Gonorrhea, Diagnosis of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
Gonorrhea
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
What sample is needed for Neisseria Gonorrhoeae?
- The best sample for men is the urethral discharge smear.
- Females can make a smear from the vagina.
- In females, a cervical smear can also be taken.
- An anal canal smear can be taken.
- Smears are made from prostatic secretions, urethra, cervix, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
What are the indications for Neisseria Gonorrhoeae?
- A urethral smear is stained to diagnose gonorrhea.
- A cervical smear is stained to diagnose gonorrhea.
- It is advised to diagnose sexually transmitted diseases.
How will you define Neisseria gonorrhea?
- Neisseria is a human pathogen and does not cause infection in animals. So, the spread is through close contact through the sexual route.
- Neisseria is sensitive to drying and does not survive out of the body.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae causes contagious diseases and is usually sexually transmitted.
- Mother can transmit the disease to the newborn.
How will you describe the bacteriology of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae?
- The incubation period is 2 to 10 days.
- These are obligate parasites of the human urogenital area.
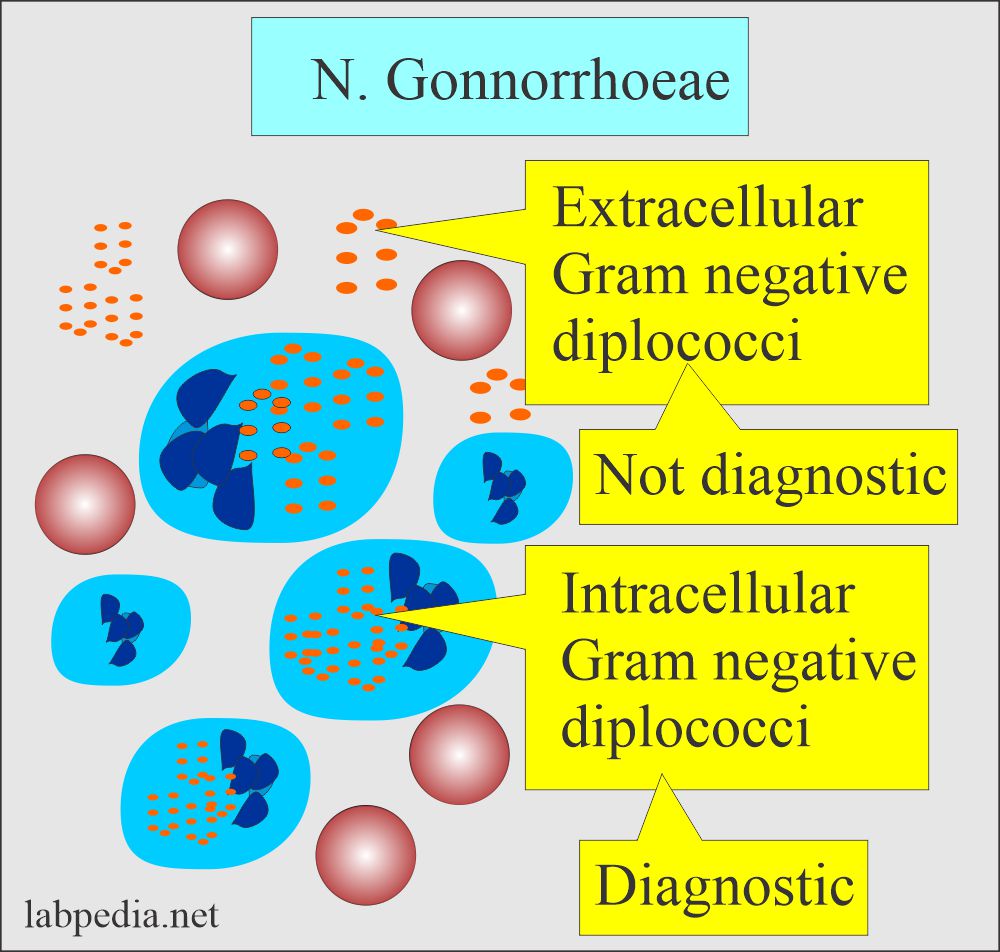
- These are characteristically seen in pairs with adjacent sides concave.
- In the purulent material, these are seen intracellularly and outside the cells.
- N. Gonorrhoeae is gram-negative bacteria that can grow in the body, like the urethra, cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes in females and the urethra in males.
- These bacteria grow in enriched media (Chocolate agar).
- Incubation is done in a moist atmosphere containing 5% to 10% CO2.
- The optimal temperature is 35 to 37 C.
- These media may contain antibiotics (Lincomycin) to inhibit the growth of other bacteria.
- Small gray glistening colonies form after 24 hours of incubation, which may become larger after 48 hours.
- The identification test is carbohydrate utilization, which produces acid only from glucose.
- There are two pathogenic Neisseria:
- N. Gonorrhoeae (Gonococcus).
- N. Meningitides (Meningococcus).
- N.Gonorrhoeae can infect any epithelium lined by columnar cells with cilia-like:
- Urethra.
- Cervix.
- Rectum.
- Pharynx.
- Conjunctiva.
- But cannot vagina, which is the squamous epithelium.
- It grows in the warm, moist area of the female reproductive system.
- It can also grow in the mouth, throat, and anus.
What are the signs and symptoms of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (Gonorrhea)?
- Neisseria gonorrhea causes:
- Genital infection.
- Proctitis.
- Oropharyngeal infection.
- arthritis.
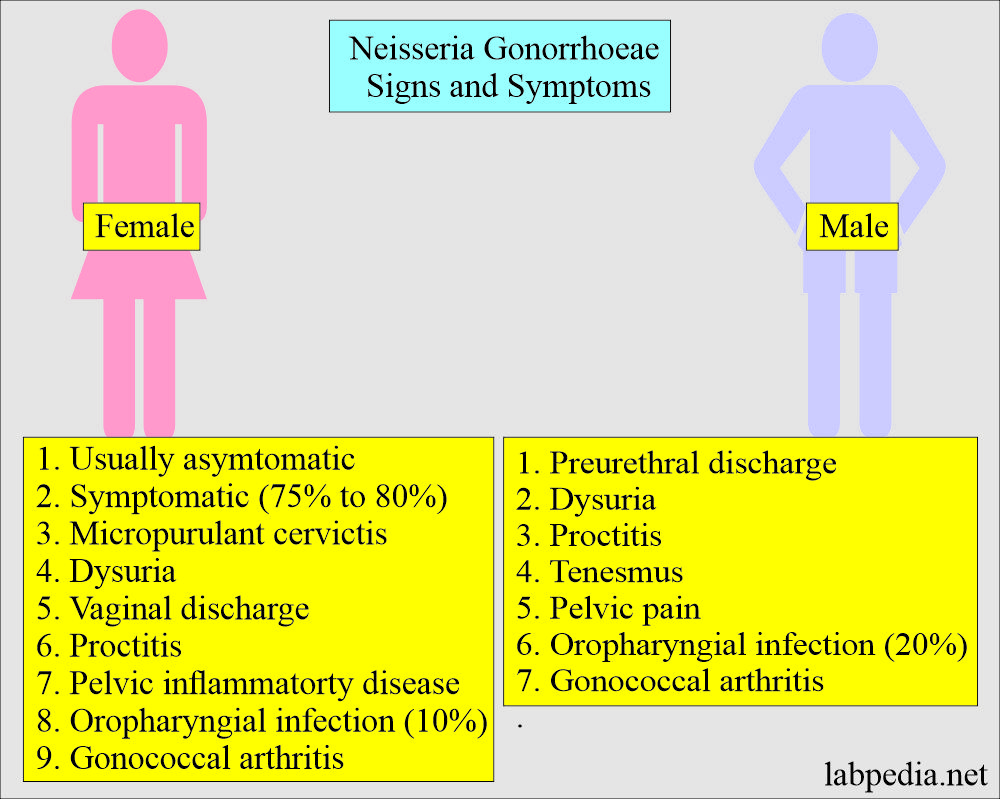
- Gonorrhea is not symptomatic in roughly 75% to 80% of the infected females and 10% to 15% of infected males.
- This is more symptomatic in men than in women.
- In the male:
- There is a urethral purulent discharge.
- There is dysuria.
- There may be proctitis and tenesmus.
- There is pelvic pain.
- In the female:
- Females are usually asymptomatic.
- Gonorrhea in females is symptomatic in about 75% to 80% and 19% to 15% in males.
- There is mucopurulent cervicitis.
- There is vaginal discharge.
- There may be dysuria.
- There may be proctitis.
- N. gonorrhea causes gonorrheal urethritis and initiates the majority of cases of acute salpingitis, a so-called pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Transmission from male to female is more efficient than from female to male.
- While pharyngeal infections are asymptomatic.
- Ascending pelvic infection occurs in 10% to 20% of the cases, leading to infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
- This may involve the rectum and oropharynx.
- Oropharyngeal infection is present in 10% of females and 20% of homosexual men.
- Pharyngeal gonorrhea is usually asymptomatic, self-limited in 10 to 12 weeks, and visible in <50% of the cases.
- Culture is needed for the diagnosis, and the smear is not diagnostic because of the nonpathogenic Neisseria species.
- Gonococcal arthritis is diagnosed by the presence of gonococci in 1/3 of the cases.
- A variable number of WBCs are found, or synovial fluid may be purulent.
- Proctitis is seen in symptomatic cases (∼ 5%). Bacterial culture on special media is confirmatory.
- Avoid contamination from the stool.
- Rectal gonorrhea is accompanied by genital gonorrhea.
What type of Gonorrheal disease is seen in females?
- Urethritis
- Conjunctivitis
- Vulvitis.
- Vaginal discharge.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Bleeding after intercourse.
What type of Gonorrheal disease is seen in males?
- Urethritis (burning micturition).
- Swollen, painful testes.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the throat.
What are the complications of Gonorrhea?
- In females, ascending pelvic infection.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) complications are:
- Infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Peritonitis.
- Abscess.
- Perihepatitis.
- There is salpingitis, which leads to infertility.
- There may be gonococcal vulvovaginitis.
- There may be bartholinitis.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) complications are:
- In male:
- Epididymis-orchitis.
- There may be cystitis.
- There may be prostatitis.
- There may be a urethral stricture.
- In the untreated mother, newborn babies can have Ophthalmia neonatorum (gonococcal conjunctivitis).
- There may be septicemia, arthritis, and meningitis due to the spread through the blood.
- Complications in both males and females:
- There may be gonococcal bacteremia, which leads to fever, joint pain, and skin lesions.
- Pericarditis, meningitis, and endocarditis are rare and are the complication of bacteremia.
- Septic arthritis.
- Gonococcal conjunctivitis.
- Complications in newborn babies:
- Ophthalmia neonatorum occurs on the first or second day of life and can damage the cornea, leading to blindness.
How will you diagnose Neisseria Gonorrhoeae?
- In males, in the case of urethritis, there is urethral discharge. Make the smear from the urethral discharge.
- Now stain with gram stain, which will show gram-negative intracellular diplococci.
- The urethral smear is diagnostic and very specific.
- In the male, ask the patient to squeeze the penis to get a good amount of material.
- The patient can apply the material directly on the slide.
- Females can make a cervical smear and do the culture.
- Endocervical smears are positive in 50% of the cases.
- Make a smear for gram stain and do the culture on Thayer-Martin media (gold standard) simultaneously before starting the antibiotics.
- Swab smears are taken from:
- Urethra.
- Endocervical canal.
- Anal canal.
- Pharynx.
- Smears may be tested by a fluorescent antibody.
- When there is no discharge, insert the swab into the urethra up to 2 cm and gently rotate.
- Endocervical specimens can be taken under direct vision using a speculum.
- Other sites for the swab are the pharynx, anorectal area, blood, CSF, and synovial fluid.
- Ultimately, it can confirm the diagnosis by culture, and these bacteria need nutrient-rich selective agar media (Thayer-Martin).
- Culture needs 48 hours to form colonies.
- It can take conjunctival swabs in infants who have conjunctivitis.
- Blood and synovial fluid may be taken in case of arthritis.
- Gram-stained smears:
- Smear is positive when you find intracellular gram-negative diplococci.
- Extracellular organisms are not diagnostic.
- Extracellular gram-negative diplococci are not confirmatory.
- Smears are only 50% positive in asymptomatic patients. These patients must have the culture of the sample.
- The smear becomes negative within a few hours of starting the antibiotics.
- In females, gram stain smears of the endocervical site are 45% to 65% positive.
- Smears from the vagina, oropharynx, and anal canal are not recommended.
- Urethral smears are >95% positive in symptomatic males.
- Smear is positive when you find intracellular gram-negative diplococci.
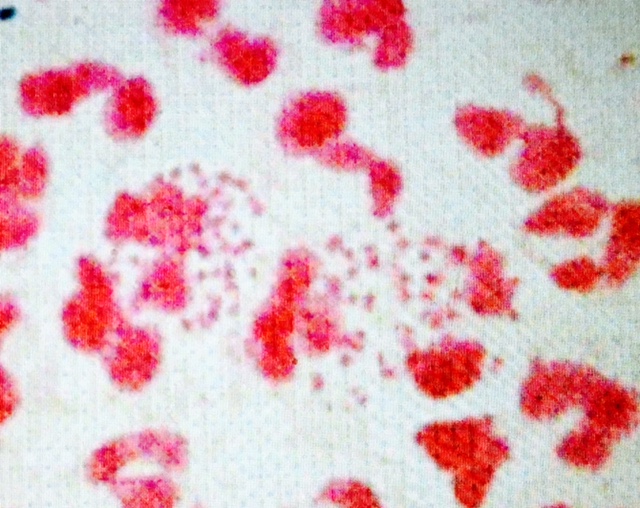
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae are intracellular bacteria (gram-negative)
- Culture:
- It is done to supplement and confirm the diagnosis of gonorrhea.
- Culture is done on special media, such as Thayer-Martin solid media.
- Take a culture sample before starting the antibiotics.
- The endocervical canal is the best site for the culture and is 82% to 92% positive.
- Rectal cultures are 30% to 50% positive. These are positive in homosexual cases.
- DNA probe tests are highly sensitive and specific.
- DNA amplification by PCR is good for testing. It can be done on urine and swab specimens.
How will you treat Neisseria Gonorrhoeae?
Sensitivity to antibiotics:
- These bacteria are sensitive to penicillin, ampicillin, tetracycline, macrolides, cefuroxime, and ciprofloxacin.
- Give a single oral dose of Amoxycillin or ampicillin.
- In 2% of the cases, gonorrhea is resistant to penicillin.
- Give probenecid to delay the excretion of medicine.
- Or a single dose of Ceftriaxone 250 mg I/M.
- Or a single dose of Norfloxacin 800 mg.
- Ciprofloxacin is given when an infection is complicated with Chlamydia infection.
- Erythromycin is given to pregnant ladies and children.
- The extragenital infection needs treatment for 5 to 7 days.
- Penicillin-resistant gonorrhea is treated with cefuroxime, cefotaxime, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, or aztreonam.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: How to diagnose gonorrhea?
Question 2: What is the special media for the growth of N. gonococci?