Progesterone Assay
Progesterone
Sample for Progesterone
- This is done on the serum of the patient.
- Always note the sex of the patient.
- In the female, note the day of the last menstrual cycle.
- The serum is stable for 7 days at 4 °C.
- Can store serum for 3 months at -20 °C.
Precautions for Progesterone assay
- Avoid hemolysed samples that will affect the result.
- Take the history of the recent use of radioisotopes because that will affect the result.
- Estrogen and progesterone therapy will interfere with the result.
Indication for Progesterone assay
- This test is part of the infertility study.
- Confirm ovulation.
- To evaluate the corpus luteum function.
- To assess the high risk for early spontaneous abortion.
Definition of progesterone
- Progesterone is a sex hormone like estrogen.
- It helps to regulate the accessory organs during the menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone is an important hormone for preparing the uterus for the reception of the blastocyst and maintaining the pregnancy.
Pathophysiology of Progesterone
- Progesterone is a female sex hormone needed to prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
- progesterone is C21 steroids.
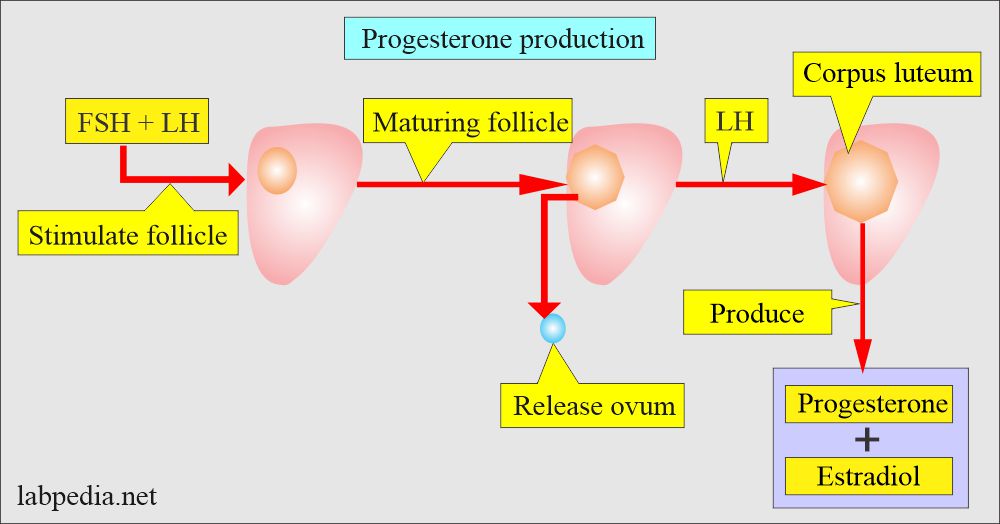
- The initiation and control of luteal secretion of progesterone are regulated by LH and FSH.
- Progesterone has no specific binding plasma protein. This is bound like cortisol to cortisol binding globulin.
- Free progesterone is 2% to 10% of the total.
- This is like estrogen as a sex hormone.
- It helps to regulate the accessory organs during the menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone acts primarily on the endometrium.
- It starts the secretory phase of the endometrium for the preparation for the implantation of a fertilized ovum.
- This is important for the implantation of the blastula that is produced by the cleavage of the fertilized ovum.
- In nonpregnant females, it is produced by the corpus luteum.
- Progesterone maintains the pregnancy.
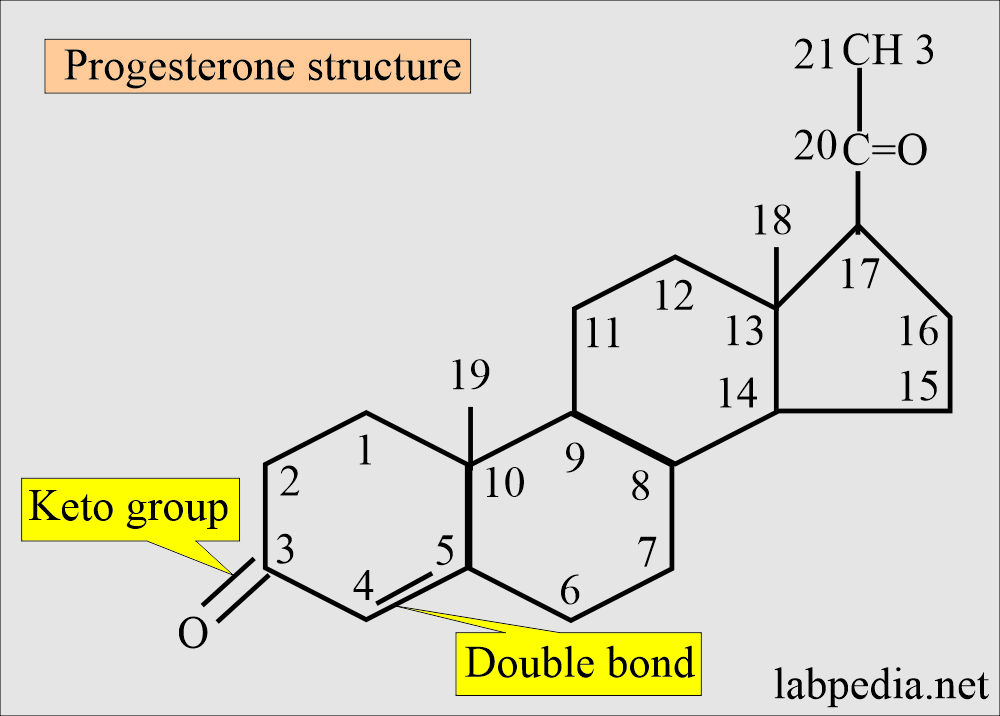
Structure of the progesterone:
- Progesterone is a C21 compound.
- Like corticosteroids and testosterone, it contains a keto group at C3 and a double bond between C4 and C5.
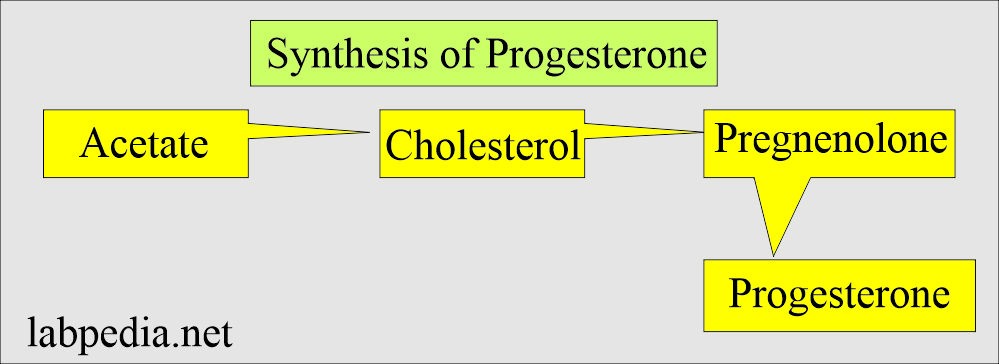
- Biosynthesis of progesterone in ovarian tissue is thought to follow the same path from acetate to cholesterol, then pregnenolone to progesterone, as it does in the adrenal cortex.
- Biosynthesis and control of luteal secretion of progesterone are regulated by LH and FSH.
Source of progesterone production:
- Progesterone is produced by the Corpus luteum (granulosa cells) of the ovary in the first week of pregnancy.
- In non-pregnant women, progesterone is secreted mainly by the corpus luteum.
- During pregnancy, the placenta is the main source of progesterone production.
- Placenta produces progesterone by 12 weeks of gestation.
- Followed by Placenta during pregnancy which starts producing progesterone.
- The adrenal cortex and testes are minor sources of male progesterone production.
- The adrenal cortex is also a minor source of progesterone in the female.
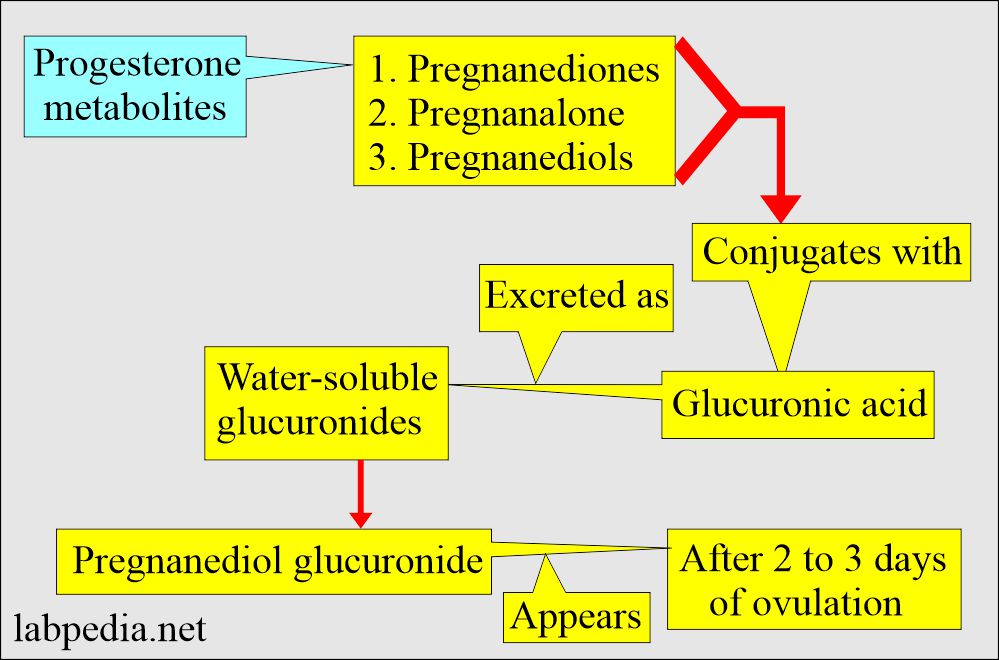
- Progesterone is metabolized into metabolites conjugated with glucuronic acid and excreted as water-soluble glucuronides.
Transport of the progesterone:
- Progesterone has no specific plasma-binding proteins.
- Progesterone is bound to corticosteroid-binding globulin
- Plasma-free progesterone varies from 2% to 10% of the total concentration. This unbound progesterone remains constant throughout the normal menstrual cycle.
Progesterone level in the body:
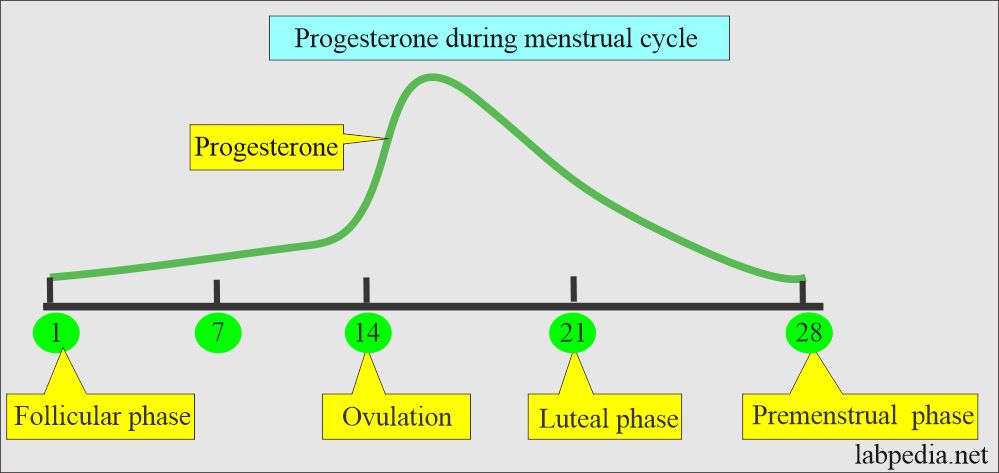
- The progesterone peak level is a mid-luteal phase of menstruation.
- In non-pregnant women, progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum.
- Progesterone in nonpregnant ladies is elevated during the luteal phase, with maximal level 5 to 10 days after the LH peak at mid-cycle.
The single best test to evaluate ovulation:
- A series of the test gives the day of ovulation when there is a peak level of progesterone.
- Plasma progesterone level starts to rise with ovulation along with LH hormone approximately 6 to 9 days.
- The level falls, and menses occur.
- After ovulation, there is a rise of 4 to 5 days, and then it falls.
- Supplementary progesterone can be given to maintain early pregnancy in case of inadequate luteal phase production of progesterone.
- There is a gradual increase in pregnancy from 9 weeks to 32 weeks of gestation.
- Its level is higher in the twin pregnancy.
Progesterone metabolites:
- Progesterone is converted into Pregnanediol, conjugated with glucuronic acid produced by the liver, and then excreted by the kidneys.
- Progesterone 2% to 10% free and rest is bound to corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG).
- Pregnanediol is most easily measured as a metabolite of progesterone in the urine and plasma.
- Pregnanediol level in the urine is unchanged even in fetal distress or even the death of the fetus.
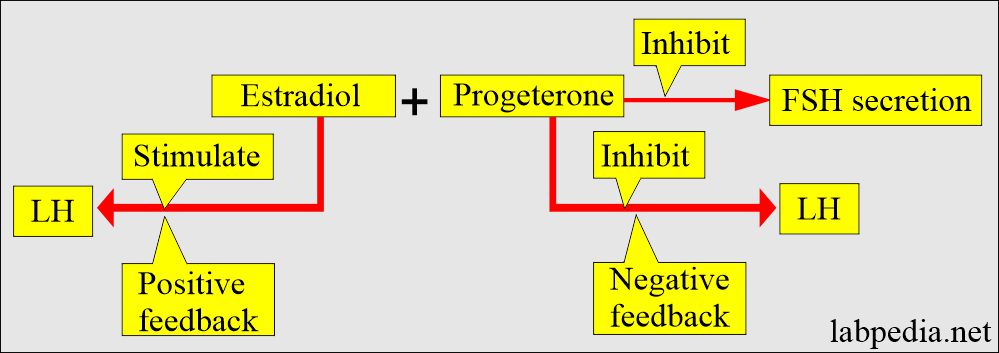
- Progesterone and Estradiol, their role in the secretion/inhibition of FSH and LH.
NORMAL Progesterone level
Source 1
| Age | ng/dL | |
| Cord blood | 8000 to 56,000 | |
| Premature | 84 to 1360 | |
| Prepubertal child (1 to 10 years) | 7 to 52 | |
| Puberty Tanner stage | Male | Female |
| 1 | <10.3 to 33 | <10 to 33 |
| 2 | <10 to 33 | <10 to 55 |
| 3 | <10 to 48 | <10 to 450 |
| 4 | <10 to 108 | <10 to 1300 |
| 5 | 21 to 82 | 10 to 950 |
| Adult | 13 to 97 | Follicular phase = 15 to 70 |
| Luteal = 200 to 2500 | ||
| Pregnancy | ||
| First trimester = 1025 to 4400 | ||
| 2nd trimester = 1950 to 8250 | ||
| 3rd trimester = 6500 to 22,900 | ||
- To convert into SI unit x 0.0318 = nmol/L
- The Tanner stage is the physical scale of the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics.
Source 2
- Adult male = 10 to 50 ng/dL
- Adult female:
- Follicular phase = <50 ng/dL
- Luteal phase = 300 to 2500 ng/dL
- Postmenopausal = <40 ng/dL
- In Pregnancy:
- First trimester = 725 to 4400 ng/dL
- Second trimester = 1950 to 8250 ng/dL
- Third trimester = 6500 to 22,900 ng/dL
Source 4
- Men = < 1.0 ng/mL.
- Women
- Prepubertal = 0.1 to 0.3 ng/mL.
- Follicular phase = 0.1 to 0.7 ng/mL.
- Luteal phase = 2 to 25 ng/mL.
- Pregnancy:
- First trimester = 10 to 44 ng/mL.
- Second trimester = 19.5 to 82.5 ng/mL.
- Third trimester = 65 to 290 ng/mL.
- There is a lab-to-lab and method-to-method variation of the normal values.
Increased progesterone level is seen in the following:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
- Molar pregnancy.
- Lipid ovarian tumor.
- At the time of ovulation.
- Pregnancy.
- Choriocarcinoma of the ovary.
- Theca Lutein cyst of the ovary.
Decreased level of progesterone seen in:
- Threatened spontaneous abortion.
- Preeclampsia.
- Toxemia of pregnancy.
- Fetal death.
- Placental failure.
- Ovarian hypofunction.
- Amenorrhea.
- Ovarian cancers.
- Short luteal phase syndrome.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the structure of progesterone?
Question 2: What is the significance of progesterone for ovulation?