March 20, 2024
Hematocrit (Hct)
What sample is needed for Hematocrit (Hct)?
- The patient’s blood is taken in EDTA.
- It is stable for 48 hours at 4 °C and 6 hours at 23 °C.
- Fetal blood:
- Collected by percutaneous blood sampling.
What are the precautions for Hematocrit (Hct)?
- The test should be performed within 6 hours of blood collection.
- EDTA is the choice of blood anticoagulant.
- Avoid hemolysis.
- Avoid clotting of the blood.
- Centrifugation must be adequate. This will give a high result.
- The buffy coat is not included in the hematocrit.
- Avoid excess EDTA.
- Avoid overdilution of the blood sample by the anticoagulant.
- Avoid a Prolonged tourniquet; it can lead to hemoconcentration and error in the Hct.
- Drugs like penicillin and chloramphenicol decrease the Hct level.
What are the Indications for Hematocrit (Hct)?
- It is used to diagnose anemia.
- Hct is done in patients with bleeding or blood loss.
- It is part of a complete blood count.
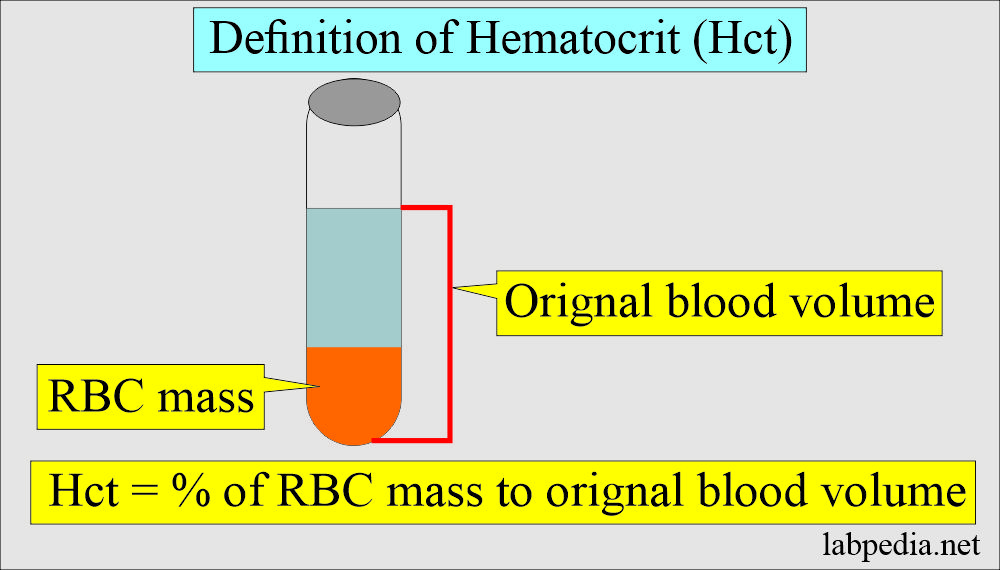
How will you define hematocrit (Hct)?
- After the centrifugation of the EDTA blood in the test tube.
- The % of the RBC column to the original whole blood volume is called hematocrit (Hct).
What is the principle of hematocrit (Hct)?
- The word hematocrit means to separate the blood where the plasma and blood cells are separated.
- This test gives information about RBC concentration and helps to see hemoconcentration.
- This is basically a measurement of total blood volume and RBC ratio as a percentage.
- In a capillary tube or Hct tube, blood is centrifuged. Cells, mainly RBCs, will settle down, and clear plasma will appear on top.
- This ratio of settled cells and upper clear plasma is calculated in %.
How will you Calculate Hematocrit (Hct) by Hemoglobin?
- This hemoglobin quality control can be done by checking Hb results in g/dL and comparing the result with hematocrit results.
- Hct results in % units, using the following formula:
- One g/dL Hb unit = 3 Hct unit
- For example, if the Hb is 13 g/dL
- Then Hct is = 13 x 3 = 39 %
- Now, compare the result with the Hct value.
What Factors Will Affect Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Abnormalities of RBC morphology will affect Hct.
- Raised values of WBC will alter the Hct.
- People from high altitudes have increased Hct.
- After the hemorrhage, values are not reliable.
- Dehydration and hemodilution will affect the Hct.
- Pregnant ladies will have low values due to hemodilution.
- Chloramphenicol and Penicillin decreased in value.
How will you discuss the pathophysiology of Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Hct is a macroscopic observation where the percentage volume of the packed RBCs is measured.
- This is also called packed cell volume or PCV.
- The Hct closely reflects the hemoglobin and RBC values.
- Hct mostly depends upon the number of RBCs
- Hematocrit means to ‘separate blood’ where blood cells and plasma are separated by centrifugation.
- Meanwhile, it is calculated by MCV in electronic counters.
- A calculated Hct is lower than 2% than the microhematocrit due to trapped plasma in a centrifuged RBC column.
- Hct is lower in pregnant women than in nonpregnant ladies.
- Females have less Hct than men.
- Hct is usually three times the Hb concentration in grams/dl.
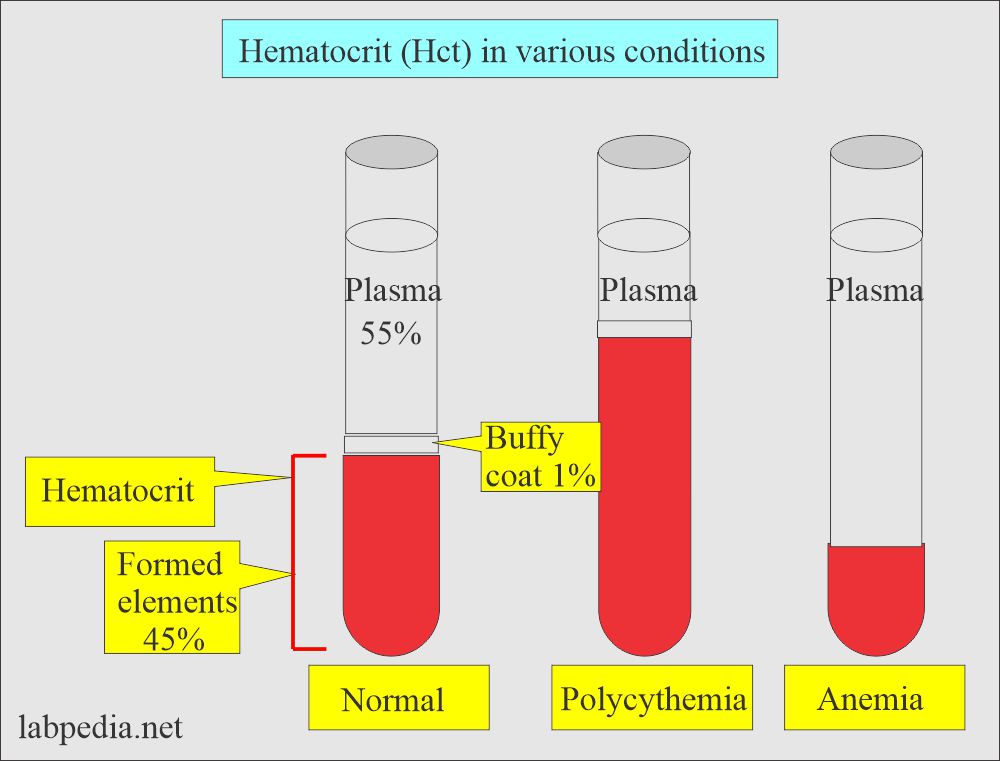
- Decreased values indicate anemia.
- Increased values indicate erythrocytosis.
- In dehydration, Hct will be falsely high due to less plasma volume, and the number of RBCs is the same.
- In the case of large-size RBCs, the Hct will be falsely high.
- Blood transfusion is not recommended if the Hb is >8 g/dl or Hct is >24 %.
- Hct is more reliable and useful than the RBC count.
- Serial hematocrit estimation:
- Serial hematocrit estimation may be used once every 2 to 4 hours to indicate blood volume changes.
- It usually takes roughly 2 hours after an acute bleeding episode for a significant change (drop) in the hematocrit.
- Occasionally, it may take more time from 6 to 12. hours.
- When there is a larger extracellular blood loss, the sooner the hematocrit value changes. In this case, this may be >2%.
- In case of dehydration:
- It will delay the drop of hematocrit.
- In the case of low plasma protein:
- In the low plasma protein, hematocrit drop is late.
How will you do the procedure for Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Microhematocrit tube method. These are as correct as the tube method.
- The Wintrobe hematocrit method is the macro method.
- Automated method.
- In an automated machine, the RBC count and MCV are calculated.
- Hb = RBC in a million x 3
- Hct = Hb x 3
- Hct = RBC in a million x 9
- This formula depends upon the value of MCHC (33).
- This factor varies depending upon the MCHC from 2.7 to 3.2.
What is the normal Hematocrit (Hct)?
Source 2
| Age | Hct % |
| Newborn | 44 to 64 |
| 2 to 8 weeks | 39 to 59 |
| 2 o 6 months | 35 to 50 |
| 6 to 12 months | 29 to 43 |
| 1 to 6 years | 30 to 40 |
| 6 to 18 years | 32 to 44 |
| Adult | |
| Male | 42 to 52 |
| Female | 37 to 47 |
| Pregnant females | >33 |
| Old people | Values may slightly decrease |
Fetal Hematocrit (Hct) level:
| Age of the fetus | Hematocrit (Hct) level |
| 18 to 20 weeks | 33% to 39% |
| 21 to 22 weeks | 35% to 41% |
| 23 to 25 weeks | 36% to 41% |
| 25 to 30 weeks | 35% to 45% |
Source 4
| Age | Hematocrit (Hct) value |
| Fetal ( 26 to 30 weeks ) | 41% to 54 % |
| cord blood ( 9 months+ ) | 32% to 40 % |
| Children | |
| 0 to 2 weeks | 44% to 64 % |
| 2 to 6 months | 35% to 49 % |
| 6 months to 1 year | 29% to 43 % |
| 1 to 6 years | 30% to 40 % |
| 6 to 18 years | 32% to 44 % |
| Men | 42% to 52% |
| Women | 36% to 48% |
| Pregnant females | > 33 % |
Hematocrit (Hct) level at various ages:
| Age of the baby | Hematocrit level |
| Newborn | 44% to 70% |
| 1 to 23 months | 32% to 42% |
| 2 to 9 years | 33% to 43% |
| 10 to 70 years |
|
| >18 years |
|
What is the significance of Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Decreased values are an indicator of Anemia.
- Decreased values are also seen in Leukemia, Lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease, and Myeloproliferative disorders.
What are the causes of increased Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Polycythemia Vera.
- Erythrocytosis.
- Extreme physical exercise or excitement.
- High Altitude.
- Dehydration leads to Hemoconcentration, e.g., diarrhea, burns, and vomiting.
- Congenital heart failure.
- Severe chronic pulmonary obstructive disease (COPD).
What are the causes of decreased Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Anemia.
- Hemoglobinopathies.
- Cirrhosis.
- Hemolytic anemia (Erythroblastosis fetalis, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Hemorrhage.
- Bone marrow failure
- Renal diseases.
- Normal pregnancy.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Malignancies like lymphoma, leukemia, multiple myeloma, and Hodgkin’s disease.
- Normal pregnancy.
- Bone marrow failure.
What is the critical value of Hematocrit (Hct)?
- Critical value of Hct = Low = <15 %
- High = >60 %.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the other name of hematocrit (Hct)?
Question 2: What is the hematocrit in a newborn?

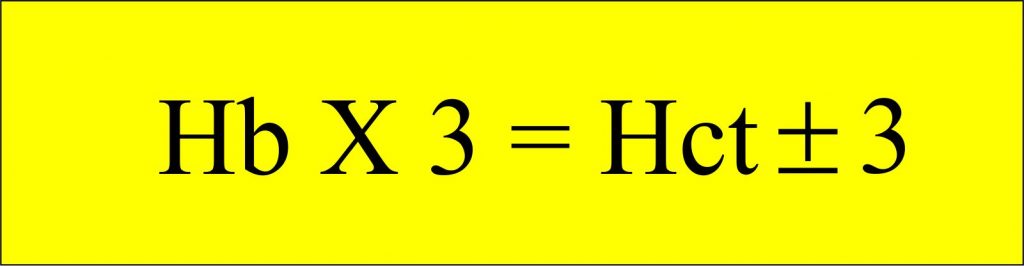
It’s hard to say