Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:- Part 1 – Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB)
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Tuberculosis is the world’s most spreading disease and developing drug resistance.
Epidemiology of M.Tuberculosis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the causative agent.
- It is estimated that 20% to 43% of the world’s population suffers from TB.
- In the USA, 15 million people are infected (Old statics).
- TB occurs in :
- Poor community is considered to be the disease of poor people.
- Malnourished people.
- Homeless.
- Overcrowded community.
- Substandard housing.
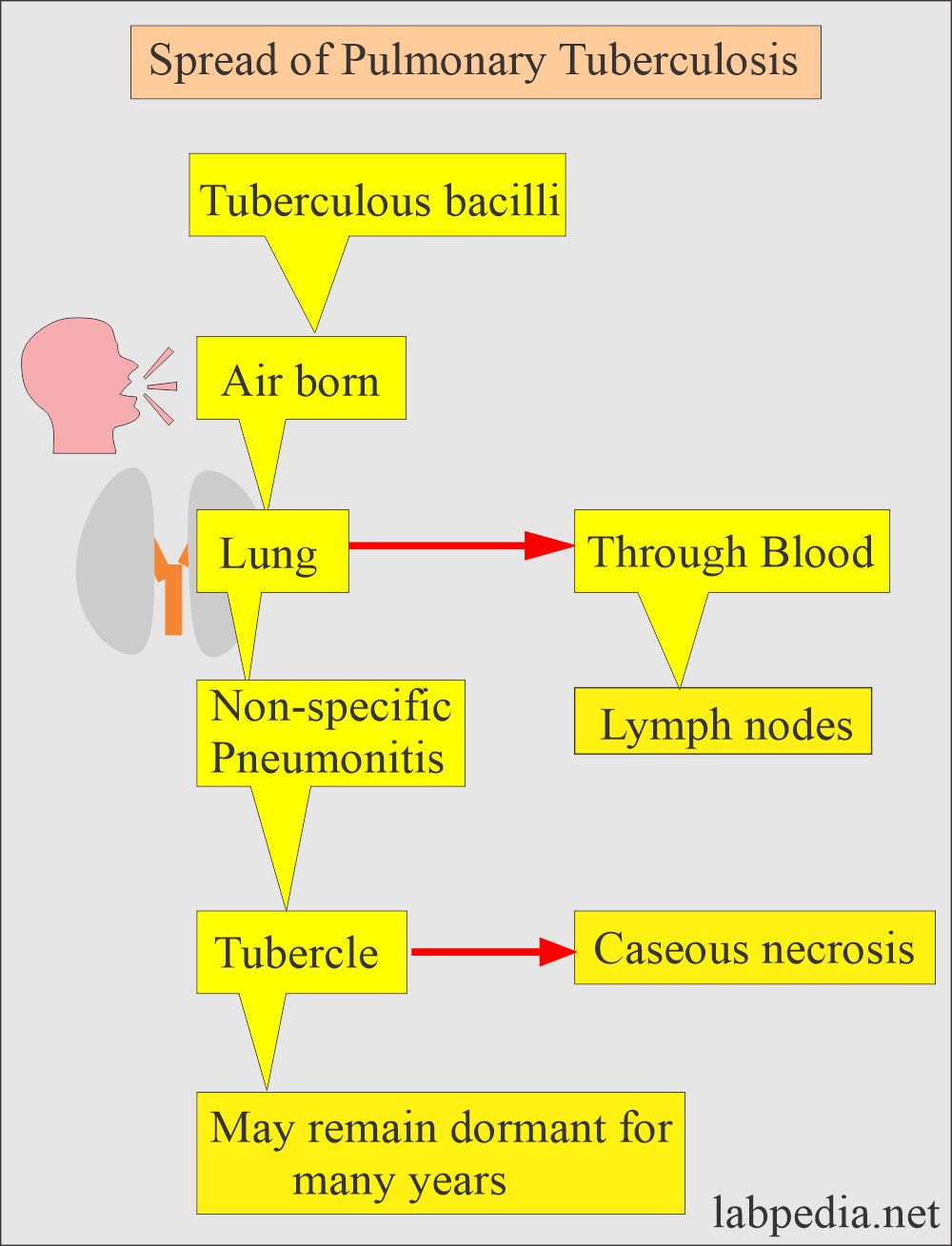
Mode of the spread of tuberculosis:
- This is an airborne disease.
- This occurs in various forms and modes.
-
- Primary TB = Clinically and radiologically is silent.
- Latent TB = Do not have active disease and can not spread the disease to others.
- Active TB = 10% of the latent TB develop active TB when not given treatment.
- Progressive primary TB = 5 % of the primary active TB with signs and symptoms.
- This is thought that 90% of the disease is a reactivation of latent TB.
Microbiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
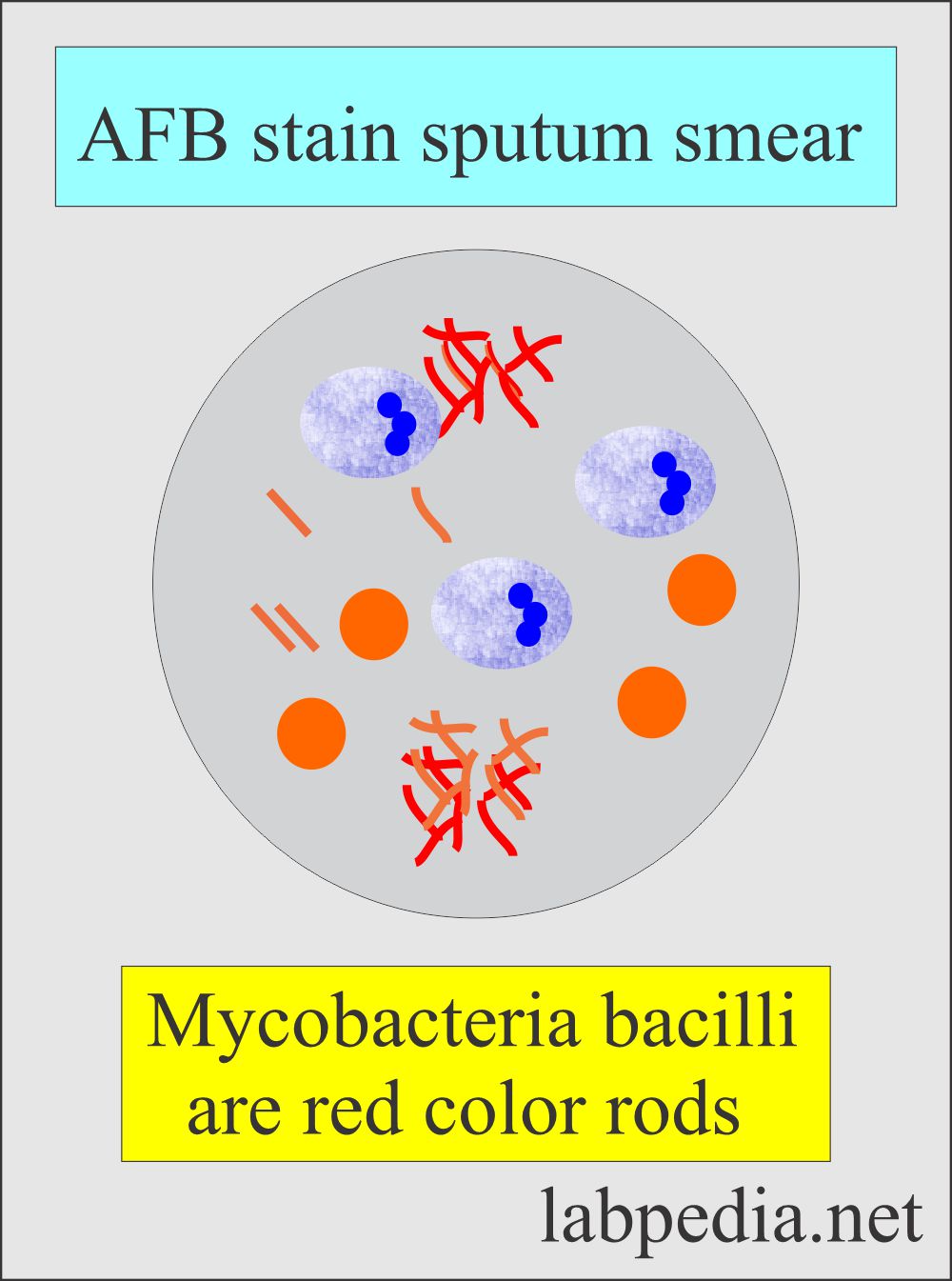
- These are acid-fast bacilli.
- These are rods shape and grow in cords.
- The growth is very slow on special media.
- They get gram stain but are very weak, which is gram stain positive.
- These are non-motile, obligatory aerobes and intracellular organisms.
- Humans are the only reservoir.
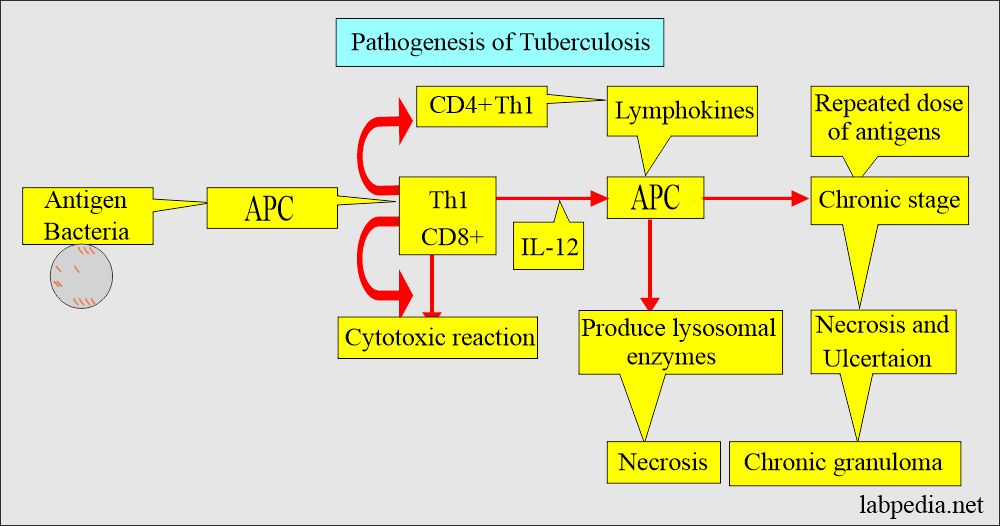
Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
- Mycobacterium tubercle bacilli cause damage by invading the macrophagic cells by Type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
- This bacteria leads to caseating necrosis and granuloma formation.
- There are multinucleated giant cells, Langhans’ type cells.
- TB bacteria consists of slightly curved or straight rods.
- It cannot be stained by the gram’s stain but are acid-fast.
- These are nonmotile and without spores.
- Pathogenic bacteria are slow-growing and may take 4 to 6 weeks.
- The common types are :
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Mycobacterium bovis.
- others are Runyon group 1 to IV.
Sign and Symptoms of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
- The patient will have the following:
- Malaise.
- Anorexia.
- Weight loss.
- Fever.
- Night sweating.
- A chronic cough is a common presentation of pulmonary TB.
- Blood-streaked sputum is common.
- The patient may have hemoptysis.
- Rarely are patients asymptomatic.
- In advanced disease:
- There may be clubbing of nails.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- The patient may develop pleural effusion.
Clinically the possibilities of tuberculosis are:
- TT (Manteaux test) positive cases, and these cases may be inactive asymptomatic people.
- Primary tuberculosis shows the Ghon complex.
- There is a lesion in the lung and involvement of the lymph nodes.
- Secondary tuberculosis involves the upper lobe of the lung because of the higher oxygen concentration.
- This is usually seen in impaired immunity.
- There may be cavity formation in the lung.
- Sputum smears are AFB-positive.
- The disease is contagious.
- Miliary tuberculosis is a widespread disease.
- It involves the lungs, CNS, kidneys, and GI tract.
- It may involve any organs, including the bones.
- Extra-pulmonary may involve CNS and leads to chronic meningitis.
- There may be the formation of tuberculoma in the brain.
- There may be the involvement of the skin.
- TB is very common in AID patients.
- In AID patients, TT may be negative due to compromised immune systems.
Laboratory diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
- Definite diagnosis depends upon the demonstration of T.Bacilli by:
- Culture.
- Culture on solid media needs 12 weeks.
- Culture on liquid media needs several days.
- PCR by DNA or RNA amplification method.
- Sputum, three consecutive samples is recommended for:
- Fluorochrome staining with rhodamine-auramine.
- AFB stain or Ziehl-Neelsen stain.
- An early morning specimen is recommended.
- Bronchoscopy is advised for bronchial washing in case of negative sputum.
- Transbronchial lung biopsy increases the diagnostic yield.
- Gastric aspiration. An early morning sample is an alternative to bronchoscopy.
- Blood culture, 15% of the case may give a positive culture to T. bacilli.
- The sensitivity should be done once the culture is positive.
- The sensitivity should be done if the sputum culture is positive after the treatment for 2 months.
- Needle biopsy of the pleura shows granulomas in 60 % of the cases.
- Pleural fluid cultures are positive in < 25 % of the cases.
- Radiology, X-ray chest shows small homogenous opacity.
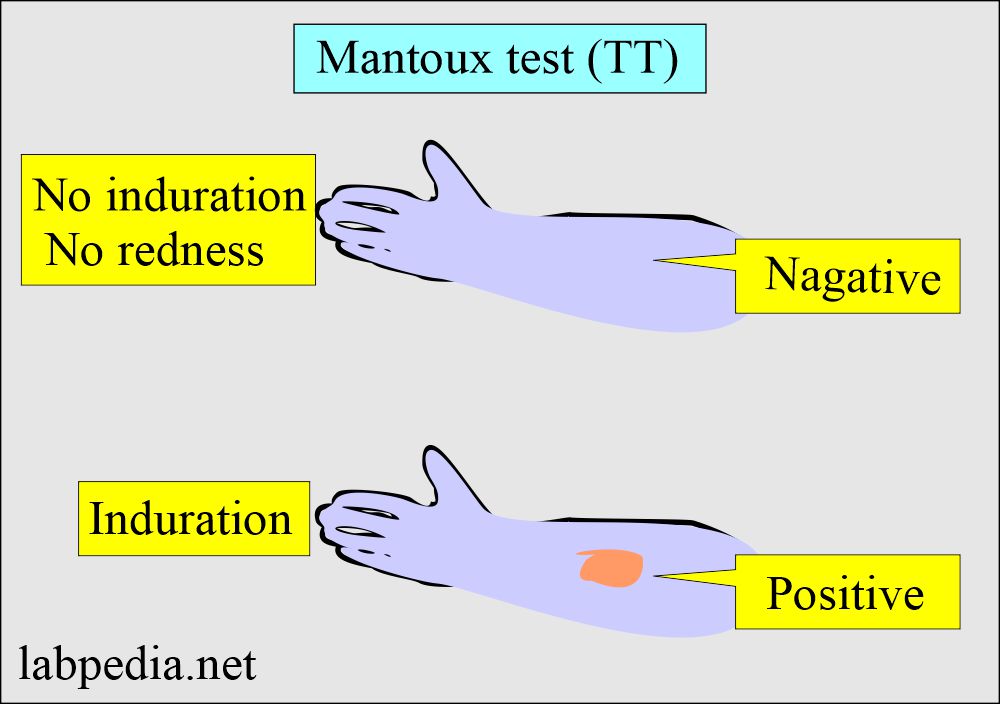
Mantoux test or Tuberculin test (TT).
- The Mantoux test (TT) will not distinguish between latent and active TB.
- 0.1 ml (5 tuberculin units) of PPD should be injected intradermally.
- The best site is the volar surface of the arm.
- Injected with 27 G needle.
- Read after 48 to 72 hours for induration (thickening of the injected area).
- After the infection, it takes 2 to 10 weeks to develop an immune response to PPD.
- Other specimens that can also be used are:
- Urine. The first-morning clean catch is collected for three consecutive days.
- Stool. This should be collected in a clean, sterile container.
- Blood. Lysed centrifuged blood is used for culture.
- Niacin test. Mycobacterium produces Niacin. Commercially available kits can test this.
Preventive measures for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- This disease can be prevented by health workers.
- If your TB test is positive, you have contact with the patient and may not have active disease.
- Vaccination like BCG is helpful in preventing the disease.
- BCG is live attenuated bacteria.
- It is not available in the USA.
Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- The following drugs are used in patients with tuberculosis:
- Isoniazid (INH).
- This is advised in TT-positive people.
- This is also given prophylactically in AIDs patients.
- Combination of drugs like:
- Isoniazid.
- Rifampicin.
- Pyrazinamide.
- Ethambutol.
- Isolation is also important to stop the spread of the disease.
- Steroids are contraindicated in these patients because there may be reactivation of tuberculosis.
- Isoniazid (INH).
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How much time for the culture of tubercle bacilli?
Question 2: When to read Mantoux test (TT)?