SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase), AST, Glutamic oxaloacetic Transaminase)
SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase)
Sample for SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase)
- This is done on the serum of the patient.
- A random sample can be used.
- The serum is stable for 24 hours at room temp. And 28 days at 4 °C.
Precautions for SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase)
- Avoid hemolysis because RBC contains AST and ALT, which will increase the value.
- Avoid any I/M injection, which will increase the SGOT level.
- Pregnancy may cause a decrease in the AST level.
- Exercise may increase the AST level.
- Another source of error is increased ALT and AST levels after exercise.
- Alcohol use will affect the result.
- It is increased due to calcium dust in the air, like construction in the laboratory.
- False decreases occur in diabetic ketoacidosis, severe liver disease, and uremia.
- There is a false decreased level in:
- Pyridixoin deficiency (Beriberi).
- Severe long-standing liver diseases.
- Uremia.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Drugs that may increase their value are:
- Antihypertensive.
- Digitalis preparation.
- Erythromycin.
- Anticoagulants like coumarine.
- Oral contraceptives.
- Isoniazid.
- Salicylates.
- Opiates.
- Hepatotoxic drugs.
- Methyldopa.
- SGOT is decreased because of the increased serum lactate-consuming enzyme during test, as seen in diabetic ketoacidosis, Beriberi, severe liver disease, uremia, and chronic hemodialysis.
Purpose of the test (Indications) for SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase)
- This is done in suspected liver diseases.
- This also helps in heart diseases to diagnose acute myocardial infarction.
- It helps in D/D of AMI and liver disease.
- It is advised in the case of blood donors for hepatitis.
Definition of aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT)
- Aspartate transaminase is also known as L-aspartate-2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase, AST.
- This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transfer of amino groups between an amino acid, and α-keto acids are called aminotransferase or transaminases.
- One of the aminotransferases is Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), or the old name was glutamic -oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT).
- SGOT shows day-to-day variation ≤10%
- It is widely distributed in tissue, with the highest concentration in the heart, liver, and skeletal muscles.
- SGOT’s lowest concentration is present in the kidneys, pancreas, and RBCs.
Distribution of the SGOT (AST) in the body:
- This enzyme is distributed in all tissues (primarily all the tissues), but the highest concentration is found in the liver, heart, and skeletal muscles.
- AST (SGOT) concentration is more in the heart >liver> muscles>kidneys>pancreas.
- According to concentration, SGOT is found in descending order:
- Cardiac muscle.
- Liver.
- Skeletal muscles.
- Kidney.
- Brain.
- Lungs.
- Pancreas.
- High concentration was seen in the cardiac muscle and liver.
- Intermediate concentration in skeletal muscle and kidneys.
- Much lower level in other tissues.
- Minimal activity (small amount) occurs in the skin, kidneys, pancreas, and RBCs.
- SGOT is found in plasma, bile, CSF, and saliva.
- It is not found in urine unless there is a kidney lesion.
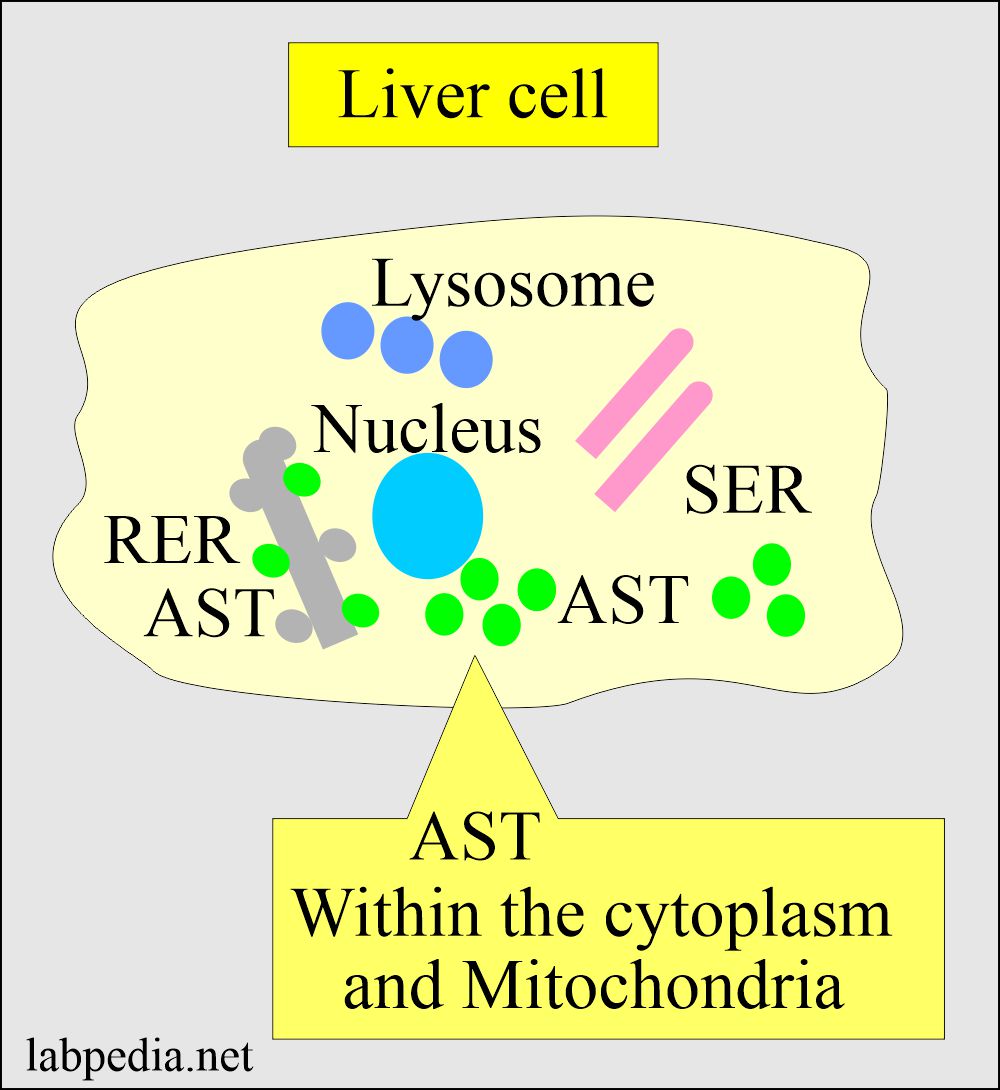
- This enzyme exists in two isoenzyme fractions:
- In the liver, it is present in the cytosolic (cell cytoplasm), and the second form is mitochondrial.
- The intracellular concentration of the SGOT enzyme is 7000 times as compared to the extracellular concentration.
- The cytoplasmic fraction isoenzyme is predominant in the serum.
- AST and ALT are increased at birth to 2 to 3 times the adult level; this will fall to the adult level by 2 to 4 months.
- Compared to serum, the SGOT level is 7800 times in the heart, 7100 times in the liver, skeletal muscles 5000 times, kidney 4500 times, pancreas 1400 times, spleen 700 times, lungs 500 times, and RBCs 15 times.
SGOT (AST) level in various tissues as compared to the serum (one unit):
| Organs | AST (SGOT) times more as comparison to serum as one unit |
| Heart | 7800 |
| Liver | 7100 |
| Skeletal muscle | 5000 |
| Kidneys | 4500 |
| Pancreas | 1400 |
| Spleen | 700 |
| Lungs | 500 |
| RBCs | 15 |
| Serum | 1 (one unit) |
Liver cell Injury:
- The injury to liver cells leads to the release of the SGOT into the blood circulation and causes an elevation in the SGOT level.
- SGOT is present in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria.
- In the blood, there is cytosolic and mitochondrial SGOT (AST).
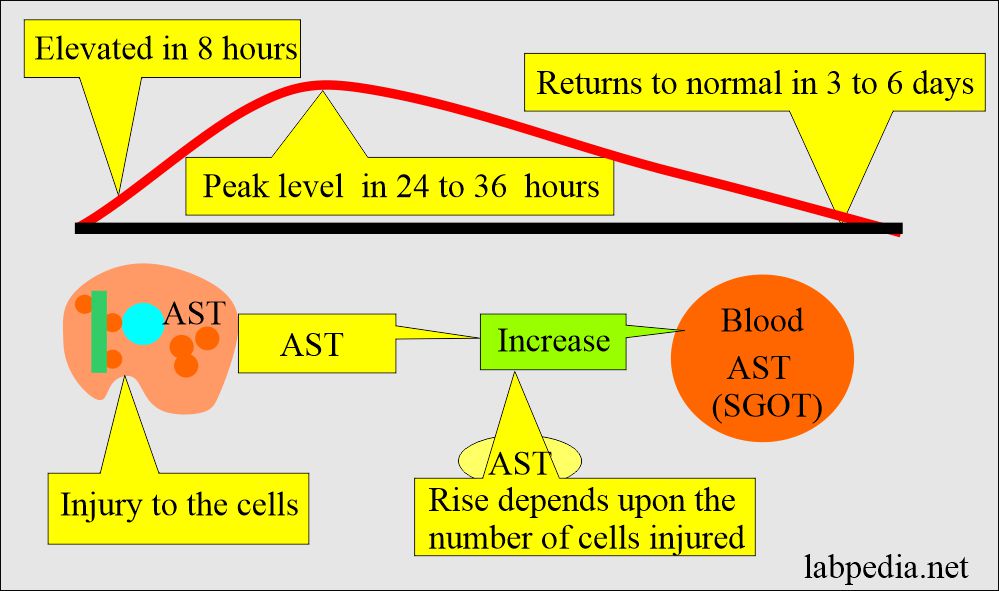
- After the injury, SGOT (AST) rises in the blood for around 8 hours, and the peak level is 24 to 36 hours and returns to normal in 3 to 6 days.
- In case of minor injury, there is only a transient rise in the SGOT (AST) level, and even it may not be noticed.
- In Acute viral hepatitis, there is a rise >10 times the normal in 75% of the cases in one study and 100% in another study.
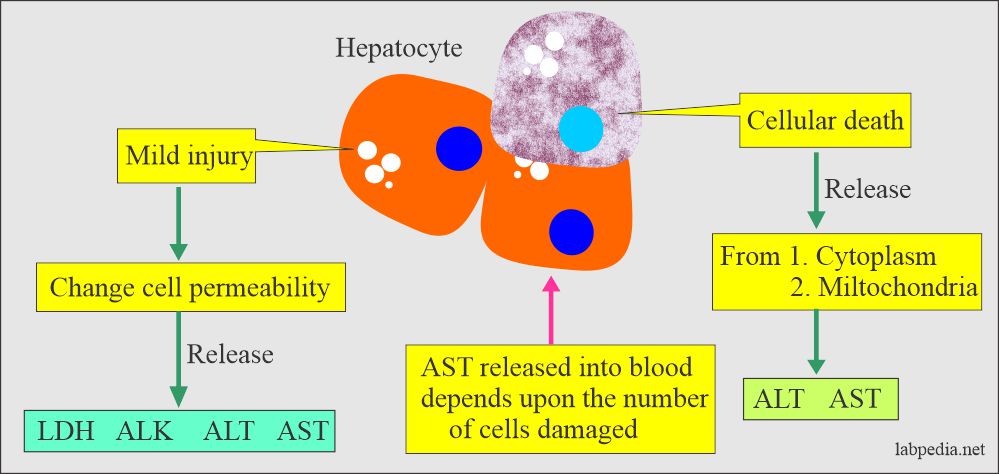
SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase): The release of the SGOT depends upon the number of hepatocytes damaged.
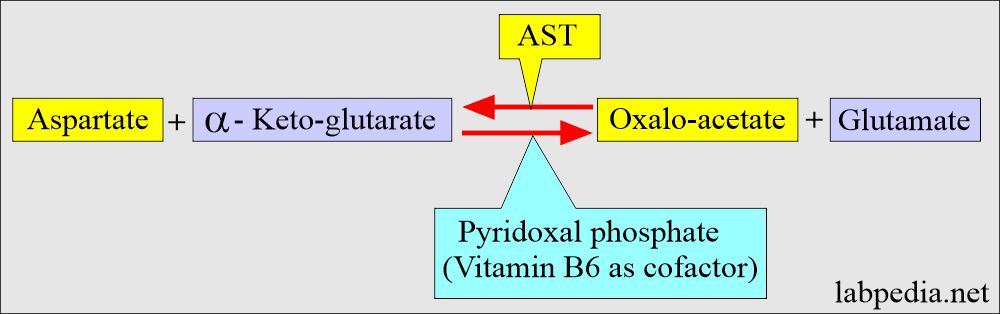
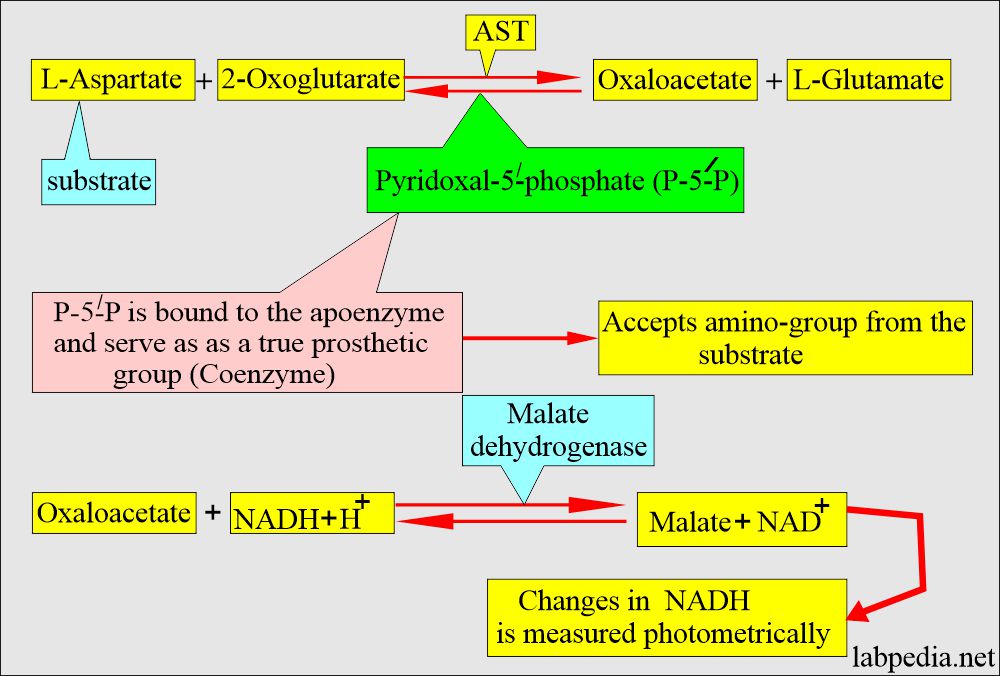
SGOT (AST) biochemical reaction:
- AST catalyzes the biochemical reaction, and it is reversible.
- The P-5-P is bound to the apoenzyme and is a true prosthetic group.
- The P-5-P bound to the apoenzyme accepts the amino group from the first substrate, aspartate, to form enzyme-bound pyridoxine-5- phosphate, and the first reaction product is glutamate. Pyridoxal-5‘- phosphate (P-5-P) functions as coenzymes in the amino-transfer reaction.
SGOT (AST) and variations in different conditions:
SGOT level 1.5 to 8 times more than the normal indicates:
- Early, late, and subclinical viral hepatitis.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Alcoholic hepatitis.
- Hepatitis due to chemicals.
- Reye’s syndrome.
- Cholangitis
- Passive congestion with centrilobular necrosis.
SGOT >8 to 10 times more than the normal indicates:
- Acute viral hepatitis.
SGOT >30 times more than the normal seen in:
- Alcoholic patients are taking acetaminophen.
- In acute extrahepatic obstructions like gallstones. The SGOT level rises to 10 times the normal value and normally returns quickly when the obstruction is relieved.
Distribution in various organs and degree of a raised level of SGOT (AST):
| SGOT (AST) level rise | Causes of raised SGOT (AST) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic application of SGOT:
- It is released into circulation and can diagnose the following conditions:
In liver diseases:
- The level may reach 100 times above the normal limit.
- In cirrhosis, there is a moderate increase, which may be around 4 times the normal limit.
- The amount of SGOT is directly related to the number of cells affected by the disease or injury.
- In chronic injury, the elevated level will persist.
- In Acute hepatitis, the level may increase 20 times than normal.
Heart diseases:
- After congestive heart failure, there is a rise in the SGOT level due to less blood supply to the liver.
- There is a rise after 6 to 8 hours of myocardial infarction damage or chest pain. Abnormal values are seen almost in more than 97% of the cases.
- This test is advised in hepatocellular diseases and coronary occlusive diseases leading to muscle necrosis.
- Renal infarction.
- Brain infarction.
- Skeletal muscle diseases. This is seen in muscular dystrophy and inflammatory conditions, and the level may reach 4 to 8 times the normal value.
- There is an elevation in pulmonary embolism.
The AST/ALT ratio, usually >1, is seen in the following:
- The patient with alcoholic cirrhosis.
- Liver congestion.
- Metastatic tumor of the liver.
- The AST/ALT ratio of <1 is seen in the following:
- Acute hepatitis.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- The ratio will be less accurate if the AST level is more than 10 times normal.
Normal SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase)
Source 1
| Age | U/L |
| Newborn | 25 to 75 |
| Infants | 15 to 60 |
| Adult | 8 to 20 |
| >60 years | Male = 11 to 60 |
| Female = 10 to 20 |
Source 2
- Newborn/ infants = 15 to 60 units/L
- Child = Value like an adult
- Adult = 0 to 35 units/L
Elderly = Slightly higher than the adults
Source 4
- Men = 14 to 20 U/L (0.23 to 0.33 µKat/L).
- Women = 10 to 36 U/L (0.23 to 0.33 µKat/L).
- Newborn = 47 to 150 U/L (0.23 to 0.33 µKat/L).
- Children = 9 to 80 U/L (0.23 to 0.33 µKat/L).
Another source
- Newborn = 25 to 75 U/L
- Infants = 15 to 60 U/L
- Adult
- Male = 15 to 40 U/L at 37C.
- Female = 13 to 35 U/L at 37C.
- Elderly = slightly higher than the adult.
- SGOT > 450 U/L in blunt abdominal injury is an indicator of liver injury.
Source 6
| Age | Normal values U/L |
| 0 to 5 days | 35 to 140 |
| <3 years | 15 to 60 |
| 3 to 6 years | 15 to 50 |
| 6 to 12 years | 10 to 50 |
| 12 to 18 years | 10 to 40 |
| Adult | 0 to 35 (females slightly low than males) |
| Elderly | slightly higher than the adults |
Increased SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase) level is seen in:
- Fulminant type of hepatitis especially viral type.
- In liver cell necrosis or injury like chronic hepatitis.
- Alcoholic hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis depends upon the cell’s activity.
- In inactive cirrhosis, usually AST level is normal.
- In active cirrhosis, the AST level is mild to moderately raised. AST level is <5 times the upper limit; in 95% of cases, the upper limit is <10 times the normal value.
- One study showed that in 15% of cases, the upper limit was >10 times the normal, which may be due to superimposed infection by the viruses.
- In cholestatic and obstructive jaundice.
- There is no rise in the enzyme unless there is secondary damage to the liver tissue.
- The elevation is mild to moderate, <10 times the normal value.
- When the obstruction is extrahepatic, there is a rapid rise in AST >10 times the normal. It falls rapidly after 72 hours.
- Liver metastasis and Hepatoma (increase maybe 5 to 10 folds and is of both enzymes).
- Around 50% of the liver’s metastatic infiltrate shows a <5 times increase in the AST level.
- In necrosis of heart muscle or skeletal muscle, e.g., acute myocardial infarction.
- In infectious mononucleosis, AST is raised in 88% to 95% of cases. Only 5% of the patients show >10 times the normal value.
- 2% may show >20 times the normal value.
- Severe exercise.
- Severe burn.
- Hypothyroidism ( in 40 to 90% of cases).
- A transient increase in acute pancreatitis, acute renal diseases, musculoskeletal diseases, or trauma may occur.
- Other diseases than liver and heart can increase the level:
- Hypothyroidism.
- Dermatomyositis.
- Polymyositis.
- Gangrene.
- Toxic shock syndrome.
- Shock.
- Mushroom poisoning.
- Pulmonary embolism and infarction.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Malignant hyperthermia.
Raised level of SGOT (AST) according to the organs involved:
| Organ involved | Causes of raised SGOT (AST) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Decreased SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase) level is seen in:
- Chronic renal dialysis.
- Acute renal diseases are leading to Azotemia.
- Vit.B6 deficiency.
- Beriberi.
- Pregnancy.
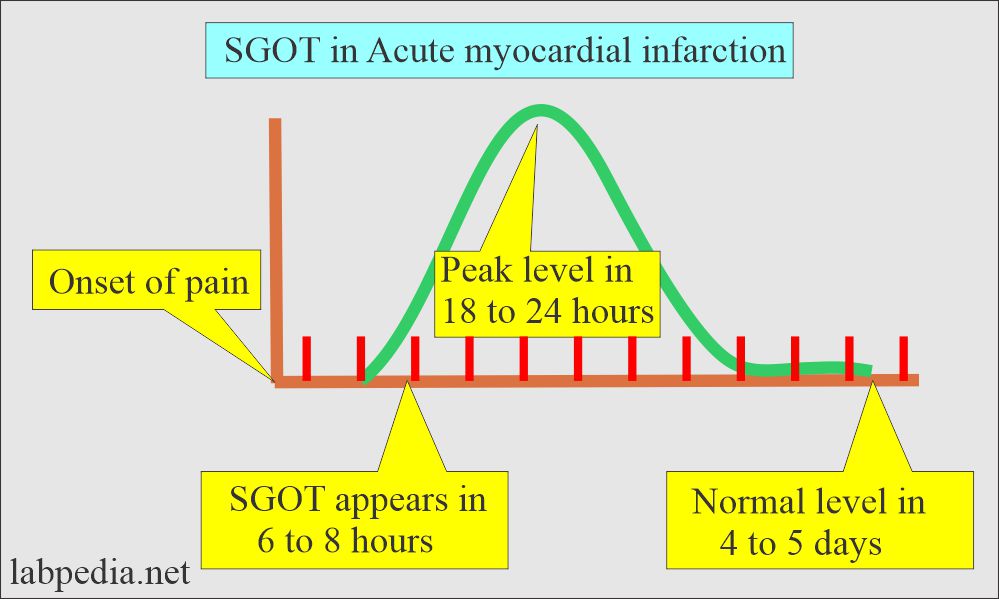
Acute Myocardial infarction (AMI) SGOT pattern:
- The SGOT level will be raised, but this is not a specific test but useful when there is a raised level of Creatine phosphokinase(CPK) and Lactic dehydrogenase(LDH).
- In Myocardial Infarction:
- SGOT appears in 6 to 8 hours after the onset of chest pain. This rise is 3 to 5 times normal.
- The peak level is between 18 to 24 hours.
- Returns to normal in 4 to 6 days unless there is no new infarct.
- The average increase in MI is 4 to 5 times normal.
- The increase of 10 to 15 times indicates massive MI (fatal infarcts).
- The abnormal level is seen in >97% of the patient if it is done at the right time.
- A myocardial injury like Angina, pericarditis, and rheumatic carditis does not rise in level.
- The small increase in the SGOT level does not indicate a favorable prognosis.
- ALT (SGPT) is usually within normal limits, or rarely only marginally increased, in uncomplicated myocardial infarction because of the small amount of ALT activity in the heart muscles.
Liver diseases SGOT (Aspartate aminotransferase) pattern:
- There is a raised level of SGOT in liver cell necrosis. This may be a 10 to 100 times increase.
- 20 to 50 times and elevations are frequent.
- Peak values are seen on the 7th or 12th days.
- Then the activity decreases, and the normal level reaches by the 3rd to 5th week in case of uneventful recovery.
- SGOT (AST) is also raised in toxic hepatitis, like infectious hepatitis.
- The SGOT level may be compared with SGPT.
- SGOT/SGPT ratio is usually greater than 1 in a patient with alcoholic cirrhosis, liver congestion, and metastatic tumors of the liver.
- A ratio of <1 may be seen in acute hepatitis and viral hepatitis.
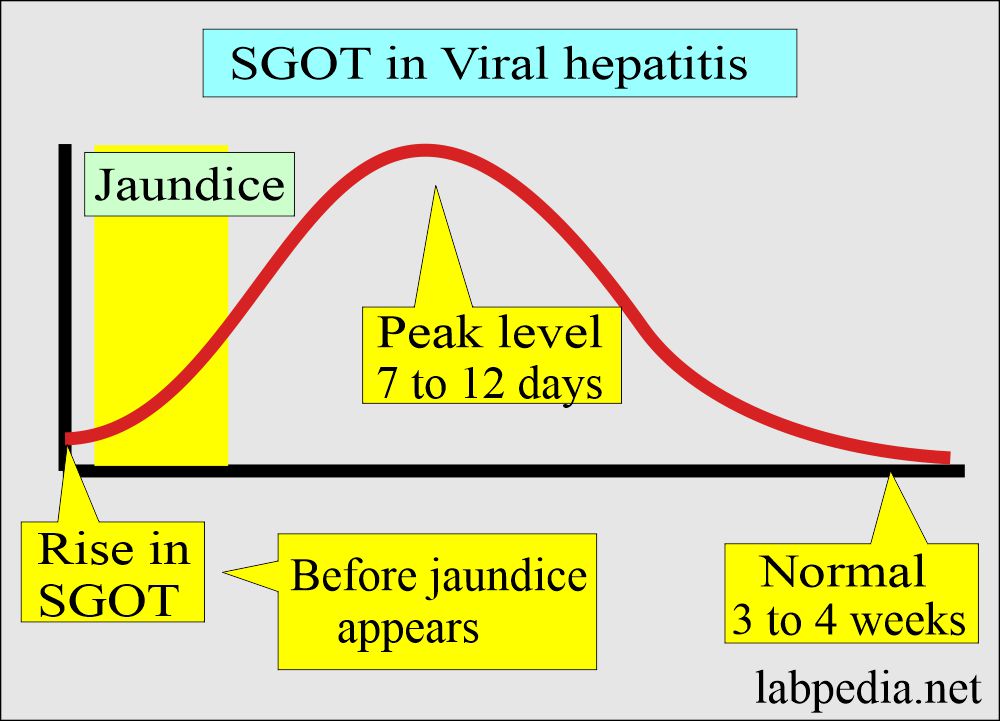
Acute viral hepatitis:
- The rise of SGOT was seen before the onset of jaundice.
- Peak level has been seen from 7 to 12 days after the onset of jaundice.
- The normal level has been seen 3 to 4 weeks after the onset of jaundice.
- Characteristically SGPT is greater than SGOT.
Table showing the increase of SGOT in various conditions:
Clinical conditions |
The rise in SGOT level with reference to normal value |
| Viral hepatitis and liver diseases | It may reach 100 times |
| Infectious hepatitis | ALT > AST |
| Toxic hepatitis | Extremely high level |
| Infectious mononucleosis | 20 times |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis | lower values |
| Extrahepatic cholestasis | Increased value |
| Cirrhosis | Normal to 4 to 5 times |
| Metastatic carcinoma | 5 to 10 times |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 4 to 5 times |
| Fatal myocardial infarction | 10 to 15 times |
| Progressive muscular dystrophy | It may reach 8 times |
| Dermatomyositis | It may reach 8 times |
| Pulmonary emboli | 2 to 3 times |
| Acute pancreatitis | 2 to 5 times |
| Crushed muscular injury, Gangrene | 2 to 5 times |
| Hemolytic diseases | 2 to 5 times |
Critical value: >20,000 U/L seen in alcohol-acetaminophen syndrome.
AST (SGOT)/ALT (SGPT) ratio:
Definition:
- AST (SGOT) is present in liver cells, microsomes, and mitochondria.
- ALT (SGPT) is present in the liver microsomes.
- In the case of severe necrosis, AST (SGOT) increases more than ALT (SGPT), but in liver cells with inflammation without much necrosis, ALT (SGPT) increases more than AST (SGOT).
Indications:
- AST/ALT ratio differentiates between the hepatobiliary system and pancreas.
Normal AST/ALT ratio:
- 0.7 to 1.4 (Depending upon the methods).
Raised AST/ALT ratio:
- Drug toxicity (>2.0).
- Alcoholic hepatitis (>2.0).
- In the case of cirrhosis (1.4 to 2.0).
- Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis (>1.5).
- In the case of chronic hepatitis, there is a slight increase (1.3).
Decreased AST/ALT ratio:
- Extrahepatic cholestasis (normal or slightly decreased).
- In the case of acute hepatitis due to drugs, viruses, and toxins.
SGOT and SGPT facts:
- AST (SGOT) is always raised in acute myocardial infarction, where ALT (SGPT) will be normal unless there is damage to the liver.
- ALT (SGPT) is more raised in acute hepatobiliary obstruction than AST (SGOT).
- ALT (SGPT) is more specific than AST (SGOT) for liver cell injury.
- AST (SGOT) is more sensitive to alcoholic liver cell injury.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of SGOT?
Question 2: When SGOT will be normal in AMI?

Sources meaning in above sgot
Please clarify your question.
My son’s age is 13 years. In his liver profile test his serumSGOT COUNT IS 99.1 , WHAT IT’S indicates
This shows liver cell damage. Would you please advise complete liver function and hepatitis profile (HBS, HCV)? What was the bilirubin level?.
My Sgot is 333
Sgpt is 198
What I can do
It’s a serious problem
Your liver functions are abnormal. It would help if you ruled out viral markers. I hope you are not using medicines or alcohol? It is a serious problem and needs thorough work to find the cause.
My Sgot is 333
Sgpt is 198
What I can do
It’s a serious problem