Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Hormones
Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Hormones
What sample is needed for the hypothalamus and pituitary glands hormones?
- The most commonly used sample is serum.
- In some cases, 24 hours urine sample is collected.
What are the indications for hypothalamus and pituitary gland hormones?
- These hormones are estimated for:
- Diagnostic purposes.
- For a therapeutic reason.
- To evaluate ovulation.
- To evaluate spermatogenesis.
- To treat endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
- To evaluate precocious puberty.
- To treat prostatic carcinoma.
- To find GH deficiency.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary glands?
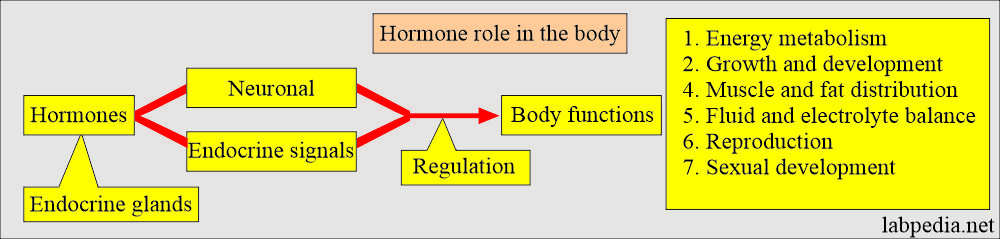
- Hormones communicate between cells and depend upon neuronal and endocrine signals to regulate body functions.
- Hormones are chemical substances that are formed in various glands.
- These hormones stimulate or inhibit the growth or function of other tissues and organs.
What are the functions of the pituitary gland hormones?
- Hypophysis regulates the endocrine system. This is called the master endocrine organ.
- It takes place by integrating signals from the brain with feedback from the concentration of hormones in the blood, leading to the intermittent release of hormones from the target endocrine glands.
- These hormones regulate growth, thyroid functions, adrenal gland functions, gonadal functions, and water and salt homeostasis.
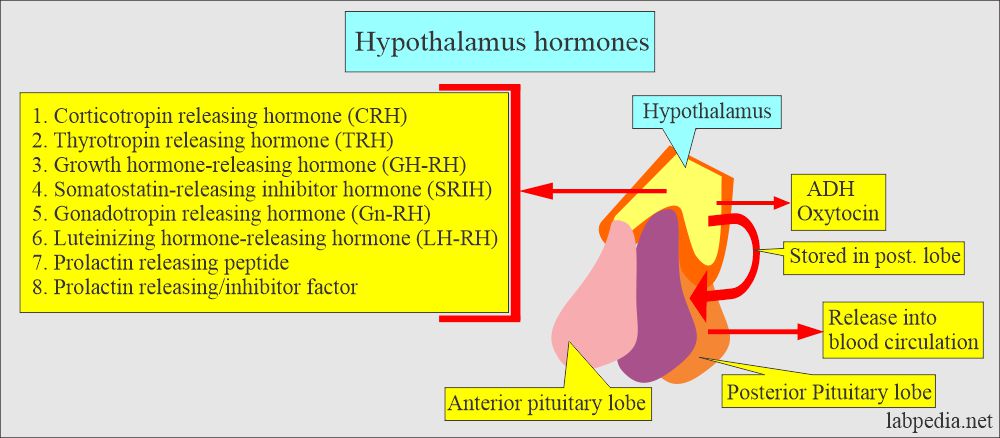
- Vasopressin (an antidiuretic hormone, ADH) and oxytocin are produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary lobes.
- So, the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis) is not a gland but a storage site for ADH and oxytocin.
How will you discuss the hypothalamus gland?
- The neurons that give rise to hypophysiotropic hormones are themselves influenced by the hypothalamic neurotransmitters:
- Dopamine.
- Serotonin.
- Norepinephrine.
- Endorphin.
- Acetylcholine.
- These neurotransmitters modify the secretory activity of the anterior pituitary gland.
- Cytokines also modify this neuroendocrine axis.
- The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is modified by interleukin 1 (IL-1) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), produced due to infection or stress.
What are the Hypothalamus Hormones?
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
- This hormone will stimulate the production and secretion of ACTH by the anterior pituitary glands.
- Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH).
- This hormone stimulates the anterior pituitary glands’ production and secretion of TSH and prolactin.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GRH).
- This hormone stimulates the anterior pituitary gland’s production and secretion of FSH and LH.
- Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GRH).
- This hormone stimulates the anterior pituitary gland’s production and secretion of GH.
- Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GIH).
- This hormone inhibits the anterior pituitary gland’s production and secretion of GH and TSH.
- Prolactin inhibiting factor (PIF).
- This neurotransmitter inhibits the production and secretion of prolactin, TSH, FSH, LH, and GH by the anterior pituitary gland.
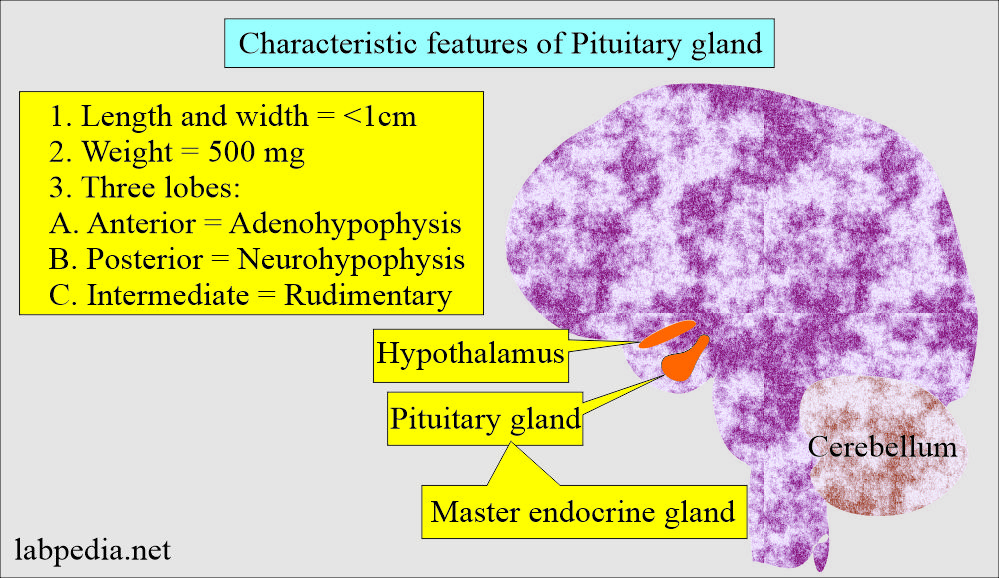
How would you describe the Anterior Pituitary Gland?
- The pituitary gland consists of three lobes:
- The anterior lobe is called adenohypophysis.
- The posterior lobe is called neurohypophysis.
- There is a middle lobe as well.
- This gland is present at the base of the skull in a bone cavity called sella turcica.
- The gland is small, measuring 1 cm or less in width/height and weighing 500 mg.
- Most pituitary gland hormones are proteins (consists of peptides) or peptides (short chains).
- The cells of the anterior lobes of the pituitary glands are divided into:
- Acidophilic cells that stain with acidic stains are around 40%.
- Basophilic cells stain with the basic dyes and are around 10%.
- Chromophobic cells do not stain with either acid or basic dyes and are around 50%.
How will you divide cells by Immunohistochemistry and hormones secreted?
| Type of the cells | Hormone secreted | Stimulant for the secretion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Secretion of the hormones from the anterior pituitary glands is controlled by the hypothalamus.
- The hypothalamus secretes small peptides that are known as releasing or inhibitory factors.
What are the inhibitory chemicals for the hormones?
| Hormone | Inhibited by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
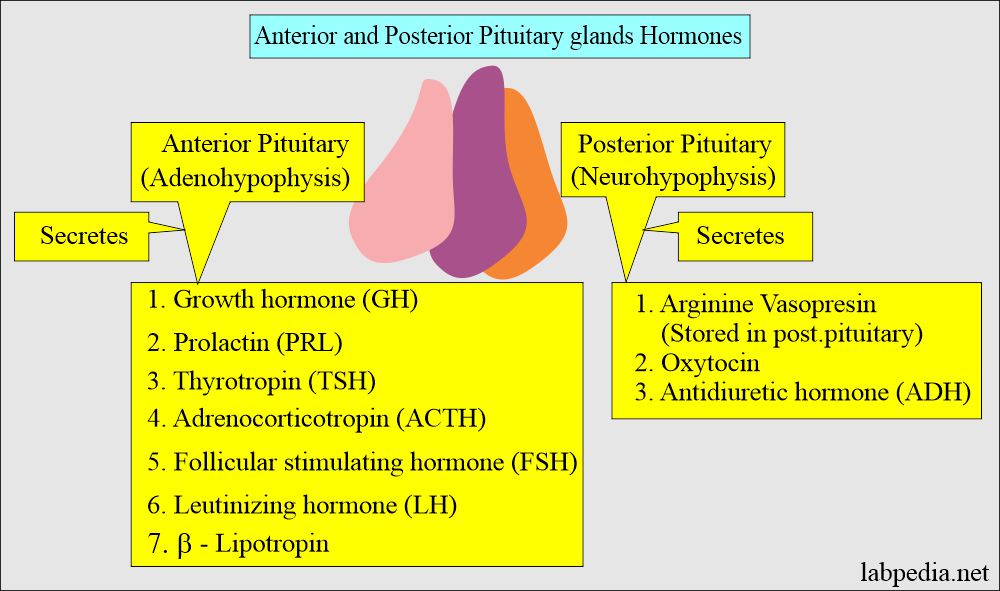
What are the Anterior pituitary hormones?
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
- This hormone stimulates the secretion of cortisol by the adrenal gland.
- Growth Hormone (GH).
- This hormone promotes growth in soft tissue, cartilage, and bone.
- Thyroid stimulation hormone (TSH).
- This hormone stimulates the secretion of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 by the thyroid gland.
- Prolactin Hormone (PRL).
- This hormone’s main role is in the initiation and maintenance of lactation.
- Prolactin induces ductal growth, the lobular alveolar system, and the synthesis of milk production.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- This hormone controls the functional activity of gonads.
- In the male, this stimulates spermatogenesis.
- Females stimulate the growth of ovarian follicles in the presence of LH. This promotes the secretion of estrogen by the mature follicle.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH).
- This hormone controls the functional activity of the gonads.
- Males produce testosterone through the Leydig cells of the testes.
- In females, it leads to the release of the ovum from the ovarian follicle, in which FSH ripens.
- It transforms the follicle into a corpus luteum that secretes the progesterone.
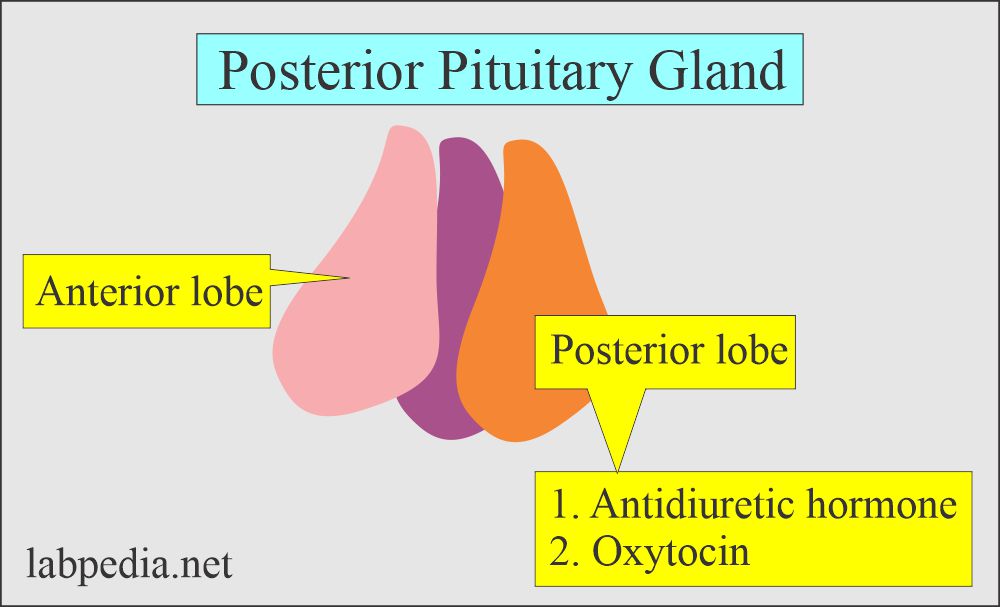
What are the Posterior Pituitary Gland hormones?
1. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH).
- This maintains water homeostasis.
- It increases water reabsorption by the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the kidneys, increasing urine concentration.
- This also leads to vasoconstriction, which increases blood pressure.
2. Oxytocin.
- This will stimulate uterine contraction during labor.
- This may be used to induce labor.
- It helps the breasts to release milk from the mammary ducts.
Question 1: What are the hormones of the posterior pituitary gland.
Question 2: What is the inhibitor of prolactin.