Metabolic Panel and Significance
Metabolic Panel
What sample is needed for the Metabolic Panel?
- Fasting blood is the best sample.
- The patient needs fasting for 8 to 10 hours.
What are the indications for a Metabolic Panel (Comprehensive metabolic panel = CMP)?
- For routine health check-ups.
- To evaluate kidney function.
- To evaluate the liver function.
- Monitor the medication that may affect the liver or kidneys.
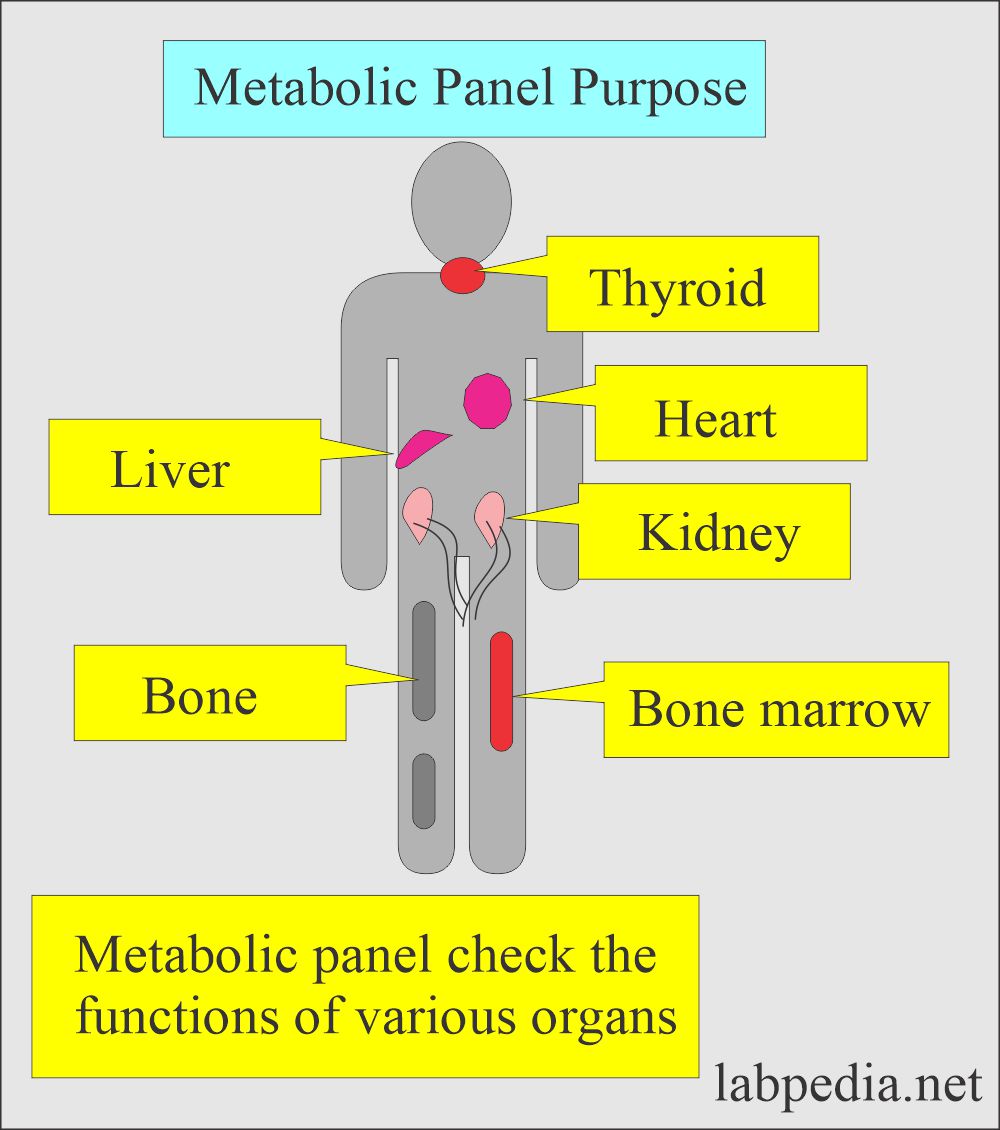
How does the metabolic panel evaluate the function of various organs?
Metabolic panel evaluates:
- Blood glucose level for diabetes mellitus.
- Serum electrolytes for hydration and acid/base balance.
- Kidney function tests.
- Liver function tests.
- Fluid electrolytes.
What are the tests included in the metabolic panel?
- Glucose
- Proteins:
- Total protein
- Albumin
- Liver function tests:
- Serum bilirubin
- SGPT ( alanine aminotransferase)
- SGOT (aspartate aminotransferase)
- ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
- Kidney function tests:
- BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
- Creatinine
- Electrolytes:
- Serum sodium
- Serum potassium
- Chloride
- Bicarbonate
- Serum calcium level
- Thyroid function tests.
- Lipid profile.
How would you summarize the comprehensive metabolic profile (CMP)?
- A comprehensive metabolic profile is called Chem14, a chemistry screen, or a metabolic panel.
The Comprehensive metabolic profile (CMP) includes:
- Glucose.
- Calcium.
- Sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, and chloride.
- Albumin.
- Total protein.
- Liver function tests (SGOT/SGPT, Alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin).
- Serum BUN and creatinine.
How will you define Metabolic syndrome (Metabolic syndrome X)?
- Metabolic syndrome is also called Syndrome X.
- Metabolic syndrome consists of the following:
- Insulin resistance.
- Hypertension.
- Abdominal obesity.
- Prothrombotic and proinflammatory conditions.
- Metabolic syndrome criteria:
- There is glucose intolerance with a fasting level of 110 to 125 mg/dL.
- Atherogenic stimulants are:
- Triglycerides = >150 mg/dL
- HDL-C = <40 mg/dL males and <50 mg/dL in females.
- Increased LDL.
- Abnormalities in fibrinolysis and coagulation.
- Exclusion of other causes of dyslipidemia like cholestasis, hypothyroidism, chronic renal failure, and nephrotic syndrome.
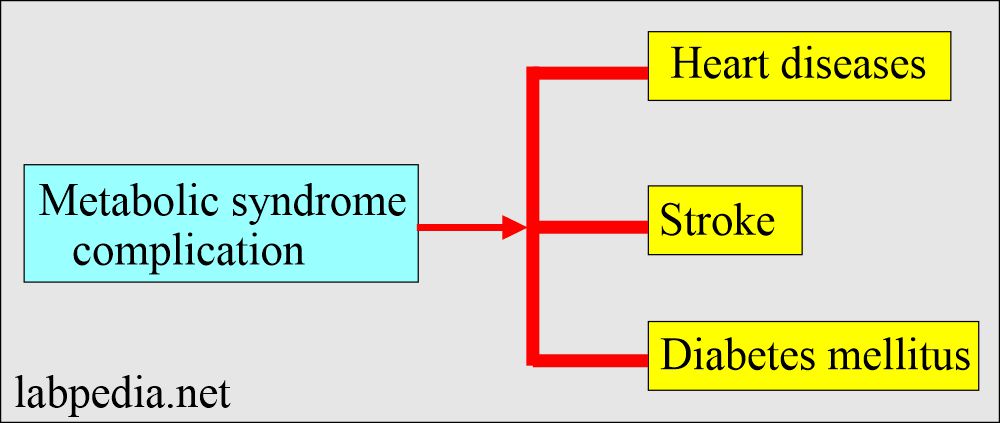
What are the complications of abnormal metabolic syndrome?
Metabolic syndrome complications are:
- Heart disease.
- Stroke.
- Diabetes mellitus.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the benefit of the metabolic panel?