Semen:- Part 1 – Semen analysis, and Semen Counting Procedure
Semen analysis
What sample is needed for Semen analysis?
- This is preferred if the patient is in the lab to collect the sample.
- Masturbation is preferred, and the entire collected semen should be submitted.
- The accepted volume is 2 to 5 mL.
- Collect the sample when the doctor or the technician is available to evaluate the motility immediately.
- 2 to 3 days of sexual abstinence is preferred.
- Prolonged abstinence should be discouraged because sperm cells’ quality, and especially their motility, will decrease.
- The proper container is also important.
- To evaluate the vasectomy, the patient must ejaculate once or twice before the semen specimen collection day. This process will clear the distal portion of the vas deference.
- Samples are unsatisfactory if the sample is obtained at the house by coitus interruptus or masturbation.
- In the house sample, instruct the patient to deliver it within one hour of collection.
- Instruct the patient to avoid cold and heat during transportation. The best is to keep the sample in closed hands (in the fist).
What are the precautions for Semen analysis?
- Don’t use condoms, particularly with spermicide.
- If brought from home, the specimen should be maintained at 37 °C during transport and examined within 3 hours of collection.
- A sterile container is needed, and the sample should be collected at a room temperature of 37 °C.
- Plastic containers are not recommended.
- Avoid extreme temperatures.
- The analysis should be done immediately after the semen has liquefied.
- Should be examined within 4 hours,
- The sample should be kept at 37 °C.
- Wait till liquefaction is complete for the examination.
- Drugs that may decrease the count are:
- Antineoplastic agents (nitrogen mustard, procarbazine, vincristine, and methotrexate).
- Direct the patient to avoid alcohol intake for several days before semen collection.
- Instruct the patient to avoid sexual activity for 2 to 3 days before collecting the sample.
- Avoid prolonged abstinence because the quality of the sperm and their motility may be decreased.
What are the Indications for semen analysis?
- This is the workup of the infertile couple.
- This is done to evaluate the quality of sperm.
- To confirm the efficacy of vasectomy (postvasectomy).
- Done for the forensic studies.
- To get semen for artificial insemination.
How will you define semen?
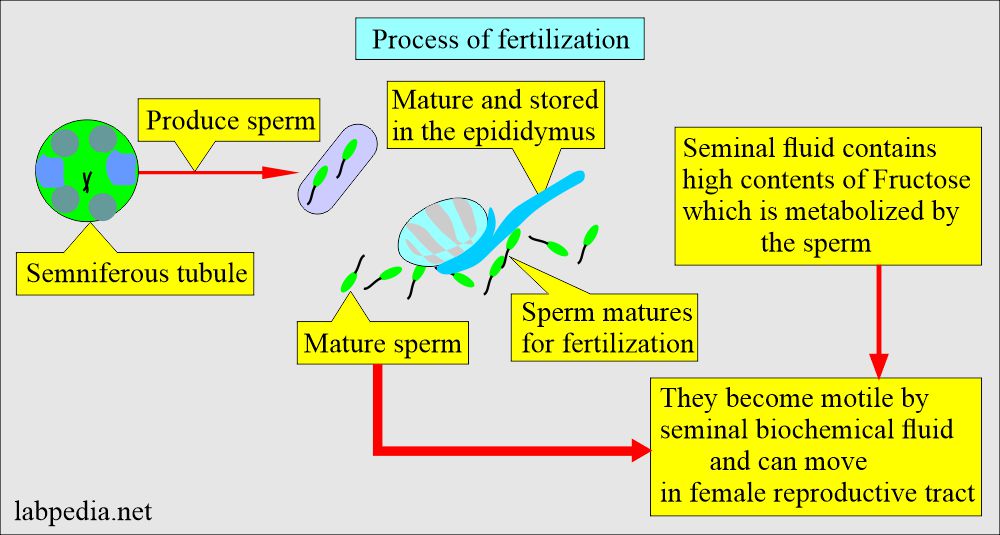
- Seminal fluid is the secretion of the prostate glands, two seminal vesicles, two Cowper glands, and testes. It serves as the vehicle for sperm transport and creates an alkaline medium. It also provides nutrition. This medium promotes the sperm’s motility and survival.
- Semen comprises various male secretion products from reproductive organs like the testes, epididymis, seminal vesicle, prostate, bulbourethral, and urethral glands.
- The ejaculated semen is a viscous, yellow-grey fluid that forms a firm gel-like clot immediately after ejaculation.
- This clotted semen liquefies at room temperature (37 °C) within 5 to 60 minutes. If it requires more than one hour, that semen is considered abnormal.
What are the components of Semen analysis?
- Volume.
- Sperm count.
- Evaluation of the normal sperm.
- Evaluation of sperm motility.
- The pH of the semen.
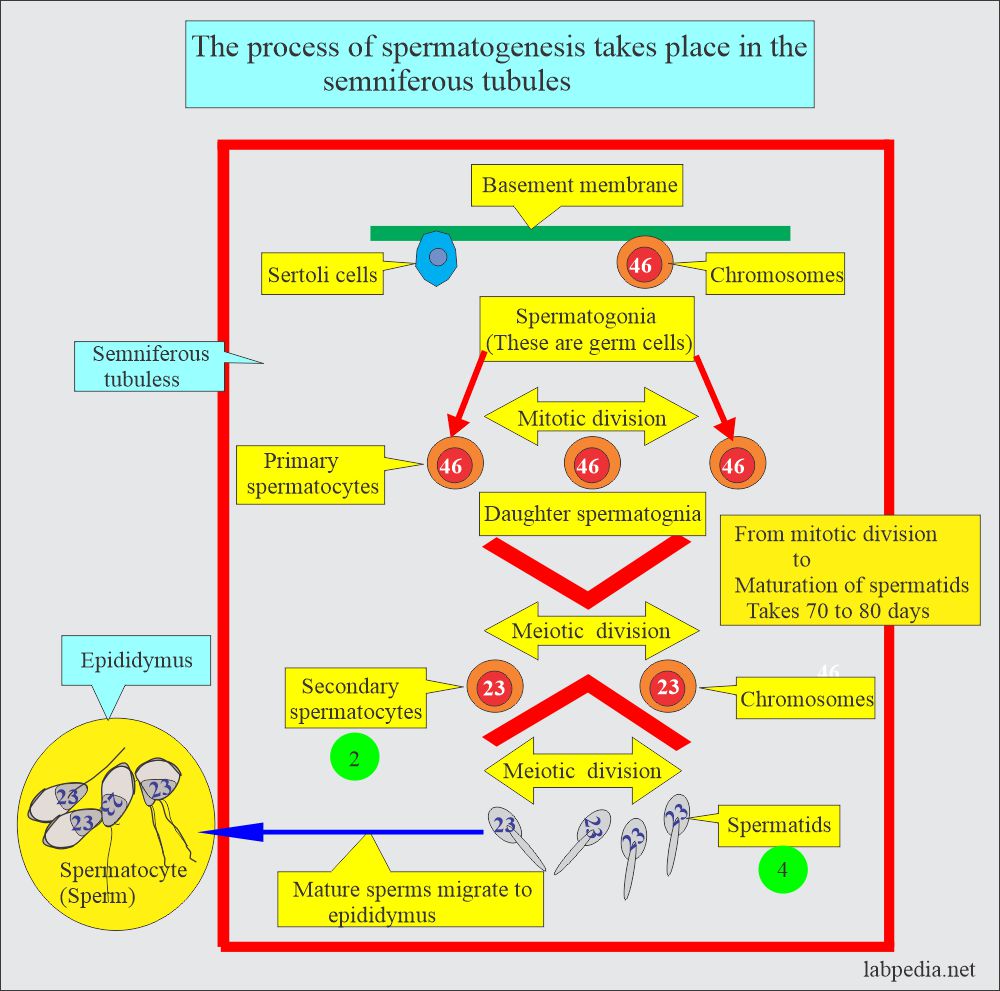
How will you discuss Spermatogenesis?
- It occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. These mature in the epididymis.
- Semen production is dependent upon the function of the testes.
- These are stimulated by testosterone.
- The testes’ testosterone concentration is 100 times more than in the peripheral blood.
- This high concentration of testosterone is needed for spermatogenesis.
- LH stimulates Leydig’s cells to produce testosterone.
- The Semniferous tubules are lined with 46-chromosome germ cells called spermatogonia.
- These cells undergo mitotic division and ultimately give rise to primary spermatocytes.
- Secondary spermatocytes give rise to spermatids by meiotic division, which will differentiate into sperm or spermatozoa containing 23 chromosomes.
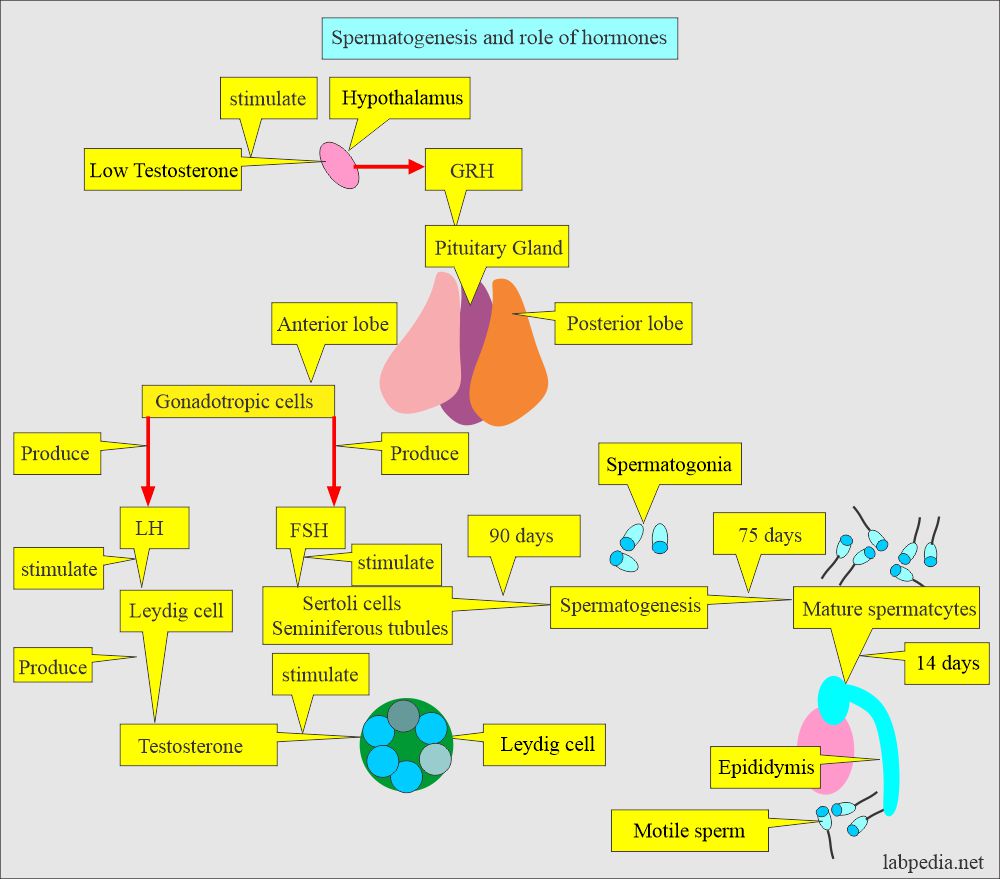
What are the Factors for spermatogenesis?
- Semen production depends upon the function of the testis.
- The hypothalamus produces a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GRH) in response to low testosterone levels.
- GRH stimulates the pituitary gland to produce the follicular stimulating hormone.
- Now, the FSH stimulates the Sertoli cell, which is the location of sperm production.
- FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells to secrete activin, which stimulates spermatogenesis.
- Besides, the Sertoli cells secrete inhibin, which inhibits FSH secretion from the pituitary gland.
- LH stimulates the Leydig cells, which produce testosterone. Testosterone then stimulates the seminiferous tubules to produce sperm.
- Spermatogenesis (in the seminiferous tubules) takes approximately 3 months.
- The maturation of the spermatogonia to mature spermatocytes takes approximately 75 days through the epididymis.
- In the epididymis, motility is acquired; it takes another 14 days.
- Spermatocytes develop from the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules. They mature in the epididymis and are ready for fertilization.
What is the role of hormones in spermatogenesis?
- In primary gonadal failure:
- FSH is raised.
- LH is raised.
- Secondary gonadal failure:
- FSH is decreased.
- LH is decreased.
How will you classify spermatocytes?
- It depends upon the sperm count:
- Aspermia (azoospermia): When there is no sperm.
- Oligospermia is when the count is <20 million/mL.
- Asthenospermia is low sperm motility.
- Necrospermia is the Normal count of the sperm but is non-motile.
- Hemospermia is when there are abundant RBCs in the ejaculate.
What are the contents of the Semen analysis?
- Volume. Check when the sample is fresh.
- Sperm count. This can be done when the semen is completely liquified.
- Motility. This should be checked when the sample is fresh and repeated when it is liquefied.
- Morphology. This can be better appreciated if the smear is stained.
What is Normal semen?
- The volume is 2 to 6 ml.
- The color is gray to white or opalescent.
- Liquefaction time is usually 10 to 30 minutes at 37 °C.
- The volume is normally 1.5 to 5 mL.
- pH varies between 7.7 and 8. A reading below 7.0 usually indicates prostatic secretion.
- The sperm count is 20 to 250 million/mL.
- Normally, the total count is more than 80 million/ml. But now, it is considered >20 million /mL fertile semen.
- Live spermatozoa of more than 50%.
- >65% of the sperm do not take stains, which are alive.
- Sperm motility >50% at one hour. This is a moderate to strong forward motion.
- Place the semen drop on the prewarmed slide at 37 °C.
- Examine under the 40x and find the motile sperm.
- Evaluate the sperm as actively motile or sluggish.
- Normally,>70% of sperms are motile after one hour when the sperms are kept at 37 °C.
- The progressive motility score is 3 to 4.
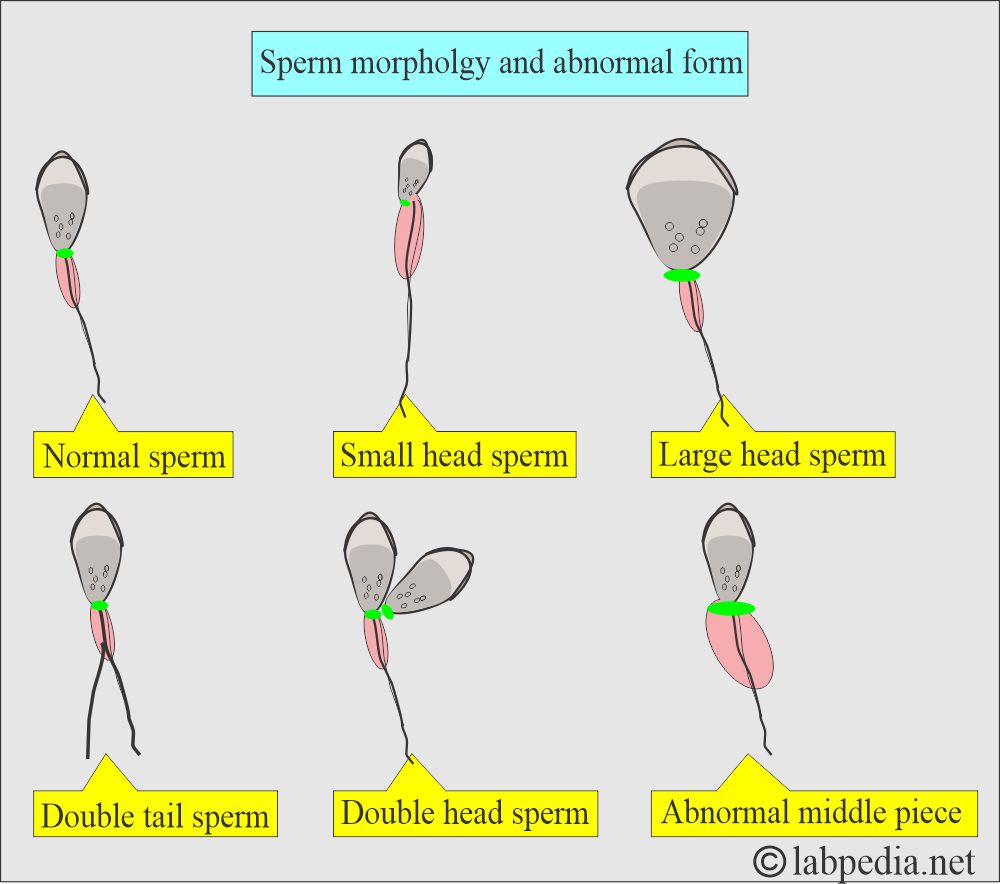
- Sperm morphology should be >30%. Typically, normal forms are >70%, and immature forms are <4%.
- Staining the slide with the Papanicolaou method.
- Count at least 200 sperm under oil emersion.
- Abnormal forms are <30%.
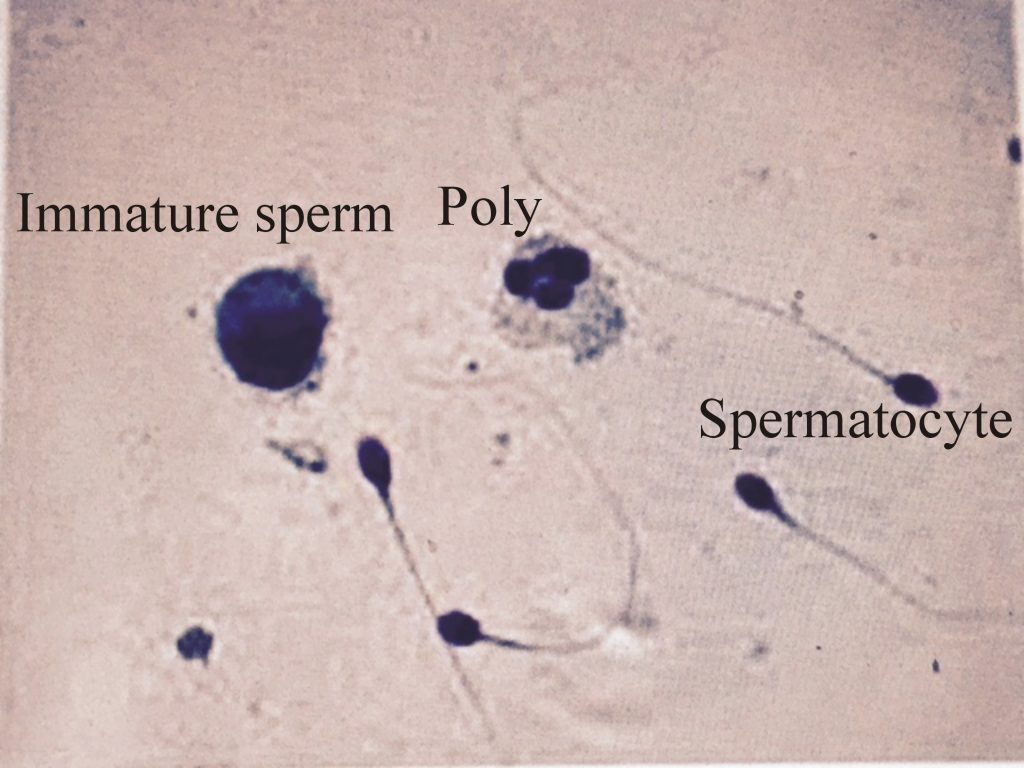
- Note immature sperms as well.
- Also, note RBCs and polys.
- Microscopy:
- WBC is 4 to 6/HPF.
- Epithelial cells are few.
- RBCs are not found.
- Aggregation may be seen, but very few.
- Crystals are amorphous phosphate.
- Stain the slide with eosine, which will only be taken up by the dead sperm.
- Clumping or agglutination of the sperms should be reported, which indicates antibodies.
- The fructose level is 150 to 600 mg/dL.
- Low or nil fructose indicates an obstruction in the ejaculatory duct.
- The spermatozoa utilize fructose.
- Acid phosphatase = 100 to 300 mg/100 ml.
- Citric acid = >3 mg/ml.
- Zinc = >75 µg/ml.
- Magnesium = >70 µg/ml.
- Inositol = >1 mg/ml.
- Glucosidase = >20 mU/ ejaculate.
- Carnitine = >250 µg/ml.
Source 2 Normal semen
- Volume = 2 to 5 mL
- Liquefaction time = 20 to 30 minutes after the collection.
- pH = 7.12 to 8.0
- Sperm count = 50 to 200 million/mL
- Sperm motility = 60 to 80% actively motile.
- Sperm morphology = 70 to 90% normally shaped.
What is Normal semen (another source)?
| Characteristic features | Values per ejaculate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
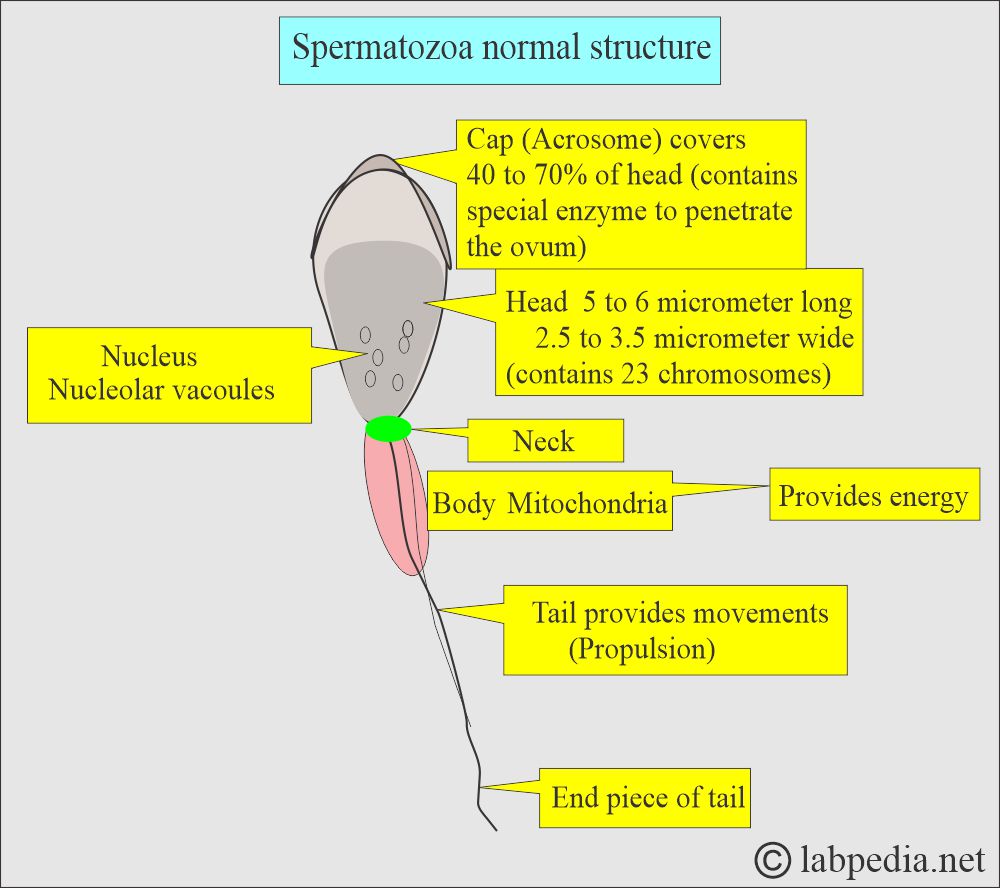
What is the normal structure of the spermatozoa?
What are the features of Pathological Semen?
- The color is brown to red. Or maybe yellow and turbid.
- Liquefaction time is >60 minutes.
- It indicates highly viscous semen. The causes of highly viscous semen are:
- Dehydration.
2. Infections.
3. Zinc deficiency
4. Hormonal imbalance.
5. Semen volume is not adequate.
6. If you do not do frequent sex activity.
7. Last is lifestyle, like smoking, alcohol overuse, and stress.
- Suppose the volume is <1.5 ml. This may be <2 ml or >5 ml.
- pH is <7.2.
- Total count <20 million /mL.
- Live sperm <35%.
- Motility <50 % after 2 hours.
- The progressive motility score is 0 to 1.
- Morphology >30% abnormal forms.
- Fructose is decreased.
What is the difference between normal and abnormal semen?
| Parameter | Normal semen | Pathological semen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How will you count Sperm?
1. What are the contents of the Sperm counting solution?
- Formalin = 1 mL
- Sodium bicarbonate = 5 grams
- Distal water = 100 mL
- Mix the above ingredients well.
- Add all the above ingredients to 100 mL of distilled water.
What is the procedure for counting the sperms?
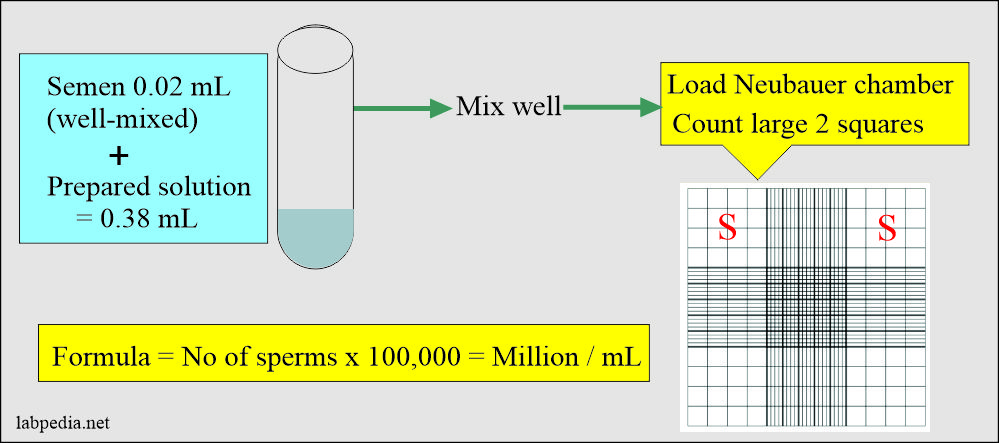
- Take 0.02 ml of semen.
- Take 0.38 mL above the solution (diluting fluid).
- Mix well above semen and diluting solution.
- Now, load the Neubauer chamber.
- Count the two large squares.
- Important to move the microscope up and down to count the sperm at different levels.
How will you calculate sperm count?
- Count in the large two square x 100,000 = count in a million/mL.
2. What is the Simplified method for sperm counting?
- Take 1 mL of semen and mix it with sodium bicarbonate-formalin solution to make a total of 20 mL.
- Fill the Neubeaur chamber with diluted semen and wait 3 to 5 minutes. So that spermatozoa get settled.
- Now count two large squares (2 sq mm).
- Calculate the number of spermatozoa in 1 mL of fluid by multiplying the number by 100,000.
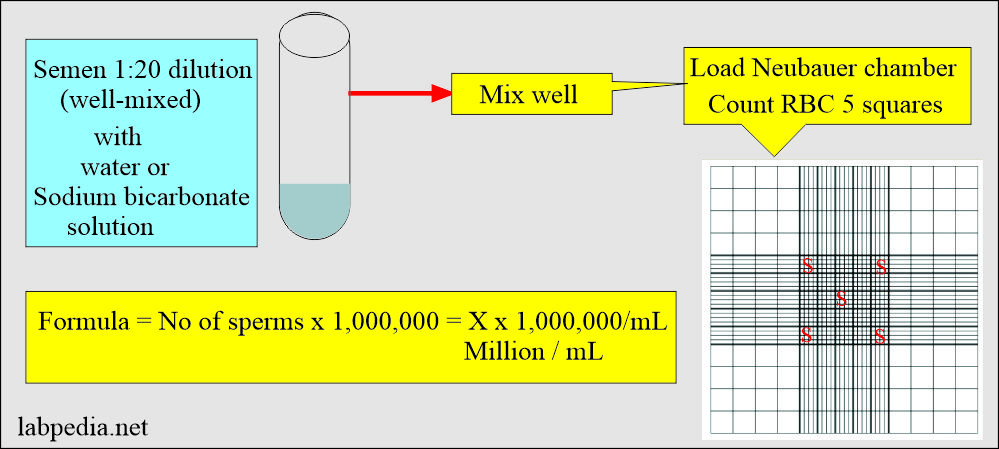
3. How will you count sperms in the semen?
- Dilute the semen with water or the above sodium bicarbonate solution.
- Take a 1:20 dilution of the semen.
- Count the five RBC counting squares (4 at the corner and one at the center).
- Calculations: Suppose the sperms are 50 in all these 5 RBC squares.
- 50 x 1,000,000 = 50,000,000/mL (million/mL).
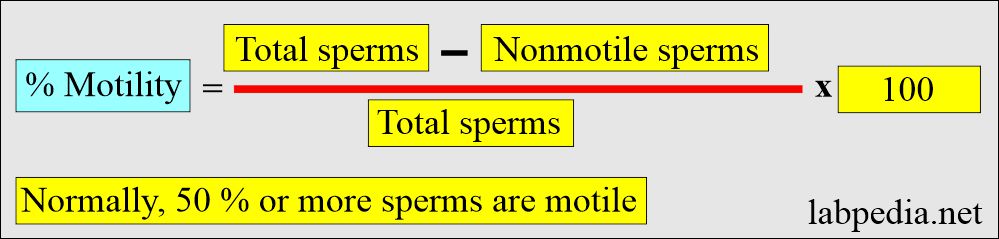
How will you calculate % motility?
- Count at least 200 motile or non-motile sperms in 5 different microscopic fields. % of the nonmotile sperm are calculated as follows:
How will you assess Sperm viability?
- The ejaculated sperm in the semen remains viable for several days in the female genital tract.
- Fertilization can occur as long as the sperms are alive, and these can survive for 5 days.
- The sperm can be preserved for decades when the semen is freezed at -20 °C.
- Sperm viability is needed when the progressively motile sperms are less in number.
What is the method used to assess viability?
- Take one drop of the semen.
- Add an equal volume of vital stain (trypan blue).
- Cover with the cover glass.
- Keep for a few minutes, but not more than 5 minutes.
- Count 100 cells, including viable sperm (not stained) and dead sperm (take stain).
- This will give you the count of viable sperms.
What are the types of sperm clumping?
Types of clumping:
- Head-to-head clumping.
- Tail-to-tail clumping.
- Mixed clumping, head-to-tail.
- Nonspecific where there is random clumping.
How will you grade the clumping of the sperms?
Grading system given by WHO :
- Grade 1+ (Mild): <10% sperm clumped.
- Grade 2+ (Moderate): 10%-50% sperm clumped.
- Grade 3+ (Severe): 50%-100% sperm clumped.
- Grade 4+ (Very Severe): All sperm clumped together.
What is the forensic value of semen analysis?
- Acid phosphatase is in high concentration in the semen.
- It is suggested that a swab from the suspected case of rape is taken, preserved in 2.5 mL of a protective broth, and stored at 4 °C or room temperature.
- A sample stored this way will keep acid phosphatase activity for one month.
- In the sample with thymolphthalein as the substrate, it was found that vaginal acid phosphatase in noncoital women is <10 U/L.
- There is a noncoital level if the vaginal sample is taken after 4 days of intercourse.
- The sampling swab can be kept in 1 mL of normal saline, but these samples are freezed and thawed at 2 to 4 °C for 24 hours before the assay.
- Creatinine phosphokinase (CPK) is a high level in semen. This can also be used for medico-legal purposes.
What is the importance of semen analysis?
- That one sample cannot confirm the infertile couple because of variation in the count of semen.
- To repeat one more sample, take the third sample at an interval of three weeks apart if possible.
- In the case of vasectomy, no sperms should be seen in the ejaculate.
How will you work for the infertile male?
- Get the report of the previous semen analysis.
- Advise antispermatozoal antibody.
- Advise luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones will affect the pituitary gland’s gonadal function and spermatogenesis.
- Sims-Huhner test. In this test, a postcoital cervical mucus smear is taken. To see the sperm mobility penetration in the mucus and maintain mobility.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is count in pathological semen?
Question 2: What is the value of acid phosphatase in medicolegal case?


i have volume 3.0ml colour whitish, and 00% actively motile and 10 % sluggishly motile and 90% non motile and abnormal formsis 50% and pus cells 4-6 and red blood cells is absent and spermatogenic cells 2-4,
so what i will do can any one tell me about that
I think you can have a testicular biopsy or ask for testosterone levels.
I think you can have a testicular biopsy or ask for testosterone levels.
What is motility
This is mostly your personal judgment. You have to screen many fields and also move the stage of the microscope up and down because you will see sperm at different levels with different motility. Also I have given the formula if you want to be more accurate.
https://www.labpedia.net/semen-part-1-semen-examination-semen-analysis-semen-count-procedure/
9 months Bedfore my wife pregnant than its misscaraige after 10days, then after we try to pregnant but not getting than now i checked the semen analysis i ejaculate 5ml and alkaline and no sperm zero sperm what reason
If your semen analysis is normal. Then think about your and wife’s age. If you both are young then wait. If no success for 3 to 5 years, then I will suggest, think about IUI, or IVF from a good center.
What is the formula for calculating percentage viability and progressive motility
I have added the procedure of how to assess the viability.
Please make correction in arrow-
But now, it is considered as > 20 million /mL as fertile semen.
Correct-
But now, it is considered as < 20 million /mL as fertile semen.
Ohh sorry you are correct
Thank u sir
Thanks.
Color. Off white
Valume: 3ml
Viscosity: slight viscouse
Progress motile: 50%
Nonmotile: 50%
Sperm morpohology 100%
Ph: 7.5
Doc im asking for your rading? Thank tou
Dear
The important thing is the total count of the sperm that you have not mentioned.
I don’t really great the calculation and how to record the motility in percentage
You can it under high resolution (HP) and focus the field by up and down the microscope. Count 100 sperm and try to differentiate active, moderate, and sluggish motility. If still, you feel difficulty, then do it in the Neubauer chamber.
total count is 387.45/ejaculate with 72% morphology and concentration 129.15 and progressive motility 36.38% with 8% rapid. is it ok
Overall your semen looks normal. Only needed motility after one hour.
once I observed by preparing a simple slide .it was as normal slide as I observed after 45mins of ejaculation. the motility was normal. does need to use any medicine for motility. if yes could you prescribe it? sir thanks for the reply.
If motility is normal, then don’t use any medication. Sometimes medication decreases the number and motility.
The technologist dilutes 100 μl of sample with 300 μl of water. In the diluted sample, 240 sperm are counted in five small squares. The volume correction factor for 25 small squares is 10,000. What sperm concentration should be reported for the patient sample?
I think I have given a simple way to calculate count.
https://labpedia.net/semen-part-1-semen-analysis-semen-examination-and-counting-procedure/
how can you accurately differentiate between rapid motility and slow motility?
When sperm leaves, the field is rapid, and when it can not, then slow or sluggish.
My semen analysis is:
Volume: 2.50
Sperm count: 166.4 million/ml
Motile sperm: 35% (after 1 hour 30%)
Morphology 41%
Please reply Dr is it normal, if not please suggest medicine.
My semen analysis:
Volume: 2.50
Sperm count: 166.4 million /ml
Motile sperm: 35% (30% after 1 hour)
Sperm Morphology: 41% normal
Please reply if the report normal, if not, please suggest medicine.
Please see this link
https://labpedia.net/semen-part-2-normal-and-abnormal-semen/
I do not think you need any medicine.
Thanks Dr for the reply but here i have question: Is it normal to concieve with 35% of sperm motility out of 166.4 million/ml sperm count? I opened the link you have shared, i found the normal motility is >60.
If semen is not liquifying even after 2 hours. What should be done?
If semen does not liquefy in 30 minutes means abnormality. In that case, IUI is the best answer. 2 hours is too much.
Semen should liquefy within 30 minutes. 2 Hours is too much, which is abnormality. The best option in such cases is IUI.
Hi there. According to your second formula for sperm count, we measure the total of the small five squares, in the central large square, and then multiply by 1000000 (if we have dilution 1:20), giving us the sperm count per ml. But we measure the 5 squares only if there are more than 50 sperm cells in total. What if there are less than 50 sperm cells? how do we perform the second formula?
I have written in a simple way:
Simplified method:
Take 1 mL of semen and mix it with sodium bicarbonate-formalin solution to make a total of 20 mL.
Fill the Neubeaur chamber with diluted semen and wait 3 to 5 minutes. So that spermatozoa get settled.
Now count two large squares (2 sq mm).
Calculate the number of spermatozoa in 1 mL of fluid by multiplying the number by 100,000.
Hi doctor
How much semen we fill hemocytometer?
Please read carefully this link:
https://labpedia.net/semen-part-1-semen-analysis-and-semen-counting-procedure/
You just need to fill the cover glass, may be one drop after thorough mixing the semen.
Hi Dr. Riaz
I would like to do an artificial insemination at home. It is ok to mix with sodium chloride 0.9. I would like to know if this helps. Thank you!
Normal saline may help, I am not sure about that. But you can get special media for sperm wash. In these media sperms can survive.
You can get sperm wash by Irvin scientific. There are also so many other sperm wash media.
Thanks for your teachings sir. I did learn a lot. Doc, can one also do a Sperm count with dilution but taking the semen directly on the Neauber counting chamber to count and if it’s possible to count all the large boxes of one portion and multiply by 1000000?
Thanks
If you take semen directly to the Neubauer chamber, there are chances for the mistakes due to clumps and irregular distribution of the sperm in the sample.
Dr. please when counting sperm cells do you count both matured and immatured cells. In addition,can one count only morphologically normal cells or both normal and abnormal as your total count.
Thanks
I think you have to count all sperms. Only then you can get idea about of the total sperm count.
How to report agglutination? ? I see dead sperms in clumps sometime. But what is the reporting approach towards it?
Classification of sperm agglutination:
✅ Type of Agglutination:
1. Head-to-head agglutination
2. Tail-to-tail agglutination
3. Mixed (head-to-tail agglutination)
4. Nonspecific (random clumping)
Severity of Grading given by WHO:
1. Grade 1+ (Mild): <10% sperm clumped.
2. Grade 2+ (Moderate): 10-50% sperm clumped.
3. Grade 3+ (Severe): 50-100% sperm clumped.
4. Grade 4+ (Very Severe): All sperm clumped together.
how to liquefy high viscous samples ? other than using incubation.
These are the causes of high viscosity of semen:
1. Dehydration.
2. Infections.
3. Zinc deficiency
4. Hormonal imbalance.
5. Semen volume is not adequate.
6. If you do not do frequent sex activity.
7. Last is lifestyle, like smoking, alcohol overuse, and stress.
Please consult urologist or Endocrinologist.
In case no improvement, then go for IUI or IQSI.
What does this mean
Absence period 3 days
Volume 2.5 ML
Consistency Normal
Liquefaction 20 Minutes
P.H 8.5
WBC 1-2
RBC Nil
Agglutination Absent
Motility
Progress 72%
Non Progress 19%
Total Motility 91%
Immotile 9%
Morthology
Normal forms 90%
Abnormal heads 7%
Abnormal tails 3%
Sperm Count 22.8*10>3
This semen sample shows low semen count and the volume. This sample be able to fertilize the ovum. If you face any problem then go for IUI or IQSI.
According to current WHO standards is >70% normal morphology the reference for normal sperm coz I from my knowledge >4% ought to be the new reference.
This is the latest information:
>4% normal forms with strict criteria by Kruger.
It means that if at least 4% of sperms in a sample will meat strict criteria, then it is considered normal range.
Sperm/mL=Number counted×50,000 but according to calcualtion you have multiplied by 1000000 (one million) instead of 50 thousand … can please explain by who have multiplied by 1M . thank u here the detail of type dilution and dilution factor
This applies when:
Neubauer chamber used
1:20 dilution
5 large squares counted
* diluent used sodium bicarbonate- Formalin solution
Thanks for the comments.