Microalbuminuria
Microalbuminuria
What sample is needed for Microalbuminuria?
- The sample is urine.
- It is better to do three random samples for a week.
- The urine sample is stable at room temperature for up to 2 days and at 8 °C for up to 14 days.
What are the indications for Microalbuminuria?
- This is advised in a diabetic patient to rule out diabetic nephropathy; even routine urine tests are negative.
- High-risk patients should be tested within a 3 to 6-month period.
- Check-in the case of hypertensive patients.
What are the precautions for microalbuminuria?
- Avoid urine after exercise.
- Avoid prolonged upright posture.
- Avoid in case of hematuria.
- Avoid blood-contaminated urine.
- Avoid in case of genitourinary tract infection.
- Avoid in case of congestive heart failure.
- Avoid in case of uncontrolled hyperglycemia or hypertension.
- Avoid in test tubes where albumin is attached.
What are the factors for False-positive microalbuminuria?
- It can get false positive results when the urine pH is≥8.0.
- When the temperature is >77 °F.
- When Tamm-Horsfall protein is present in the urine.
How will you define microalbuminuria?
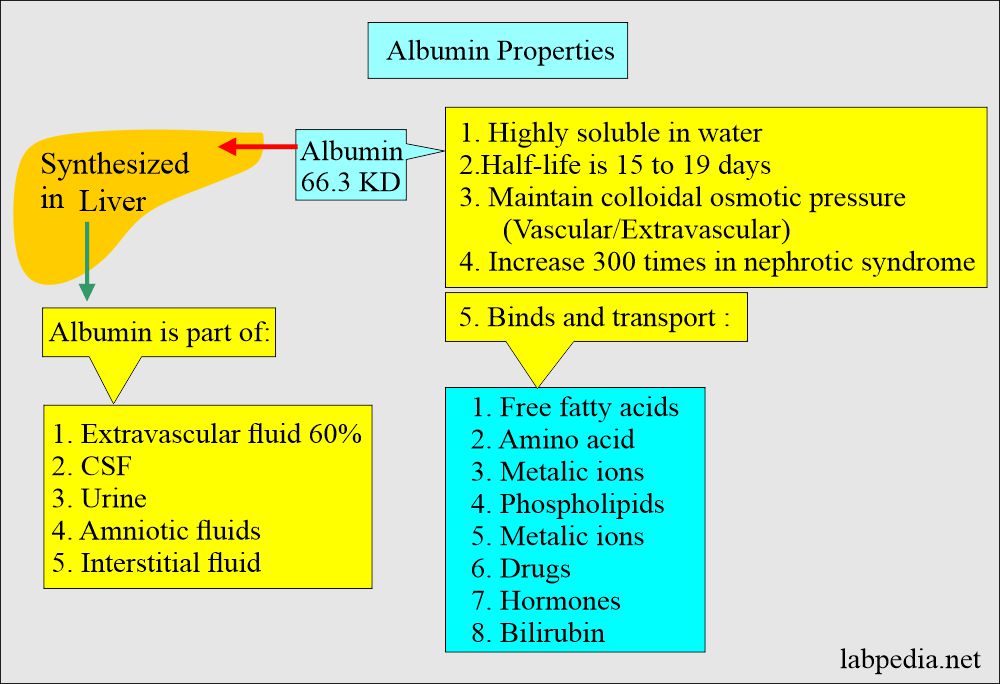
- Microalbumin is a misnomer. This does not refer to any different form of albumin; instead, a small amount of albumin is excreted in the urine.
- Microalbuminuria is defined as persistent proteinuria below the detection limit of routine reagent strips but greater than normal.
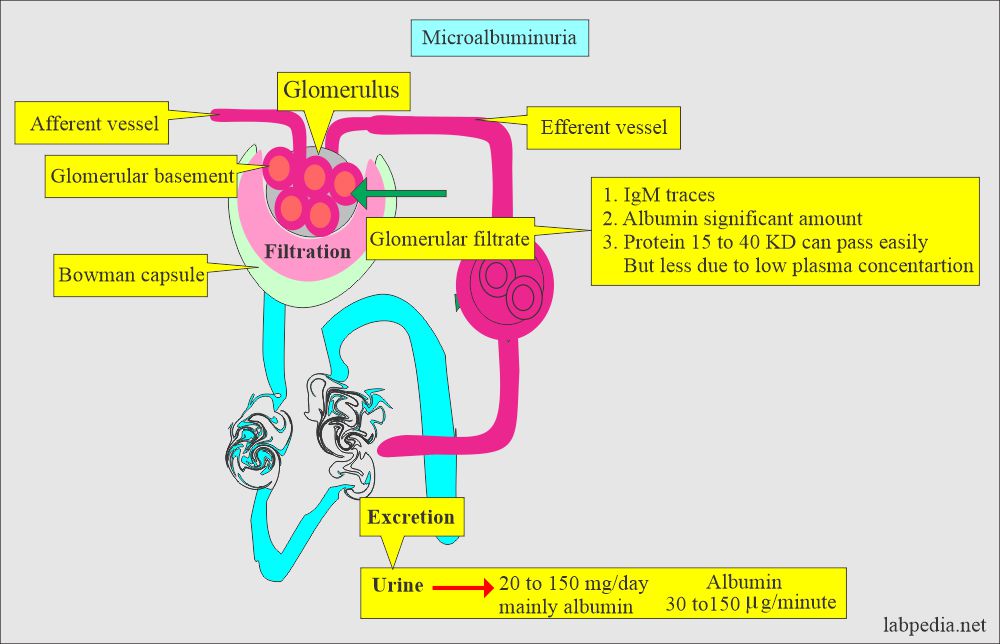
- This is defined as the excretion of 30 to 150 µg/min protein in the urine and is not detected by dipsticks but can be measured by sensitive methods.
- Microalbuminuria is predictive of diabetic nephropathy.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Diabetic microalbuminuria?
- Albumin excretion of 20 to 200 µg/minute (30 to 300 mg/24 hours) detected 2/3 determinations done in the last 6 months.
- Microalbuminuria may be found in non-diabetic hypertensive patients.
- The subclinical state of selectively elevated albumin excretion rate is called microalbuminuria.
- Normally, the glomeruli excrete a small amount, which the tubules reabsorb.
- When the disease increases, the albumin excreted by the glomeruli is more than reabsorbed by the tubule, leading to microalbuminuria, which is not detected by ordinary methods.
- There are structural changes in the glomeruli leading to increased glomerular permeability.
- Increased glomerular permeability increases urinary exertion of proteins like albumin and IgG.
- Albumin remains normal in the first 5 years of diabetes mellitus type 1.
- This urinary albumin excretion precedes and is highly indicative of diabetic nephropathy and is called microalbuminuria.
- Early detection of microalbumin may predict end-stage renal nephropathies in Diabetes type 1 (IDDM) patients.
- This test is useful for diagnosing Angiopathic changes in diabetic patients before gross proteinuria is seen.
- Evidence suggests that lowering blood pressure and controlling hyperglycemia will alter the disease’s course and prevent irreversible nephropathy.
What is the significance of the Microalbuminuria?
- It is the first sign of diabetes complications (Risk factor predictor):
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Hypertension.
- Stroke.
- Kidney failure.
- Death.
- Diabetic patients with microalbuminuria have 5 to 10 times more chances for cardiovascular mortality, retinopathy, and end-stage kidney.
- The presence of microalbuminuria in nondiabetic patients is an indicator of lower life expectancy because of hypertension and cardiovascular disease risk.
- Nondiabetic nephropathies may show microalbuminuria.
- Microalbuminuria indicates early stage and risk factors for cardiovascular or renal disease.
What are the recommendations for microalbuminuria in diabetic patients?
- Diabetic patients should have an annual checkup of microalbuminuria (3 to 6 months).
- if 2 out of 3 measurements are >20 mg/L, start the treatment (intervention).
What are the causes of Microalbuminuria?
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Myoglobinuria.
- Nephrotoxic drugs.
- Bence-Jones proteinuria.
- Hemoglobinuria.
- Any kind of Nephropathy.
- Hypertension.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Atherosclerosis ( Generalized vascular disease ).
- Lipid abnormalities.
- Pre-eclampsia.
What are the complications of microalbuminuria?
- It shows poor glycemic control.
- High blood pressure.
- Development of advanced retinopathy.
- Development of neuropathy.
- Advanced nephropathy.
- Ultimately, renal failure.
- Increased vascular damage.
- Risk for cardiovascular disease.
What is the interpretation of microalbuminuria?
| Albumin excretion in urine | Normal range of urine albumin | Clinical albuminuria | Microalbuminuria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Albumin/creatinine ratio >30 mg/g predicts an overnight excretion rate of 30 µg/minute.
- Albuminuria <0.3 g/day will be detected only by sensitive methods like nephelometry or electrophoresis.
What is normal Albumin in the urine?
Source 1
- Albumin in urine <30 mg/24 hours
- Or <20 mg/day.
- Or <20 mg/L (urine collected in 10 hours).
Source 2
- 0.2 to 1.9 mg/dL
Abnormal value
- Albumin >30 mg/24 hours.
- Or >20 mg/L (in 10 hours).
Limits with various dipsticks:
- Albusure 2 to 3 mg/dl
- Micral 1.5 to 2 mg/dl
- Micro-Burnintest 4 to 8 mg/dl
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is microalbuminuria?
Question 2: When to check microalbuminuria in diabetic patients?

Thanks for these wonderful information
Thanks.
if possible canput references
I have added one more reference. Mostly references are given in the end of each topic.