Thyroid:- Part 2 – Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Thyrotropin, and Graves’ Disease
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
What sample is needed for Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)?
- Venous blood is taken, and the test is done on the patient’s serum.
What are the indications for Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)?
- TSH differentiates Hypothyroidism from hyperthyroidism.
- TSH is used to diagnose primary hypothyroidism.
- TSH is used to differentiate primary from secondary hypothyroidism.
- TSH also differentiates hypothyroidism due to the hypothalamus (Tertiary hypothyroidism).
- TSH level is also done for suppressive or replacement therapy.
- TSH has also been done in a newborn with primary hypothyroidism with a low T4 level.
How will you define thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)?
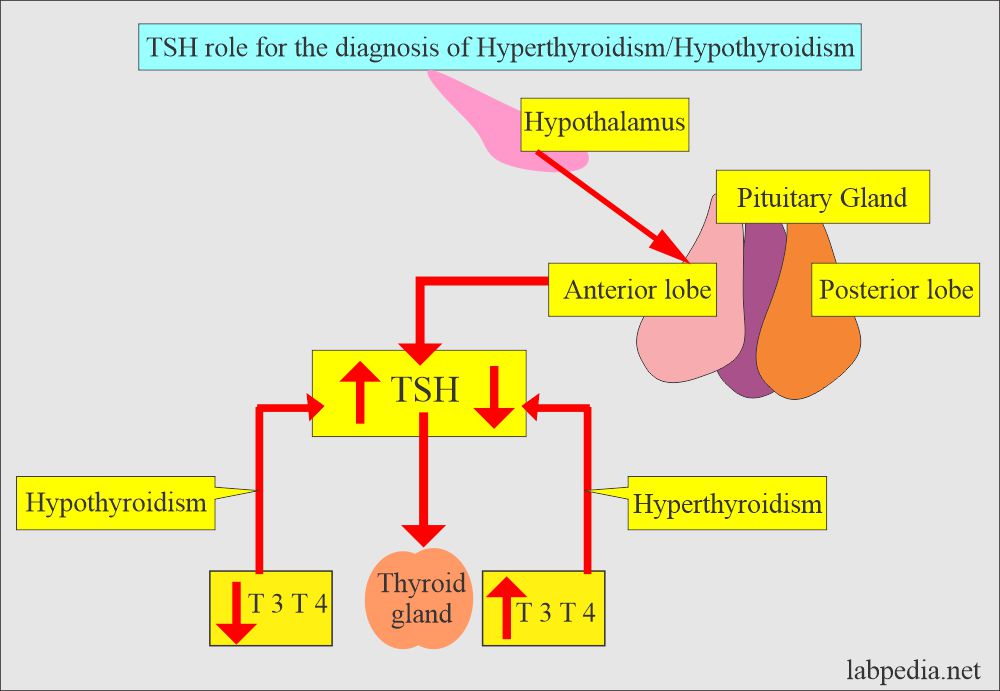
- The anterior pituitary gland produces TSH.
- TSH plays an important role in regulating the thyroid glands’ activity, which produces important hormones for the body.
- TSH controls the metabolism, growth, and development of the body.
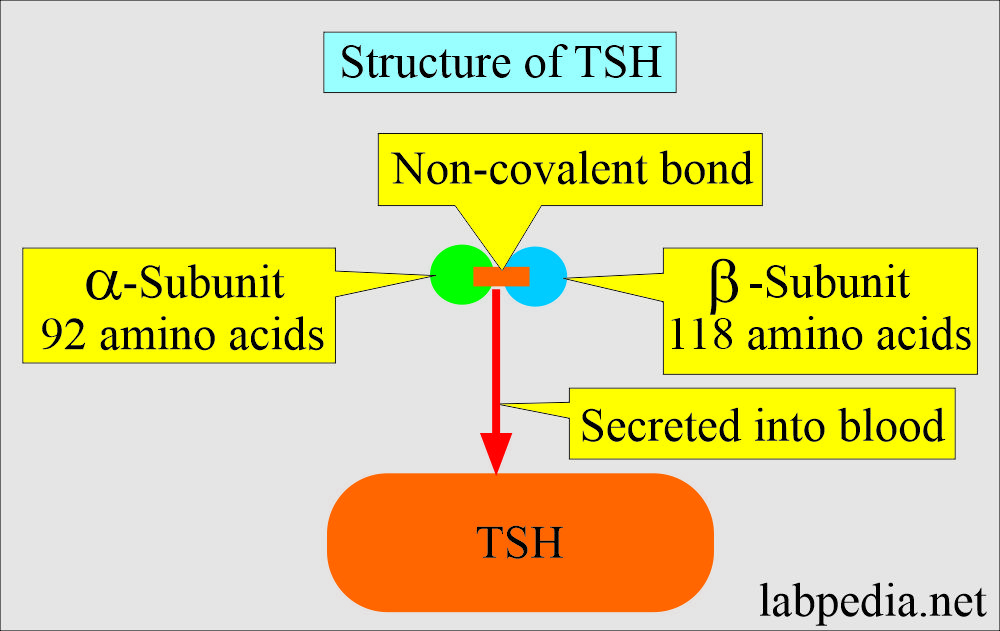
What is the structure of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)?
- TSH is a glycoprotein hormone composed of two polypeptide chains, alpha and beta.
- Alpha (α) subunit consists of 92 amino acids.
- The beta (β) subunit consists of 118 amino acids, and the biological activity is because of the Beta subunit.
- TSH molecular weight is 28,000 Da.
- It arises from the prehormone and prohormone.
- It has a short half-life of minutes to a few hours compared to other hormones like steroids.
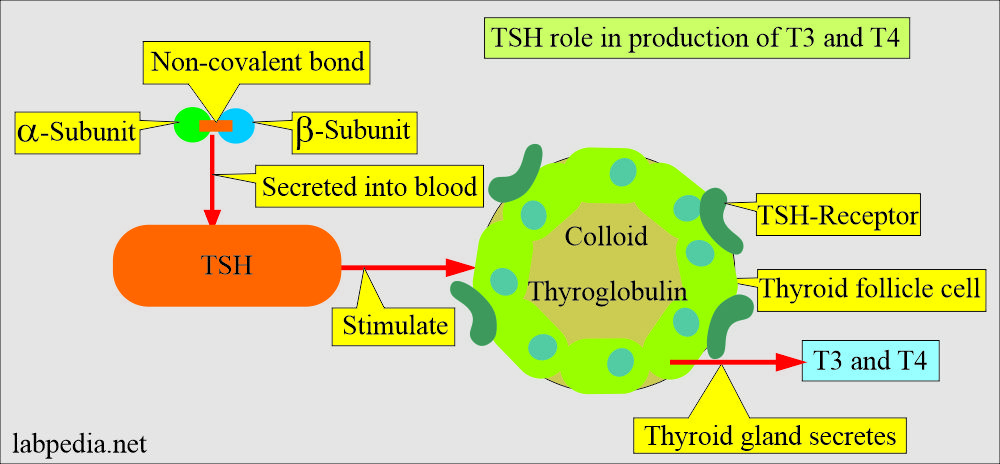
- TSH binds with the specific receptors for TSH found in the cytoplasmic membrane of the thyroid cells.
- It releases the second messenger that activates cAMP and protein kinase and stimulates further biochemical reactions.
- TSH is transported free and not bound to protein carriers in the body fluids.
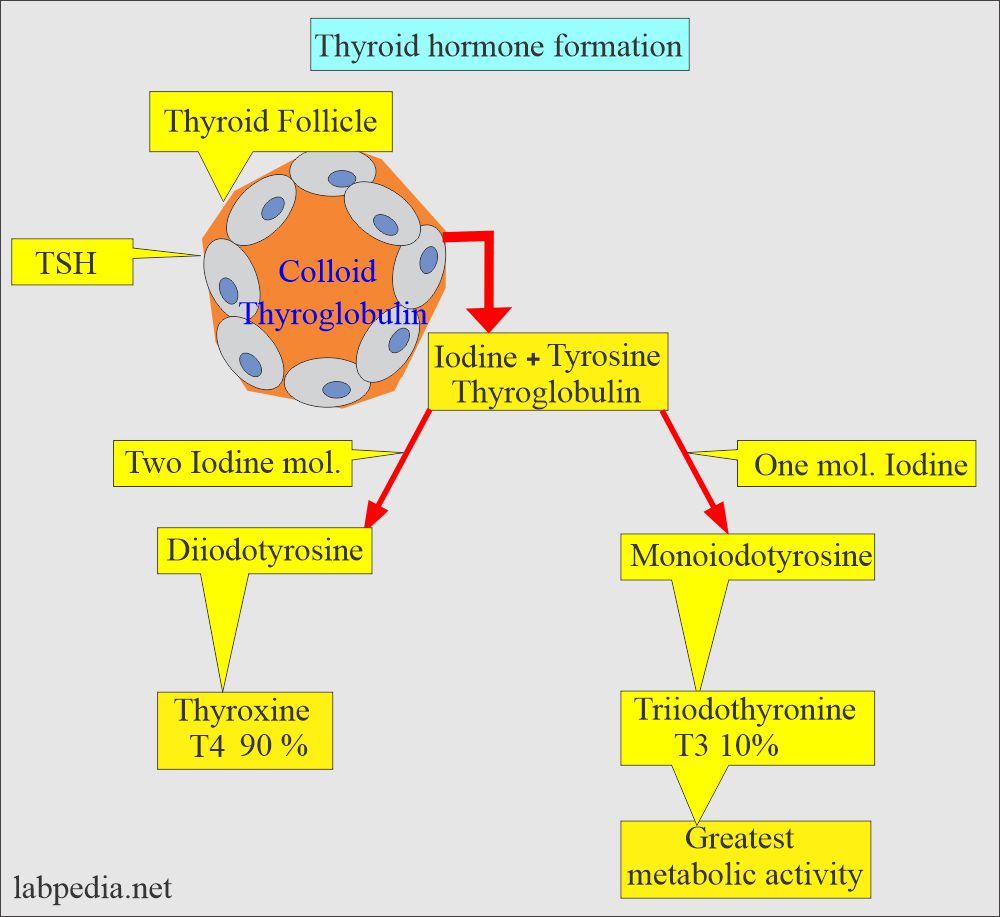
- With other adrenergic neuropeptides, TSH binds to the cytoplasm membrane receptors, and the thyroid gland secretes the T4 and T3.
- The thyroid gland has large hormone stores and a slow normal turnover rate.
What is the role of TSH?
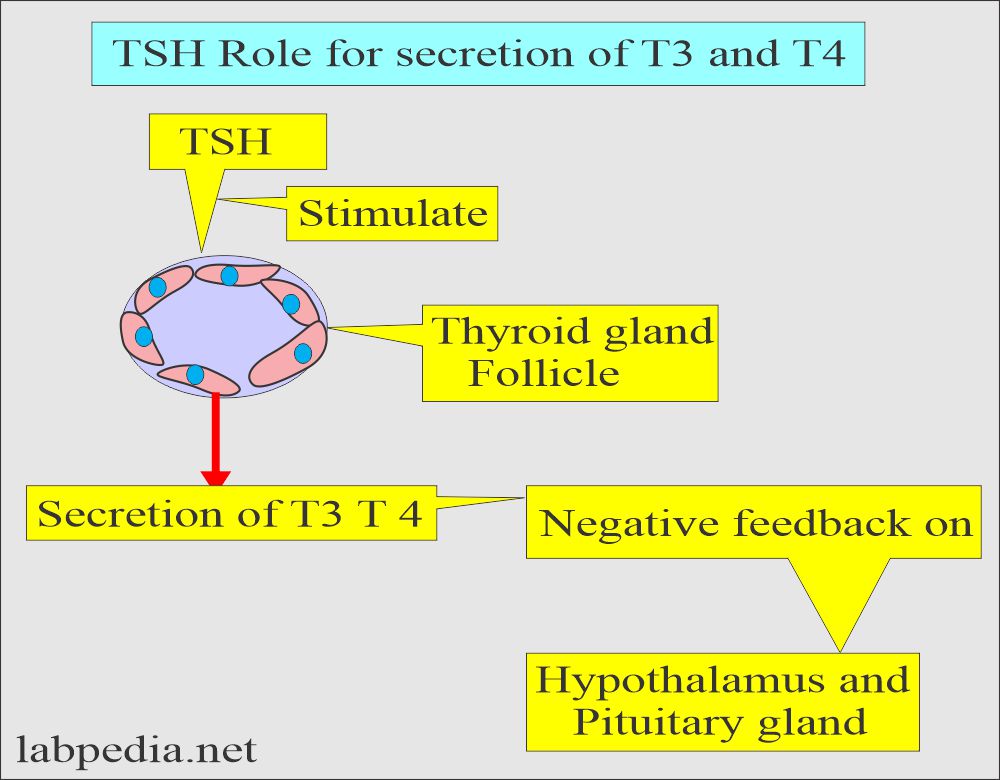
- The pituitary gland produces TSH, which stimulates the thyroid gland to distribute stored hormones.
- TSH stimulates the secretion of T4 and T3.
- TSH secretion is regulated by T4 and T3 feedback inhibition.
- Low levels of T3 and T4 are stimuli for TSH and TRH.
- TSH influences our bodies in different ways.
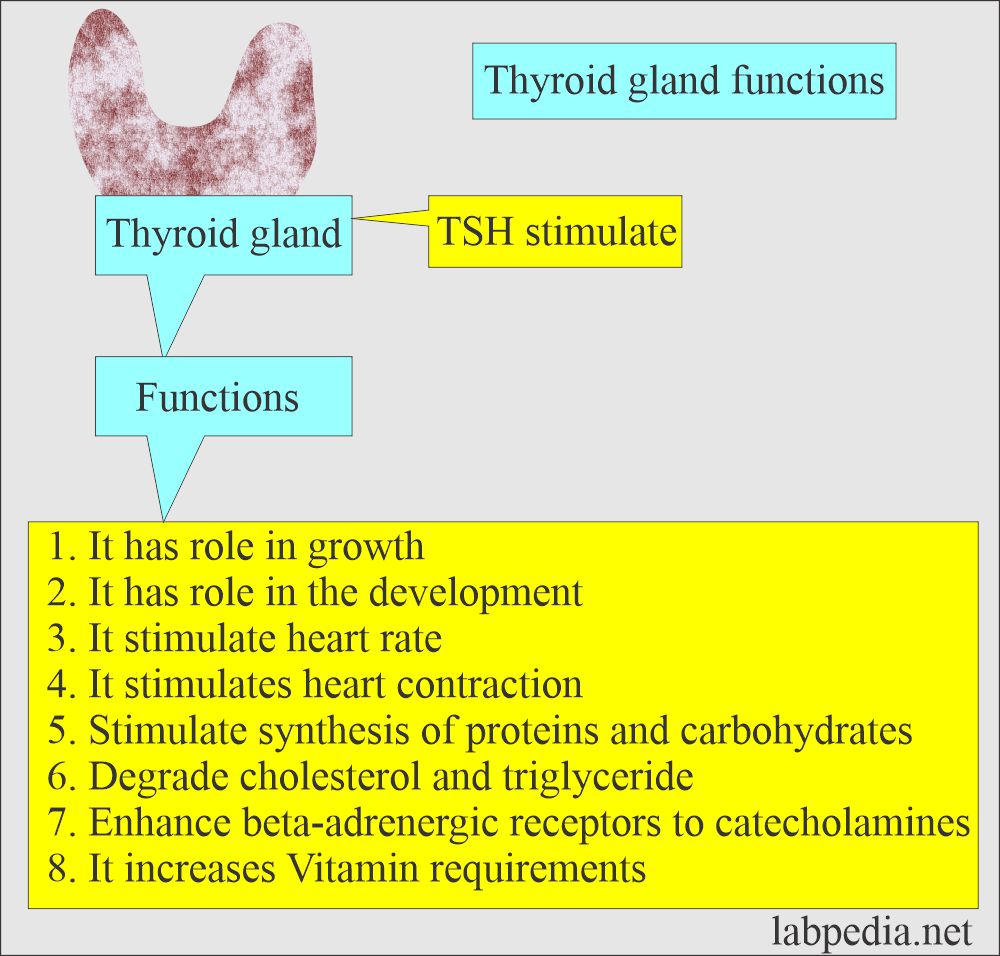
What are the functions of TSH and the thyroid gland?
- TSH stimulates the thyroid gland and leads to the secretion of T3 and T4.
- T3 and T4 have specific functions.
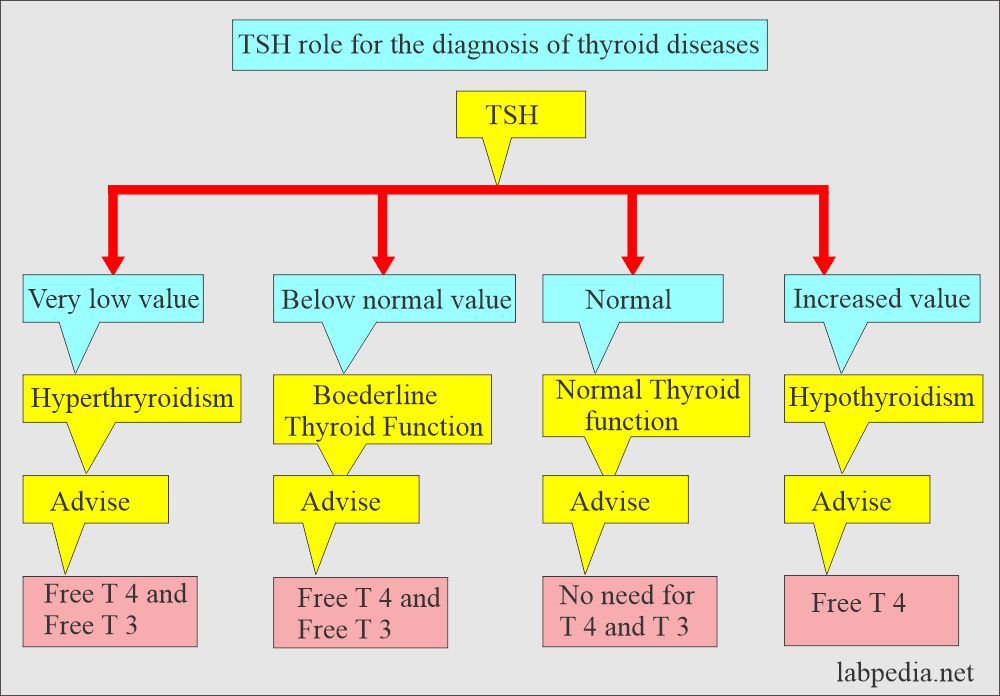
What are the interpretations of TSH?
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus regulates TSH stimulation.
- TSH is the single most common test for primary hypothyroidism.
- In the damaged Pituitary and hypothalamus, TSH and TRH are low or zero in spite of low T3 and T4.
- If there is clear evidence of hypothyroidism and TSH is normal, then think about the possibility of hypopituitarism.
- TSH level is high in primary hypothyroidism.
- TSH levels are low in hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid disorder = T4 decreased + TSH normal or raised
- Pituitary disorder = T4 decreased + TSH decreased
What is the normal TSH level?
Source 1
| Age | µU/mL |
|
Premature infants 28 to 36 weeks gestation |
0.7 to 27 |
| 1 to 4 days | 1.0 to 39 |
| 2 to 20 weeks | 1.7 to 9.1 |
| 5 months to 20 years | 0.7 to 6.4 |
| Adults | |
| 21 to 54 years | 0.4 to 4.2 |
| 55 to 87 years | 0.5 to 8.9 |
| Pregnancy | |
| First trimester | 0.3 to 4.5 |
| Second trimester | 0.5 to 4.6 |
| Third trimester | 0.8 to 5.2 |
- To converts into SI unit x 1.0 = mU/L
Source 2
- Adult = 0.4 to 5.6 mIU/L
- Newborn = 3 to 20 mIU/L
- Cord blood = 3 to 12 µU/mL
- Values vary between laboratories.
Another source
- Adult
- 21 to 54 years = 0.4 to 4.2 mU/L
- 55 to 87 years = 0.5 to 8.9 mU/L
- Newborn = 1.7 to 9.1 mU/L
- 0.3 to 3.04 mIU/L (another reference)
- Pregnancy
- First trimester = 0.3 to 4.5 mU/L
- Second trimester = 0.5 to 4.6 mU/L
- Third trimester = 0.8 to 5.2 mU/L
(Normal values vary from lab to lab and different methodologies)
- Adult = 0.4 to 4.2 µIU/L ( SI units are the same )
- Neonates = 3 to 20 µIU/L
What are the causes of increased TSH levels?
- Adults and neonates with primary hypothyroidism.
- Congenital Cretinism.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- The hypothyroid patient received inadequate treatment.
- Thyrotoxicosis due to pituitary tumors.
- Thyrotropin-producing tumors, e.g., ectopic TSH produced by lung and breast cancers
- TSH antibodies.
- Large doses of iodine.
- Chronic and severe illness.
What are the causes of decreased TSH levels?
- Primary Hyperthyroidism.
- Secondary and tertiary hypothyroidism.
- Overtreatment in a hypothyroid patient.
- Treated Grave’s disease patient.
What is the picture of thyroid hormones in various diseases?
| Clinical disease | TSH | T3 | T4 | Free T4 |
| Primary Hypothyroidism | increased | decreased | deceased | deceased |
| Secondary Hypothyroidism | decreased | decreased | decreased | decreased |
| Primary Hyperthyroidism | decreased | increased | increased | increased |
| Secondary hyperthyroidism | increased | increased | increased | increased |
Graves disease
How will you define Graves disease?
- Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the thyroid glands, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- There is an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
What is the mechanism of Graves’ disease?
- It is one of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism.
- The immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland.
- These antibodies are called thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins.
- What are the risk factors:
- If there is a family history of autoimmune diseases.
- It is more common in females.
- Smoking is a risk factor and leads to ophthalmopathy.
- If there is stress or emotional trauma.
- It causes the increased size of the thyroid gland.
- It increases the amount of hormones.
What will be the clinical presentation?
- There is an increase in the size of the thyroid gland (Goiter).
- There is weight loss even with increased appetite.
- Heartbeats are irregular, leading to tachycardia or arrhythmias.
- There is nervousness, irritability, and anxiety.
- There is heat intolerance and sweating.
- There are tremors of hands or fingers.
- The patient may have weakness or fatigue.
- These patients typically have exophthalmos.
- The eyes are dry and irritable.
- These patients’ eyes may be red.
- These patients have sensitivity to light.
- These patients may have overall vision problems.
- These patients’ skin is red or swollen, called graves’ dermopathy.
How will you diagnose Graves’ disease?
- There is a high level of T4 and T3.
- There is a decreased level of TSH.
- There is the presence of antibodies (thyroid-stimulating antibodies).
- Check the eyes for the Graves’ ophthalmopathy.
- Advise Ultrasonography for goiter.
- Advise radio-iodine uptake to assess the thyroid function.
- TSH is decreased.
- Free T4 is increased.
How will you differentiate different thyroid diseases?
| Clinical disease | Free T4 | Total T4 | T3 | TSH | Thyroglobulin |
| Hyperthyroidism primary clinical | Increased | Increased | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| Hyperthyroidism subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism primary clinical | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Increased | Normal/Increased |
| Hypothyroidism primary subclinical | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased | Normal |
| Hypothyroidism Secondary | Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal/Decreased | |
| T3 thyrotoxicosis | Normal | Normal | Increased | Decreased | Normal |
| TSH-secreting tumors | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal |
| Pregnancy with hyperthyroidism | Increased | Increased | Increased | Normal | Increased |
| Pregnancy with hypothyroidism | Decreased | Increased | Increased | Increased | Increased |
| Goiter | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Thyroid carcinoma | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Increased |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | Variable | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| Nephrosis | Decreased | Decreased | Normal | Decreased |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What will be the value of TSH in hypothyroidism?
Question 2: What will be the value of TSH in hyperthyroidism?
- Note, please see more details on the thyroid function test.