Insect Bites
Insect Bites
How will you define insect bites?
- There may be puncture wounds on the skin inflicted by blood-sucking insects.
- Insects may bite when it is agitated, defend themselves, or when they want feed.
- Insects typically inject formic acid.
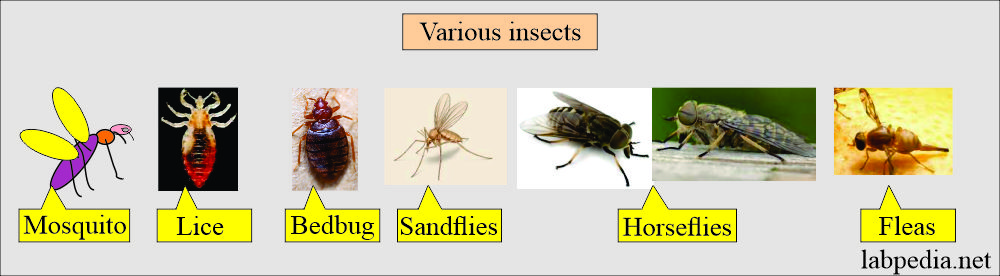
What are the types of insects that can bite?:
- Mosquitos (Machar)
- Lice (Joon)
- Sand flies.
- Bedbugs (Khatmal)
- Fleas (Passo).
- Hornet )Bhir)
- Wasps (Bhir)
- Bees (Shahid flies, Shalid ki makhi).
- Ticks (Chachar)
- Horse flies.
- Midges.
- Gnats.
- Mites.
How will the clinical presentations (Signs and symptoms) be?
- Mostly, insects cause mild, temporary pain after bites.
- There may be itching for a day or two.
- Some people may have severe skin reactions.
- Some of these insects may transmit diseases.
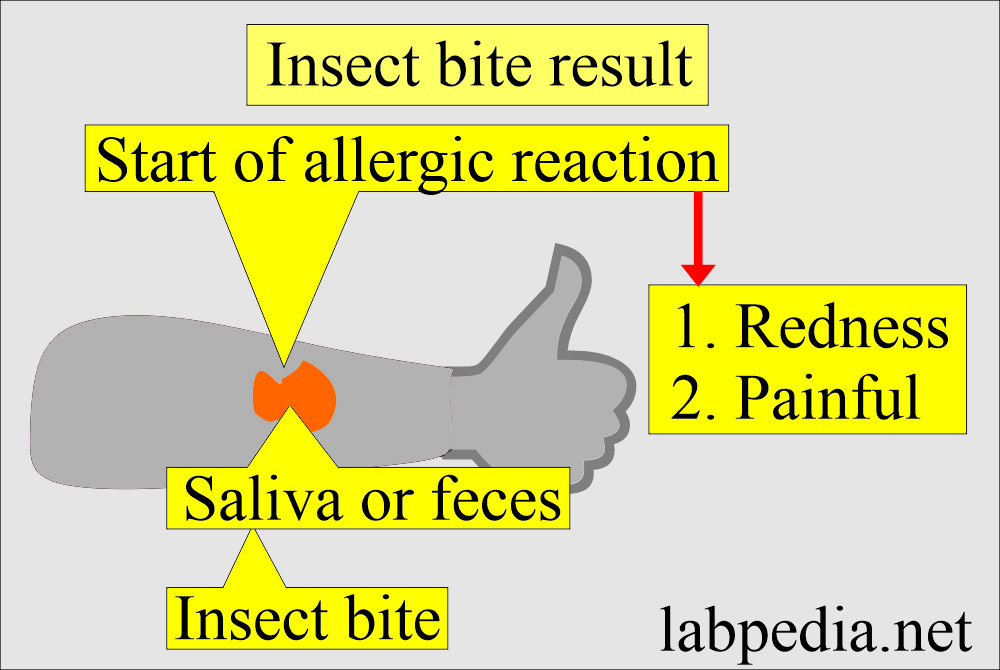
- After the insect bites due to saliva or feces, the allergic response starts from red pimples to painful swelling.
- There may be itching rashes.
- The severity of the insect bite reaction varies from mild to severe.
- Some people may go into shock.
How will you explain the mechanism of the insect bites?
- Most of these insects suck blood.
- The mouth parts of these insects are specially adapted to pierce the skin and suck blood.
- Insect bites are most common on the exposed skin of hands, arms, heads, and legs.
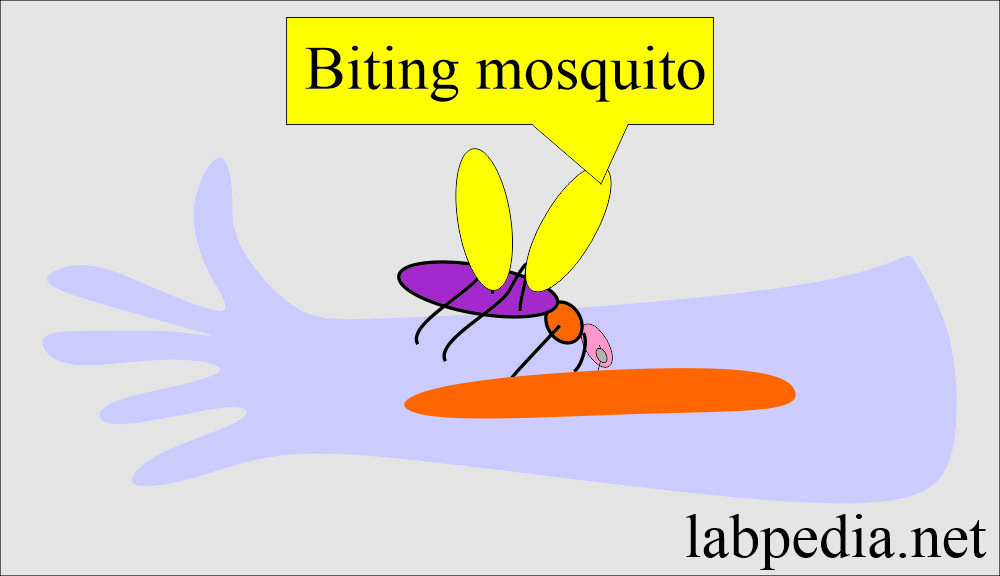
- Mostly, mosquitoes bite at night when there is darkness.
- When a mosquito female’s stomach is full, she will leave only then and inject saliva.
- Interestingly, only the female mosquito bites because she needs more protein to produce the ova. In contrast, male mosquitos are vegetarian and live on flower nectar and plant sap.
- Other insects causing bites in the dark are cat or dog fleas.
- These fleas may be hiding in carpets, sleeping baskets, or sofas.
- Horse flies are easily seen and produce painful bites.
- All these insects provoke a reaction on the skin that is an allergic response of the host to the saliva or the feces of these insects.
How can you Prevent insect bites?
- It is important for hikers and campers to protect themselves from mosquito bites.
- You can protect yourself outdoors by wearing gloves, trousers, socks, and full-sleeve shirts.
- Can use insect repellents.
- Before going to the bedroom, you can spray the insecticide-containing pyrethroid.
- Can use mosquito nets.
- You can burn the mosquito coils containing pyrethroid.
- Eliminating mosquito populations in areas endemic to Malaria and Dengue is difficult. Therefore, using treated mosquito nets and insect repellents on exposed parts of the body and wick repellents for outdoor activities and evening parties can be worthwhile.
How will you treat insect bites?
- Never squeeze the bite area; scrap to remove the sting.
- Some people suggest the application of vinegar immediately. This is effective against the hornets and wasps.
- Wash the bite area thoroughly with soap and water.
- Apply soothing ointment like calamine lotion.
- Avoid scratching the bite area.
- In case of a severe reaction, immediate medical consultation should be done.
- Can apply antihistamine containing local cream.
- In the case of lice, apply insecticide lotion.
- In the case of fleas, the whole family needs insecticide treatment to kill the flea population.

Thanks.
Thank you nice work.