Mycetoma Diagnosis and Causative Agents
Mycetoma
What sample is needed for mycetoma?
- Get a sample from the lesion.
- Can take a biopsy of the lesion.
How will you define Mycetoma?
- Mycetoma means fungal growth or maduromycosis of the foot.
- Mycetoma term refers to severe, deeply chronic, locally progressive, destructive, suppurative, and granulomatous disease.
- It begins in the subcutaneous tissue, usually of the hand and foot.
- This involves subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and bone.
- It is characterized by tumefaction, draining sinuses, and the presence of granules.
How will you discuss the pathology of Mycetoma?
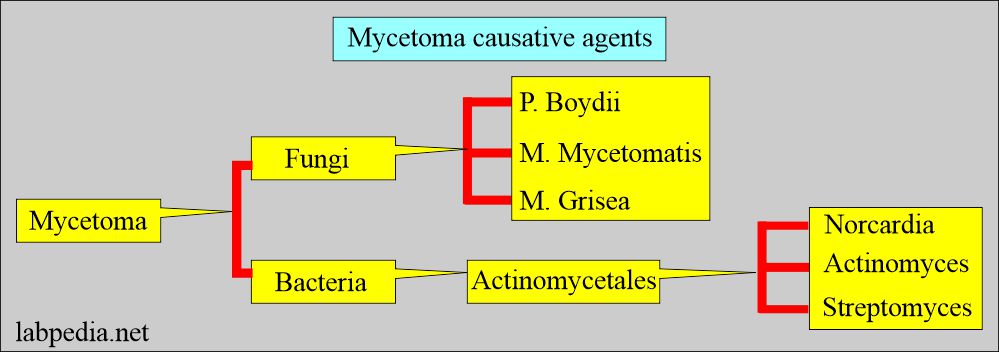
- Two types of microorganisms cause Mycetoma:
Bacterial causes are:
- These are aerobic actinomycetes, which cause mycetoma, which is called actinomycetoma in more than 50% of cases.
- The organism in this group are:
- Nocardia brasiliensis.
- Actinomadura pelletieri.
- Actinomadura madurae.
- Streptomyces somaliensis.
- Actinomyces are:
- Actinomyces israelli. It produces actinomycosis.
- This chronic internal abscess formation will develop the sinus tract to the skin.
- There is purulent exudate containing yellow granules called sulfur granules.
- These sulfur granules are masses of actinomycetes.
- Actinomyces bovis.
- Actinomyces israelli. It produces actinomycosis.
Fungal causes are:
- Fungal infection is caused in the other 50% of the cases.
- This is called Eumycetoma, also known as maduromycosis, and is caused by a true fungus.
- There are at least 23 types of filamentous fungi that cause Mycetoma. An important one is:
- Pseudallescheria boydii (There are yellow granules).
- Madurella mycetomatis (There are big black granules).
- Medurella grisea.
How would be the presentation of mycetoma?
- Mostly, the feet are involved, and less common hands and other sites are involved.
- This chronic, suppurative, granulomatous inflammation can involve subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and bone.
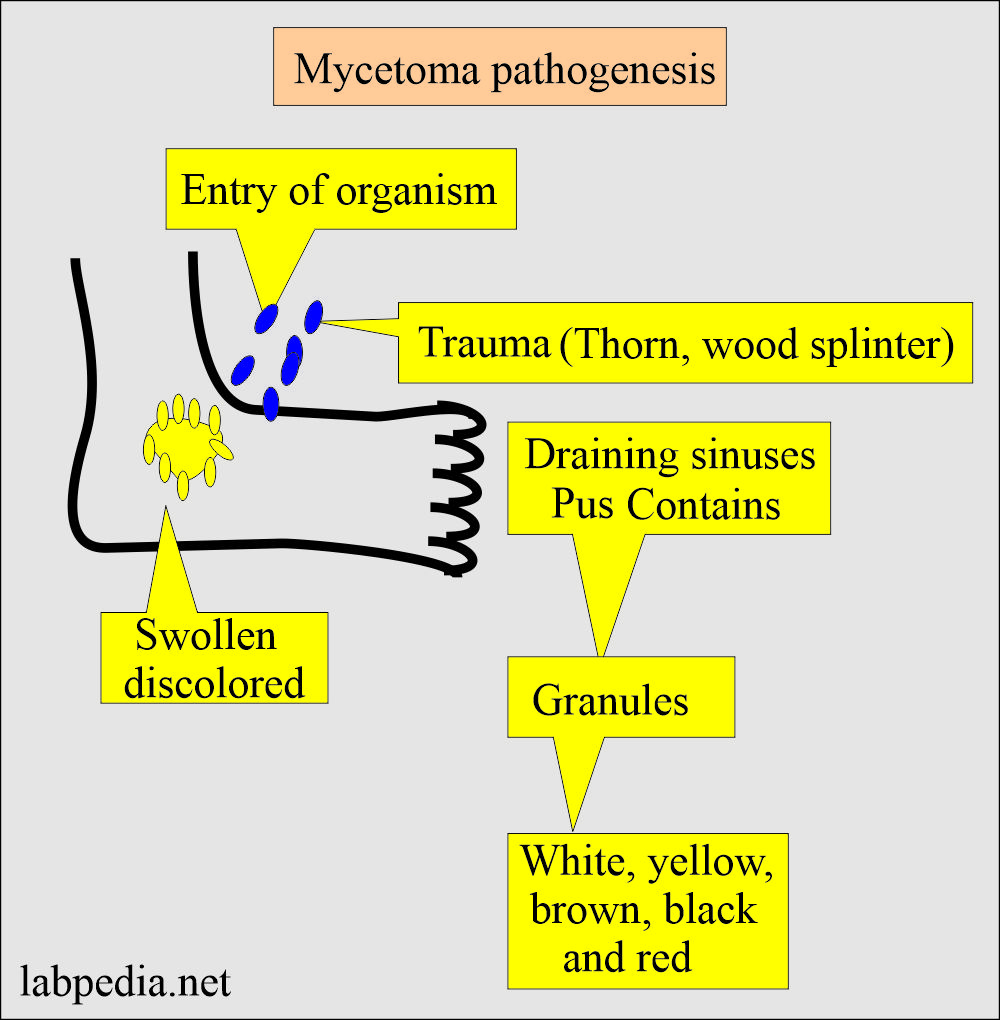
- The etiological agents enter the body through the foot from the soil, possibly due to trauma.
- When the foot is involved, where it is swollen and discolored, numerous draining sinuses form.
- This disease is characterized by tumor formation and draining of the abscess.
- There is the presence of granules or grains in the pus.
- Depending upon the causative agents, these granules have different colors: white, black, yellow, and brown.
- Mycotic mycetoma is more common in men than in women.
- Mycotic mycetoma is usually due to an injury to the foot.
How will you discuss the pathogenesis of mycetoma due to fungi?
- When fungi are implanted in the subcutaneous tissue following the trauma.
- There is a destructive granulomatous lesion that drains through multiple sites.
- There is local spread but no dissemination.
- The most common site is the foot, and this infection is called the Medura foot.
- Causative agent:
- Important fungi are filamentous, including:
- Medurella mycetomatis.
- Medurella grisea.
- Phialophora verrucosa.
- Important fungi are filamentous, including:
- Pathogenesis of fungal Myecetoma:
- First, fungi are implanted into the tissue after trauma, which may be splinter.
- It produces destructive granulomatous inflammation.
- Later on, this lesion drains through multiple sinus tracts.
- There is local spread but no widespread dissemination.
- This is common in barefoot people.
How will you diagnose mycetoma?
- Collect the granules from the lesion.
- Then, wash the granules with the saline, crush it, and spread it on the slide.
- Also, the culture of the material should be taken into account. Culture is done on the Sabouraud’s medium for fungus.
- Prepared slides are stained with Gram’s stain :
- The filaments are less than or equal to 1.0 micrometers in diameter, a diagnostic of aerobic actinomycetes called actinomycetoma.
- If the filaments are 2 to 5 micrometers and hyphal in shape, the diagnosis of fungal infection is called eumycetoma.
- These granules can also be seen in the KOH 10% solution.
How will you treat mycetoma?
- The prognosis of Eumycetoma is poor.
- These patients undergo surgical debridement and oral Itraconazole 200 mg twice a day for a prolonged period of time, and their response is only 70%.
- These patients may be given combination therapy.
- Mostly, these are treated by surgery.
- Chemotherapy is not effective and is given for a prolonged time.
- Treatment surgical and chemotherapy are ineffective when the mycetoma is due to fungi.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What are the causes of mycetoma?
Question 2: What is the common site for the mycetoma?