Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:- Part 3 – Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (AFB) Culture
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (AFB) Culture
What sample is needed for the AFB culture sample?
- AFB cultures can be done on sputum.
- Material from other tissues like the endometrium and chronic ulcers.
- Biopsy from the lung may be taken when the possibility of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is suspected.
- Pleural fluid should be at least 2 ml and refrigerated until the culture is done.
- Bronchial washing should be at least 2 ml and also refrigerate until processed for culture.
What are the Indications for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Culture (AFB)?
- For the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the sputum.
- For the diagnosis of TB meningitis.
- For the diagnosis of tuberculosis in other sites like lymph nodes, chronic ulcers, and pleurisy.
- Any patient with a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss, and hemoptysis.
What are the precautions for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Culture (AFB)?
- Pulmonary tuberculosis can be diagnosed from sputum. Always try to get deep sputum and avoid saliva.
- When tissue is taken from the patient, it is smeared on the slides and stained when it is fresh.
- The smear sensitivity is low, so the culture follows it.
What is the microbiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (AFB)?
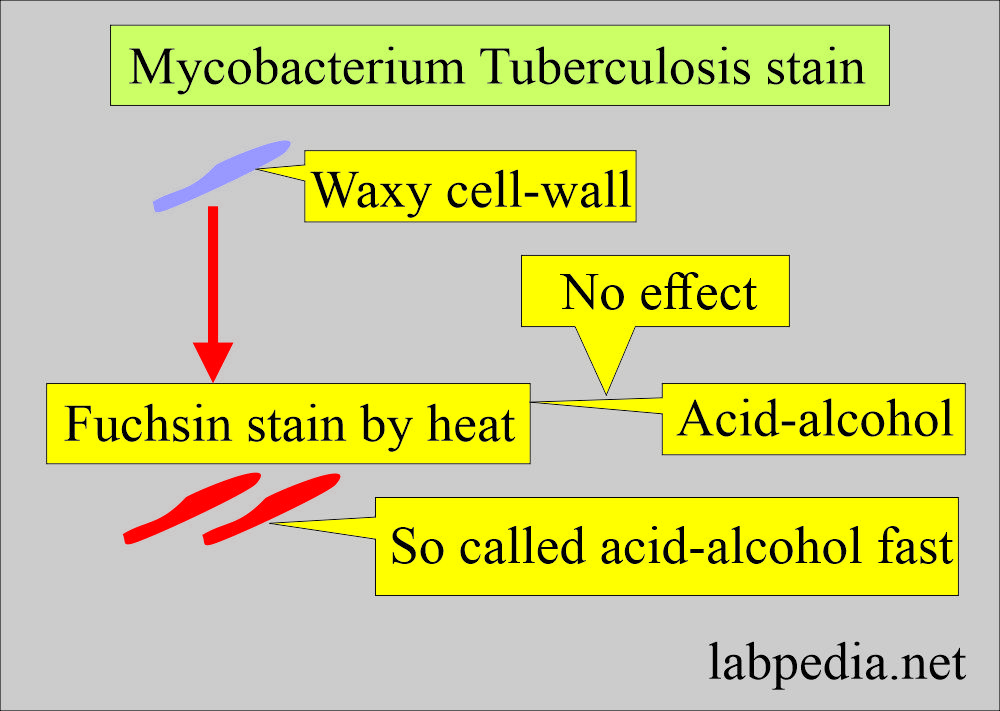
- Mycobacteria are called acid-fast because after mordanting in the stain, they resist decolorization by the strong acids.
- This staining property is due to the cell wall composition, which has high lipid contents.
- These have poor staining with gram stain.
- One of the cell lipids forms a complex with acid and mycolic acid.
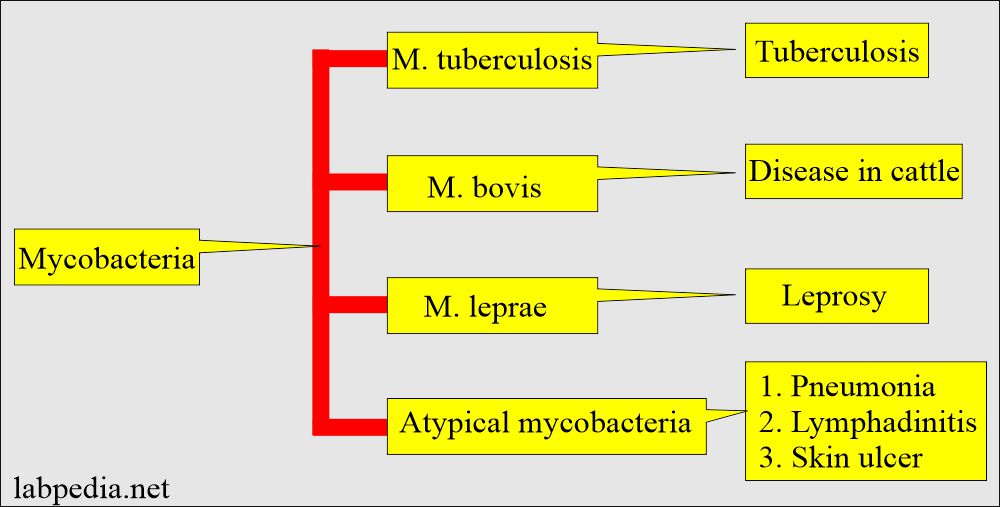
- Mycobacteria are divided into:
- Fast-growing, which forms colonies in 2 to 3 days.
- Slow growing, which forms the colony in 1 to 3 weeks.
- The most common AFB is Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB).
- These pleomorphic rod-shaped bacteria contain a large amount of mycolic acid in the wall, making it difficult to stain.
- When heat or other agents are used to force carbol fuchsin to enter the cytoplasm, the bacteria resist decolorization with a dilute acid-alcohol solution. Therefore, they are called acid-fast bacilli.
- Mycobacterium is a gram-resistant and non-motile bacteria.
- These are intracellular pathogens.
- Tuberculosis, M.bovis, M.africanum, and M. microti are all commonly known as Tuberculosis (T B).
- Tuberculosis is pathogenic for humans, while M. bovis usually for animals.
- Mycobacteria are:
- Obligate anaerobes easily grow in the lungs with high oxygen content.
- These are facultative intracellular pathogens, usually involving mononuclear phagocytes.
- These are slow-growing bacteria and may take a few days to weeks.
- These are Hydrophobic with a high lipid content in the cell wall.
- Because the cells are hydrophobic and tend to clump together, they are impermeable to the usual stains, e.g., Gram stain.
- They are known as “acid-fast bacilli” because of their lipid-rich cell walls.
- Once stained, the cells resist decolorization with acidified organic solvents and are therefore called “acid-fast.”
- Morphology:
- These are slender, beaded bacilli and nonsporing.
- Colonies are rough, dry, and yellow in color on the Lowenstein-Jensen media.
- These are slow-growing bacteria in this medium.
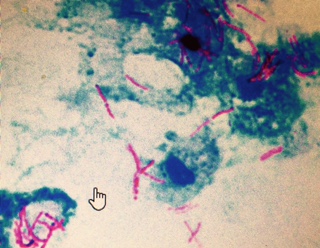
- At least 5000 Acid-fast bacilli must be present in each mL of the specimen to be seen on the microscopic smear.
What are the media for the culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Solid medium:
- The culture is done using a special culture medium called L. J (Lowenstein-Jensen ) medium. Bacilli need 4 to 6 weeks to grow.
- LJ medium contains a whole egg, asparagine, glycerol, and material that inhibits the growth of infectious material, such as malachite green.
- It takes 4 to 6 weeks to grow bacilli at 37 °C.
- These are obligate aerobics and do not grow on ordinary media.
- This is eugonic growth on the LJ medium.
- These are obligate aerobes and do not grow on ordinary media.
- Keep culture for 6 to 8 weeks before the media is discarded.
- Smear from the culture shows these AF Bacilli as red color rods single or in clusters. Morphologically, these are pleomorphic.
Liquid medium:
- These are better than solid mediums.
- The growth is rapid, and it takes 12 to 16 days instead of 4 to 6 weeks.
- These are more easily contaminated, so need antimicrobial agents.
- Incubation with additional CO2 is not required.
Automated system:
- Continuously needs monitoring to see the growth for 6 weeks.
Important facts:
- Acid-fast bacilli may be found in tuberculosis caseous material, but tubercle bacilli recover more quickly in sputum.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the principle of AFB stain?