Liver histology
Histology
There are three compartments:
-
Portal tract.
-
Central vein.
-
Intervening parenchyma or lobule.
The liver is an exocrine organ and it has metabolic functions.
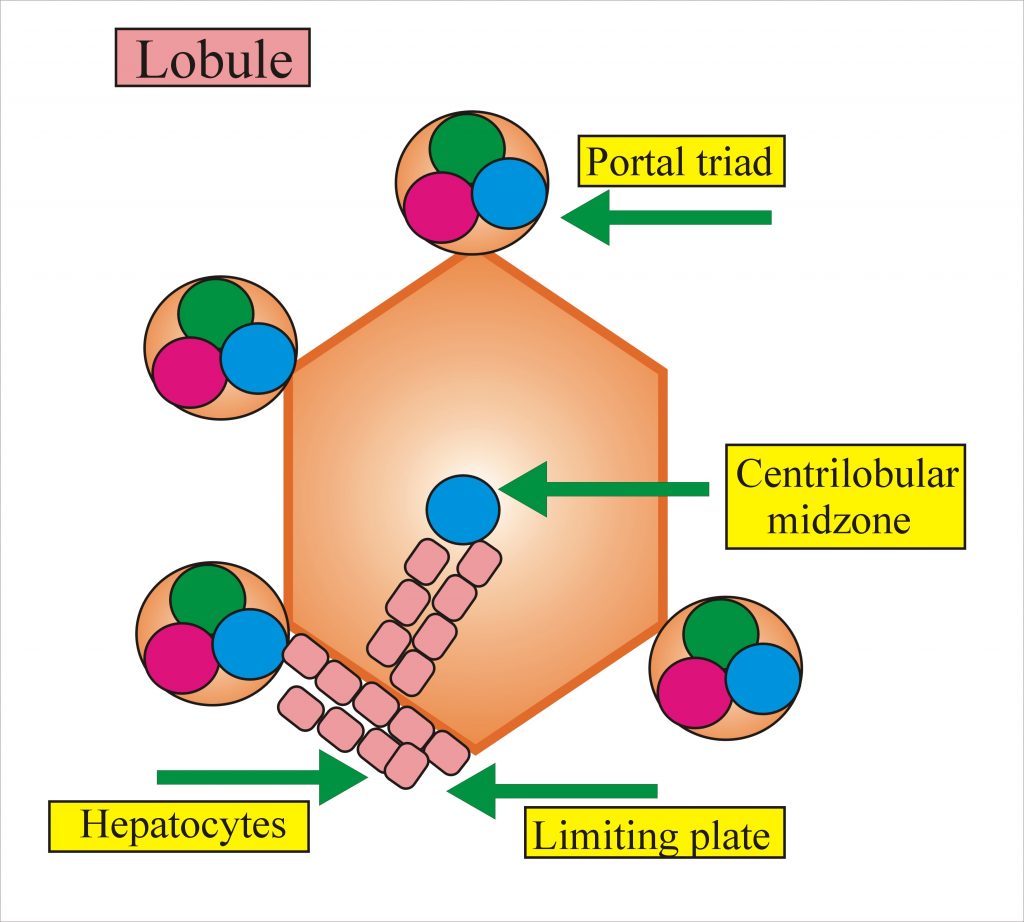
Kiernan in 1833 introduces the concept of lobule which measures 0.5 to 2 mm in diameter with 4 to 5 portal spaces.
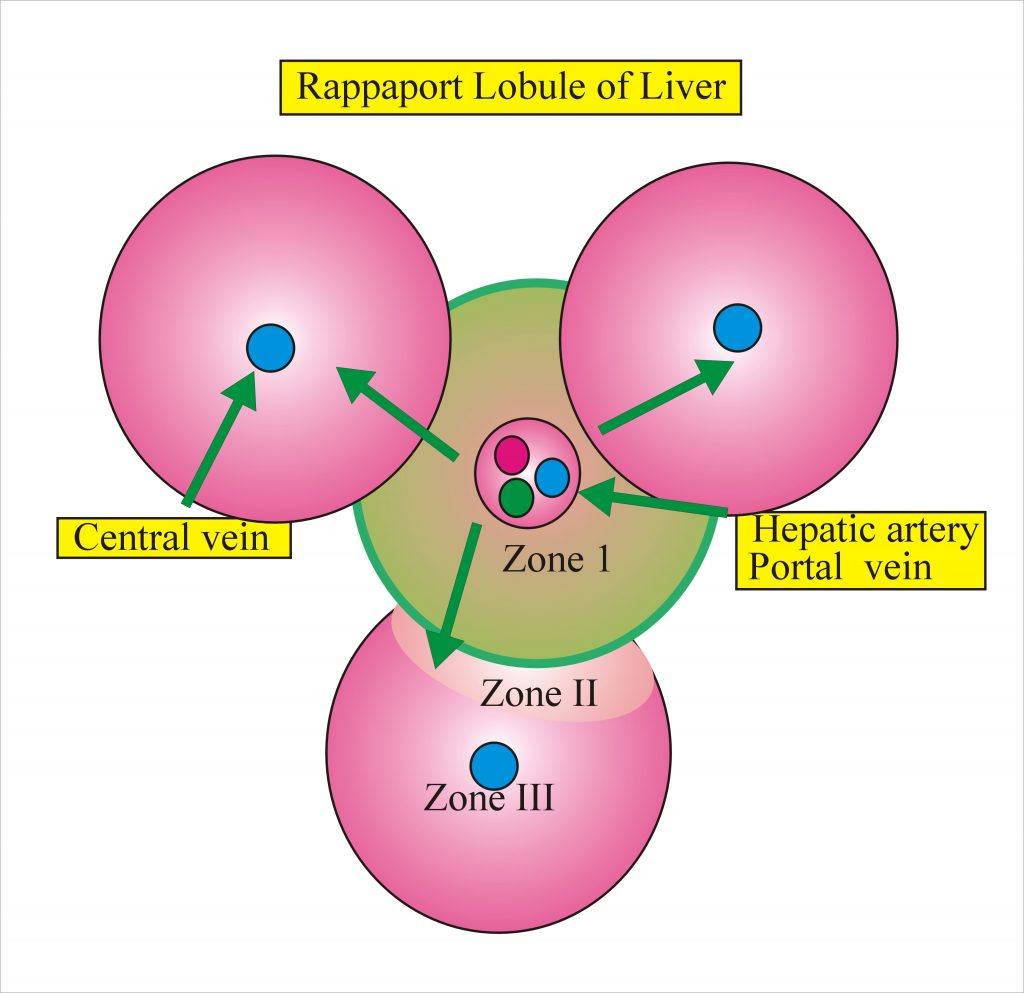
Rapaport et al in 1945 introduced the concept of the functional unit which is called acinus or metabolic lobule. This concept depends on oxygen supply and nutrients.
Zone I: This zone has the best blood supply and prone to most toxic injuries. if an injury occurs in this zone, well be the first to regenerates. In this zone glycogen synthesis, glycogenolysis, protein, and formation of plasma protein take place.
Zone II: in this zone, there is reasonable blood supply, it shares function with zone I and zone III
Zone III: This zone has the poorest blood supply and prone to more hypoxic injury. In this zone, there is glycogen storage, lipid, pigment formation and metabolism of drugs and chemicals.
In the liver 80 % are hepatocytes. In 70 kg man, there are roughly 250 billion hepatocytes.
Zone I is around the hepatic artery and portal vein while zone III is around the central vein where there is poor blood supply.
Limiting plate is the hepatocytes which line up the portal Triad.
Histology
Fawcett in 1955 described that 60 % of the liver cells are polygonal 20 to 30 um in diameter. Lifespan in ( experimental animals ) is 150 days. If 80 to 90 % of the liver is resected rest of the liver regenerates to full size.
Each hepatocyte is six-sided structure, in between, there is a sinusoid lined by endothelial cells. In between there are cells derived from monocytes, they can clear micro-organism and cancer cells.
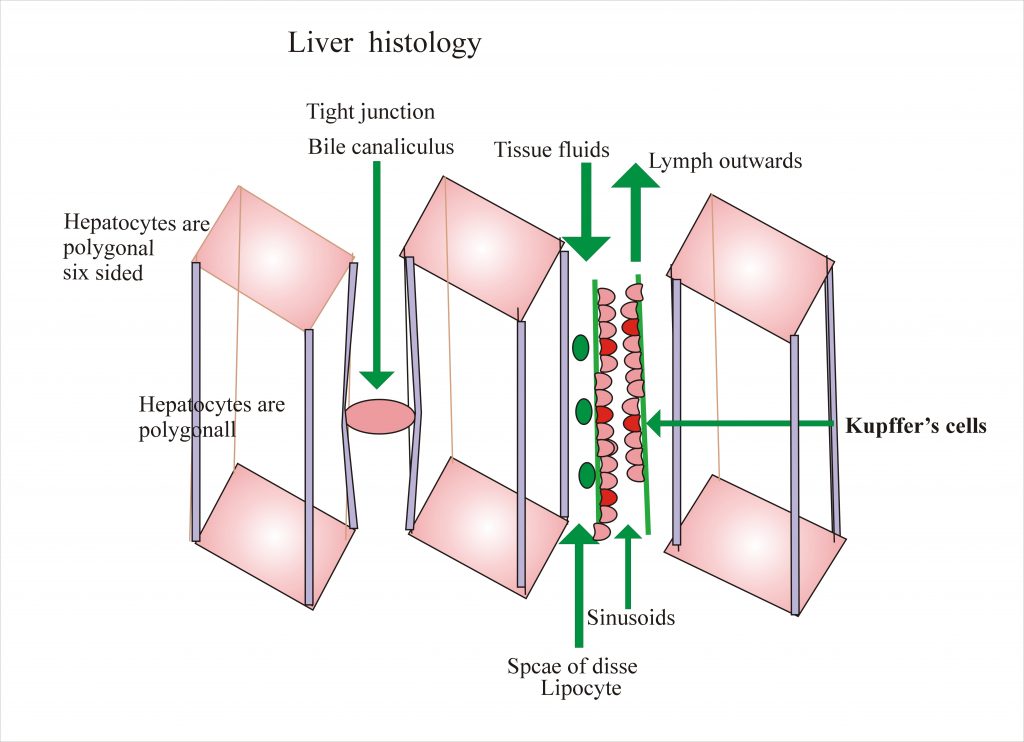
The bile duct is between the wall of two adjacent hepatocytes. This is basically a groove which continues with other grooves. In between the hepatocytes and sinusoid, there is a space called space of Disse. this is 300 to 400 nm wide. In this space, there is tissue fluid and lymph flows outwards. In this space, there are lipocytes these are called Ito cells. These lipocytes store fat and vitamin A.
In between the hepatocytes and sinusoid, there is a space called space of Disse. this is 300 to 400 nm wide. In this space, there is tissue fluid and lymph flows outwards. In this space, there are lipocytes these are called Ito cells. These lipocytes store fat and vitamin A.
Mitochondria
This is an energy providing unit through the citric acid cycle. In this unit oxidative phosphorylation, beta-oxidation of fatty acid and heme synthesis takes place.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
There is a synthesis of albumin, triglyceride, lipoprotein, G-6-PD, Glycogenosis, specific protein for blood coagulation and enzymes take place.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
There is bilirubin conjugation, detoxification, synthesis of steroids and Cholesterol and bile acid place. The synthesis ability is increased by phenobarbitone.There is an accumulation of glycogen and metabolism of drugs.
Golgi Apparatus
It is the packing site for lipoprotein and glycoproteins. It is filled with LDL.
Lysosome
It contains various hydrolytic enzymes. It stores ferritin, lipofuscin, and bile pigments, and copper. Because of the presence of enzymes, there is disposition and catabolism of endogenous and exogenous substances.
Kupffer’s cell
These cells belong to the reticuloendothelial system. The Kupffer’s cells are the largest cells of the mononuclear phagocytic system.They can endocytose bacteria, endotoxins, effete cells and has a role in iron metabolism. These cells have a receptor for Fc portion of IgG, C3b, receptor for insulin and glycogen.
Endothelial Cell
These cells have Fc receptor. Determine the exchange of fluid and particulates from space of Disse and hepatocytes.
Lipocytes
Lipocytes are also called as Ito cells and they store vitamin A and other fat-soluble vitamins. Lipocytes takes an active role in fibrogenesis and may lead to cirrhosis.
Fibers
These are lying in the space of Disse. These may play an active role in portal hypertension.
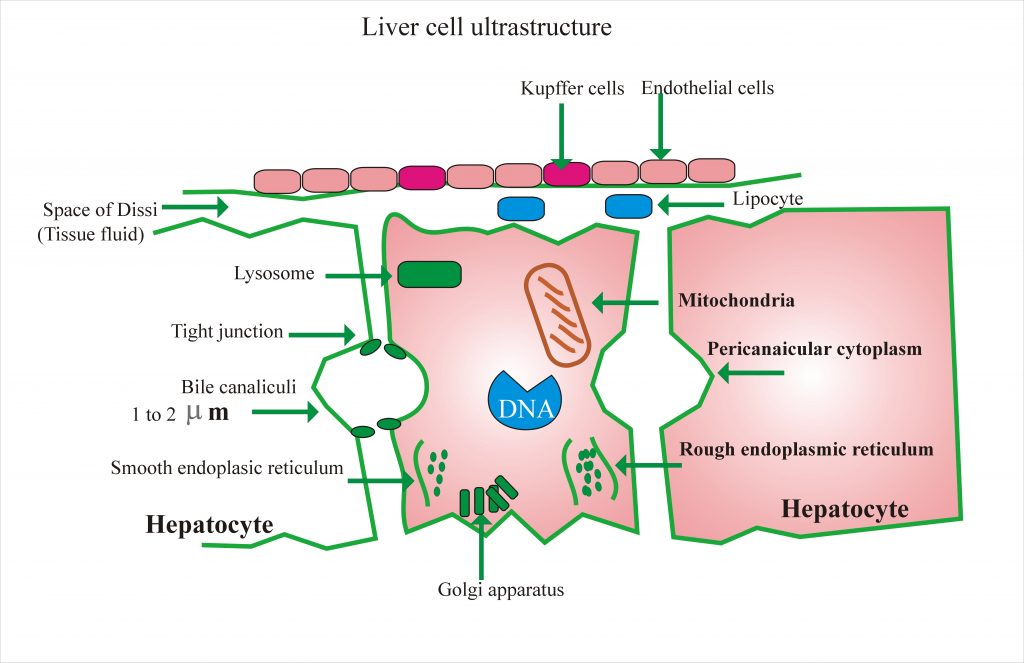
This ultrastructure of the liver cell can be elaborated better by the following diagram.
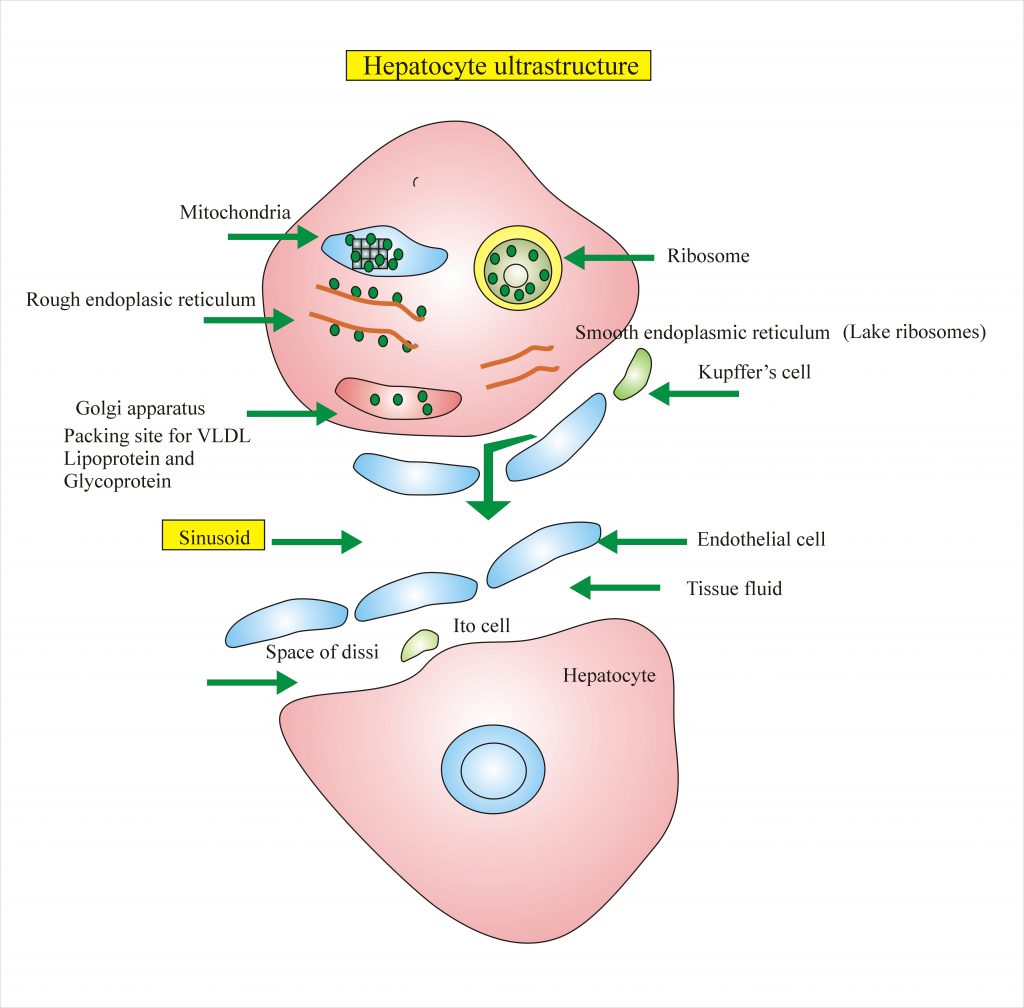
Plasma membrane and the membrane Traffic
The plasma membrane is rich in the receptors. This is the specific site for hormones and metabolites. Most molecules enter hepatocytes through these receptors.
Function Of The Liver
- Intermediary metabolism of protein, lipids, and carbohydrates
- Storage of some food stuff and minerals.
- Production of bile helps emulsification and absorption of dietary fats.
- Purification of blood vessels and toxic substances
- Converts substances to most active form eg T4 to T3.
