Liver:- Part 2 – Liver function tests and Jaundice Classification
Liver Function Tests
What sample is needed for Liver Function Tests?
- The venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
What tests are recommended to evaluate liver functions?
- Total Bilirubin.
- Direct bilirubin.
- Indirect bilirubin.
- SGPT.
- SGOT.
- Alkaline phosphatase.
- Gamma-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT).
- Total protein.
- Albumin
- A / G ratio.
- Prothrombin time (PT).
- Ultrasound of the abdomen to evaluate the liver or any other mass in the abdomen.
- Viral markers.
What are the normal values of liver function tests?
| Test | Normal value |
| Total bilirubin | o.3 to 1.0 mg/dL |
| Conjugated bilirubin | 0.1 to 0.3 mg/dL |
| Unconjugated bilirubin | 0.1 to 0.8 mg/dL |
| Newborn total bilirubin | 1.0 to 12.0 mg/dL. |
| Alkaline phosphatase |
Adult = 30 to 120 units/L Child <2 years = 85 to 235 units/L 2 to 8 years = 65 to 210 units/L 9 to 15 years = 60 to 300 units/L 16 to 21 years = 30 to 200 units/L |
| SGOT (AST) |
Adult = 0 to 35 units Elderly = values slightly higher than adult Newborn and infants = 15 to 60 units/L |
| SGPT (ALT) |
Adult and child = 4 to 40 units/L Infants may be twice high as the adult value |
| Albumin |
Adult = 3.5 to 5 g/dL Premature infants = 3 to 4.2 g/dL Newborn = 3.5 to 5.5 g/dL Infant = 4.4 to 5.4 g/dL Child = 4 to 5.9 g/dL |
| Total protein | 6.4 to 8.3 g/dL |
| A/G ratio | 0.8 to 2.0 |
| Gamma-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT). |
>45 years = 8 to 38 units/L Female <45 years = 5 to 27 units/L Childlike adult level Newborn = 5 times higher than the adult level |
| Prothrombin time (PT) |
11 to 12.5 seconds Anticoagulant therapy = 1.5 to 2 times control |
| Ultrasound | No organomegaly |
| Viral markers | Negative |
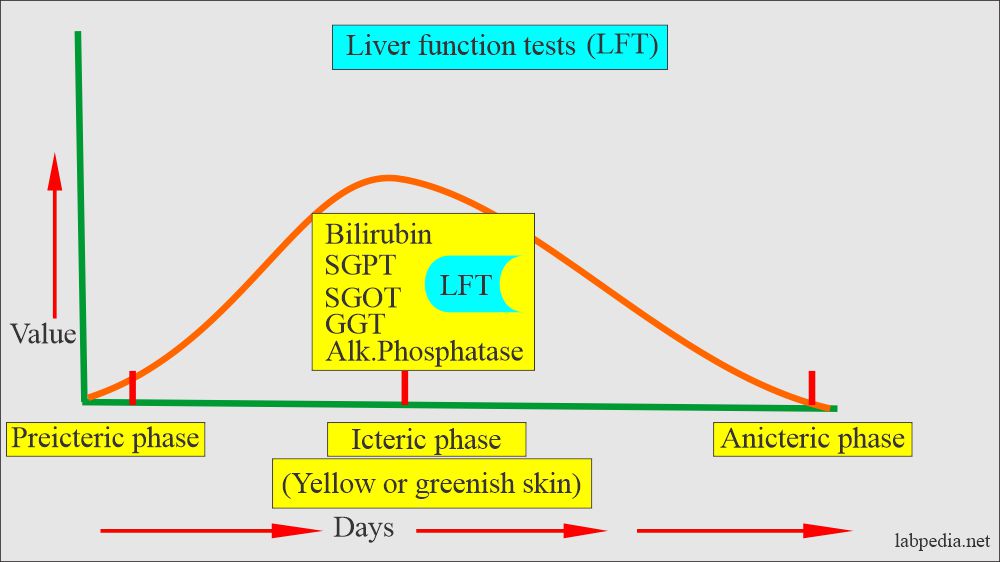
What are the phases of jaundice?
- Preicteric phase.
- Icteric phase.
- Nonicteric phase.
Preicteric phase:
- In this phase, urine, bilirubin is usually positive 1 to 6 days before the onset of clinical jaundice.
- Urinary urobilinogen is usually increased.
- The BSP test is usually the first test to become positive in this phase.
- Thymol flocculation, turbidity tests, and cephalin flocculation tests are positive in the late phase of jaundice.
Icteric phase:
- Direct bilirubin is increased.
- Urinary urobilinogen is increased, and bile is present in the urine.
- Alkaline phosphatase may or may not be elevated.
- The thymol turbidity and flocculation tests and cephalin-flocculation tests were positive.
- The Bromsulphalein test is not helpful.
Nonicteric phase:
- Urinary urobilinogen is increased.
- Thymol-flocculation and turbidity and cephalin flocculation tests are usually positive.
- The Albumin-globulin ratio shows high globulin and low serum albumin.
- Alkaline phosphatase and cholesterol ester may or may not be helpful.
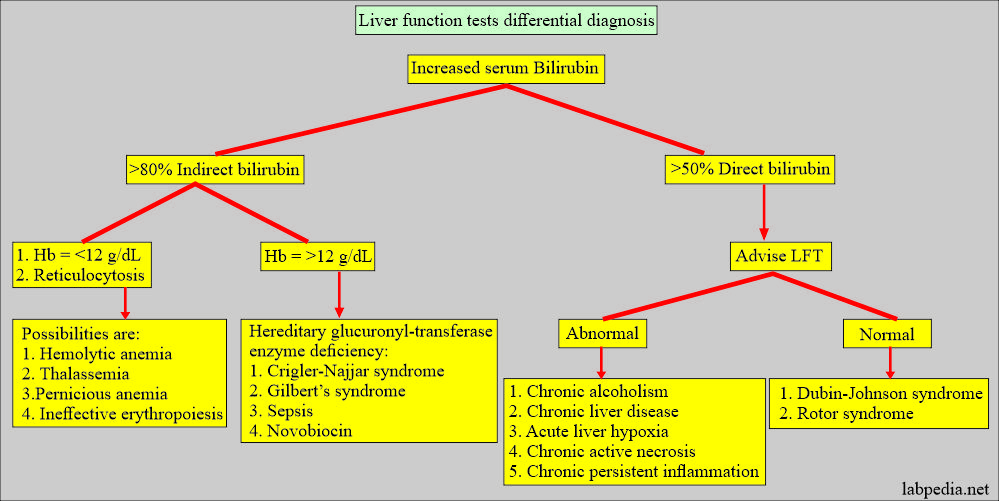
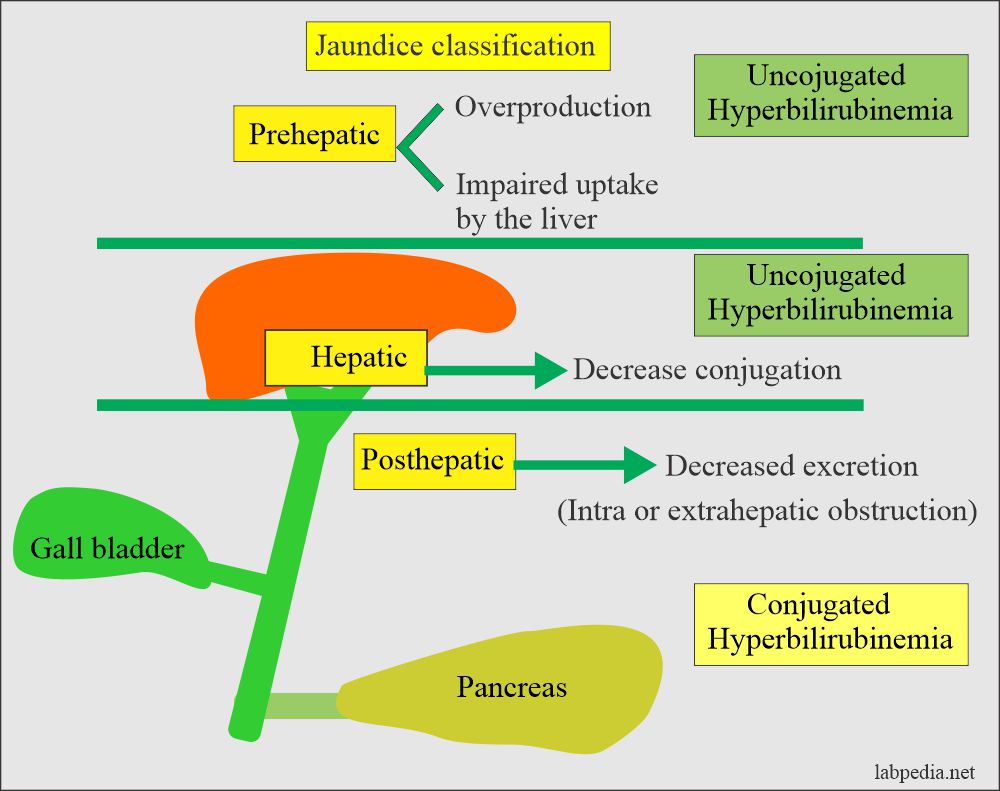
How will you classify jaundice?
- The major causes of jaundice are:
- Pre-hepatic jaundice where there is hemolysis.
- Hepatic jaundice is where intrahepatic biliary tract obstruction occurs.
- Post-hepatic jaundice is when extrahepatic biliary tract obstruction occurs.
- Please see more details in the LFT part.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the value of GGT?
Question 2: Which bilirubin will raise in obstructive jaundice?

I am very thankful to you for sharing this type of informatic site for us thank you so much sir
Thanks.
An asymptomatic 24 yr male, no comorbidities on LFT has mildly raised serum bilorubin as well as mildly raised direct bilirubin, with rest all enzymes normal. HOW DO I INTERPRET THIS OR WHAT FURTHER INVESTIGATIONS DO I ASK HIM TO DO?
This is one of the congenital jaundices. Please see this topic and this may solve your problem.
https://labpedia.net/gilberts-syndrome-signs-symptoms-and-diagnosis/