Malarial parasite:- Part 5 – Plasmodium ovale, Benign Tertian Malaria
Plasmodium ovale
What sample is needed for Plasmodium ovale?
- Malarial parasites (MP) may be diagnosed with a fever from a patient’s blood smear.
- The best time to make a smear is during shivering.
- Make thick and thin blood smears.
- A serum is needed for a serological method and PCR.
What are the indications?
- For the diagnosis of the malarial parasite.
How will you define Plasmodium Ovale?
- Plasmodium ovale was described in 1922.
- Plasmodium ovale leads to benign tertian malaria and causes fever for 48 hours.
- It infects young RBCs, and these have fimbriated cytoplasm.
- Untreated cases may have relapses for up to 5 years.
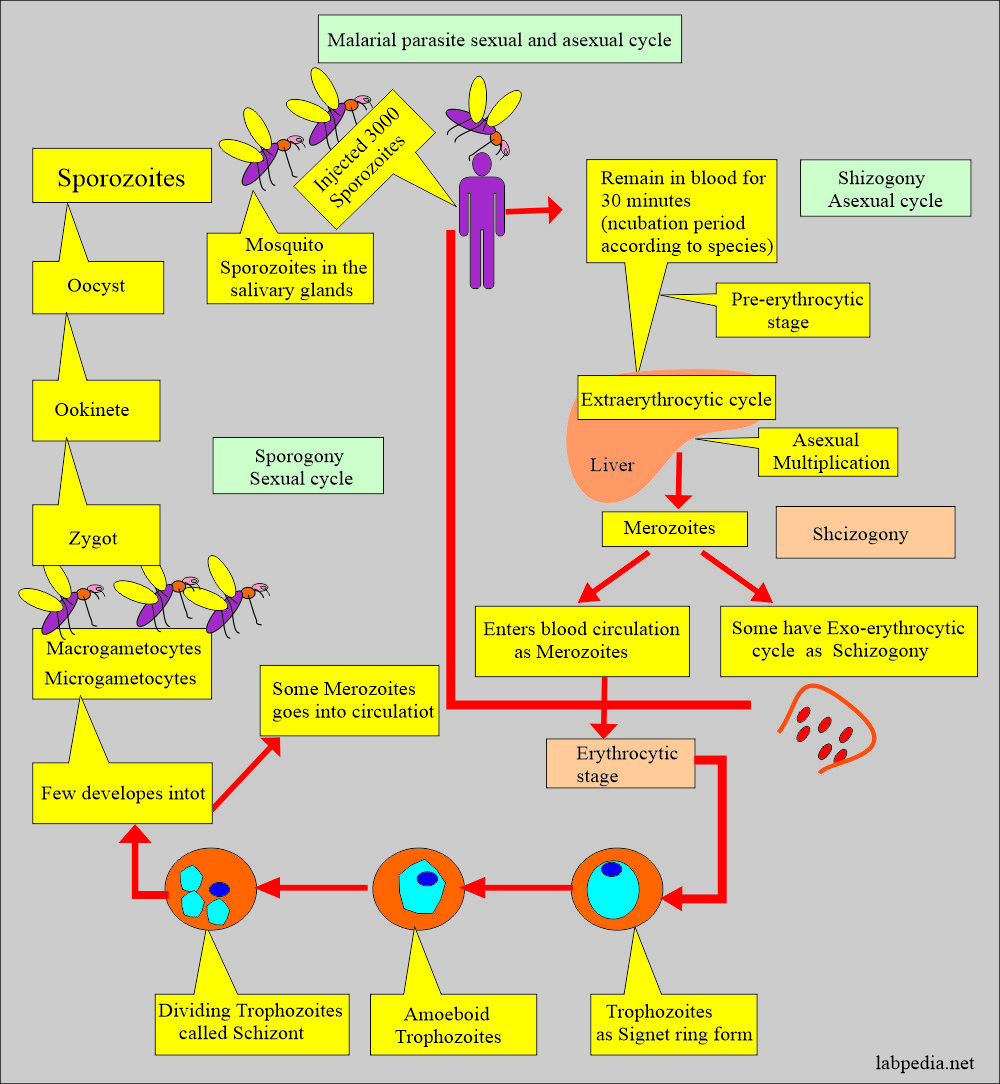
Discuss Plasmodium ovale life history?
- 8% of cases are in parts of Africa.
- Few cases in Asia.
- Plasmodium ovale represents only a small percentage of infections.
- Plasmodium ovale is dormant in the liver, which can become active without a mosquito bite.
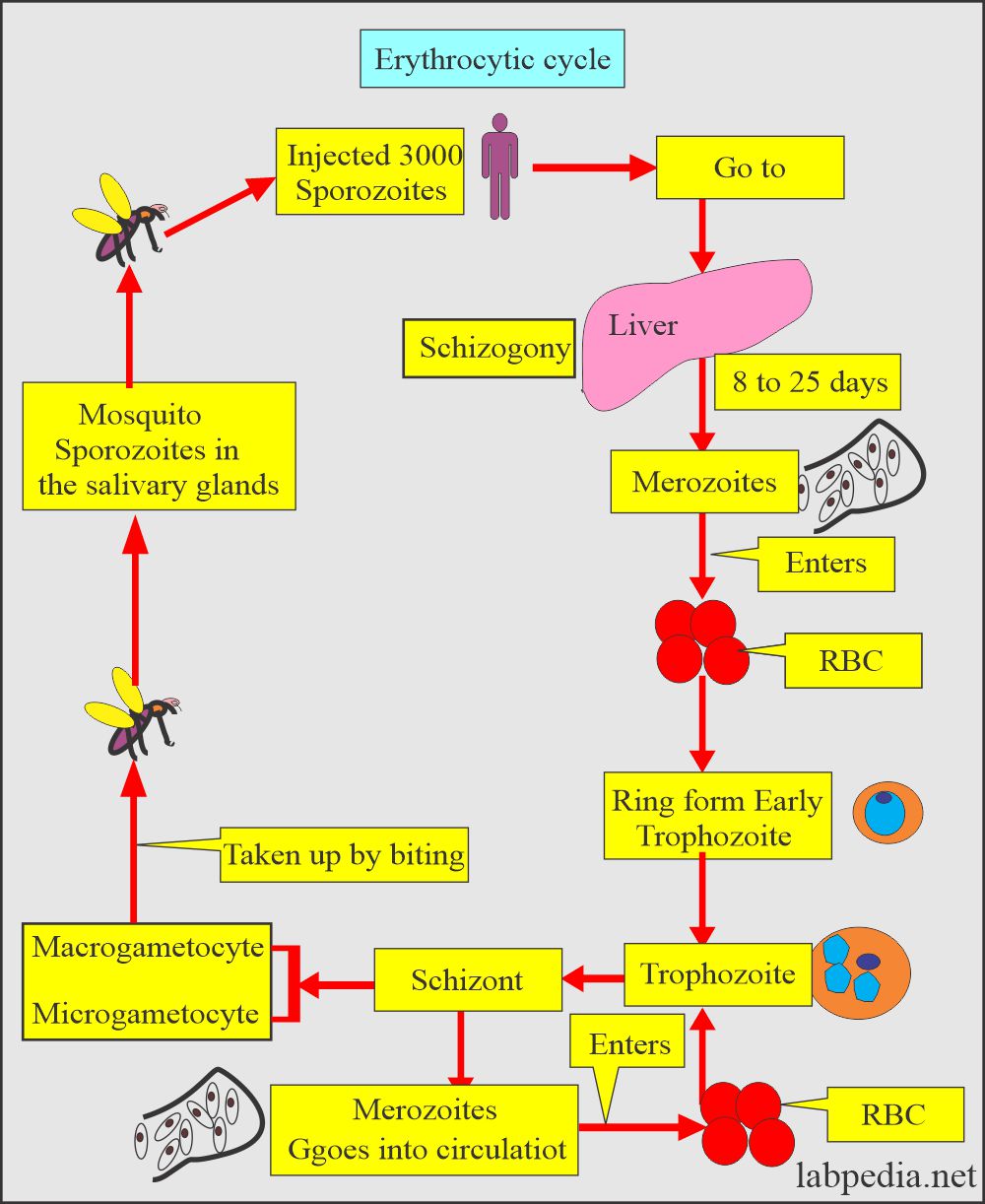
How will you describe the erythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium ovale?
- Ring form is like P. vivax.
- The difference is that there is a ring larger than the P. vivax.
- The ring is also thicker.
- Trophozoites maintain their ring form.
- The amoeboid tendency is common.
- Schizonts consist of dividing chromatin surrounded by the cytoplasm.
- There are Rossetts of merozoites, 8 on average.
- 3/4 of the cell is occupied by the parasite.
How will you discuss the clinical presentation of Plasmodium ovale?
- Initial symptoms are flu-like.
- The typical paroxysm is every 48 hours.
- Relapse may take place, and there is spontaneous recovery.
- The above feature is not seen in the P. vivax.
How will you diagnose Plasmodium ovale?
- History of the patient in suspected areas.
- Blood smear:
- Make a blood smear when the patient has a fever. Thin and Thick smears are made.
- A thick smear is more helpful in finding M.Parasites.
- A thin smear is good for identifying the type of malarial parasite.
- Collect blood 6 to 8 hourly till 48 hours to declare negative for malaria.
- Giemsa stain is the best choice.
- Serologic methods are based on immunochromatic techniques. Tests often use a dipstick or cassette format and provide results in 2-15 minutes.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): Parasite nucleic acids are detected using the PCR technique.
- This is more sensitive than smear microscopy.
- This is of limited value for diagnosing acutely ill patients because of the time needed for this procedure.
How will you control Mosquitoes?
- Try to eliminate breeding places:
- Fill the vacant land and pump out the water.
- Remove the junk and water-retaining debris.
- Destroy the larvae:
- Clean the drains.
- Try to remove algae from the ponds.
- Add larva-eating fish to the ponds.
- Use of the insecticide:
- The best example is DDT.
- Use of mosquito repellent:
- Pyrethroid repellent.
- N, N- diethyl meta tolbutamide.
- Use of mosquito nets.
- Use clothes to prevent mosquito bites.
- Train people for malaria prevalence.
- Train the people for the detection of malaria, treatment, and follow-up.
How will you treat Plasmodium ovale?
- Antimalarial drugs are quinidine, chloroquine, primaquine, pyrimethamine, sulfadoxine, mefloquine, tetracyclines, and proguanil.
- Chloroquine is the drug of choice and is best for P. falciparum.
- This is effective for the erythrocytic stage and not for the liver stage.
- Must use primaquine to eradicate P. ovale and P. vivax.
- there are chloroquine resistant cases of P. falciparum.
- Amodiaquin, piperaquin and pyronaridine are close to chloroquin.
- In some areas, Amodiaquine is less toxic, cheap, and effective against chloroquine-resistant P. falciparum.
- Mefloquine is effective against choloquin resistant P. falciparum.
- Quinine and quinidine are still the first lines of therapy against P. falciparum.
- Primaquine is a synthetic drug and is the drug of choice for eradicating the liver stage from P. vivax and P. ovale.
- Antibiotics and Inhibitors of folate synthesis are slow-acting antimalarial drugs.
- Halofantrine and lumefantrine are related to quinine and are effective against the erythrocytic stage.
- Malaria drug-resistant strains are emerging.
What is the duration of the various cycles in malarial parasites?
| Type of malarial parasite | Sexual cycle in the mosquito | Length of asexual cycle | Length of the sexual cycle |
| Plasmodium falciparumm | 9 to 10 days | 5 to 7 days | 36 to 48 hours |
| Plasmodium vivax | 8 to 9 days | 8 days | 48 hours |
| Plasmodium ovale | 14 days | 9 days | 48 hours |
| Plasmodium malariae | 15 to 20 days | 15 to 16 days | 72 hours |
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Which smear thick or thin you will prefer?
Question 2: From where merozoites go into blood?