Lactase Enzyme Deficiency, Lactose Intolerance
Lactase Enzyme Deficiency
What samples are needed to detect Lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Most tests available to diagnose lactase enzyme deficiency are done on stool.
- The blood sample is needed to estimate blood glucose levels.
- Small intestinal biospy.
- Breath test.
How will you define lactase enzyme deficiency?
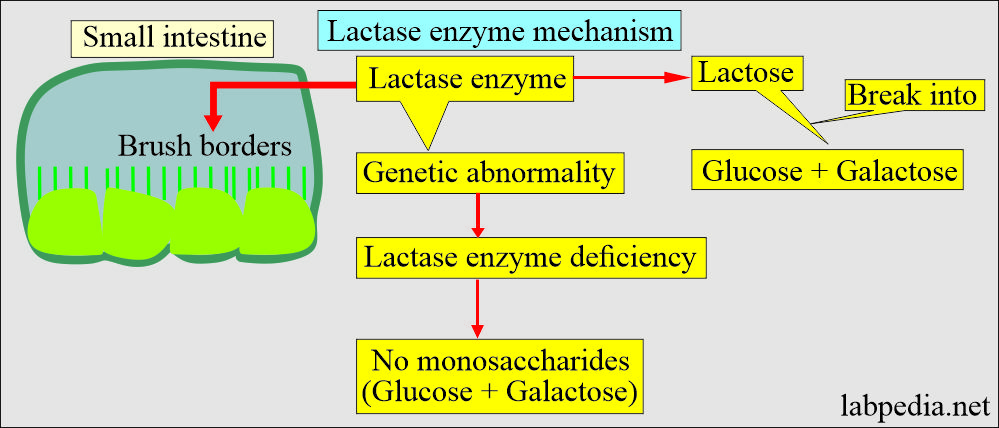
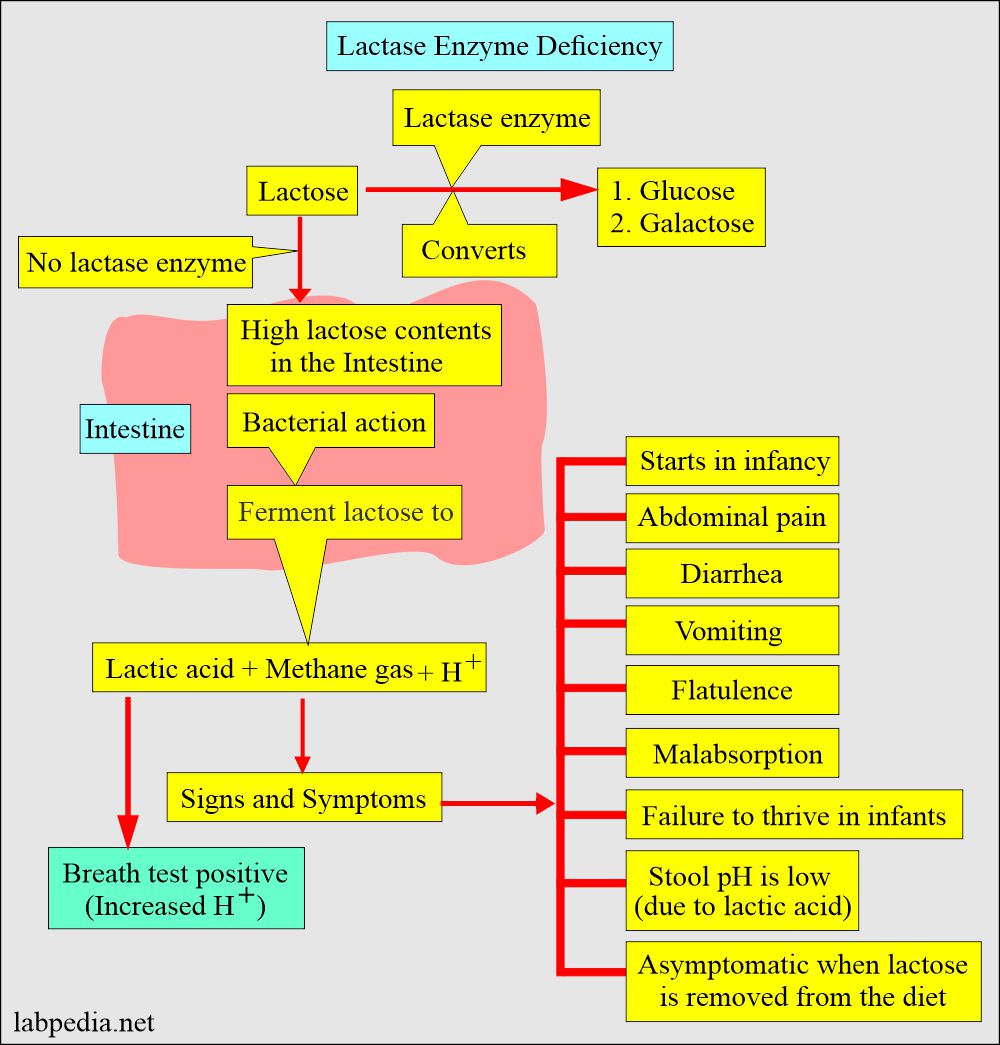
- Lactose is a disaccharide and is mainly found in dairy products. Lactose needs a lactase enzyme for its digestion. Lactose intolerance develops when the lactase enzyme is deficient; lactose will not break into glucose and galactose.
- Lactose intolerance starts in infancy, with S/S of diarrhea, vomiting, and failure to thrive.
- The patient becomes asymptomatic when lactose is removed from the diet.
What is the epidemiology of Lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Northern Europeans have normal lactase enzymes, and only 10% to 15% develop lactase enzyme deficiency (Lactose intolerance).
- The highest incidence is seen in the Asian population like Chines and Japan.
- Native American >90% show lactase enzyme deficiency (Lactose intolerance).
- Jews, African Americans, South Americans, and Eastern Europeans have a lesser deficiency, but still, it is seen in 60% to 70%.
How will you discuss the Pathophysiology of lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Lactose is a disaccharide and is mainly found in dairy products. Lactose needs a lactase enzyme for its digestion. Lactose intolerance develops when the lactase enzyme is deficient; lactose will not break into glucose and galactose.
- Lactose is a disaccharide and is mainly found in dairy products.
- Lactose needs a lactase enzyme for digestion. When the lactase enzyme is deficient, lactose will not break into glucose and galactose, causing lactose intolerance.
- Lactose intolerance starts in infancy, with diarrhea and vomiting. There is failure to thrive.
- The patient becomes asymptomatic when lactose is removed from the diet.
What is the mechanism of lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Lactose sugar is present in:
- Milk and milk products.
- Ice cream.
- Yogurt.
- Many types of cheese.
- In case of a lactase enzyme deficiency, lactose can not break into glucose and galactose.
- The brush borders of the small intestine have the enzyme lactase.
- When there is a genetic abnormality of lactase enzyme deficiency, milk sugar can not break into monosaccharides.
What are the types of Lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Primary, Congenital:
- It is the genetic deficiency of the lactase enzyme.
- Lactase enzymes appear between 26 to 34 weeks of gestation has 1/3 activity compared to full-term babies.
- At 35 to 38 weeks of gestation is around 70%.
- Full activity is seen at the 40th week of gestation.
- This deficiency appears at the age of 3 to 5 years.
- This appears in the newborn.
- Lactase enzymes appear between 26 to 34 weeks of gestation has 1/3 activity compared to full-term babies.
| Gestational age (Fetal age) | Lactase enzyme appearance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
- These babies will present with vomiting, diarrhea, malabsorption, and failure to thrive.
- This may be seen in premature babies.
- Secondary (acquired):
- The lactase enzyme deficiency is due to:
- Gluten sensitivity enteropathy.
- Enteritis.
- Bacterial growth in the intestine.
- Inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s disease.
- Giardia lambelia infestation.
- Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas.
- Other causes of lactase enzyme deficiency:
- There is some degree of lactase enzyme deficiency in adults, but severe deficiency occurs due to the following:
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Short-gut syndrome.
- Malabsorption syndrome.
- Severe acute gastroenteritis.
- Prolonged protein-calorie malnutrition.
- Certain antibiotics like neomycin and kanamycin.
- The small bowel is loaded with lactose when lactose is in the intestine.
- Intestinal bacteria lead to its fermentation and give rise to:
- Gas formation.
- The osmotic gradient leads to osmotic diarrhea.
What are the clinical features of Lactase enzyme deficiency?
- There is abdominal floating.
- Abdominal cramping.
- There is flatus.
- Diarrhea.
- There is bloating.
- These symptoms are worse after the meal.
- Lactase deficiency in full-term babies or young children is rare.
- These patients do not thrive.
What are the normal values of Lactase enzyme deficiency?
- Normal = Glocuse change from the normal value = >30 mg/dL (>1.7 mmol/L).
- Inconclusive = 20 to 30 mg/dL
- Abnormal = <20 mg/dL (<1.1 mmpl/L) (positive for lactase enzyme deficiency).
- Breath test (H+) = <10 ppm increase from the baseline is abnormal.
How will you diagnose Lactase enzyme deficiency?
Screening tests for lactase deficiency are:
- Stool for pH.
- Normal stool pH is 7.0 to 8.0
- A stool below a pH of 6.0 suggests lactase deficiency.
- Stool sugar at a time when the patient is symptomatic.
- Check for the reducing sugars or glucose by oxidase method.
- The presence of glucose in the stool suggests lactase enzyme deficiency.
Lactose tolerance test principle:
- The principle is like the glucose tolerance test.
- The patient is provided with lactose overload.
- Serum glucose levels are estimated by fasting (before lactose administration) and after administration at 15, 30, 60, and 90 minutes.
- Normal lactase enzyme activity results in postdose glucose elevation of >20 mg/dL (1.1 mmol/L).
- Lactose will not break into glucose and galactose in the lactase enzyme deficiency; plasma glucose levels will not increase in the blood.
- This test is a GTT (glucose tolerance test) to detect intestinal disaccharidase (lactase) enzyme deficiency.
- Glucose fasting level is compared with other glucose levels to increase or decrease.
- What are the precautions for a lactose tolerance test?
- Avoid strenuous exercise.
- Smoking can increase blood glucose levels.
- Don’t allow smoking during the test and 8 hours before the test.
- Enterogenous steatorrhea. Patients with diabetes mellitus may have increased 20 mg/dL despite the lactase enzyme deficiency.
- The patient must fast 8 to 12 hours before the test.
- The patient should not eat dark bread, beans, sugars, or high-fiber food within 24 hours of the test.
- Don’t allow gum chewing.
- Don’t allow antibiotic therapy 2 weeks before the test.
- Procedure for lactose tolerance test:
- After an overnight fast.
- Give 50 grams of lactose mixed with 200 mL of water. (1 to 2 grams lactose/kg of body weight).
- You can give this with flavored fluid or soft drinks.
- Draw the blood sample at 0 (fasting), 30, 60, and 90 minutes intervals. (Some labs check fasting glucose at 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes).
- Some labs check galactose instead of glucose levels.
- Interpretations:
- There is flat lactose tolerance, meaning no glucose level rises.
- At normal lactase enzyme level, glucose elevation is >20 mg/dL (1.1 mmol/L) over baseline.
- Lactose in the urine produces a positive test for reducing sugars but is negative by the glucose oxidase method.
- Take a single blood sample 40 minutes after the test and check the galactose level.
Hydrogen breath test:
- It is considered the most accurate of the tolerance tests.
- It is based on the expiratory hydrogen in the breath.
- Oral Lactose is given to the patient, and the hydrogen in the breath is retested at 30, 60, and 2 to 4 hour intervals.
- Lactose deficiency results in the deposition of excess lactose in the colon, where bacterial fermentation produces excess hydrogen, which is excreted through the lungs in a breath.
Small intestinal biopsy:
- It can be done by endoscopy to evaluate the contents of lactose enzyme in the tissue.
- Tissue biopsy has added advantages to differentiate the sprue.
Summarise the diagnostic tests for lactase enzyme deficiency are?
- Lactose intolerance test.
- Hydrogen breath test.
- Small intestinal biopsy with tissue assay of lactase enzyme.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: Which test is more accurate for lactase enzyme deficiency?
Question 2: What is the advantage of small intestinal biopsy for the diagnosis of lactase enzyme deficiency?