Platelets:- Part 3 – Platelet Indices
Platelet Indices
This is the automated calculation of the platelets indices, which consists of the following:
- Mean platelet volume (MPV).
- Plateletcrit (Pct).
- Platelet distribution width (PDW).
What are the indications for Platelet Indices?
- Platelet indices are potentially useful markers for the early diagnosis of thromboembolic diseases.
- MPV and PDW help discriminate causes of thrombocytopenia as hypoproductive or hyper-destructive, like immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
- An increase in both mean platelet volume (MPV) and platelet distribution width (PDW) due to platelet activation was suggested due to:
- Platelet swelling.
- Pseudopodia formation.
- MPV and PDW are simple platelet indices that increase during platelet activation.
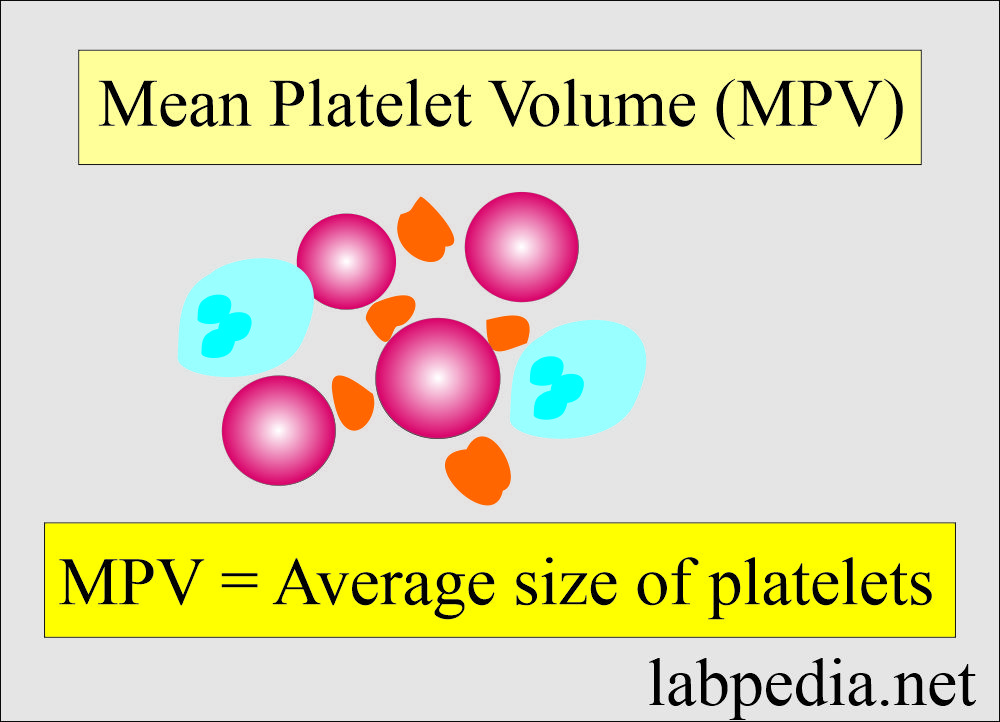
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
How will you define MPV?
- MPV represents the average size of the platelets.
- It is determined from the arithmetic mean of the platelets histogram provided by the hematology analyzer.
- MPV is a machine-calculated measurement of the average size of platelets found in blood and is typically included in blood tests as part of the CBC.
- Primarily with thrombocytopenia when it is due to Impaired production, as in aplastic anemia.
- MPV is very useful in the case of thrombocytopenia.
What is the source of error in calculating MPV?
- Major source of error is fragmented RBCs.
When will it be MPV higher?
- When platelets are destroyed.
- This may be seen as an inflammatory bowel disease.
- In immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
- In various thrombocytopenias.
- In the case of increased-sized platelets like myeloproliferative diseases and May-Hegglin syndrome.
- Also seen in Bernard-Soulier syndrome, where the platelets are large.
- It may also be related to preeclampsia and recovery from transient hypoplasia.
When will there be Low MPV values?
- It will be associated with bleeding.
- The release of immature platelets to the circulation, which is larger in size, leads to raised MPV.
- In the case of ineffective platelet formation in the bone marrow, as their size is smaller, there is low MPV
What is the normal MPV?
- It ranges from 7.4 to 10.4 fL
Plateletcrit (Pct)
How will you define plateletcrit (Pct)?
- Plateletcrit measures the total mass as a percentage of the volume occupied in the blood.
- Plateletcrit is an effective screening tool for detecting quantitative platelet abnormalities.
- Normal platelet count has a Plateletcrit within the 0.20 to 0.36% range.
What is the normal plateletcrit (Pct)?
- Plateletcrit- 0.22 to 0.23%.
- Sensitivity and specificity for detection of :
- Thrombocytopenia at the Plateletcrit cutoff range of 0.20 – 0.36% is 97% and 80%.
- Thrombocytosis is 94% and 98%.
Platelet distribution width (PDW)
How will you define Platelet distribution width (PDW)?
- It is the measure of variability in the size of platelets.
What are the important facts about PDW?
- PDW is a simple, practical, and specific marker of activation of coagulation.
- PDW is a more specific marker of platelet activation since it does not increase during simple platelet swelling.
- PDW has received attention due to its usefulness in distinguishing between reactive thrombocytosis and thrombocytosis associated with a myeloproliferative disorder.
- The determination of the PDW reference range is fundamental.
- Mean platelet volume (MPV) and platelet distribution width (PDW) are helpful in the differential diagnosis of aplastic anemia and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- An increased PDW is an indication of the anisocytosis of platelets.
What is the normal Platelet distribution width (PDW)?
- Standard PDW ranges from 9 to 14 fL.
What is the outcome of platelet indices?
- Patients with decreased platelet count and increased MPV and PDW are more prone to severe diseases, poor prognosis, and high risk of mortality.
- PDW is the preferred platelet index in Diabetes mellitus patients to predict clinical status.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is platelet distribution width (PDW)?
Question 2: What is the importance of PDW?