Pancreatic Functions and Acute pancreatitis
Pancreatic Functions
What sample is needed for Pancreas functions?
- The serum of the patient is required.
- The serum for lipase is stable at room temperature for several days if there is no bacterial contamination.
- The serum for amylase is stable at room temperature for 7 days and at 4 °C for one month.
- Urine: Amylase is unstable in acidic urine. Adjust the pH to the alkaline range before storage.
- A urine sample can take one hour or 24 hours.
- Store at 4 °C.
What are the precautions for Pancreatic function tests?
- Avoid contamination with saliva.
- Lipemic serum, EDTA, Citrate, and fluoride decrease the amount of amylase.
What tests are advised for pancreatic functions?
- The following blood tests are done to diagnose the pancreatic disease:
- Serum amylase.
- Serum lipase.
- In acute pancreatitis, there is an elevation of amylase and lipase.
- Amylase is less specific for pancreatitis than lipase because the salivary glands also produce amylase.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of the Pancreas?
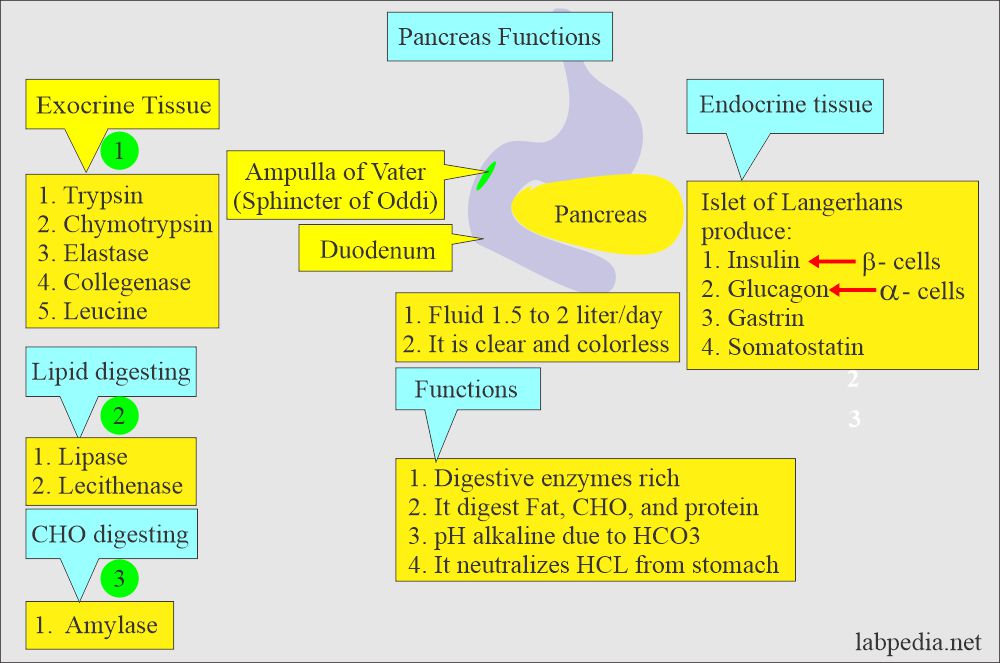
- The pancreas weighs 70 to 105 grams and is located in the curve of the duodenum.
- The pancreas is the gland with exocrine and endocrine functions that play a very important role in digestive function.
- It produces pancreatic juice rich in bicarbonate and digestive enzymes.
- Bicarbonate neutralizes acid coming from the stomach.
Pancreatic enzymes and functions
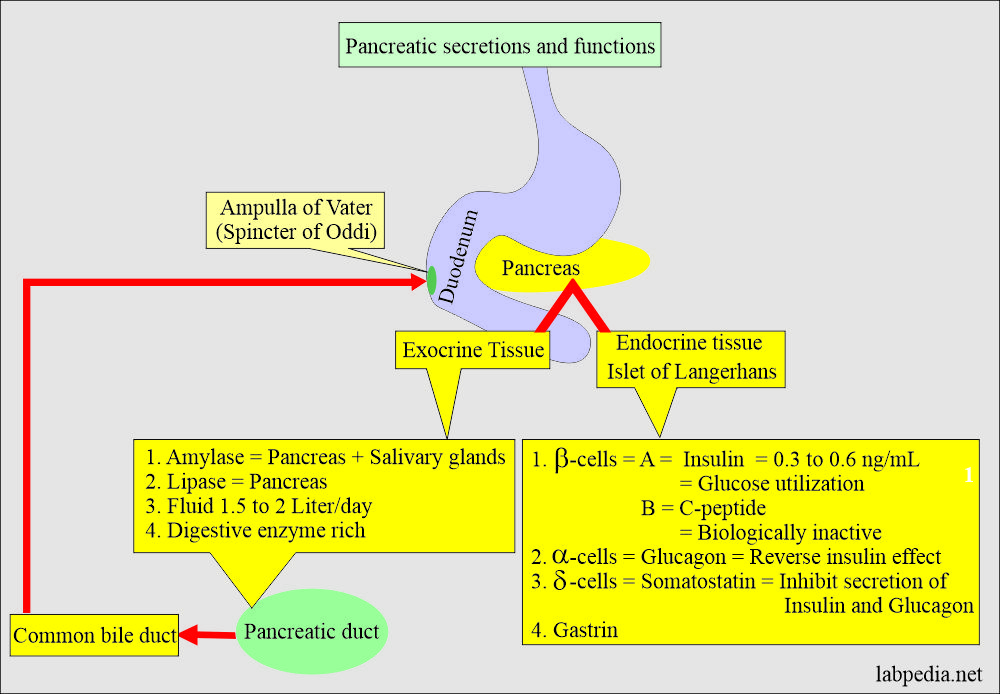
What are the contents of the Pancreas?
Endocrine tissue:
- Islets of Langerhans are small, 0.1 to 0.15 mm in D.
- Its secretion goes directly into blood circulation. It has no link with the ducts.
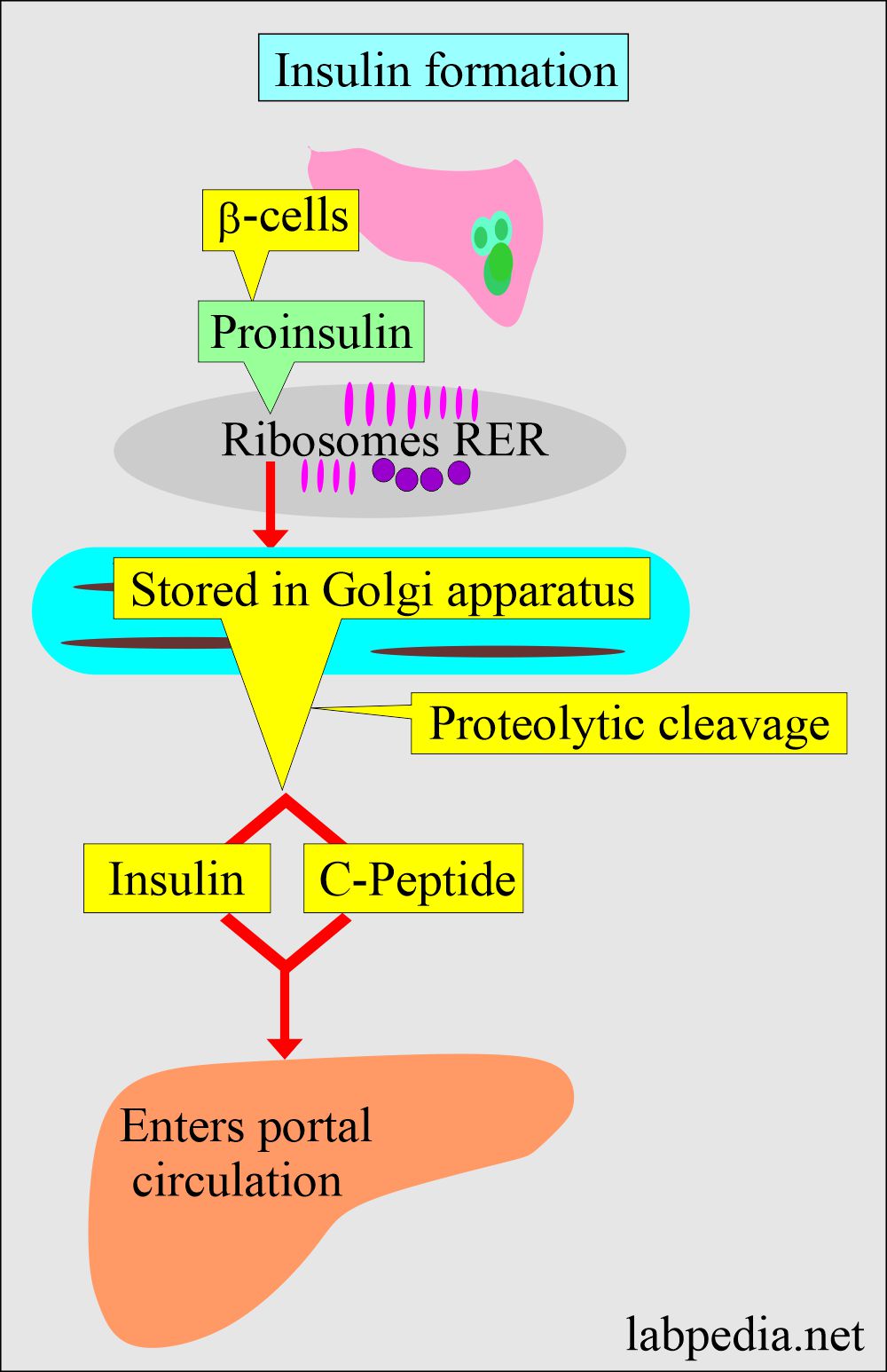
β (Beta)- cells:
- These are the most numerous cells which produce insulin.
- Insulin is a small protein with a molecular weight of 6000.
- Insulin is a potent hormone that promotes glucose uptake and glycogen storage, triglycerides synthesis, and protein synthesis.
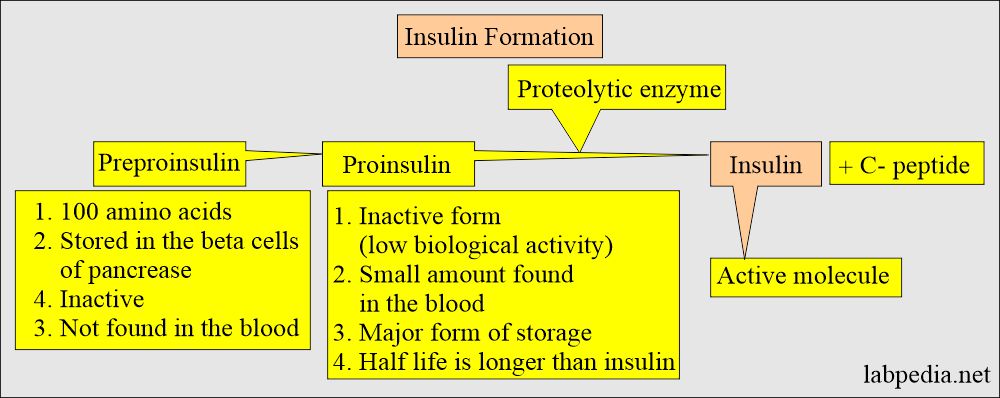
- It is produced as proinsulin, which is inactive.
-
- This is known as an antidiabetic hormone.
- Insulin’s normal value is 860 pg/mL, which does not exceed this value in a normal person.
- Insulin will increase in the adenoma of the pancreas (Insulinoma).
α (Alpha)- cells:
- It produces glucagon.
- Glucagon is a polypeptide hormone produced by alpha cells in the islet cells.
- Glucagon raises blood sugar by activating the liver phosphorylase, which will break down glycogen.
- Glucagon stimulates the hydrolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue to fatty acids and glycerol.
- Glucagon also reduces the secretory response of the parietal cells to all stimuli except histamine.
δ (Delta)- cells:
- These cells produce somatostatin, which inhibits the action of insulin and glucagon.
Exocrine tissue:
- This produces the digestive enzymes from the acinar cells of the pancreas.
What are the digestive enzymes of the pancreas?
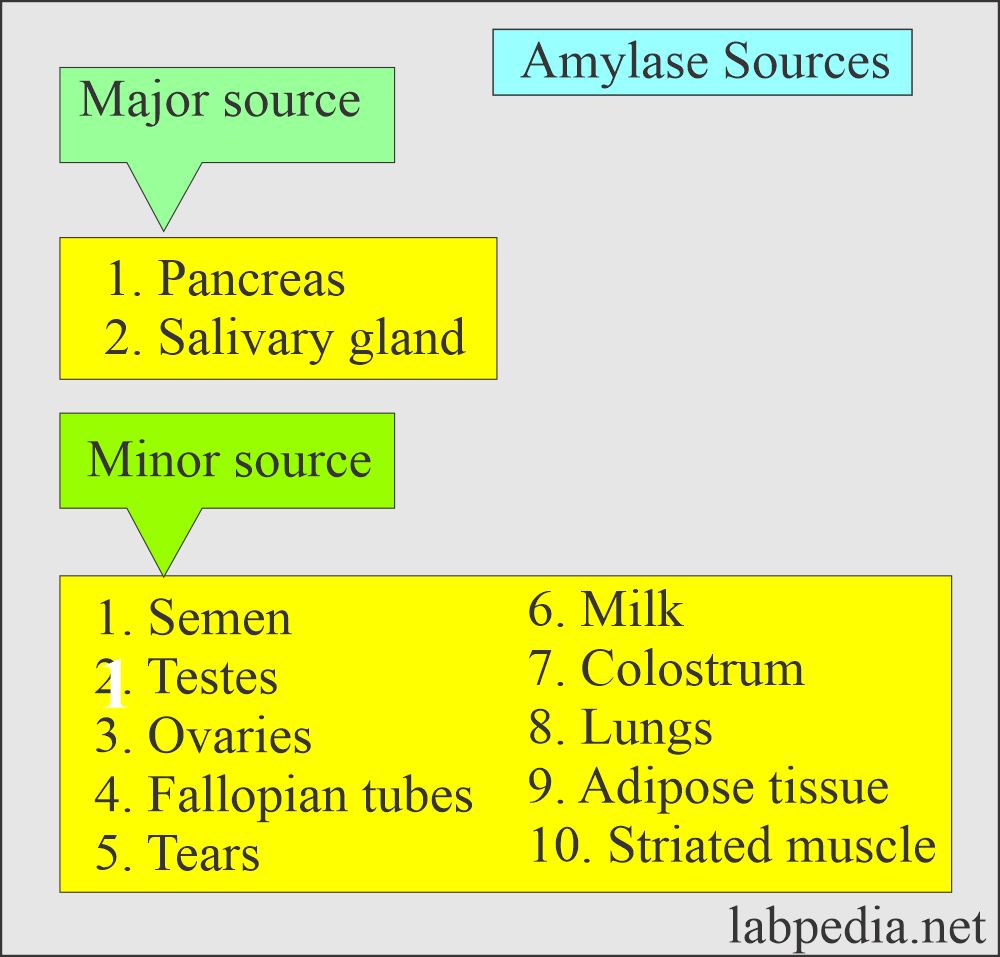
Amylase:
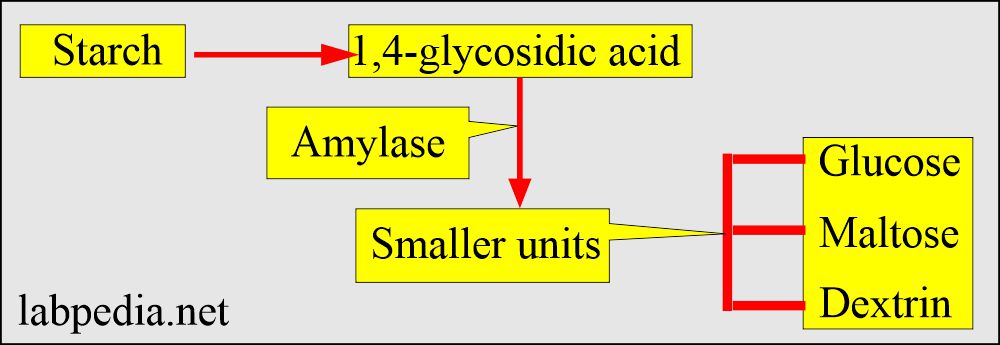
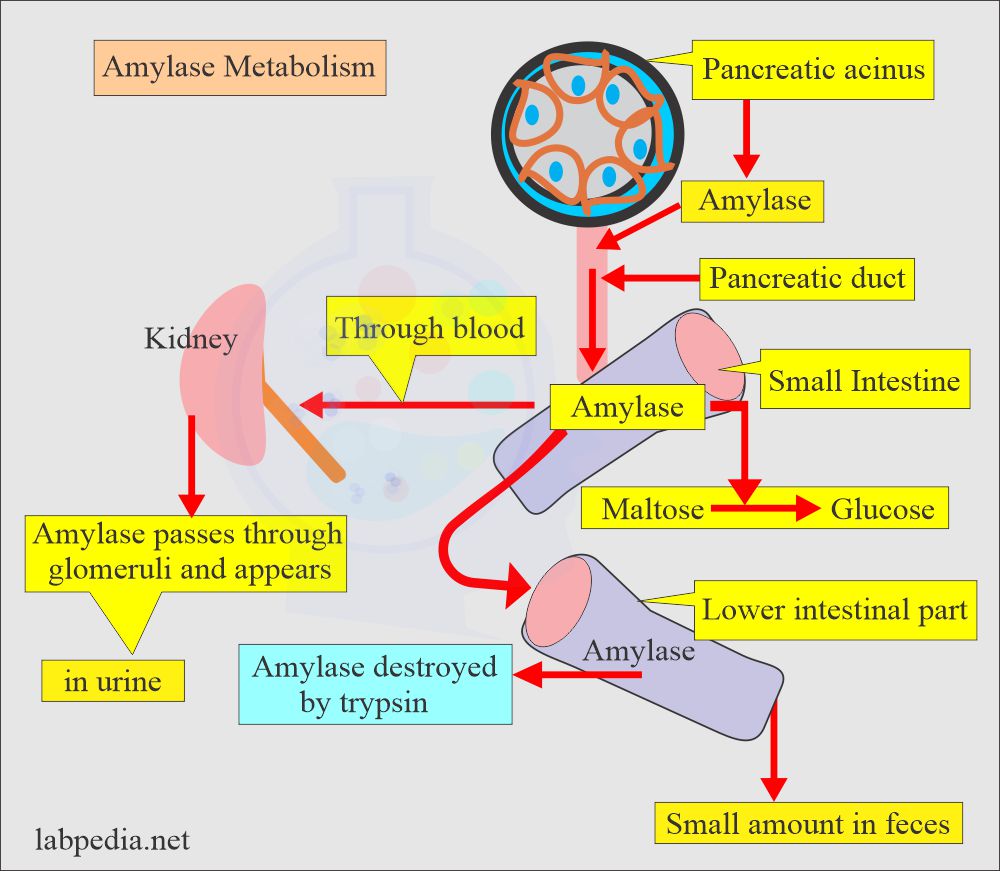
- Amylase is a digestive enzyme.
- Amylase present in human tissue is α- amylase.
- Amylase breaks down the body’s starch.
- Alcoholics will raise the level of amylase, which is salivary gland origin.
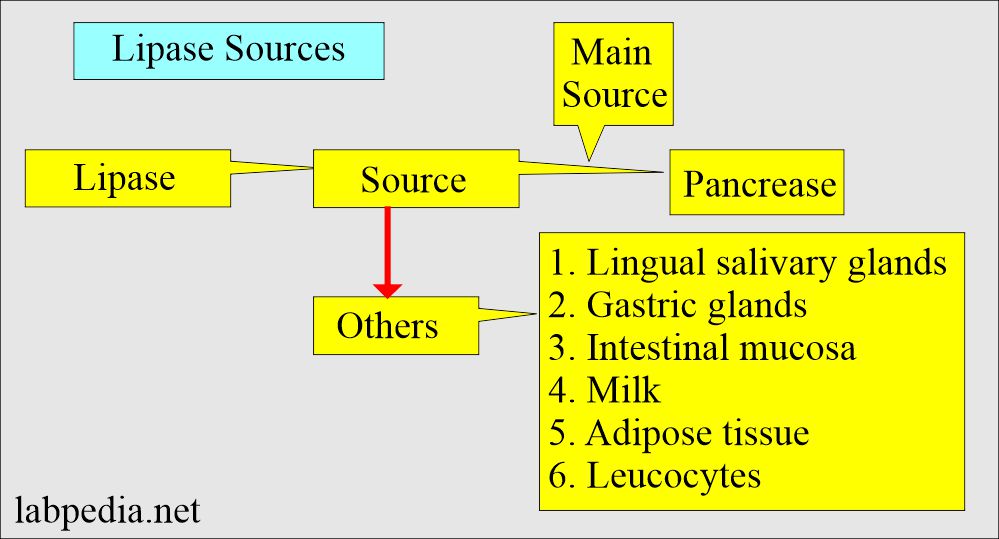
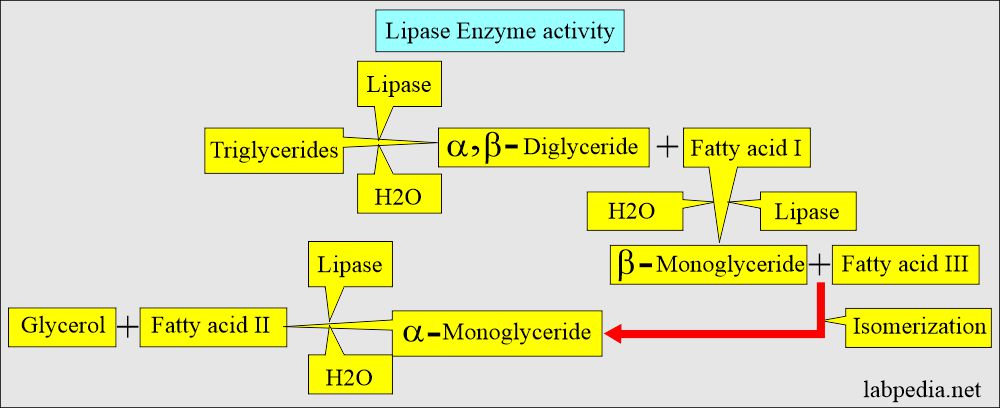
Lipase:
- Lipase helps to digest fats.
- This is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 54000 and an isoelectric point of about 5.8.
- Lipase concentration in the pancreas is about 100 times greater than in other tissues.
- Lipase is technically difficult to measure. However, it is not cleared in urine, so it remains in the blood even when amylase becomes normal.
What are the Proteolytic enzymes?
- Trypsin is a main proteolytic enzyme.
- Chymotrypsin is secreted as chymotrypsinogen A and B.
- Collagenase digests collagen and is the enzyme that initiates destruction in necrotizing pancreatitis.
- Elastase especially digests elastin, which is the most resistant of all body proteins to lytic agents.
Peptidases are:
- Carboxypeptidase removes amino acids one by one from the carboxyl ends of the peptide chain.
- Aminopeptidase removes the amino acids from the end of peptide chains, which have a free amino group.
Nucleases are:
- Ribonuclease.
- Deoxyribonuclease hydrolyzes the respective nucleic acid.
What are the normal values of pancreatic enzymes?
Source 1
Lipase serum
- <200 U/L (with triolein)
- <160 U/L (with olive oil)
- With RIA = <112 µg/L
- To convert into SI unit x 0.017 = µKat/L
Amylase serum
- Newborn 2 to 4 days = 5 to 65 U/L
- Adult = 27 to 131 U/L
- 60 to 90 year = 24 to 151 U/L
- To convert into SI unit x 0.017 = µKat/L
Amylase urine
- 1 to 17 U/hour (Beckman)
- 170 to 2000 U/L (Phadebas)
- 5 to 27 U/hour (Abbott TDx)
- The values vary from different methodologies.
Source 2
Amylase serum
- 60 to 120 Somogyi units/dL (30 to 220 units/L) .
- Newborn = 6 to 65 units/L
Urine amylase 24 hours
- up to 500 Somogyi units.
Lipase serum
- 0 to 160 units/L
(Values vary according to the method).
- Critical value = More than three times the normal.
What are the symptoms of acute Pancreatitis?
- There is sudden epigastric pain in 90% to 100% of the patients, which may radiate to any side but mostly to the back.
- Acute pancreatitis is due to the blockage of pancreatic ducts or direct injury to the pancreatic tissue by:
- Toxin.
- Inflammation.
- Trauma.
- Impaired blood flow to the pancreas.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting. There is vomiting in 30% to 96% of the cases.
- There is abdominal distension in 70% to 80% and paralytic ileus in 50% to 80% of the cases,
- Jaundice may be seen in 8% to 30%.
- Hypotension and shock develop in 30% to 40% of the cases.
- Diagnosis in typical cases is easy, but similar symptoms may be seen in various diseases.
How will you diagnose acute pancreatitis?
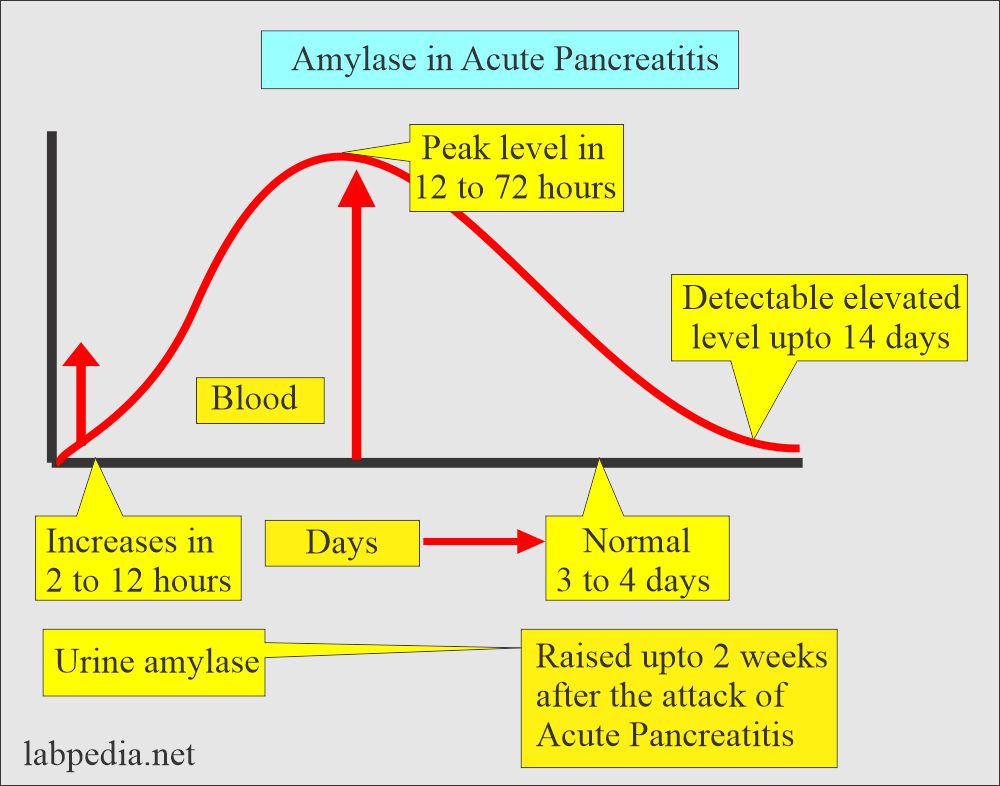
- For the first few days, check amylase at least twice a day.
- >500 Somogyi units favor acute pancreatitis.
- The peak is short and may be missed.
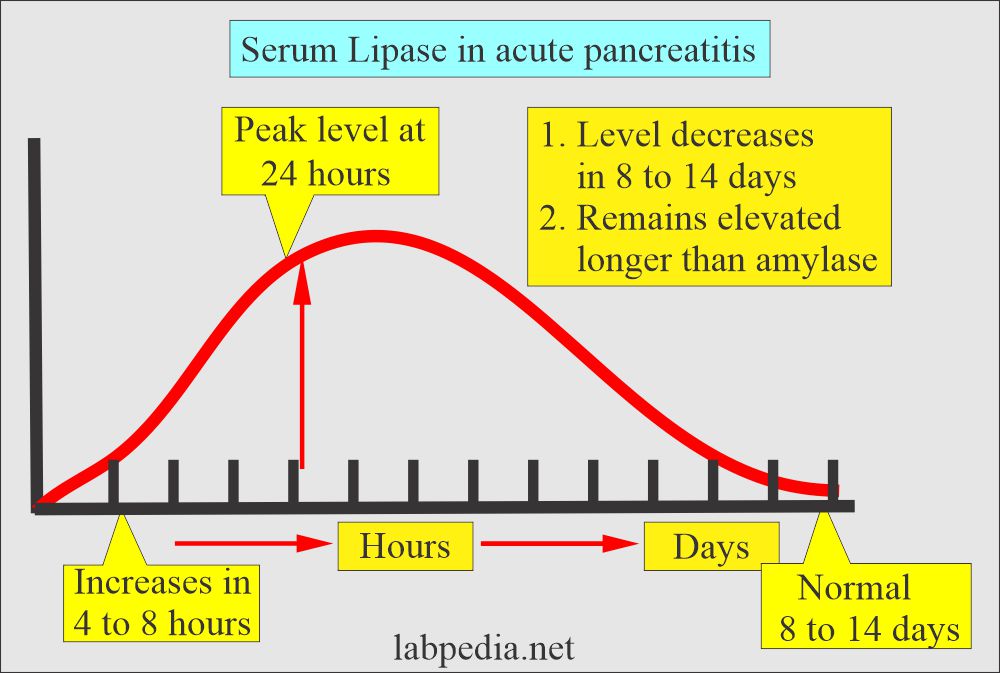
What are the conditions where Lipase is increased?
- Acute Pancreatitis.
- Pancreatic cyst or pseudocyst.
- Pancreatic cancers.
- Chronic pancreatitis
- peptic ulcer with perforation of the pancreas.
- Gastric cancer with perforation of the pancreas.
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Certain drugs like deoxycholate and glycocholate.
- Chronic liver disease
What are the conditions where Amylase is increased?
- In Acute pancreatitis, it is increased 4 to 6 times normal.
- The increase occurs within 4 to 8 hours of the onset.
- Remain elevated till the cause is removed.
- Chronic pancreatitis initially, there is a mild increase and, later on, decrease due to damage to the pancreas.
- Increased in pancreatic duct obstruction.
- Pancreatic cancers.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the source of insulin?
Question 2: What is the effect of alcohol on amylase secretion?