Immunoglobulin Electrophoresis, Immunoglobulins Pattern in Various Diseases
Immunoglobulin Electrophoresis
What sample is needed for Immunoglobulin Electrophoresis?
- Venous blood is needed to prepare the serum.
- A random sample can be taken.
What are the Indications for Immunoglobulin Electrophoresis?
- It is advised to diagnose many diseases like Multiple Myeloma etc.
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
- Immunoglobulin electrophoresis is advised if there is a spike in the gamma band in serum electrophoresis.
- Hypersensitivity reactions.
- Immune deficiency.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Chronic infections.
- Intrauterine fetal infection.
- Hypogammaglobulinemia.
- Agammaglobulinemia.
- Analbumionemia.
- Bisalbuminemia.
- Afibrogenemia.
- Atransfferenemia.
- Cirrhosis.
- Acute-phase proteins.
How will you define immunoglobulin electrophoresis?
- It is the immunochemical method that separates the various proteins and immunoglobulins.
- This technique can be used in the serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- It is used to evaluate gammopathies.
- It is said that no pattern is pathognomonic of any single disease.
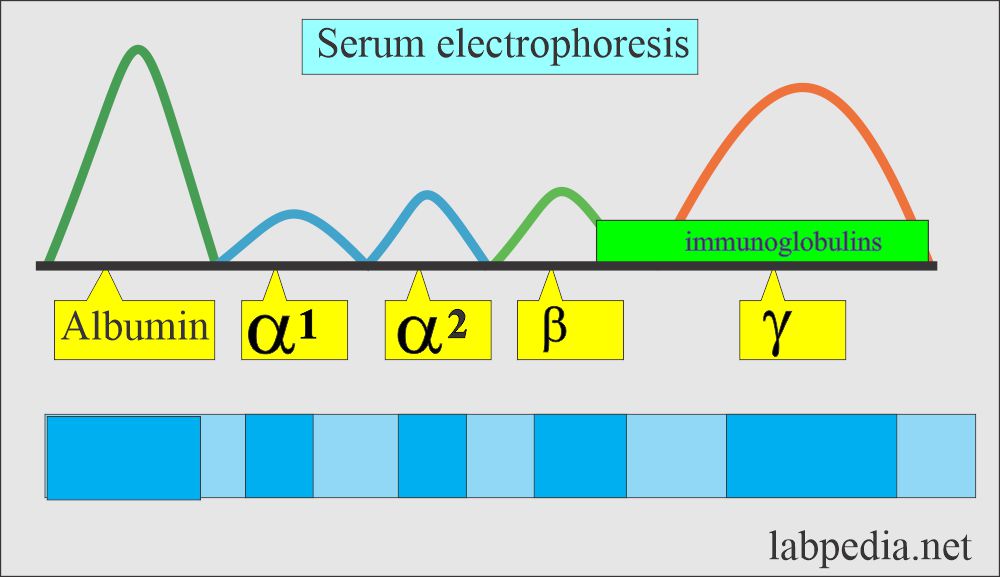
What are the components of serum proteins?
- Albumin
- Globulins.
- Globulins are of two types:
- One formed in the liver.
- The second is produced by the immune cells.
- One of the globulin is called gamma globulin.
- The antibodies are made of gamma globulin called immunoglobulin (Ig).
- There are five main types of immunoglobulins (Ig) labeled:
- IgG, which is 75% of the total Ig.
- γ-region is predominantly composed of IgG.
- IgM is 10% to 12%
- IgA consists of 15% of the total Ig.
- IgE
- IgD
- IgG, which is 75% of the total Ig.
- IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE share the junction of β and γ-globulin.
Give some examples of immunoglobulin electrophoresis patterns in various diseases?
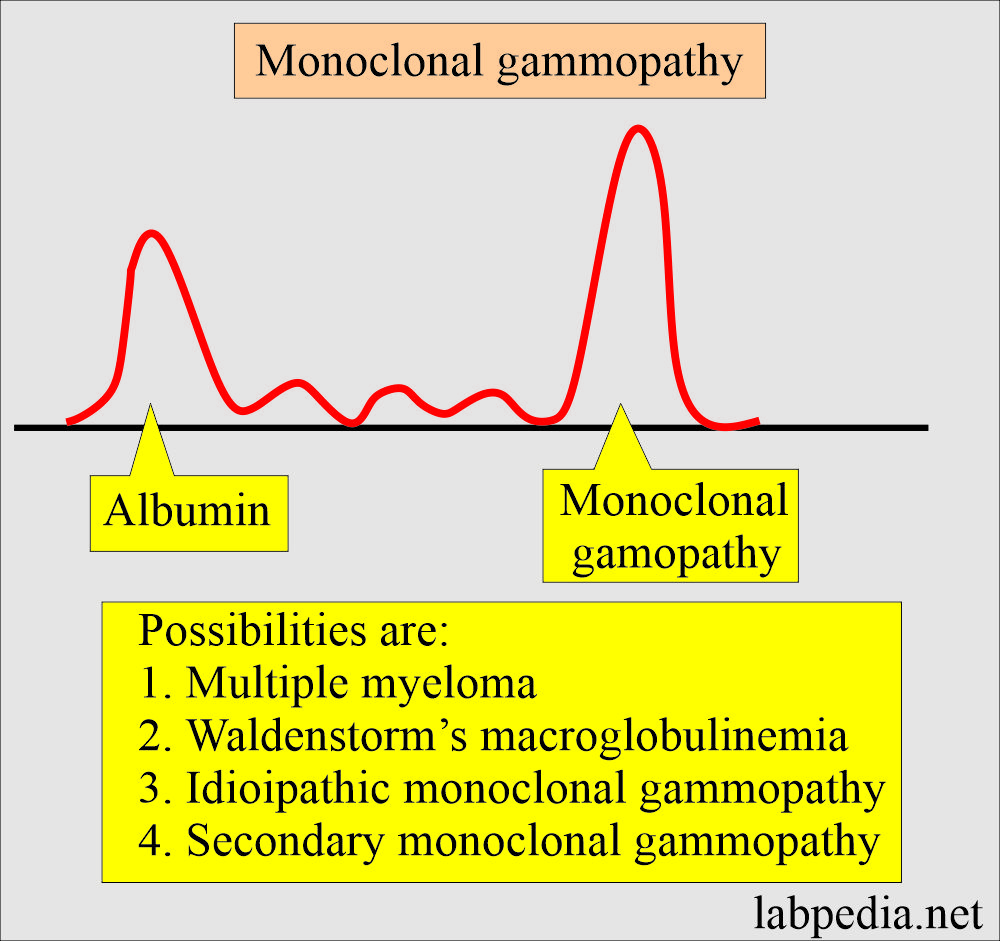
What is the pattern in the Multiple Myeloma?
- In myeloma, Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia showed a prominent γ- fraction, monoclonal gammopathy band.
- A monoclonal gammopathy band has also been seen in idiopathic or secondary gammopathy.
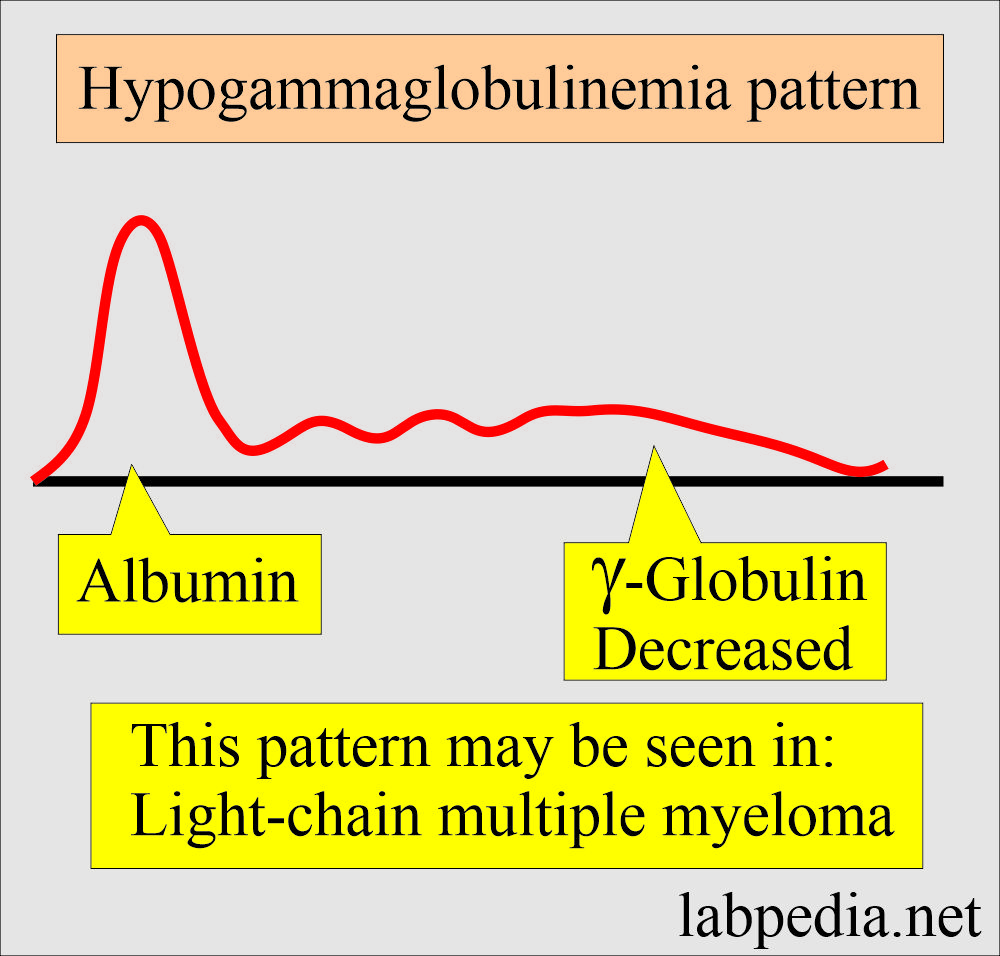
What are some examples of hypogammaglobulinemia patterns?
- There are decreased γ-globulins.
- There are no changes in other globulins.
- It may represent a light chain variant of multiple myeloma (nearly 20% of multiple myeloma).
- In light chain myeloma, urine is positive for Bence Jones proteinuria.
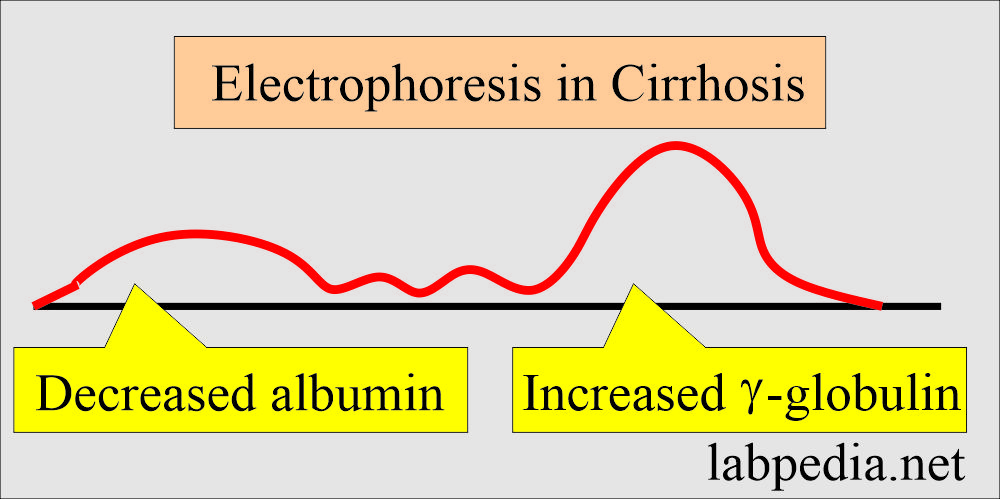
What is the pattern in Cirrhosis?
- Electrophoresis in cirrhosis typically shows low albumin.
- There is a moderate or considerably raised band of gamma-globulin.
- β-peak is mixed with the γ-globulin.
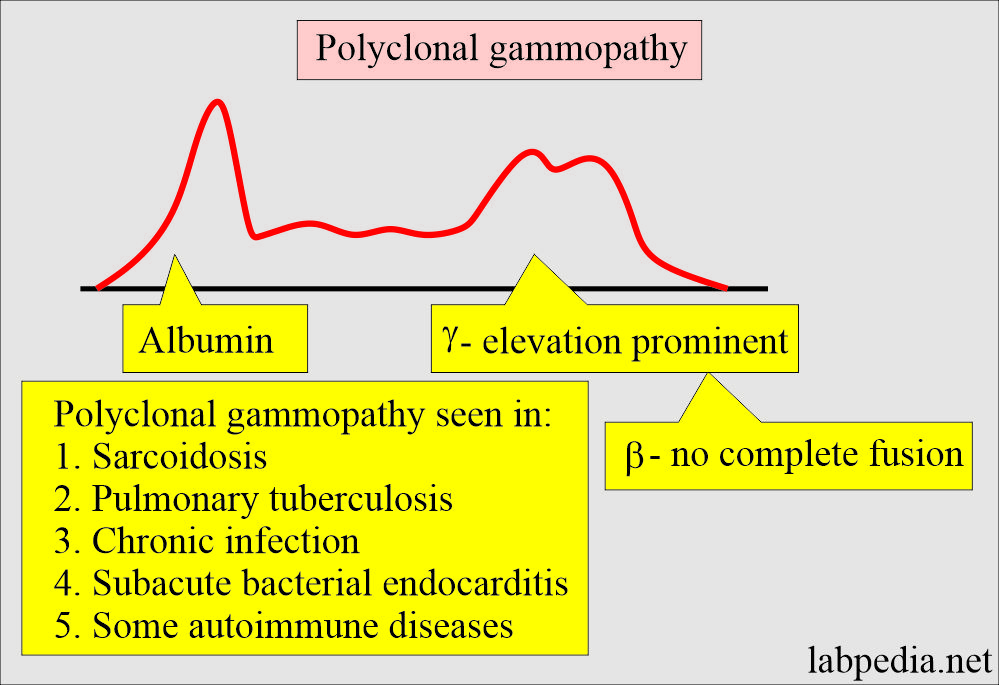
What is the pattern of Polyclonal gammopathy?
- There is a significantly increased gamma-globulin level involving the entire band.
- There is no thin spike-like appearance.
- There may be some β-globulin bridging with the γ-band.
- It is seen in:
- Some cases of cirrhosis.
- Chronic infection.
- Granulomatous diseases like sarcoidosis or pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Subacute endocarditis.
- Some cases of rheumatoid arthritis, polyarteritis nodosa, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
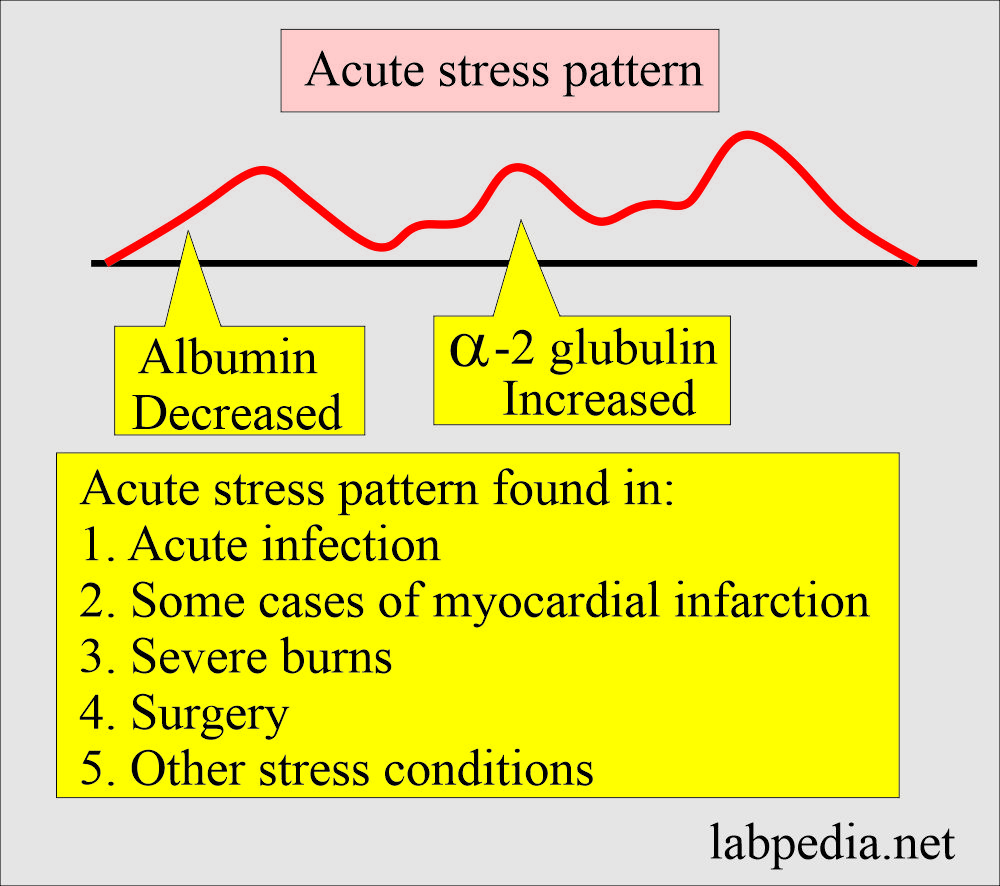
What is the pattern in Acute reaction?
- It consists of decreased albumin.
- There are raised α-2 globulin levels.
- This pattern is seen in early acute infection and some cases of acute myocardial infarction.
- This may be seen in severe burns, surgery, and other stress conditions.
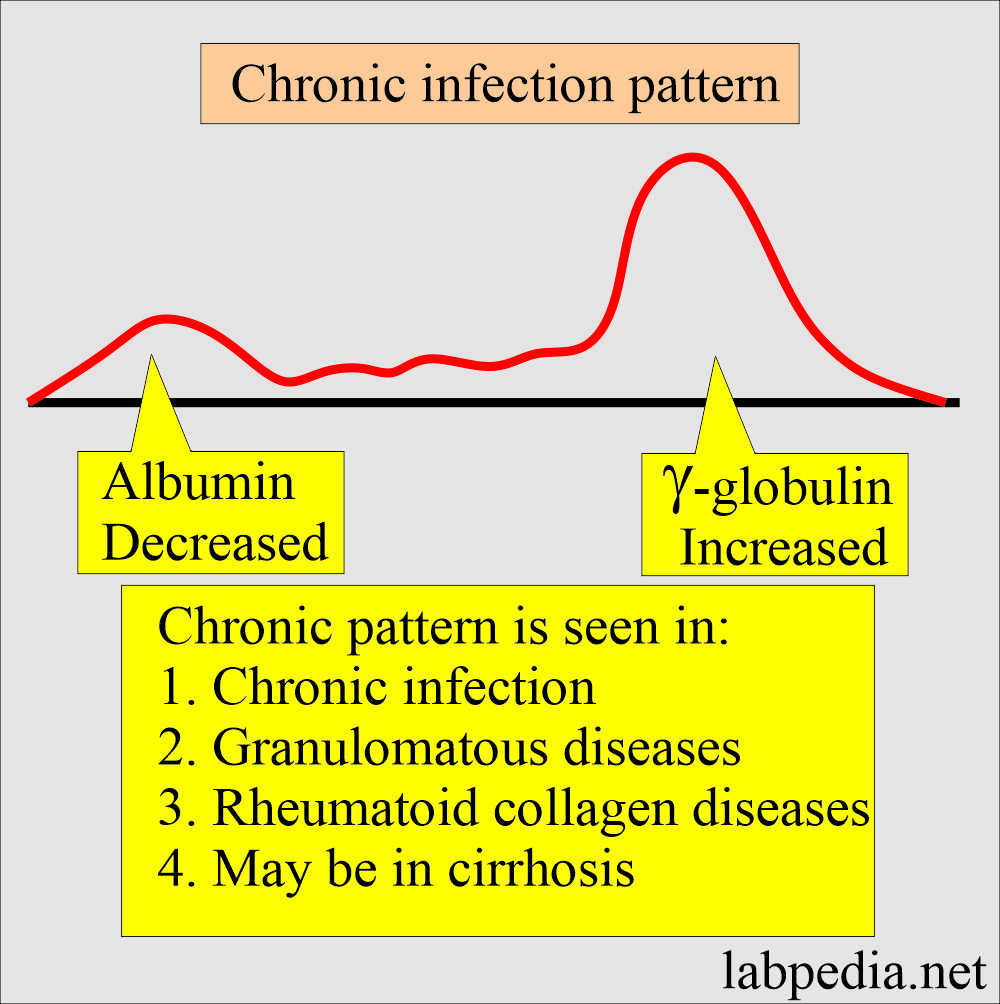
What is the pattern of the chronic inflammatory process?
- There is decreased albumin.
- There is a moderately increased γ-globulins.
- α-2-globulin is normal or slightly raised.
- This pattern is found in:
- Chronic infections.
- Granulomatous diseases.
- Rheumatoid collagen diseases.
- It may be found in cirrhosis.
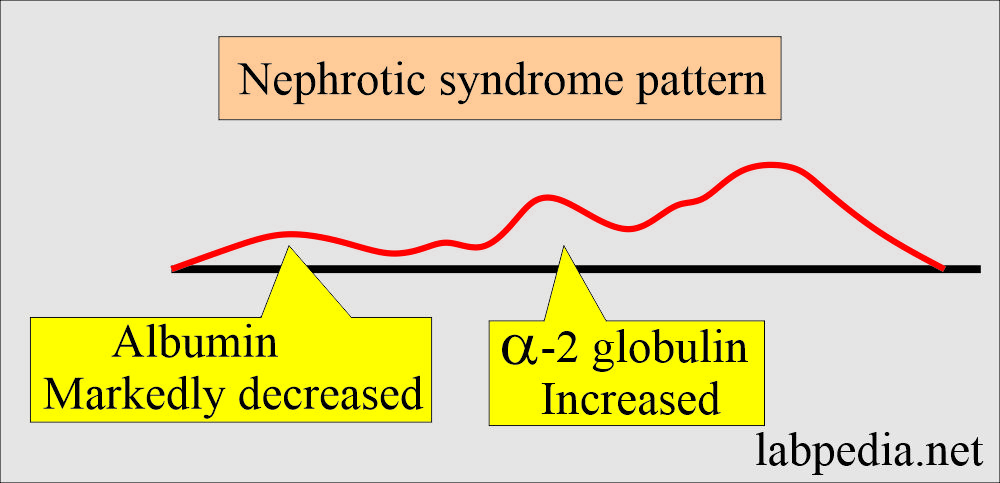
What will the pattern of Nephrotic syndrome be?
- There is a markedly decreased level of albumin.
- There is a moderate increase in α-2 globulin level.
- This α-2 globulin level of nephrotic syndrome is slightly or moderately greater than in acute infection.
What is the Normal level of Immunoglobulins?
| Age | IgG | IgM | IgA | IgD | IgE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | 565 to 1765 mg/dL | 55 to 375 mg/dL | 85 to 385 mg/dL | minimum | minimum |
| 2 to 5 months | 200 to 700 mg/dL | 25 to 100 mg/dL | 4 to 80 mg/dL | ||
| One year | 430 to 1200 mg/dL | 35 to 125 mg/dL | 15 to 110 mg/dL | ||
| 4 to 12 years | 460 to 1600 mg/dL | 50 to 250 mg/dL | 25 to 350 mg/dL |
What are the conditions where there is an increased IgG level?
- Multiple myelomas (Monoclonal IgG gammopathy).
- Hyperimmunization reaction.
- Chronic granulomatous infection.
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome, and SLE.
What are the conditions of decreased IgG level?
- Agammaglobulinemia.
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
- AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome).
- Nephrotic syndrome.
- Protein-losing enteropathy.
When will you see an Increased IgM level?
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
- Chronic infections.
- Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and SLE.
- Acute infection is a primary immune response.
- Chronic liver diseases like biliary cirrhosis.
When will you see a decreased IgM level?
- Agammaglobulinemia.
- Hypoproteinemia is seen in nephrotic syndrome and protein-losing enteropathy.
- AIDS
- Immunosuppression is due to drugs like steroids and dextran.
When will you see an increased level of IgA?
- Primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Chronic infectious.
When will you see a decreased level of IgA?
- Hypoproteinemia due to nephrotic syndrome and protein-losing enteropathy.
- Ataxia.
- Immunosuppression is due to drugs like steroids.
- Congenital isolated deficiency of IgA.
- Telangiectasia.
When will you see an increased IgE level?
- Allergic reactions like hay fever, asthma, eczema, and parasites.
- In an anaphylactic reaction.
When will you see a decreased IgE level?
- Agammaglobulinemia.
When will you see an Increased monoclonal gammopathy?
- Multiple myelomas.
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
When will you see an Increased polyclonal gammopathy?
- Amyloidosis.
- Chronic liver disease.
- Chronic infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
When will you see an increased monoclonal gammopathy in urine?
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia.
- Multiple myelomas.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the appearance of albumin in nephrotic syndrome?
Question 2: What is the picture in acute stress?