Neuroblastoma and Its Diagnosis
Neuroblastoma
What sample is needed for Neuroblastoma diagnosis?
- A 24-hour urine sample is recommended for the estimation of VMA (Vanillyl mandelic acid) because of the variety of secretions throughout the day.
- Collect urine in the sterile container containing acid HCl (10 ml) as a stabilizer.
- Measure the volume and keep 50 ml at 4 °C until the test is run or freeze for a longer period.
- Urine is collected for 24 hours for HVA (homovanillic acid), like VMA.
How will you define Neuroblastoma?
- This is a common tumor in infancy and is extracranial.
- This is an embryonal malignancy of the sympathetic nervous system arising from the neuroblast.
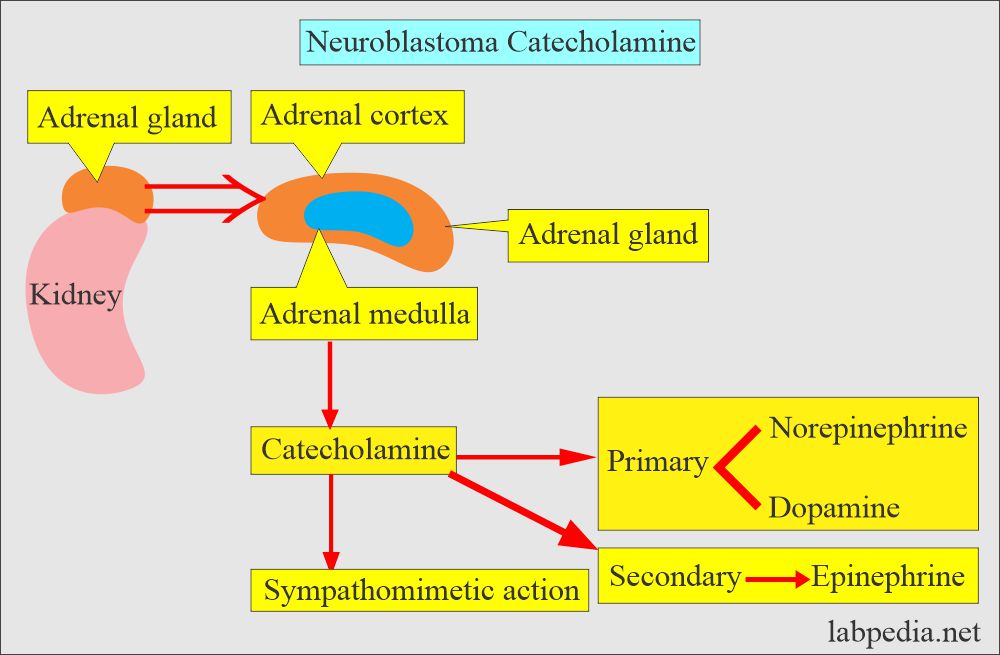
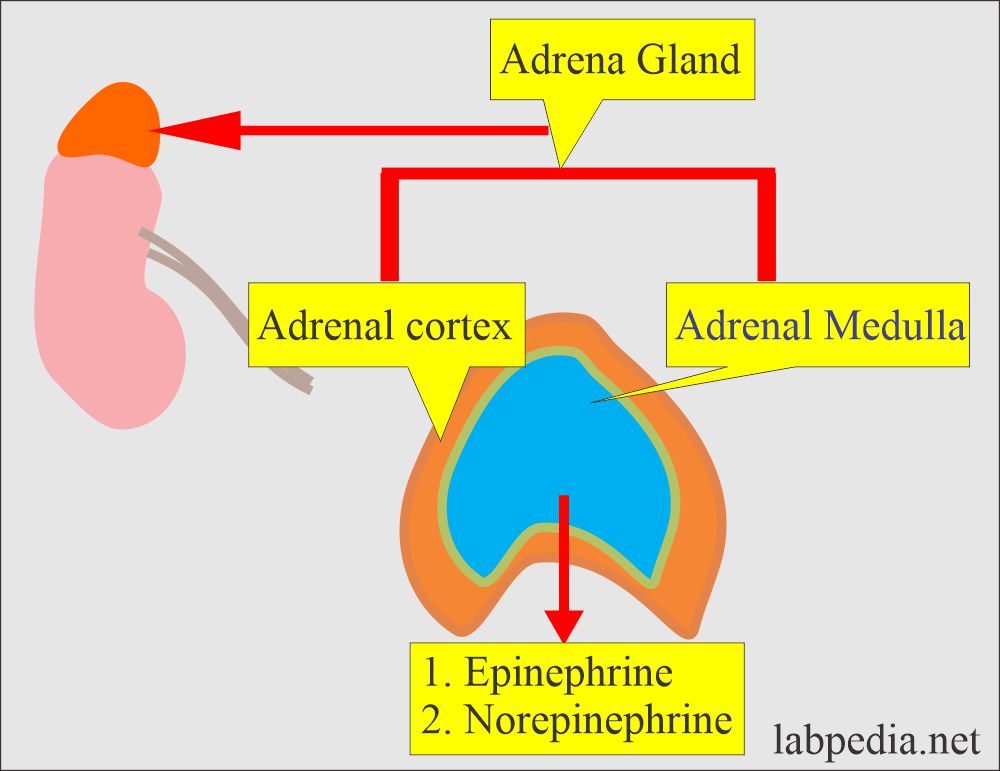
- Neuroblastoma most commonly arises in and around the adrenal glands.
- A malignant tumor arises in the adrenal medulla or sympathetic chain.
- 70% have metastasis at the time of diagnosis.
- This is the second most common tumor under the age of 3 years.
- Neuroblastoma can also originate in the abdomen, chest, neck, and near the spine.
- When it is of neural crest origin, this tumor may arise anywhere in the sympathetic nervous system from the head to the pelvis.
- 75% arise within the abdomen.
- Nearly 50% in the adrenal gland.
- Other 50% paravertebral autonomic ganglia.
- Origin in the brain is rare.
What is the pathophysiology of Neuroblastoma?
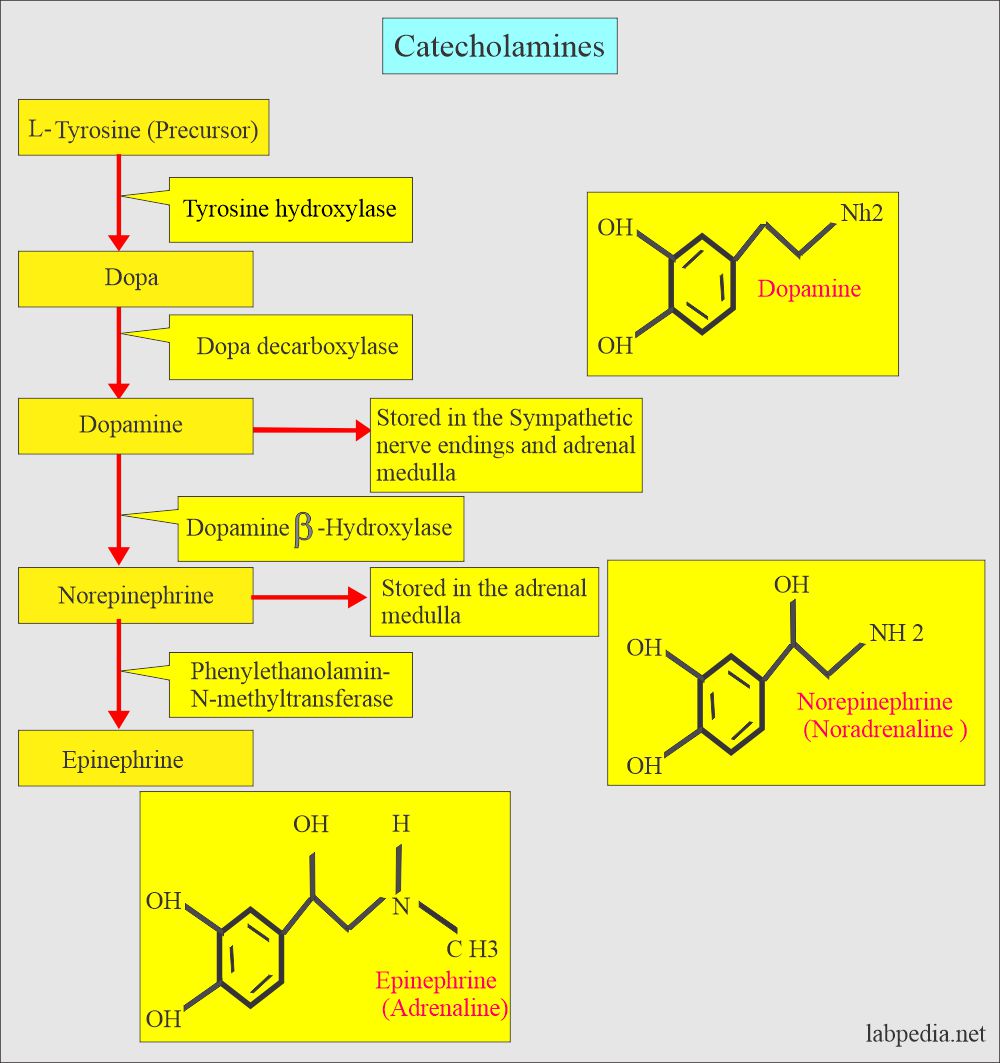
- Neuroblastoma >90% associated with increased production of:
- Catecholamines.
- Catecholamines metabolites.
- There is increased excretion in the urine of:
- Norepinephrine.
- VMA (Vinyl mandelic acid)
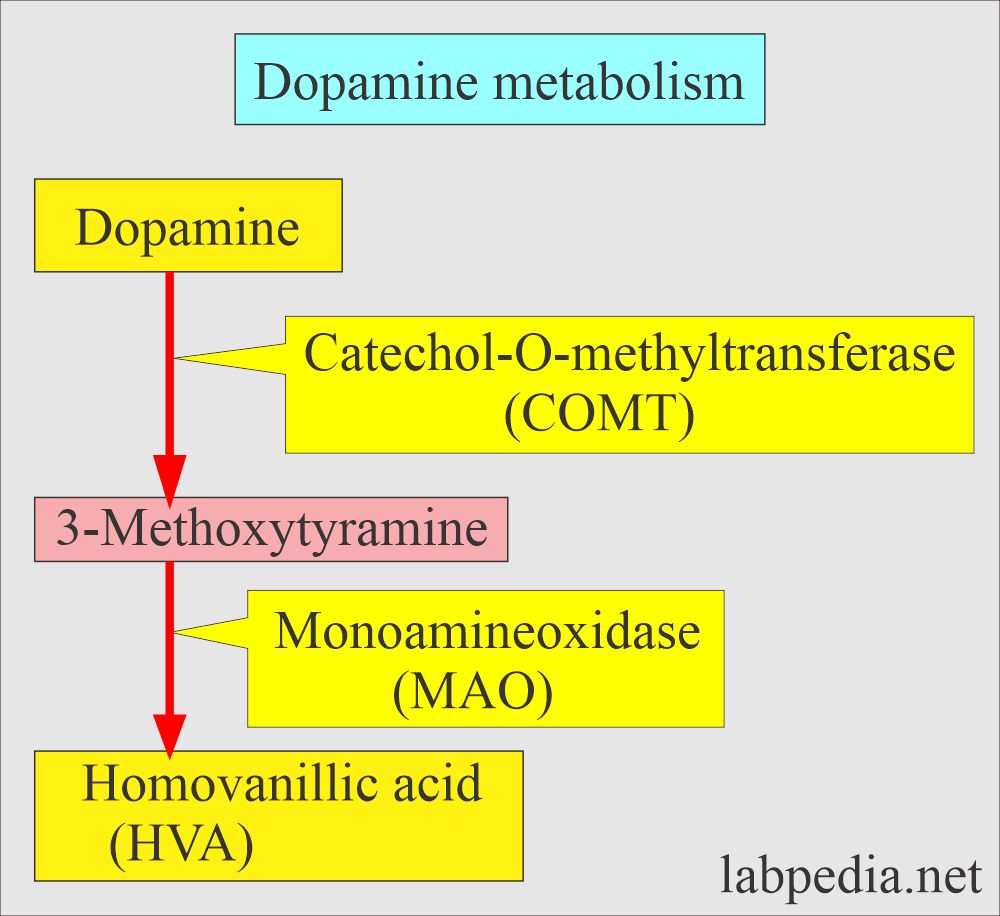
- HVA (Homovanilic acid).
- Dopamines.
- Dopamine excretion in the urine is increased in Neuroblastoma.
- The precursor is L-Tyrosine, which ultimately gives rise to Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Epinephrine.
What are the signs and Symptoms of neuroblastoma?
- It will affect children 5 years or younger.
- 80% to 90% of the cases are seen under the age of 5 years.
- This accounts for 15% of all childhood cancer deaths.
- It is rare for older children.
- The most common site is the adrenal medulla for Neuroblastoma, but it can arise anywhere along with the sympathetic system.
- There may be abdominal pain.
- There may be a mass under the skin, but it is not tender.
- There may be changes in bowel habits, like diarrhea and constipation.
- While the neuroblastoma of the chest may give rise to wheezing and chest pain.
- The eyeball may be protruded from the sockets (proptosis).
- There may be dark circles and bruises around the eye.
- Other signs and symptoms may be seen as:
- Back pain.
- Bone pains.
- Fever.
- There is unexplained weight loss.
- There is:
- Hypertension.
- Sweating.
- A headache.
- Tachycardia.
- These patients may have:
- Metastasis to lymph nodes, bone marrow, bone, skin, and liver.
- There may be hepatomegaly and ascites.
- The patient may have signs and symptoms due to the secretion of certain chemicals that give rise to paraneoplastic syndrome.
- There may be spinal cord compression, leading to pain and paralysis.
- 90% of the cases are associated with excessive production of catecholamines and catecholamine metabolites.
- So, the estimation of catecholamines helps:
- In the diagnosis.
- In the screening of this tumor.
- It helps to follow the treatment effect.
- Increased excretion of dopamine is characteristic of Neuroblastoma.
- There is a unique feature in the natural history of this tumor, which is a spontaneous regression or sometimes therapy-induced maturation.
What are the normal Adrenal gland’s hormones?
| Patient position | Norepinephrine pg/mL | Epinephrine pg/mL | Dopamine pg/mL |
|
120 to 680 | <60 | <87 |
|
125 to 700 | <90 | <87 |
|
110 to 410 | <50 | <87 |
What are the VMA normal values?
- A 24-hour urine sample is collected in a container containing HCl.
- 10 mL of HCl, 6 mol/L for 24 hours of the urine sample is required.
| Age of the patient | VMA mg/day | VMA mg / g Creatinine |
|
1.0 to 2.6 | 4.0 to 10.8 |
|
2.0 to 3.2 | 4.0 to 7.5 |
|
2.3 to 5.2 | 3.0 to 8.8 |
|
1.4 to 6.5 |
What is the normal Homovanillic acid (HVA)?
- It is also elevated in almost all cases.
- HVA is the main urinary metabolite of Dopa and Dopamine.
- This can be used for the diagnosis and the treatment follow-up of Neuroblastoma.
- 24 hours after the urine sample is collected.
- Add 10 mL of HCl (6 mol/L) for 24 hours sample.
- Normal values in the urine are:
| Age of the patient | HVA mg/day | HVA mg/ g Creatinine |
|
1.4 to 4.3 | 5.4 to 15.5 |
|
2.1 to 4.7 | 4.4 to 11.5 |
|
2.4 to 8.7 | 3.3 to 10.3 |
|
1.4 to 8.8 |
How will you diagnose neuroblastoma?
- Urine Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) is elevated in almost all cases. VMA is the end product of norepinephrine and epinephrine.
- VMA is the major catecholamine metabolite, and it represents 60% of the total metabolites of Norepinephrine and Epinephrine.
- The more poorly-differentiated tumor produces more HVA than VMA.
- Other tumor markers which are nonspecific but used to follow tumor activity are:
- Neuron-specific enolase (NSE).
- Lactate dehydrogenase.
- Ferritin.
- Ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI may help in diagnosing the tumor.
- A biopsy of the tissue is needed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Bone marrow aspiration may be advised to rule out infiltration by the tumor.
What is the differential diagnosis of neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma (Benign)?
| Urinary concentration | Neuroblastoma (Ganglioneuroma) | Pheochromocytoma (Benign) |
|
Increased | Normal (Increased in malignant form) |
|
Increased | Normal (Increased in malignant form) |
|
Increased | Increased |
|
Increased | Increased |
|
Increased | Increased |
How will you treat Neuroblastoma?
- The first choice is surgery. One can remove the whole tumor. Still, surgery may be needed for surgical pathology to know the grade of the tumor.
- In some cases, chemotherapy may be given prior to the surgery to shrink the tumor.
- The third choice is radiotherapy.
What is the prognosis of Neuroblastoma?
- This depends upon the tumor stage and the patient’s age.
- Younger children under the age of one year have a better prognosis than older children.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How you will diagnose neuroblastoma?
Question 2: What other hormone will be raised in poorly differentiated neuroblastoma?