Semen:- Part 2 – Normal and Abnormal Semen
Normal and Abnormal Semen
What sample is needed for semen analysis?
- This is preferred if the sample is collected in the lab.
- Masturbation is preferred, and the entire collected semen should be submitted.
- The accepted volume is 2 to 5 mL.
- Collect the sample when the doctor or the technician should be available to evaluate the motility immediately.
- 2 to 3 days of sexual abstinence is preferred.
What are the Precautions for semen analysis collection?
- Don’t use condoms, particularly with spermicide.
- If brought from home, the specimen should be maintained at 37 °C during transport and examined within 3 hours of collection.
- A sterile container is needed, and the sample should be collected at a room temperature of 37 °C.
- Plastic containers are not recommended.
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
- The analysis should be done immediately when the semen is liquefied.
- Should be examined within 4 hours,
- The sample should be kept at 37 °C.
- Wait till liquefaction is complete for the examination.
What is the summary of the normal semen?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the difference between normal and abnormal semen values?
| Parameters | Normal values | Abnormal values |
| Volume | 2 to 5 mL | <2 or >5 mL |
| Color | grey to white (Opalescent) | Brown to red |
| Sperm density (count) | >2o million/mL | <10 million/mL |
| Total sperm count | 20 to 250 million/mL | <20 million/mL |
| Motility |
|
|
Motility score (evaluated 2 to 4 hours after ejaculation) Motility is graded as follows:
|
|
|
| Liquefaction | Immediate (within 10 to 30 min) | >60 min |
| pH | 7.2 to 7.8 | <7.2 |
| Viability | >65% do not take stain and are alive | % of dead cells is more (than 65%) and take stains |
| Morphology | >70% normal <4% immature form | >30% abnormal form |
| Immature form | <4 % | >4 % |
| Defective heads | <35 % | >60 % |
| Defective tails | <20 % | >25 % |
| WBC count | 0 to 2000/mL | Increased number |
| The aggregate of >10 sperms | Absent | Seen in prostatitis |
| Fructose | 150 to 600 mg/dL | Decreased level/absent |
| Acid phosphatase | 200 to 300 mg/mL | |
| Citric acid | >3 mg/mL | |
| Zinc | >75 µg/mL | |
| Magnesium | >70 mg/mL | |
| Glucosidase | >20 mU per ejaculate | |
| Prostaglandins | >20 mU per ejaculate | |
| Inositol | >1 mg/mL | |
| Carnitine | >250 µg/mL | |
| Glycerophosphorylcholine | >650 µg/mL |
- The following table is modified from the WHO Laboratory Manual 1992.
What is the difference between normal and abnormal semen (Another source)?
| Parameter | Normal | Pathological |
| Coagulation | Coagulates | Delayed |
| Liquefaction | Complete in 10 to 30 minutes | Delayed |
| pH | 7.2 to 7.8 | |
| Volume | 2 to 6 mL | <1.5 mL |
| Sperm density x106/mL | >20 | <10 |
| Total sperm count x106/mL/per ejaculate | >80 | <20 |
| Progressive motility score (after 2 to 4 hours of ejaculate) | 3 to 4 | 0 to 1 |
| Live spermatozoa | ≥50% | <35% |
| One hour after ejaculating | ≥70% | |
| After 3 hours of ejaculating | ≥60% | |
| After 4 hours of ejaculating | >50% | <35% |
| Normal spermatozoa | ≥60% | <35% |
| Defective heads | <35% | >60% |
| Defective mid-piece | ≤20% | >25% |
| Defective tails | ≤20% | >25% |
| Immature forms | <4% | |
| Semen smear | Mostly, no RBC or WBC are seen. |
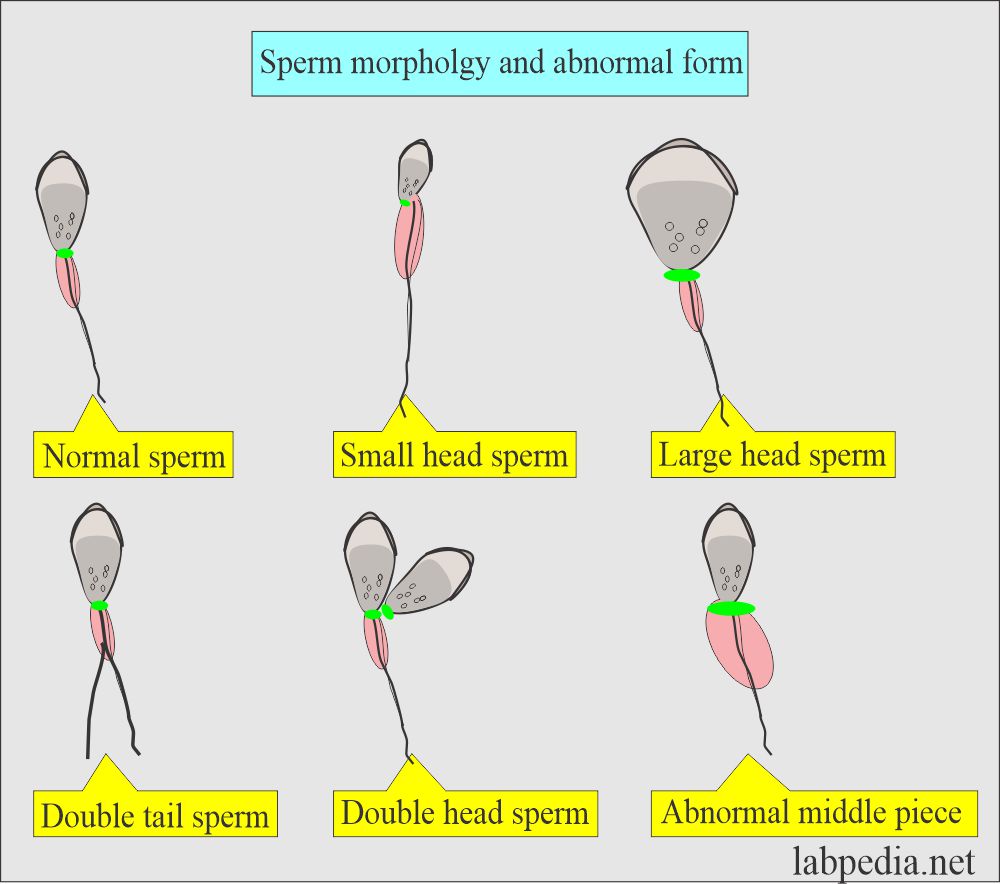
What are the possible abnormal forms of the sperm?
What are the drugs that may decrease the count?
- Cancer chemotherapy ( Vincristine, methotrexate, procarbazine, and nitrogen mustard).
- Estrogen therapy.
- Cimetidine.
- Methyltestosterone.
Important note:
- Single semen analysis is not conclusive because the sperm count varies from day to day.
- A semen analysis should be done twice or thrice for the best result.
- Please see more details in semen analysis part 1.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: When will you call abnormal semen when the count is?
Question 2: What is the abnormal volume of the semen?