Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)
Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)
What sample is needed for Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)?
- The serum the patient needed.
- This test can also be done on the plasma.
- The sample is stable for 4 hours at room temp.
- By refrigerating, the sample is stable for 3 days.
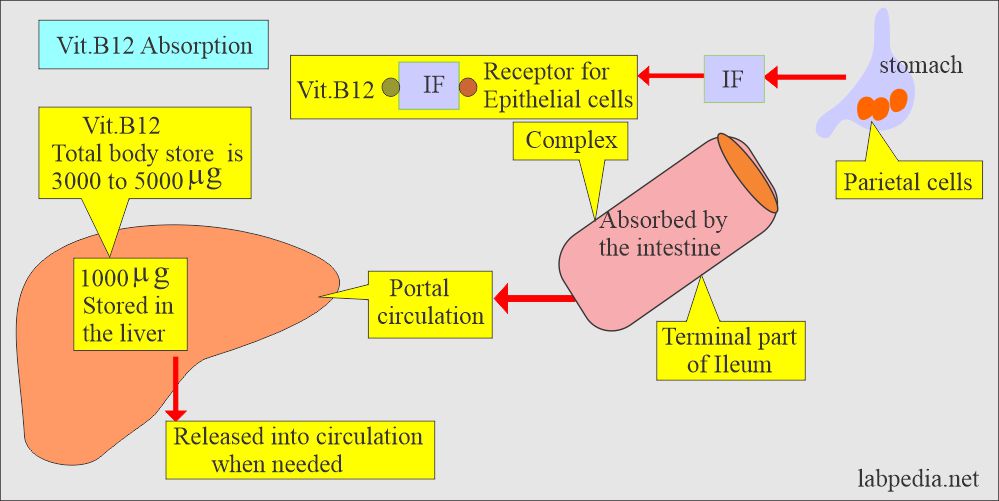
- For the assay of intrinsic factors (IF), aspiration of gastric juice is necessary.
What are the Indications for Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)?
- To diagnose pernicious anemia.
What are the precautions for Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)?
- Avoid injection of vit.B12 within 48 hours of testing.
What is the mechanism of megaloblastic anemia?
- Megaloblastic anemia is due to a deficiency of vit.B12, the major cause.
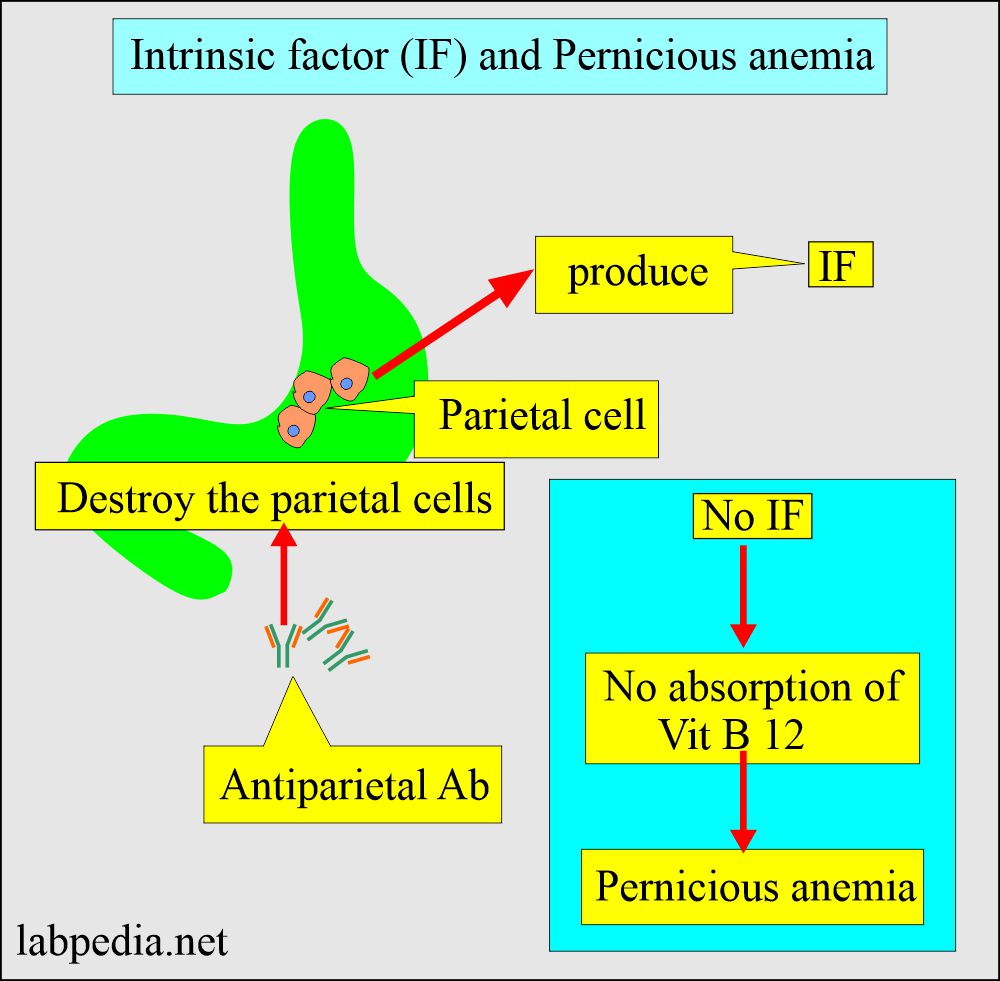
- Intrinsic factor is secreted in the stomach, which is needed to absorb the vit. B12.
- The intrinsic factor is the protein produced by the parietal cells.
- The activation of the immune system produces antibodies against the intrinsic factor.
What is the mechanism of Pernicious anemia?
- In Megaloblastic anemia, IF is decreased or absent.
- This may be due to autoimmune diseases.
- IF-Ab is found in a high percentage of children with juvenile pernicious anemia.
- IF-Ab is 50% to 70% positive in patients with pernicious anemia.
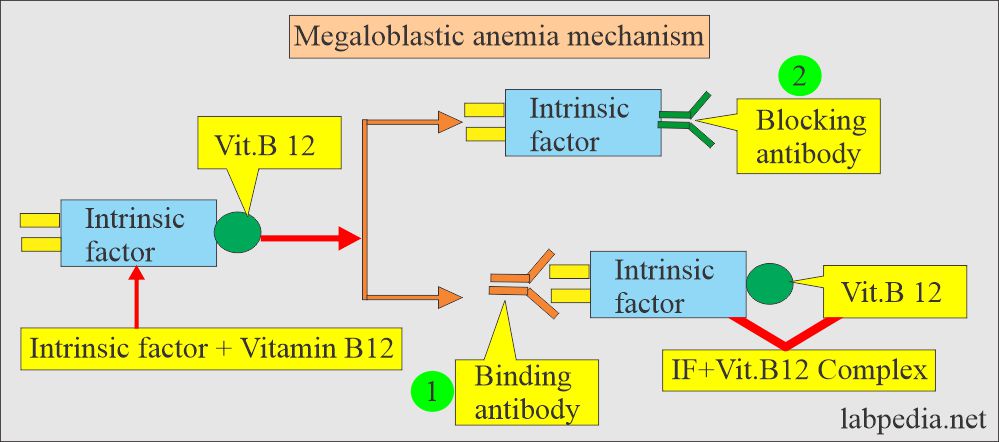
- IF-Ab is of two types :
- Type 1 blocking Ab, which is more common, blocks the binding of vit. B12 to IF. It is found in the serum of pernicious anemia cases around 40% to 50%.
- Another reference states that this antibody is usually present in around 60% to 75% of pernicious anemia patients.
- This antibody is diagnostic of pernicious anemia.
- Type II binding Ab (antibody) binds with the site on the intrinsic factor and is away from the vit. B12 site or combined with IF+Vitamin B12 complex.
- These are found in 40% of the pernicious anemia cases.
- The second antibody is less common, affecting the binding of IF in the ileum.
- Type 1 blocking Ab, which is more common, blocks the binding of vit. B12 to IF. It is found in the serum of pernicious anemia cases around 40% to 50%.
- Positive IF-Ab is confirmatory and is the cause of the disease.
- Negative IF-Ab does not rule out megaloblastic anemia because 50% of the patients do not show this antibody.
- One can supplement IF-Ab with an anti-parietal antibody test to diagnose Pernicious anemia.
- Pernicious anemia rarely needs the vit.B12 absorption test called the Schilling test.
- Testing the intrinsic factor antibody and the anti-parietal antibodies is easier, quicker, and more accurate.
- False-positive result:
- False-positive results are reported in diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency, thyroid diseases, and various gastric abnormalities.
Anti-parietal cell antibody:
- It is detected in 76% to 91% of the cases with pernicious anemia.
- It is much more nonspecific than the IF-Ab test.
- It is found in:
- 5% to 10% of the normal person.
- 30% to 60% of the patients with idiopathic atrophic gastritis.
- 12% to 28% of patients with diabetes mellitus.
- 25% to 35% of patients with thyrotoxicosis.
- 25% of the patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
What is the normal value of Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF Ab)?
- Intrinsic factor antibody = Negative.
What are the conditions where a Positive test for Intrinsic factor Antibody (IF-Ab)?
- Increased IF-Ab is seen in a patient with pernicious anemia.
- The IF antibodies are present in 3% to 6% of hyperthyroidism and insulin-dependent diabetes.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the mechanism of antibody for pernicious anemia.
Question 2: What is the mechanism of pernicious anemia.