Metabolic syndrome and Prevention
Metabolic syndrome
What sample is needed for the Metabolic syndrome?
- The best sample for metabolic syndrome diagnosis is serum after 8 to 12 hours of fasting.
How would you define metabolic syndrome?
- This is also known as Syndrome X. Actually, this is insulin resistance syndrome. These individuals have various metabolic abnormalities and have more risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
- These people have increased risk and show accelerated atherosclerosis.
- Metabolic syndrome patients have at least 3 out of 5 conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes mellitus.
- It can cause other complications as well.
- Each condition is treatable with changes in lifestyle or medications.
- Other names of metabolic syndrome are:
- Metabolic syndrome X.
- Insulin-resistant syndrome.
- Dysmetabolic syndromee.
What is the incidence of metabolic syndrome in the USA?
- It is a pretty common problem in the USA.
- In the USA, about 1 out of 3 Americans have metabolic syndrome.
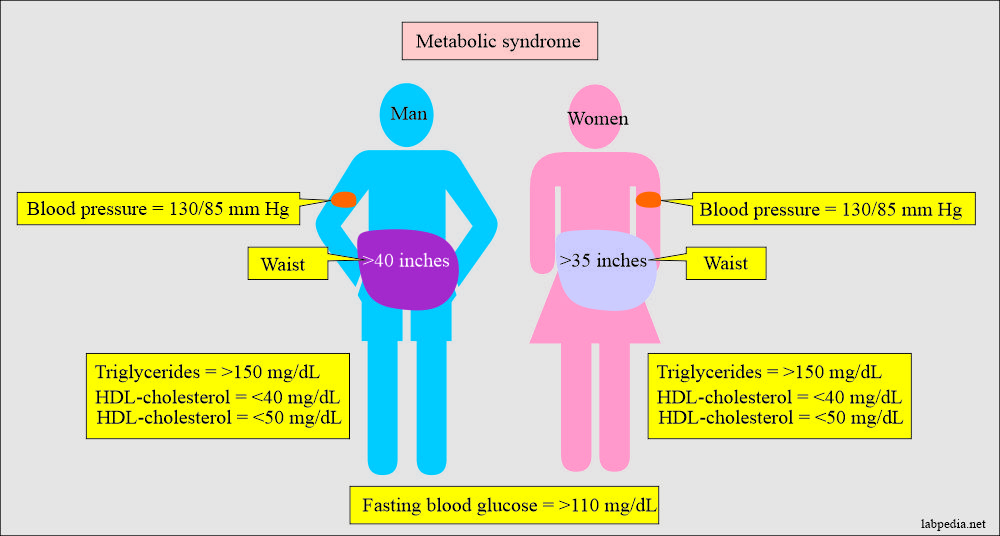
What are the criteria for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome?
- Three or more of the following parameters, when positive, indicate metabolic syndrome:
- Abdominal obesity. This is defined by having a waist circumference:
- In men = 40 inches (102 centimeters or cm) or more.
- In women = 35 inches (89 cm) or more.
- Waist circumference cutoff points can vary by race.
- BMI >25.
- Triglycerides >150 mg / dl.
- HDL-cholesterol <40 mg /dl for men and < 50 mg/dl for women. (This is called good Cholesterol).
- LDL- cholesterol >100 mg/dl (This is called bad cholesterol).
- Fasting glucose >110 mg/dl.
- Some studies suggest a High blood sugar level, with a fasting blood glucose test result of 100 mg/dL or more.
- If it is, 100 to 125 mg/dL is a prediabetic group.
- If it is >125 mg, this group is called diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertension when:
- Systolic blood pressure is 130 mm Hg or more.
- Diastolic blood pressure 85 mm Hg or more.
What is the presentation of the metabolic syndrome?
- Symptoms due to metabolic syndrome are variable depending upon the presence of the disease.
- High blood pressure, increased triglycerides, and high LDL do not show obvious symptoms.
- Hyperglycemia may cause symptoms in some of the patients.
- You may see acanthosis nigrans due to increased blood glucose levels.
- Increased thrust (Polydypsia).
- Polturia, especially at night.
- Blurred vision.
- Easy fatigability.
What is the mechanism of metabolic syndrome?
- There are several factors contributing to metabolic syndrome.
- Scientists mostly believe that insulin resistance is the main factor.
- It is believed that the muscles, fat, and liver do not respond to insulin, which they normally do.
- It may be due to pancreatic function, where insulin is needed to control blood glucose.
- The pancreas produces more insulin to do the job, which leads to hyperinsulinemia.
- Hyperinsulinemia (insulin resistance) and increased blood glucose levels lead to:
- Obesity.
- Fatty liver.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Insulin resistance may also be seen in:
- Excess weight around the belly.
- In the case of less physical activity.
- Some of the medications are corticosteroids and antihypertensive medication.
- Genetic transmission from the parents.
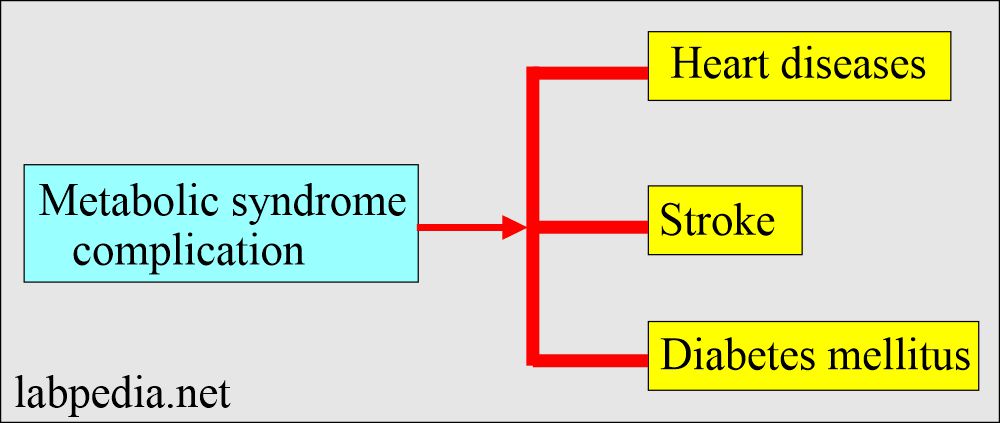
What are the complications of metabolic syndrome?
- There is an increased risk of:
- Heart disease:
- High cholesterol and high blood pressure can cause atherosclerosis, narrow the arteries’ lumen, and may lead to a heart attack.
- Stroke:
- This may also be due to atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes:
- It may develop If you don’t make lifestyle changes to control your insulin resistance, and your glucose levels will continue to increase. You may develop diabetes as a result of metabolic syndrome.
How will you diagnose the metabolic syndrome?
- Physical examination. They will check your blood pressure and the circumference of the waist.
- Lipid profile including triglycerides level.
- Comprehensive metabolic panel.
- Blood glucose level.
- If these 3 tests out of 5 are positive, then you are diagnosed as a patient with metabolic syndrome.
How would you prevent the metabolic syndrome?
Try to follow the advice:
- Aggressive lifestyle changes can delay or even prevent the development of severe health problems.
- Commit to a healthy diet.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Try to take white meat or fish.
- Avoid red meat.
- Avoid processed or deep-fried foods.
- Don’t use table salt.
- Fish is rich in omega-3, which protects against vascular diseases. It should be eaten three times a week.
- Low carbohydrates, even those high in saturated fats, may improve the cholesterol profile.
- Exercise: Make a habit of regular, moderately strenuous physical activity for at least 30 minutes.
- Regular check-ups like :
- Blood pressure.
- Cholesterol.
- Check Blood sugar levels regularly.
- Make other lifestyle changes if the test values are going the wrong way.
How would you treat the metabolic syndrome?
- Lose weight:
- If you lose 5% to 10% of your body weight, that can reduce the insulin levels needed by the body.
- By losing weight, blood pressure may also be controlled.
- Exercise:
- Daily exercise of 30 minutes or more is recommended. This may even be brisk walking every day.
- Stop smoking:
- Cigarette smoking leads to:
- Increases insulin resistance.
- Worsens the health consequences of metabolic syndrome.
- Cigarette smoking leads to:
- Food Changes:
- Food changes in the food style also help to prevent metabolic syndrome like :
- Eat more fiber-rich foods.
- Your food should include whole grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables.
- Mechanism of food: These food items are packed with dietary fiber, which can lower your insulin levels.
- Food changes in the food style also help to prevent metabolic syndrome like :
- Sleep:
- Try to get good sleep for at least 6 to 8 hours.
- Smoking:
- Quit or avoid smoking.
- Stress:
- Try to decrease the stress because stress increases the cortisol level in the body.
- Steroids increase blood glucose levels, lead to hypertension, and increase triglyceride levels.
- Yoga, breathing exercises, or physical exercise can manage stress.
- Medications:
- For blood glucose, anti-cholesterol drugs, and sleep disturbance.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What are the complications of metabolic syndrome??
Question 2: What is the main complication of metabolic syndrome?

[…] https://labpedia.net/metabolic-syndrome-and-prevention/ […]