Syphilis:- Part 2 – VDRL (Venereal disease research laboratory test)
VDRL (Venereal disease research laboratory test)
What sample is needed for the VDRL test?
- This is done on the patient’s serum.
What are the indications for the VDRL test?
- This is a screening test for syphilis.
How will you discuss Syphilis microbiology?
- Syphilis is a venereal disease.
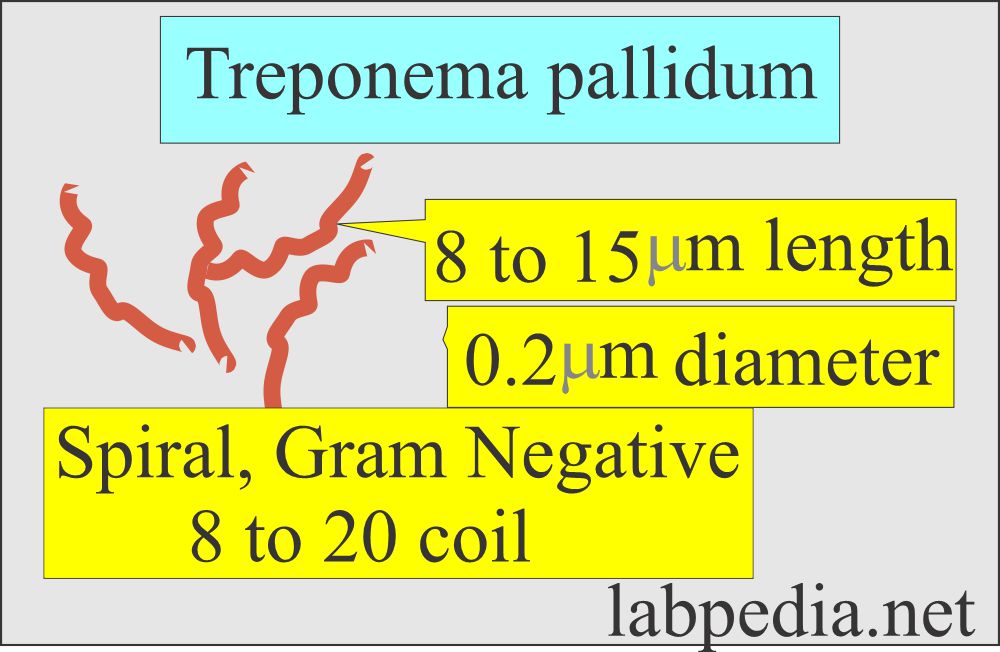
- The causative agent for syphilis is Treponema pallidum, which is a spirochete.
- The spirochete is 8 to 15 µm in length, gram-negative organisms.
- Spirochaetes are microaerophilic, but this organism cannot be cultured in vitro.
- This is motile with rotation around its long axis and flexion and extension laterally.
- T.pallidum survives in the patient with syphilis, and it has no other habitat.
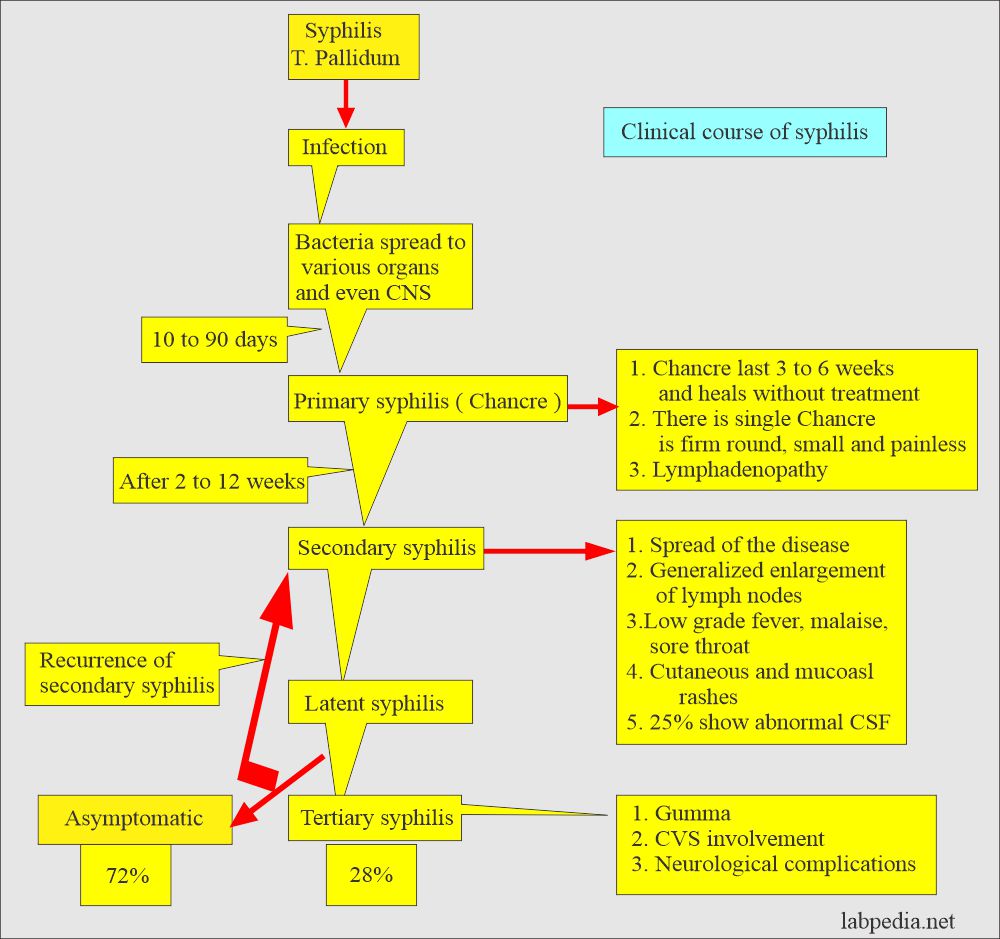
- The untreated disease has three stages, which may last many years.
- Primary stage.
- Secondary stage.
- Tertiary stage.
VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) Test
- This test will detect antibodies against Treponema Pallidum, which appears in 4 to 6 weeks.
- VDRL is a nontreponemal test that detects reagin and antibodies that act against cardiolipin as an antigen.
- During primary and tertiary syphilis, the test may be falsely negative.
- Another nontreponemal test is Rapid plasma reagin (RPR).
- VDRL is a screening test.
- VDRL may show the negative result is late syphilis.
- Other treponemal antibody tests are:
- TP-PA ( particle agglutination T.pallidum ).
- FTA-ABS ( fluorescent treponemal antibody test).
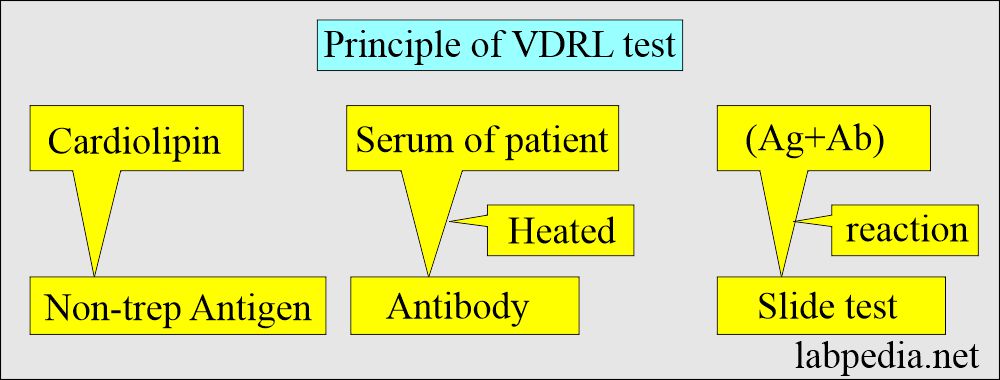
What is the principle for the VDRL test?
- This test is performed using a cardiolipin-lecithin cholesterol antigen.
- Heat-inactivated serum from the patient is used.
- Cardiolipin is prepared from beef heart.
- This test can also be done on the CSF as well.
- Advantage:
- This is inexpensive.
- This is reproducible.
- Disadvantage:
- Not 100% specific for syphilis.
- Confirm by FTA-ABS or TP-MHA test.
- Run positive and negative control.
What is the normal VDRL test report?
- A negative test means that no antibody to syphilis has been detected.
- This screening test is most likely positive for Secondary and latent syphilis.
What are the causes of negative VDRL tests?
- No syphilis.
- Done when antibodies are still not developed.
- In the late or inactive phase.
- The patient has an immune deficiency.
- Lab error.
What are the causes of false-positive tests?
- HIV
- Lyme disease
- certain types of pneumonia
- Malaria
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Can you get a false positive VDRL test?
Question 2: What is the principle of VDRL test?