Solutions:- Part 2 – Preparation of Molar, Normal, and Dilution
Solutions
How will you define a solution?
- It is a mixture of liquids where the minor component is solute and dissolved in the major component, a solvent.
- This solute and solvent are uniformly distributed.
- These are the formulas for the preparation of various solutions.
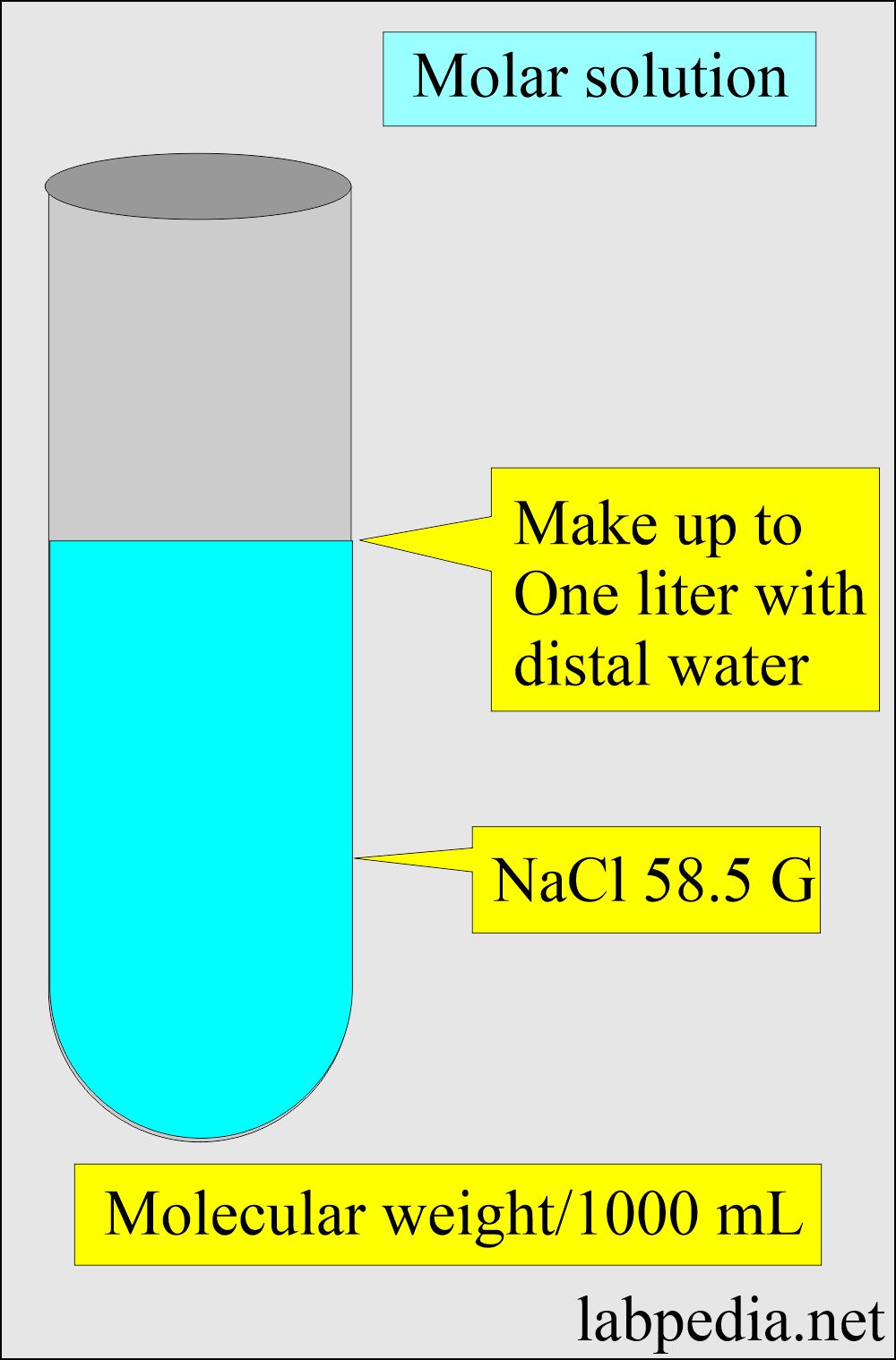
What is a Molar solution?
- It contains one mole (molecular weight) of solute in a solution (solvent), equaling one liter.
- Molar solution = Molecular weight in gram/liter in the solution.
- Example:
- I molar solution of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Sodium atomic weight = 23
Chloride atomic weight = 35.5
Total molecular weight = 58.5 gram/mol
Now dissolve 58.5 grams of NaCl in distilled water and make the solution to one liter.
What is a Normal solution?
- The normal solution is defined as the gram equivalent weight per liter of the solution (solvent).
- Normal solution = gram equivalent weight of solute/liter of the solution (solvent) = Eq.wt/L.
- These solutions are expressed as N.
- Gram equivalent weight = Gram molecular weight/valency.
- Example of Gram equivalent weight, e.g. NaCl
- NaCl gram molecular weight = 58.5 g
- Valency =1
- 58.5/1 = 58.5 gram equivalent weight.
Example
How to make a 1 N sodium chloride solution?
- The molecular weight of NaCl is 58.5.
- Gram equivalent weight of NaCl = molecular weight/1 (valency).
- So dissolve 58.5 grams of NaCl in distilled water and make up one liter.
- Dissolve 58.5 grams of NaCl in distilled water to make one liter.
How do you make a Percent solution?
- This is per hundred part of the total solution.
- There are three possibilities for a percent solution.
- Weight/weight:
- It is a percentage of solute in 100 grams of final solution equal to solute + solvent.
- For the 5% solution, take 5 grams of NaCl dissolved in 95 grams of water, around 95 mL.
- Weight/volume:
- 5 grams of NaCl dissolved in water, and the volume made 100 ml is called a 5% solution of NaCl.
- Volume/volume:
- It is composed of two solutions. e.g., if we take 5 mL of acid and dilute it to 100 mL of water, it will be a 5% solution of that acid.
How will you perform the Dilution?
- It is common to prepare the serum dilution with a high concentration of chemicals like urea in the blood if it is above 300 mg/dL.
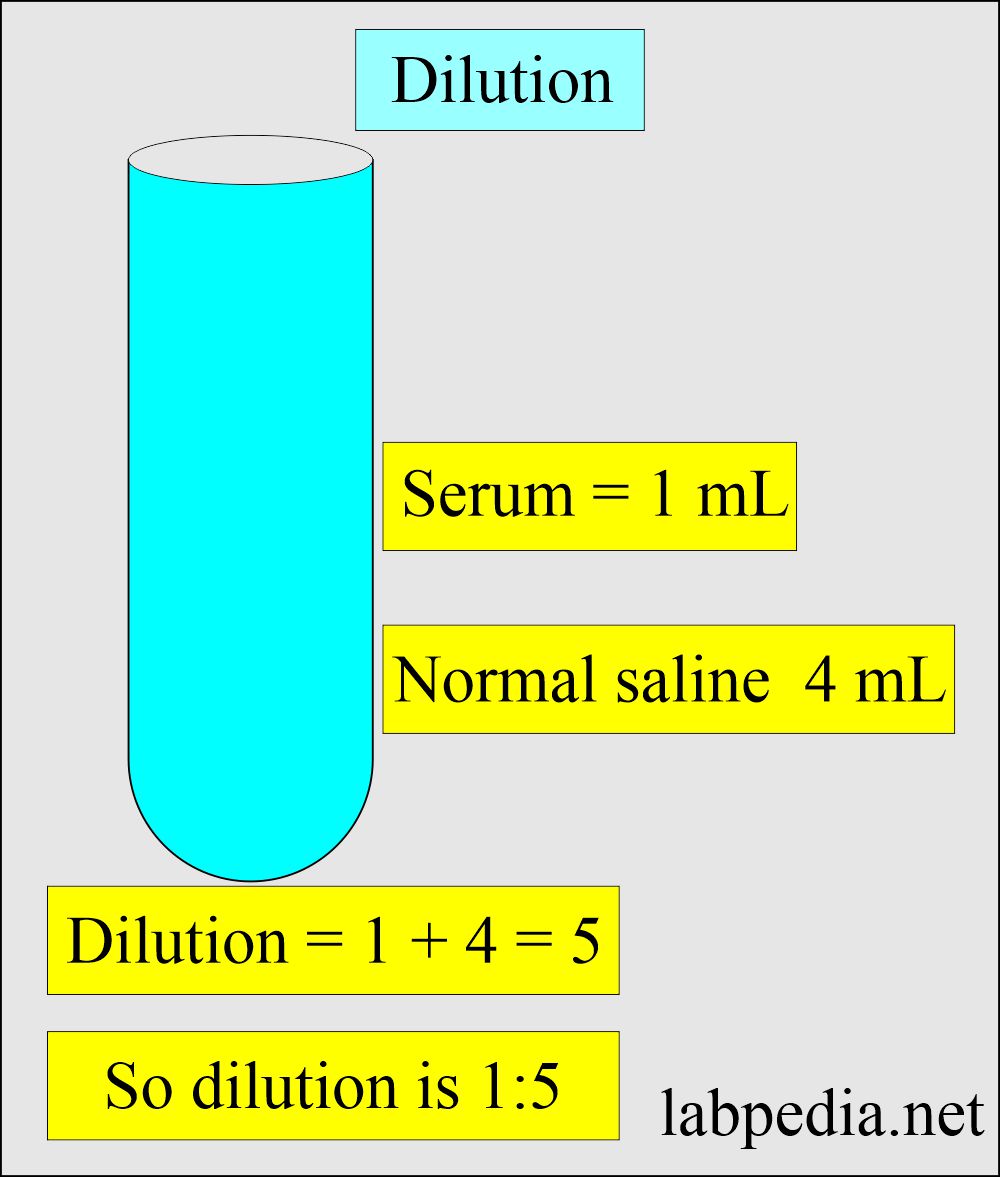
- If we make a dilution of serum like this:
- Serum = 1 ml
- Diluting fluid 4 mL
- This will be a dilution of 1:5 (1+4 =5).
- This dilution can be made from the stronger solution by this formula:
- How will you make a dilution of sodium hydroxide 1?
- Make 250 mL of sodium hydroxide solution of 0.25 mol/L from a solution of 0.4 mol/L solutions.
- C = o.25 mol/L
- V = 250 mL
- S = 0.4 mol/L
- Calculation = 0.25 x 250 / 0.4 = 156.25 mL
- Make 250 mL of sodium hydroxide solution of 0.25 mol/L from a solution of 0.4 mol/L solutions.
- How will you dilute HCL 2?
- Make 500 ml of HCL acid, 0.01 mol/L from a 1 mol/L acid.
- C = 0.01
- V = 500
- S = 1
- Calculation = 0.01 x 500 / 1 = 5 mL of HCL acid.
- Make 500 ml of HCL acid, 0.01 mol/L from a 1 mol/L acid.
- How will you dilute the body fluids?
- Make 5 ml of 1 in 10 dilutions of the serum.
- C = 1:10
- Volume = 5 mL
- S = 1
- Calculations = 1/10 x 5 / 1 = 0.5 mL of the serum and 4.5 mL of the saline = 0.5 : 4.5 = 1:10 dilution
- Make 5 ml of 1 in 10 dilutions of the serum.
Question 1: What is the difference between the molar and normal solution?
Question 2: What is a formula for the dilution of various fluids?
Question 3: What are types of % solution?