Reticulocyte Count (Retic count), and Interpretations
Reticulocyte Count
What sample is needed for Reticulocyte Count?
- EDTA blood is the best sample.
- Collect 5 to 7 mL of venous blood in the lavender-top tube.
- No fasting sample is needed.
What are the indications for reticulocyte count?
- Reticulocyte count differentiates anemia caused by bone marrow failure, hemorrhage, or hemolysis.
- To check the effectiveness of Pernicious anemia, folate, and iron deficiency treatment.
- To assess the recovery of bone marrow function in aplastic anemia.
- To find out the effect of the radioactive material on exposed workers.
- Check bone marrow function in chemotherapy, radiation, and bone marrow transplantation patients.
What Precautions are needed for the reticulocyte count?
- Avoid counting insufficient numbers of RBCs and reticulocytes.
- RBC inclusions may be mistaken for reticulocytes like Pappenheimer, basophilic stippling, or Heinz bodies.
- Howell-jolly bodies may be mistaken as reticulocytes. Even the machine can count these as reticulocytes and give a false count.
- Pregnancy may cause an increase in the reticulocyte count.
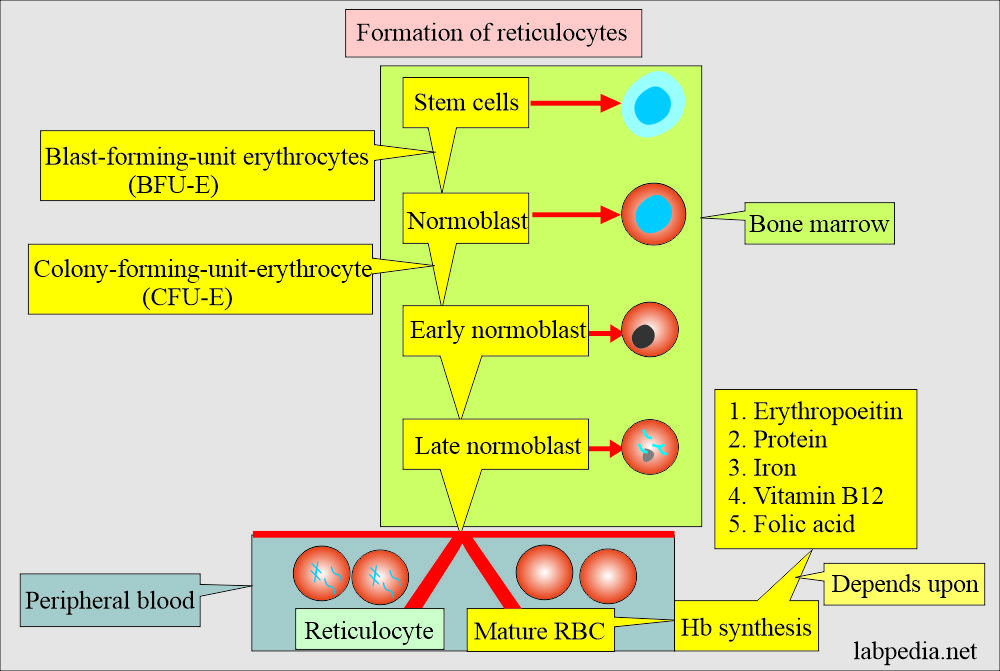
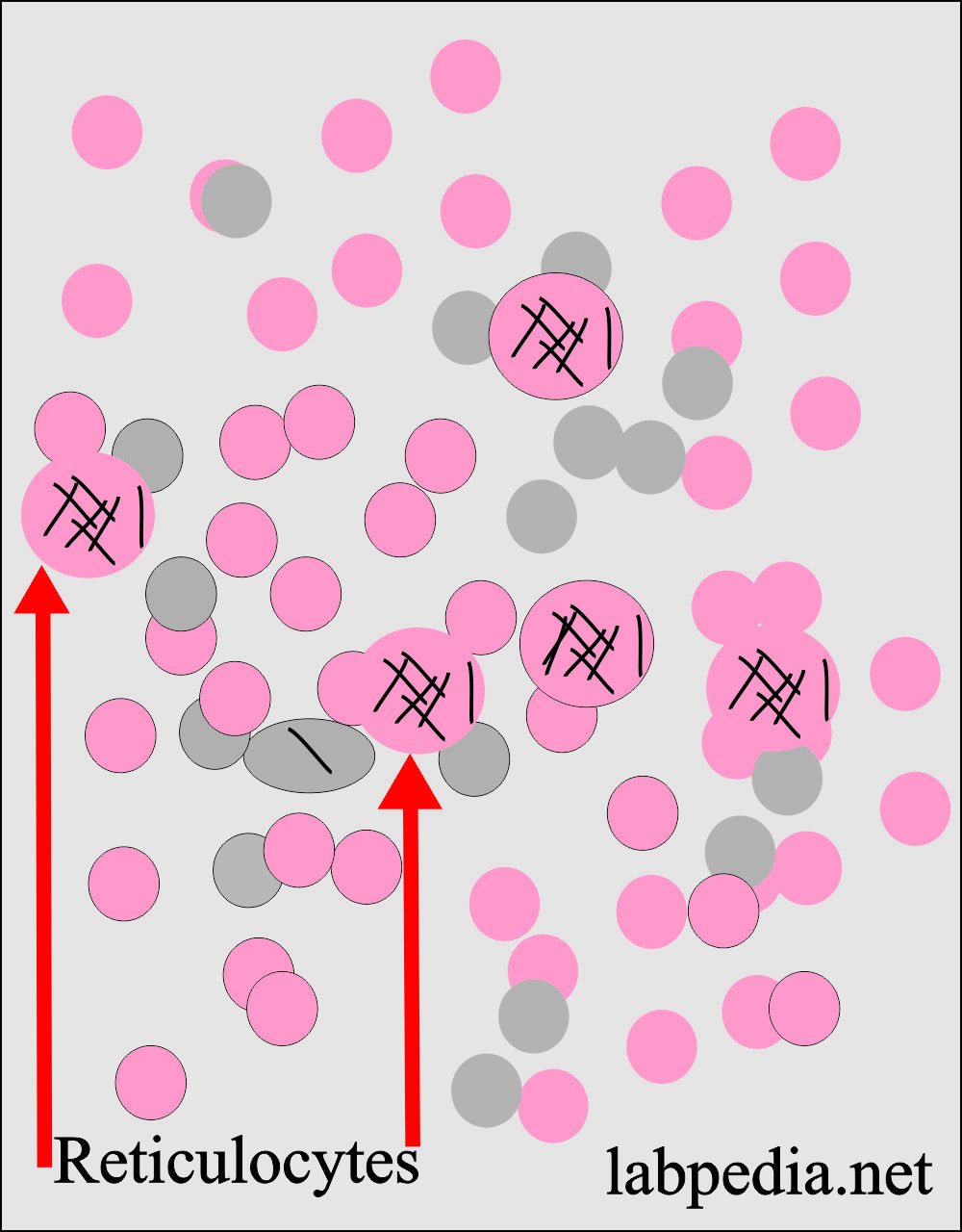
How will you define reticulocytes?
- Reticulocytes are present in between the nucleated RBCs and mature peripheral blood RBCs.
- The reticulocytes are young, immature, nonnucleated RBCs.
- Reticulocytes are nonnucleated, fully hemoglobinized RBCs.
- The reticulocytes contain the reticular material, which is basically RNA, and it stains grey-blue (Aggregates of ribosomal RNA) with supravital stains like new methylene blue or brilliant cresyl blue.
- This is the microsomal and ribosomal material left in the RBCs.
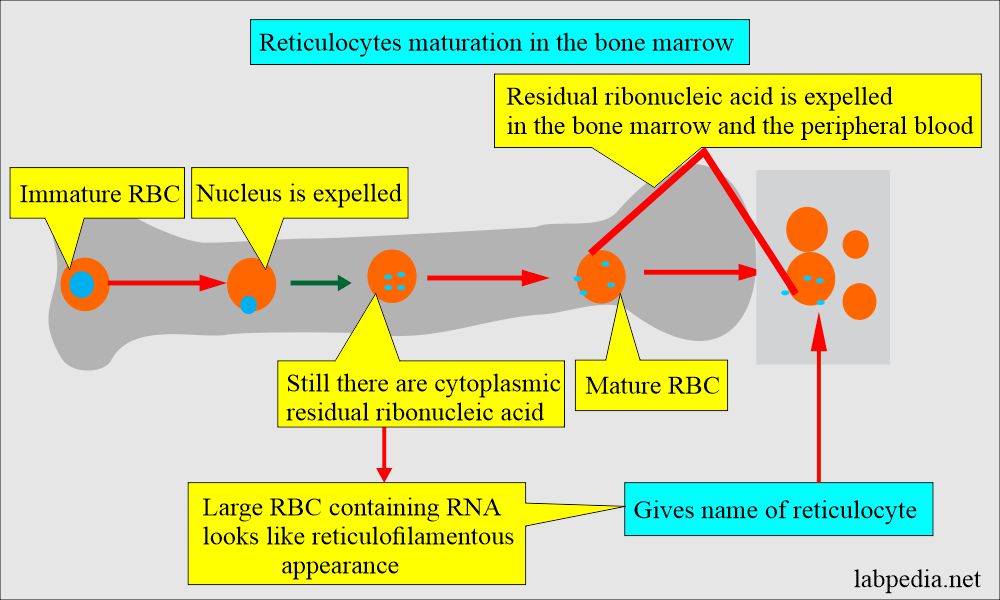
- These large RBCs containing ribosomal RNA material look like reticulofilamentous material, giving the name reticulocytes.
- The role of RNA is to synthesize hemoglobin, which mature RBCs need for oxygen transport.
What is Reticulocyte maturation in the bone marrow?
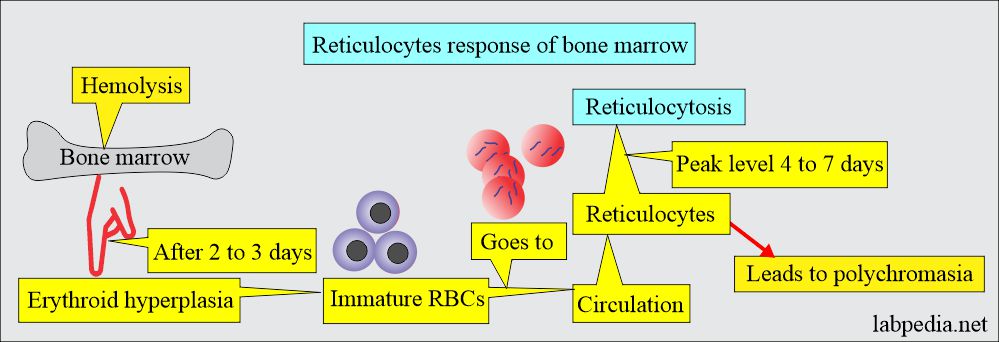
- Reticulocytes lose the reticulum 24 to 27 hours after entering the blood circulation.
- However, the premature stress reticulocytes have increased reticulum and need 2 to 2.5 days to lose their reticulum, resulting in longer peripheral blood maturation time.
- When Hb is low, the maturation time is longer, allowing more Hb to be produced by the reticulocytes’ ribosomal RNA.
- RNA is precipitated as a dye-protein complex.
How will you express Reticulocyte activity?
- Absolute count.
- Reticulocyte production index.
- Reticulocyte %.
What is the relation of reticulocyte with hematocrit?
| Hct % | Maturation time of reticulocytes (days) |
| 45 | 1.0 |
| 35 | 1.5 |
| 25 | 2.0 |
| 15 | 2.5 |
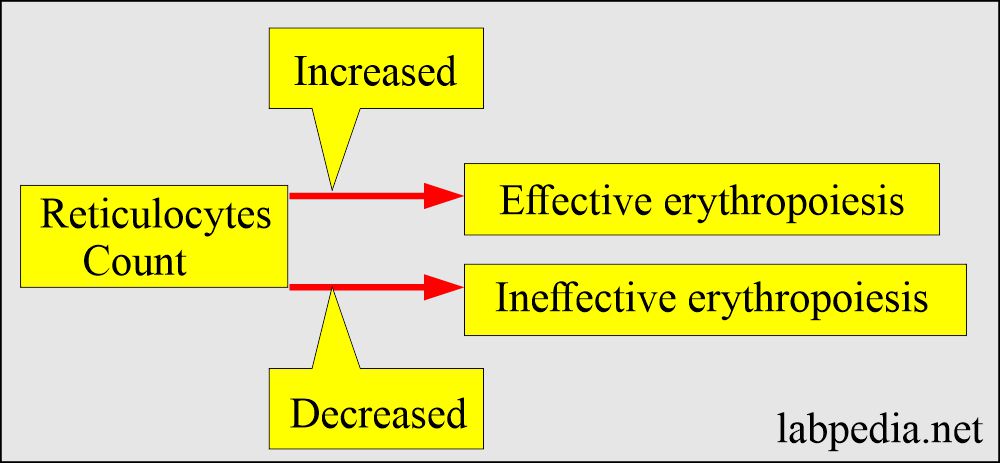
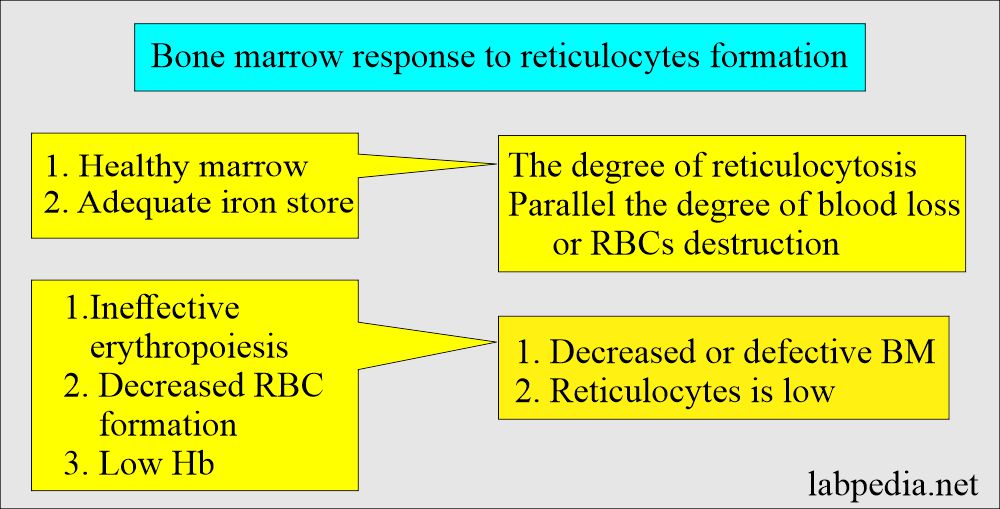
- Increased reticulocytes indicate that bone marrow releases increased RBCs into the peripheral blood.
- Reticulocytes reflect replacing the daily RBCs destroyed each day, which is 1% of the red cell mass.
- Normal or low reticulocyte counts in anemia indicate inadequate bone marrow response or some anemia.
- Increased reticulocyte count indicates an overproduction of RBCs that may compensate for hemolysis or hemorrhage.
How will you describe the life of reticulocytes in the peripheral blood and bone marrow response?
- When RBCs are released into the peripheral blood, they contain reticular material, which remains 1 to 2 days before the cell fully matures.
- RBC average life span = 100 to 120 days in the peripheral blood.
- Reticulocytes’ average life span = 1.0 days in the peripheral blood.
- Bone marrow replaces approximately 1% of the adult RBC every day.
- Other sources are:
- Reticulocytes circulate in the peripheral blood for 1 to 2 days.
- 0.5 to 2.5% of the peripheral blood has normal reticulocytes, which indicates normal bone marrow activity when hemoglobin is normal.
- RBC’s mature form circulates in the peripheral blood for 120 days.
- When hemoglobin is low, and reticulocytes are 0.5 to 2.5%, it indicates that anemia’s response is inadequate. This will be due to defective or decreased bone marrow production or a decreased amount of erythropoietin.
- In anemia, hemoglobin falls, the number of circulating RBCs falls, and the number of reticulocytes increases.
What is the response of Reticulocytes and bone marrow?
| Reticulocyte count and Hb | Bone marrow activity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
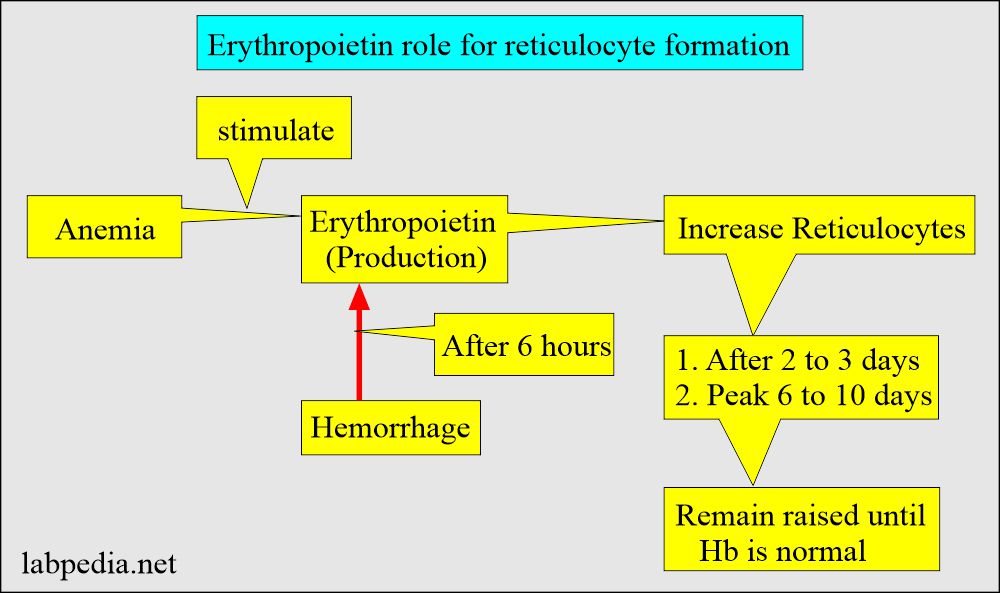
What is the response of Reticulocytes to blood loss?
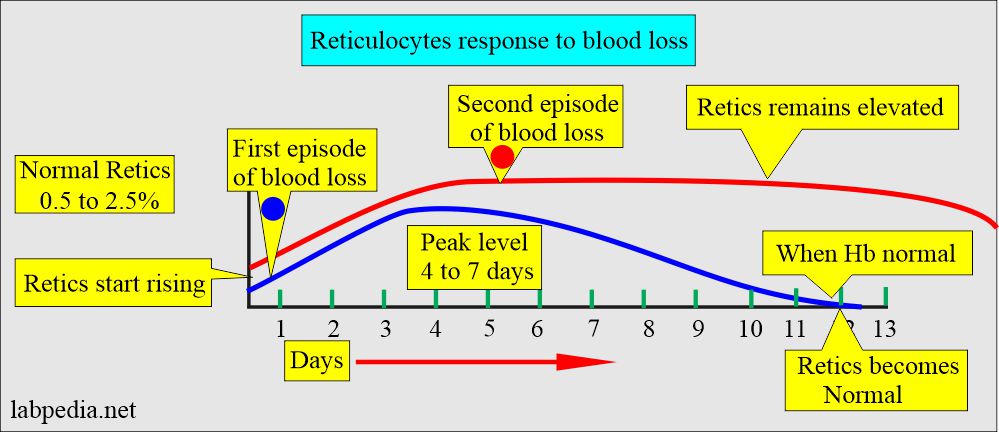
- The reticulocyte is the single most useful test to detect the hemolytic state.
- Reticulocytosis in a single episode of blood loss starts after 2 to 4 days, and the peak level is between 4 to 7 days. When hemoglobin becomes normal, then reticulocyte counts also become normal.
- In the case of persistent reticulocytosis, a second rise in the reticulocyte count indicates a continuing or second episode of blood loss. In iron deficiency anemia or anemia due to blood loss, the reticulocytes will become normal in 4 to 7 days when the iron supplement is given.
What are the functions of Reticulocyte count?
- It gives bone marrow function.
- Elevated reticulocytes in the presence of normal hemoglobin indicate erythrocyte activity.
- Anemia typing and diagnosis can be made on reticulocyte count.
- >3% reticulocytes indicate hemolytic anemia, indicating compensatory bone marrow response.
- <2% will be seen in:
- Hypoproliferative disorders.
- Maturation abnormalities like microcytic or macrocytic anemia.
What are the Methods to Stain Reticulocytes?
- Reticulocytes are not easily visible with the Wright or Giemsa stain.
- These are recognized as immature red blood cells in the peripheral blood smear.
- Reticulocytes need special vital stains like new methylene blue or cresyl blue stains.
- Reticulocytes are larger than normal RBCs and may be recognized as macrocytes. When present in sufficient numbers, they may increase MCV.
- In contrast to red-orange RBCs, reticulocytes in Wright’s stains look gray or blue-gray; this condition is called polychromatophilia.
How will you describe the New Methylene blue stain (NMB) for reticulocyte count?
- This new methylene blue stain is more specific for the reticulocytes.
- The staining visualizes reticulocytes with vital dyes like methylene blue that precipitate the RNA and organelles, forming a reticulum network.
How will you prepare a New methylene blue (NMB) stain?
- New methylene blue = 0.50 gram
- Sodium chloride = 0.70 gram
- Sodium oxalate =0.13 gram
- Deionized water = 100 mL
- Mix these three reagents for at least 15 minutes, filter them, and store them at room temperature.
- Filter before use all the time.
What is the procedure of NMB stain?
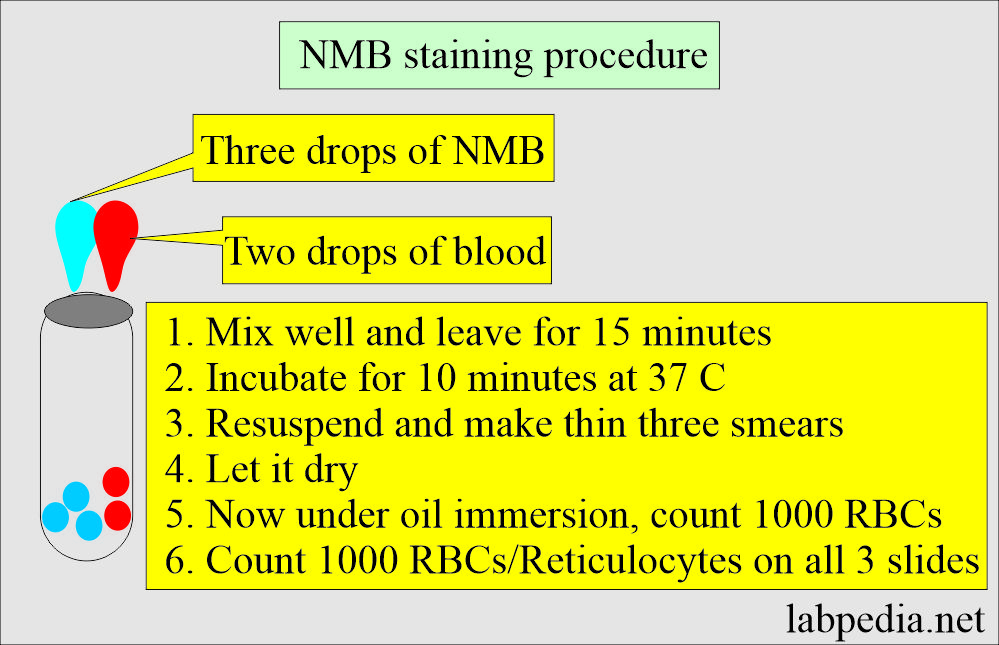
- Add two drops of blood to three drops of NMB solution.
- If Hb is low, then add one more drop of blood.
- Mix and leave it for 15 minutes.
- Incubate the mixture for 10 minutes at 37 °C.
- Resuspends the cells before making the slides.
- Now, make three thin smears and let them dry.
- Count a total of 1000 RBCs under the 100 x oil immersion lens.
- Try to make a thin smear with around 100 cells per field.
- Keep a record of reticulocytes as well.
- Reticulocytes appear greenish-blue and have different concentrations of reticulum formation.
- Count the reticulocytes on all three slides and compare the distribution.
How will you Calculate reticulocytes?
- Count RBCs and reticulocytes as well.
- If RBCs are 1000 and reticulocytes are 8.
- Example : Reticulocytes = 8/1000 x 100 = 0.8%
How would you describe brilliant cresyl blue?
- Mix the blood with this stain and incubate for 15 to 30 minutes.
- Now, make the smear from this blood sample.
- Count 5oo cells and calculate the percentage of reticulocytes out of 500 cells.
How will you Report reticulocyte count?
Reticulocytes %:
- The reticulocytes are reported as the percentage of total RBCs counted.
- Reticulocytes % = Count 1000 RBCs and the number of reticulocytes.
- In the case of decreased reticulocytes, count 2000 RBCs.
- When 1000 RBCs are counted, the following shorthand formula may be used:
- % Reticulocytes = No. of reticulocytes counted/1000 RBCs.
How would you describe Absolute Reticulocyte count?
- It is reticulocyte numbers in 1 mm3 of whole blood. This is not % of the RBCs.
- It has more value than the % reticulocytes.
- The normal range = is 24 to 84 x 109/L. (another reference is 25 to 75 x 109/L).
- Another reference to calculate absolute reticulocyte count:
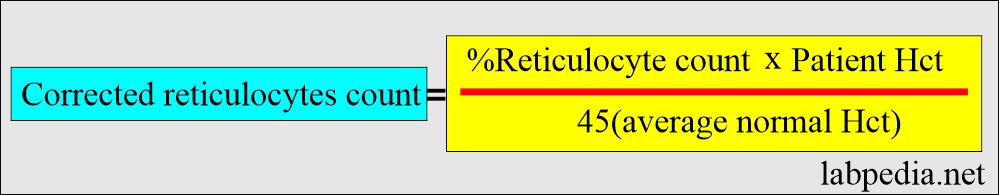
How would you describe Corrected reticulocyte count?
- In anemia, reticulocyte % is not a true reflection of reticulocyte production.
- A correction factor must not be applied to overestimate marrow production because each reticulocyte is released into whole blood containing few RBCs, which means low Hct, thus increasing the percentage.
- The formula calculates the corrected reticulocyte count.
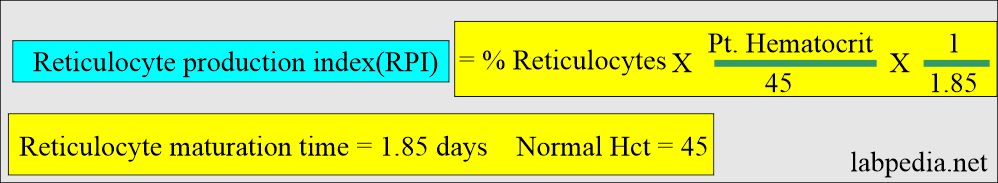
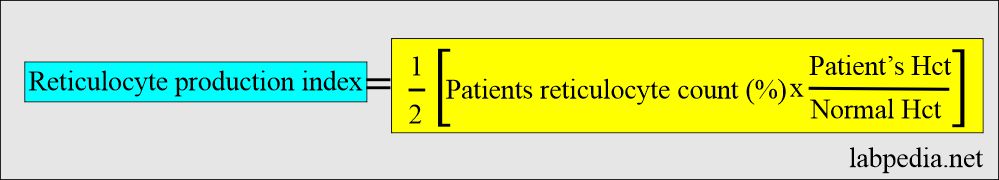
How would you describe the Reticulocyte production index (RPI)?
- The peripheral smear should be carefully reviewed for polychromatic macrocytes, which can indicate stress reticulocytes.
- It needs correction for both RBC count and the presence of stress reticulocytes. The value obtained is called the Reticulocyte production index.
- RPI corrects the hematocrit to a normal value of 45% and considers the reticulocytes’ maturation time at a particular hematocrit.
- At 1.0 day = 45% Hct.
- At 1.5 days = 35%. Hct.
- At 2 day = 25%. Hct.
- At 2.5 day = 15%. Hct. An RPI of >2.5 to 3.0 is generally indicative of hemolytic anemia.
What is the Normal reticulocytes?
Source 1
| Age | % |
| Newborn | 3 to 7 |
| 0ne day | 3 to 7 |
| 3 days | 1 to 3 |
| 7 days | 0 to 1 |
| one month | 0.2 to 2.0 |
| 1.5 month | 0.3 to 3.5 |
| 2 month | 0.4 to 4.8 |
| 2.5 month | 0.3 to 4.2 |
| 3 month | 0.3 to 3.6 |
| 4 to 12 month | 0.2 to 2.8 |
| Adult | 0.5 to 1.5 |
Source 2
- Adult/elder/child = 0.5 to 2%
- Infants = 0.5 to 3.1%
- Newborn = 2.5 to 6.5%
- Reticulocyte index = 1.0
Source 4
| Age group | % reticulocytes |
| Newborns | 3% to 6% of total RBCs counted (Drops to adult levels in 1 to 2 months) |
| Adult | 0.5% to 1.5% (Females may have a slightly higher %) |
| Reticulocyte index (RI) | 1% corrected reticulocyte count |
| Hct correction for anemia = RI | Reticulocyte count x (patients’s Hct/45 x 1/1.85) |
Source 5
- Adult = 0.5% to 2% of the RBCs
- 24 to 100 x 109 reticulocytes/L.
- Newborn = 3 to 7%
- One week = 1.8 to 4.6%
- One month = 0.1 to 1.7%
- 6 months = 0.7 to 2.3%
- >6 months = 0.5 to 1.0%
Another source
- Adult = 0.5 to 1.5 % of total RBCs counted.
- Newborn = 3% to 6 %.
What are the causes of increased reticulocyte count?
- Hemolytic anemia:
- Immune hemolytic anemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Sickle cell disease.
- Primary RBC membrane defect.
- Hemolytic disease of the newborn.
- Deficiency of RBC enzyme.
- Malaria.
- The bone marrow tries to compensate for RBCs’ shortened life and produces many RBCs, some of which are immature reticulocytes.
- The post-hemorrhage Increase occurs after 3 to 4 days. This indicates that the bone marrow is trying to compensate for blood loss. There is a possibility of immature RBCs, which are reticulocytes.
- After treating anemia, in the case of deficiency anemia, the marrow responds by increased RBCs reticulocyte production when treatment is given, like iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid.
- An increased retics may be used as an index of the effectiveness of the treatment.
- After an adequate dose of iron in iron-deficiency anemia, the reticulocyte increase may exceed 20%.
- There is also an increase in the retics when pernicious anemia is treated by blood transfusion or vitamin B12.
What are the causes of decreased reticulocyte count?
- Aplastic anemia.
- Anemia of chronic disease.
- Untreated iron deficiency and pernicious anemia.
- Radiation therapy.
- Bone Marrow infiltration by tumors leads to bone marrow failure.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Alcoholism.
- Adrenocortical hypofunction.
- Anterior pituitary hypofunction.
- Chronic diseases.
- In these diseases, marrow production of the RBCs and reticulocytes is decreased.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of reticulocytes count:
Question 2: What will happen to reticulocytes in malaria?





What is the work of sodium chloride and sodium citrate in reticulate count staining
I searched to find the reference for sodium chloride and oxalate in the stain but could not find it. But I think their functions may be to stabilize the RBCs.
Thank you, I have some questions is absolute count better than percentage, if so what are the condition which absolute count is better
Absolute reticulocytes are better than a percentage. It will be raised in all the same conditions.
Hi I have a retic count of 4.8 and absolute retic count of 152.1 any advice my mcv and mch always raised now I have a platlets count of 7 iron is fine . Two years going on with symptoms.
Your reticulocytes count is raised. You need a consultation by the clinical hematologist to find the cause of raised reticulocytes.
Good Morning. Excellent information for those of us who dedicate ourselves to learning, teaching, and relearning to update what has been learned and applied in practice. Very useful information that we give as very good and valid.
Thanks.
why this confusion here.. your definition in mm3 but you give reference in Liter??!!!!
Absolute Reticulocyte count:
It is reticulocyte numbers in 1 mm3 of whole blood. This is not % of the RBCs.
It has more value than the % reticulocytes.
The normal range = is 24 to 84 x 109/L. (another reference is 25 to 75 x 109/L).
ASAT/ALAT is raised, indicating liver cell injury. I hope you are not taking alcohol. Try more fruits and their juices.
ASAT/ALAT is raised, indicating liver cell injury. I hope you are not taking alcohol. Try more fruits and juices.
I am sorry, I am using different references and quote all of those.
I remember my teacher telling me to count even one stained particle as a retic, but theres no reference to that. Could find reference to only 2 or more. Could you please clarify!
Please visit again and you will find the reference.
https://labpedia.net/reticulocyte-count-retic-count-and-interpretations.
Hello, I’ve found a lot of sources saying that, after major acute blood loss, reticulocyte percentage will often surpass 3%, but I am unable to find anything regarding the upper limit of that percentage. What would be the upper limit of the peak percentage (6-10 days after hemorrhage) for an otherwise healthy adult?
The reticulocyte is the single most useful test to detect the hemolytic state.
Reticulocytosis in a single episode of blood loss starts after 2 to 4 days, and the peak level is between 4 to 7 days. When hemoglobin becomes normal, then reticulocyte counts also become normal.
In the case of persistent reticulocytosis, a second rise in the reticulocyte count indicates a continuing or second episode of blood loss. In iron deficiency anemia or anemia due to blood loss, the reticulocytes will become normal in 4 to 7 days when the iron supplement is given.
Oh thank you for the correction! What is the range of reticulocyte percentages that would occur during such a peak in reticulocytosis? I know this would vary between individuals, but I imagine there is a range that most cases fall within?