than T4 and Free T4, but TSH is still a better test.
- It is advised in Grave’s disease to evaluate antithyroid drug effects.
- It is a better indicator of thyrotoxicity in hyperthyroidism.
How will you define triodothyronine total (T3)?
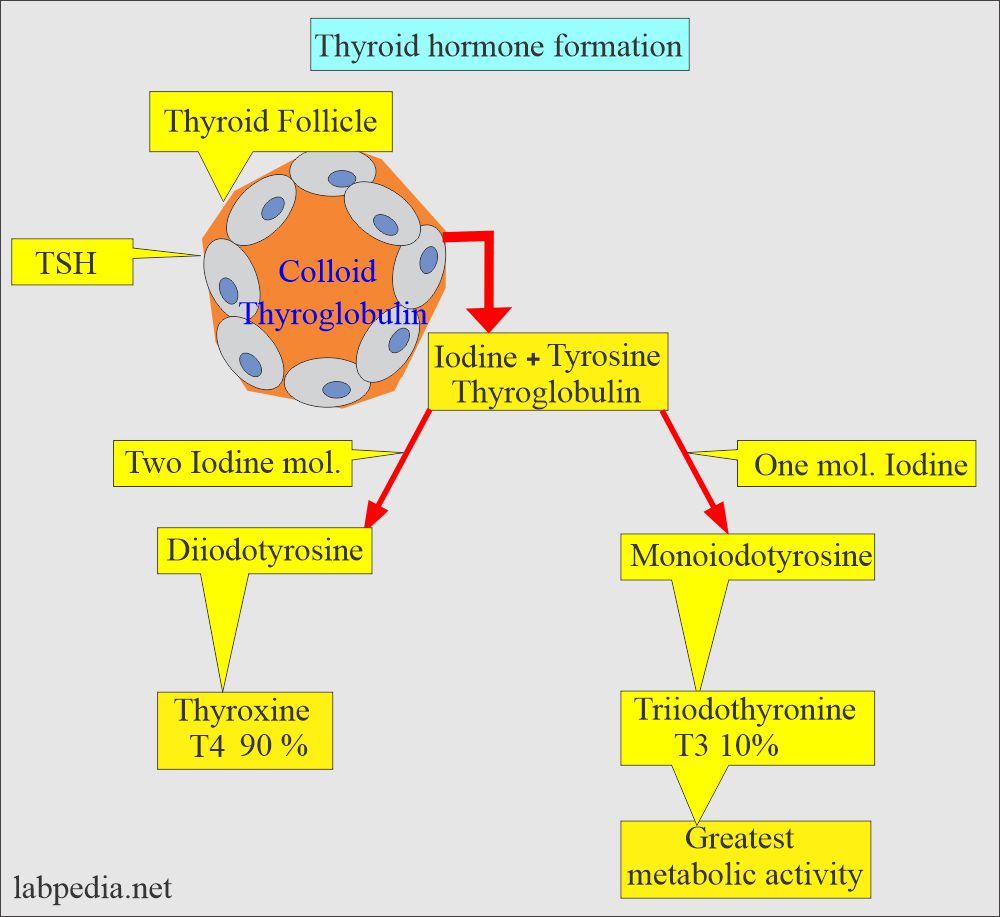
- Thyroxine (T4) is converted to Triiodothyronine (T3) in the peripheral tissues.
- ∼20% is synthesized by the follicular cells.
- Most T3 is bound to proteins; a small amount, 0.3%, is free (unbound) and biologically active.
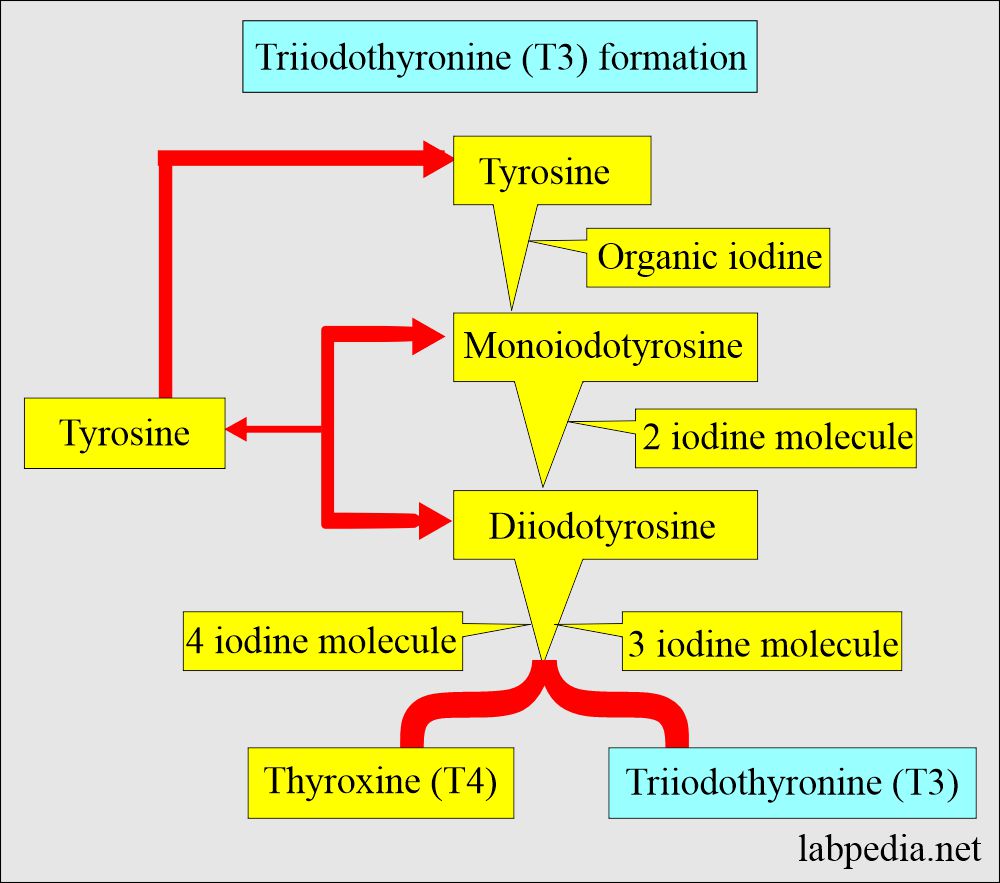
What is the mechanism of formation of Triiodothyronine (T3)?
- Tyrosine combines with organic iodine to form monoiodotyrosine.
- Monoiodotyrosine, along with another molecule of iodine, will form Diiodotyrosine.
- Monoiodotyrosine + diiodotyrosine = Triiodothyronine ( T3 ).
- Thyroxine (T4) is converted to T3 in peripheral tissue.
- 20% is synthesized by the follicular cells of the thyroid gland.
- T3 has three iodine atoms compared to T4, which has 4 iodine atoms.
- A large amount of T3 is formed in the liver by T4.
- T3 is less stable than T4 because it is less tightly bound to serum protein.
- 7% to 10% of the thyroid hormone is T3.
- 70% of T3 is bound to thyroglobulin (TBG) and albumin.
- There is a very small amount of free (unbound form) T3 (0.3%), which is biologically active.
What is the mechanism of Metabolism of thyroid hormones (T4 and T3)?
- The liver converts T4 to T3, so the T3 level is less useful for hypothyroidism.
- A T3 level helps to diagnose Hyperthyroidism.
- If T3 and T4 are raised, it indicates hyperthyroidism.
- A rare form of hyperthyroidism is called T3 toxicosis, where T3 is raised and T4 normal.
- Free T3 is metabolically active.
How will you discuss Reverse T3 (rT3)?
- It is advised to distinguish low T3 sick thyroid from true hypothyroidism.
- It is a hormonally inactive isomer of T3.
- It is usually increased in hyperthyroidism.
- It is usually decreased in hypothyroidism.
What is normal Triiodothyronine Total (T3)?
Source 1
Triiodothyronine (T3) Total
- Cord blood (>37 weeks) = 5 to 141 ng/dL
- 1 to 3 days = 100 to 740 ng/dL
- 1 to 11 months = 105 to 245
- Children
- 1 -5 years = 105 to 269 ng/dL
- 6 to 10 years = 94 to 241 ng/dL
- 16 to 20 years = 80 to 210 ng/dL
- Adult
- 20 to 50 years = 70 to 204 ng/dL
- 50 to 90 years = 40 to 181 ng/dL
- Pregnancy
- Last 5 months = 116 to 247 ng/dL
- To convert into SI unit x 0.0154 = nmol/L
- Last 5 months = 116 to 247 ng/dL
Another source 1
Free T3
- Cord blood (>37 weeks ) = 15 to 391 pg/dL
- Child and adult = 260 to 480 pg/dL (4.0 to 7.4 pmol/L)
- Pregnancy
- First trimester = 211 to 383 pg/dL
- Second and third trimesters = 196 to 338 pg/dL
Another source 2
T3 total
| Age | ng/dL |
| 1 to 3 days | 100 to 740 |
| 1 to 11 months | 105 to 245 |
| Children 6 to 10 years | 95 to 240 |
| 11 to 15 years | 80 to 215 |
| Adults 16 to 20 years | 80 to 210 |
| 20 to 50 years | 75 to 220 |
| Adult > 50 years | 40 to 180 |
- According to another source, the values are:
- Adult = 80 to 200 ng/dL.
- Adolescent (12 to 23 years) = 82 to 213 ng/dL.
- Children (1 to 14 years) = 105 to 245 ng/dL.
- Pregnancy = 116 to 247 ng/dL.
- (Values vary from lab to lab)
What are the causes of increased levels of Triiodothyronine Total (T3)?
- Primary hyperthyroidism like :
- Grave’s disease.
- Toxic thyroid adenoma.
- Acute thyroiditis. In the early stages, the thyroid produces more T3.
- Ectopic thyroid tissue, e.g., Struma ovarii.
- Increased Thyroid-binding globulin is seen in pregnancy, Hepatitis, and congenital hyperproteinemia.
What are the causes of decreased levels of Triiodothyronine Total (T3)?
- Hypothyroidism is seen in :
- Cretinism.
- Surgical ablation.
- Myxedema.
- Hypothalamic failure.
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Iodine insufficiency.
- Pituitary insufficiency.
- Renal failure.
- Cirrhosis.
- Advanced cancer.
- Hepatic diseases.
How will you interpret Triiodothyronine T3?
| Disease | Triiodothyronine (T3) |
|
Increased |
|
Decreased |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
|
Increased |
|
Normal |
|
Normal |
|
Decreased |
|
Normal |
How will you differentiate different thyroid diseases?
| Clinical disease | Free T4 | Total T4 | T3 | TSH | Thyroglobulin |
|
Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
|
Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Normal |
|
Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased | Normal/Increased |
|
Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal |
|
Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal/Decreased | |
|
Normal | Normal | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
|
Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal |
|
Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal | Increased |
|
Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
|
Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
|
Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased |
|
Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
|
Decreased | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is reverse T3?
Question 2: Is there any value of T3 in hypothyroidism?
- Please see more details on thyroid function and T3 Free.