Estrogens = Estrone E1, Estradiol E2, Estriol E3
Estrogens
What sample is needed for Estrogens?
- It is done on the patient’s serum, which is separated immediately.
- It can be stored at 2 to 8 °C for 2 days in a glass test tube.
- Get a sample regarding the menstrual cycle.
What are the indications for estrogen?
- Estrogen level is estimated to assess sexual maturity.
- To assess menstrual problems.
- To assess fertility problems.
- In males to assess the gynecomastia and feminization syndrome.
- In pregnant women, assess fetal health.
- This can be done as a tumor marker in the hormone estrogen-producing tumors.
How will you describe the pathophysiology of estrogens?
Estrogen
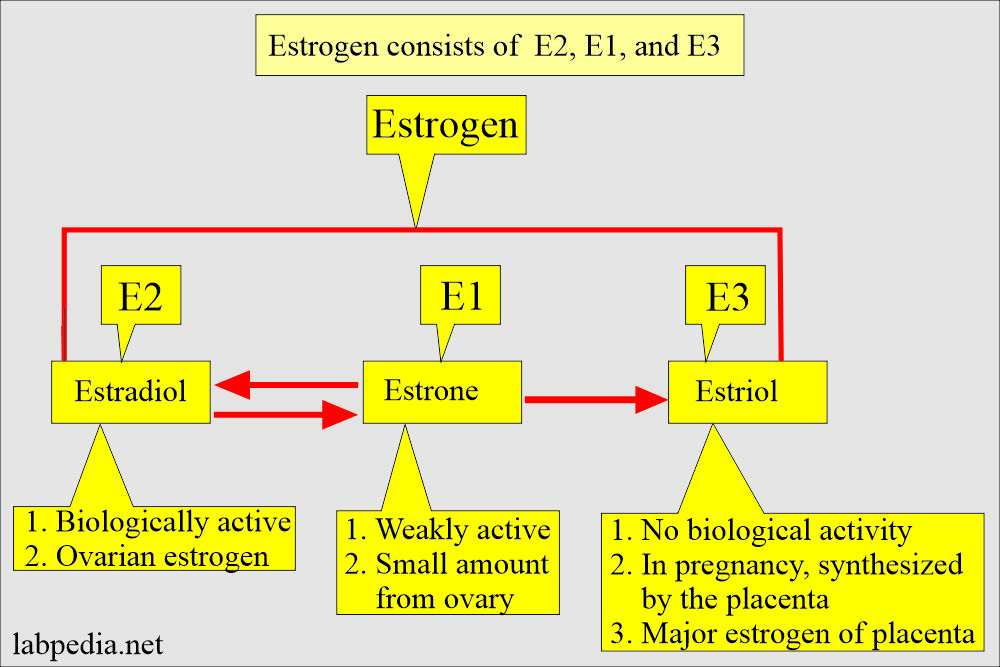
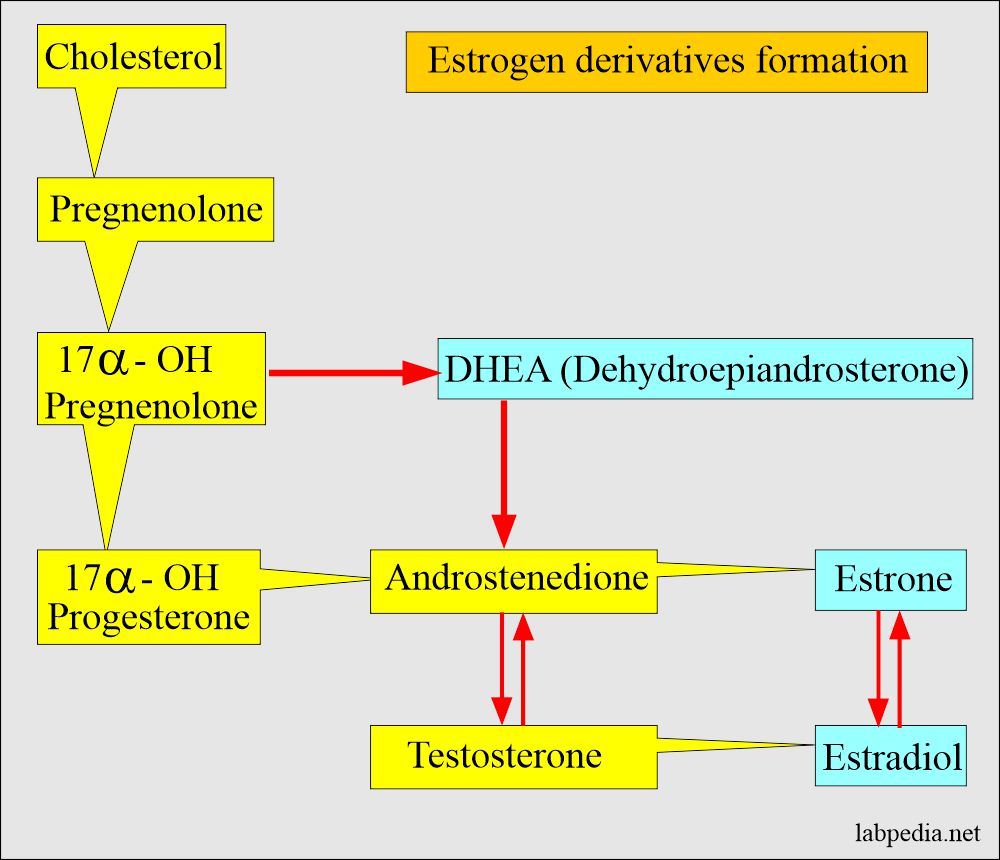
- More than 20 estrogens are identified, but only three have clinical significance, and these are:
- Estrone (E1).
- Estradiol (E2). This is predominantly ovarian estrogen.
- Estriol (E3).
Estrogen types and synthesize sites
- Estrogen consists of C18 steroids. At the same time, progesterone is a C21 steroid.
- All of these estrogens are derived from androgenic precursors like DHEA and androstenedione. The adrenal cortex, ovaries, and testis synthesize these hormones.
- Estrogens are the sex hormone responsible for the following:
- The development and maintenance of female sex organs.
- Female secondary sex characters.
-
Estradiol (E2)
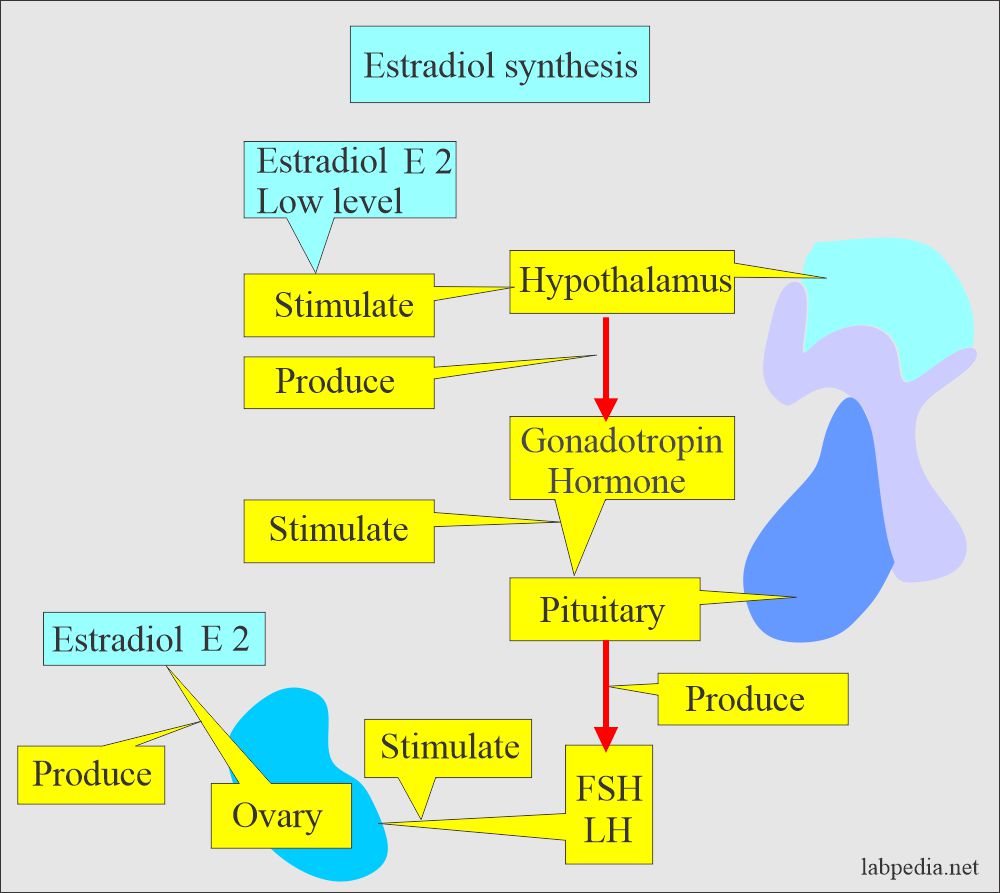
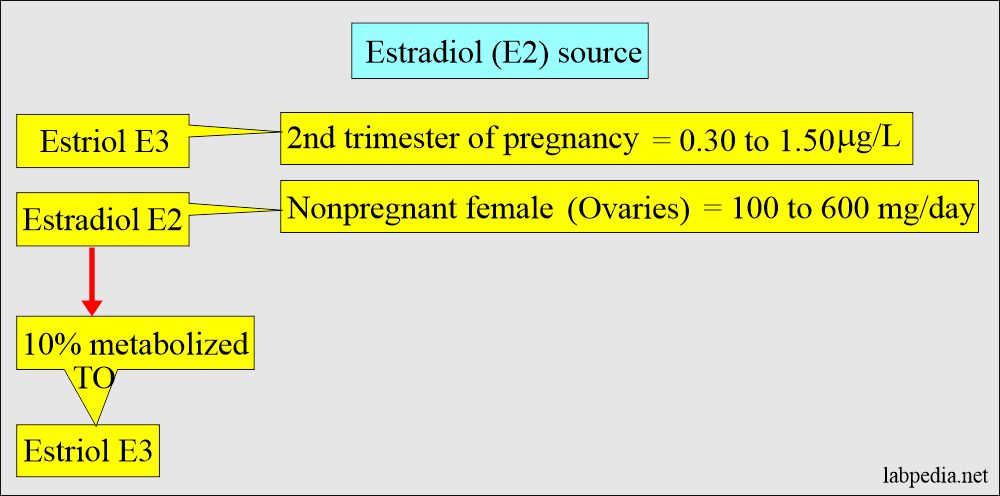
- The most potent estrogen is estradiol (E2), secreted by the ovaries. Its measurement is sufficient to evaluate ovarian function.
- Ovaries lack 21-hydroxylase and 11-β-hydroxylase, so they can not produce glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids like the adrenal cortex.
- Human ovaries produce sex steroids, estrogen, progesterone, and androgens.
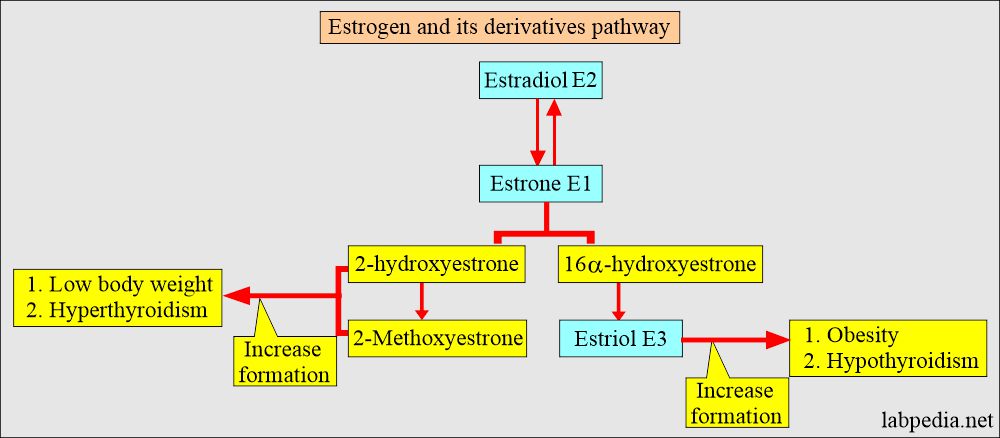
- Estrogen’s main site for inactivation in the liver.
- The main biochemical reactions are hydroxylation, oxidation, and methylation.
What are the functions of the estrogen hormones?
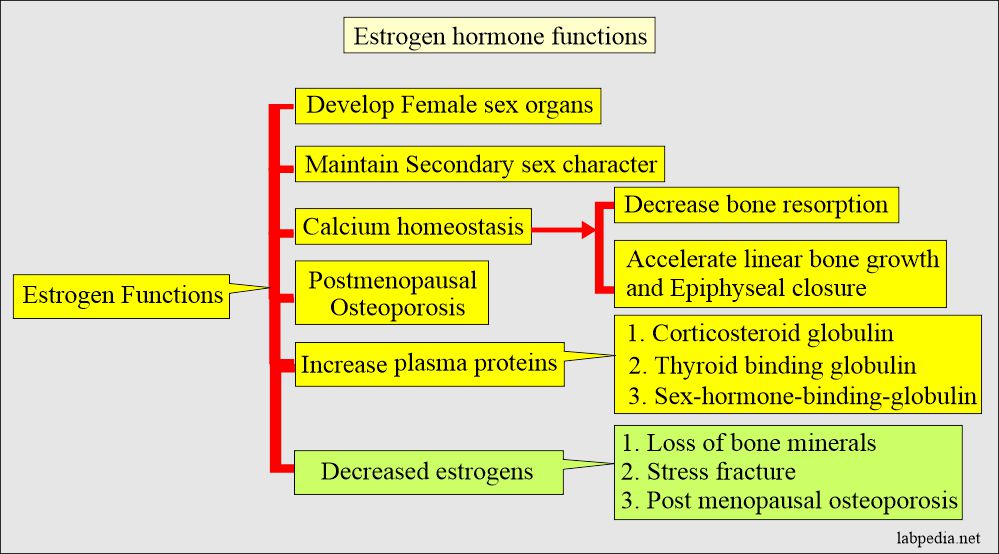
- It develops and maintains the female sex organs.
- It develops secondary sex characters.
- It regulates the menstrual cycle (with the help of progesterone).
- Maintain breast and uterus growth.
- It maintains pregnancy.
- It also helps calcium homeostasis and has a beneficial effect on bone.
- It also accelerates linear bone growth and results in epiphyseal closure.
What will be the effect of Estrogen Depletion?
- Loss of bone mineral contents.
- There are increased stress fractures.
- There is postmenopausal osteoporosis.
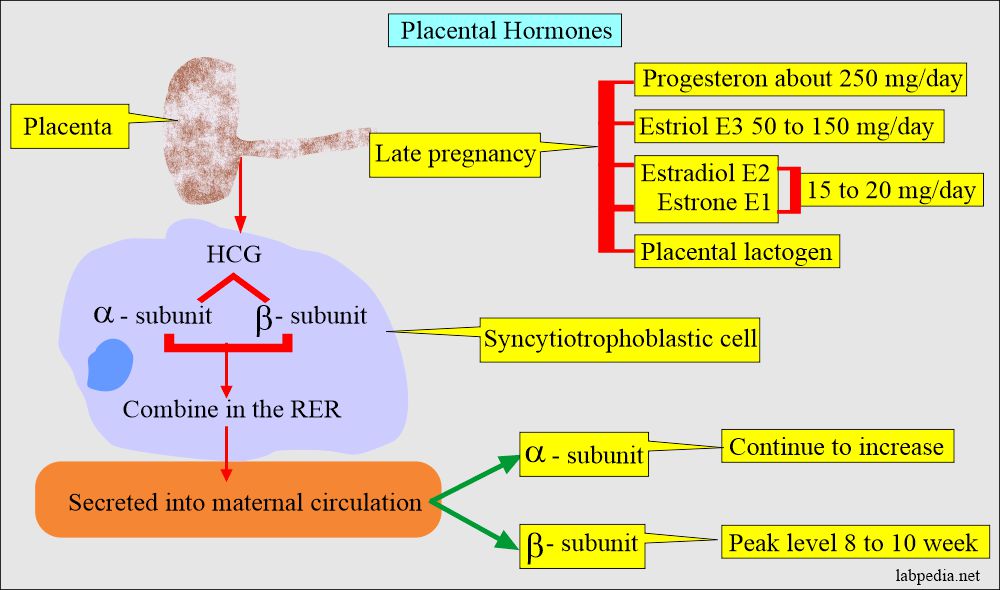
What is the source of estrogen secretion?
- The main source of estrogen in pregnant women is the placenta, which is in mg. This is mainly the estriol.
- The main source in non-pregnant women is the ovary in µg quantity. This is mainly estradiol.
- Ovarian Follicles.
- Corpus luteum from the ovary.
- Placenta during pregnancy.
- A minute amount is produced from:
- Adrenal glands.
- Testes.
- Estradiol and progesterone are the main secretory products of the ovary.
Estradiol (E2)
- It is a more potent hormone and is predominantly produced in the ovary. It exists in a reversible state with estrone.
- Estrone has a weaker biological function.
- The final product is estriol (E3), a steroid without biological activity.
- E2 is produced exclusively by the ovary; its measurement is often considered sufficient to evaluate ovarian function.
- The low estradiol level stimulates the hypothalamus to produce a gonadotropin hormone-releasing factor.
- These hormones stimulate the pituitary to produce a Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
- These two hormones (FSH and LH) stimulate the ovary to produce E2, which will provide the peak during the ovulatory phase.
How is Estradiol transported in blood?
- 97% of the estradiol E2 in the blood is bound to plasma proteins.
- It has a high affinity and is specifically mainly bound to sex hormone-binding globulins (SHBG).
- Nonspecifically bound to albumin.
- SHBG increases by the estrogens, so these are higher in females than males.
What is the significance of Estradiol (E2)?
- Menstrual and fertility problems.
- Menopausal status.
- Gynecomastia.
- Sexual maturity.
- Feminization syndrome.
- As a tumor marker of the ovary.
Estrone E1
- The ovary produces in small quantities.
- It is produced directly from androstenedione, mostly in the peripheral tissues.
- The plasma estrone level is an indicator of estradiol production because this is an end product of estradiol metabolism.
- This is the major hormone after menopause.
Estriol E3
- The metabolism of estradiol or estrone forms Estriol in nonpregnant women.
- Estriol is the major hormone in pregnant women.
- Estriol has no hormonal activity.
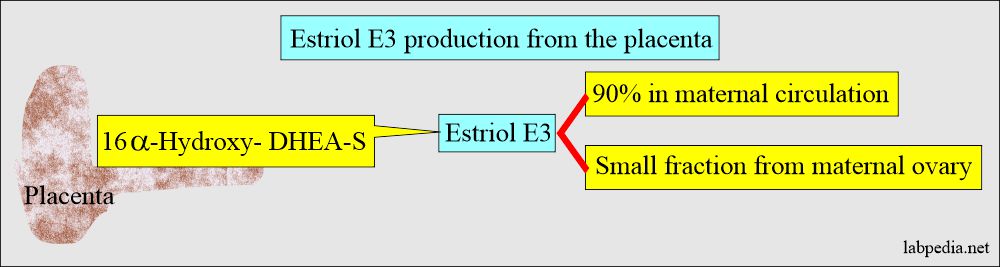
- It is produced in large quantities in the last trimester of pregnancy by the placental conversion of the fetal adrenal steroids, synthesized by DHEA derived from the fetal adrenal glands.
- In pregnancy, it is formed by the placental tissue and is a major component.
- Estriol E3 is produced from the placenta from the estrogen precursors. The placenta may produce some estradiol.
- Excretion of Estriol E3 in pregnancy increases around the 8th week of gestation and continues to rise shortly before the delivery.
What is the significance of Estriol (E3)?
- Serial urine and blood estriol estimation assess placental function and fetal maturity in high-risk pregnancy.
- The concentration of unconjugated E3 in the third pregnancy is from 5 to 40 ng/mL, while the total E3 is 40 to 500 ng/mL.
- This estimation on three occasions gives the idea about fetal well-being.
- It tells fetal well-being means placenta-fetus-viability.
- A sudden drop in the level of estriol in the last trimester of the pregnancy is a signal for fetal-placental abnormality.
- The measurement of secreted estriol is important for estrogen: Estrogen and its derivatives pathway.
- Decreasing values indicate fetoplacental deterioration.
- Serial studies usually start at 28 to 30 weeks of gestation and are repeated weekly.
- E3 values are taken for three consecutive days at the same time. If there is a decrease of more than 30%, then there is a possibility of danger to the fetus.
- The value of unconjugated E3 is more reliable than the total E3.
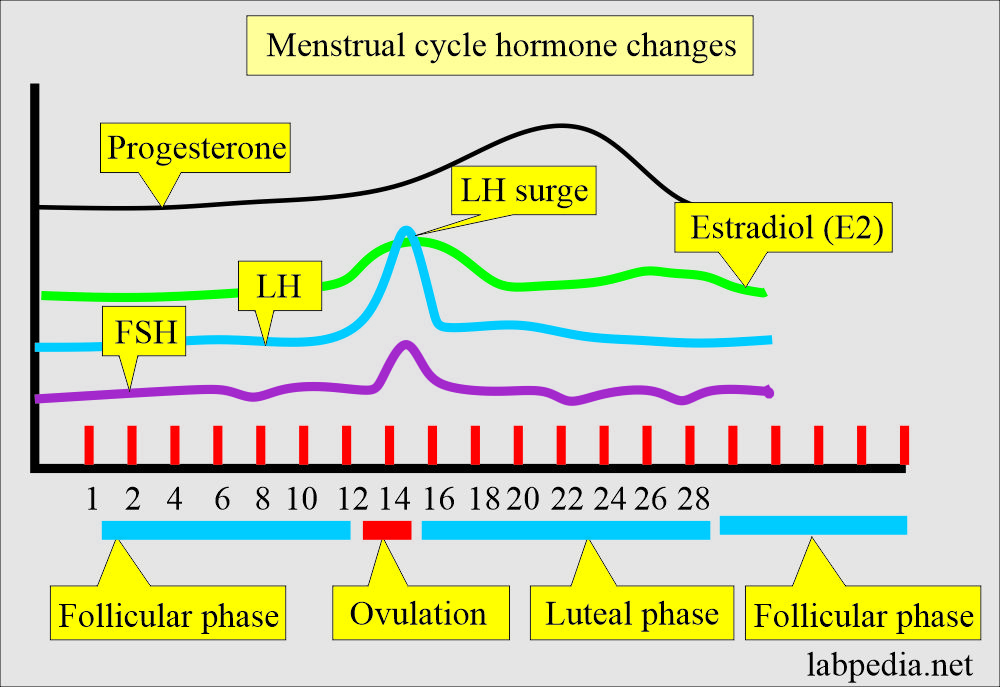
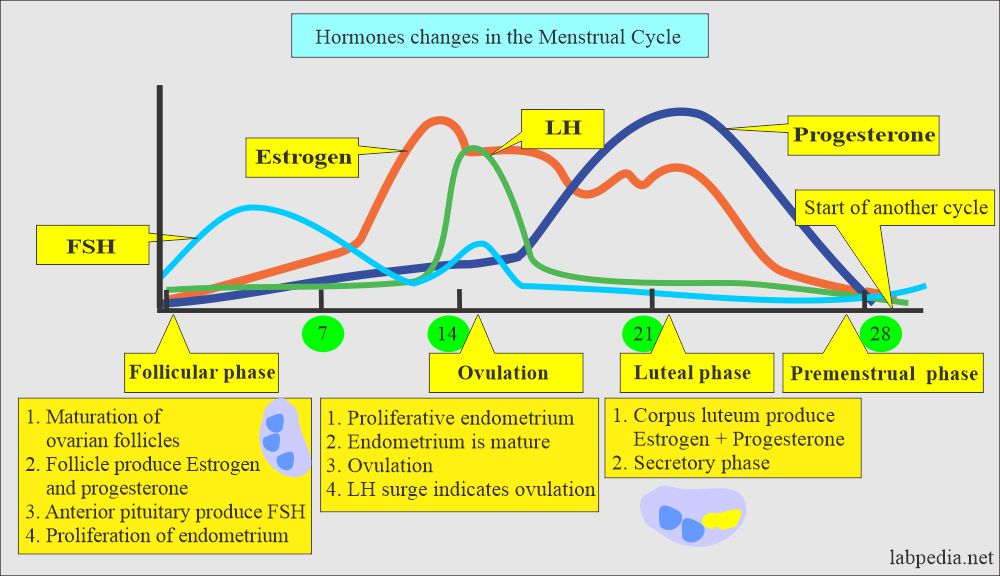
Menstrual cycle
How will you define the menstrual cycle?
- A menstrual cycle begins when a female gets her period or menstruates.
- This is the monthly shedding of the uterus lining.
- Menstrual blood is partly blood and partly tissue from the inside of the uterus.
- It enters from the uterus to the cervix and is then excreted from the vagina.
- Menstruation is dependent upon the hormones from the pituitary glands and partly from the ovary.
- Menstruation makes the uterus ready for implantation of the fertilized ovum.
- The menstrual cycle varies from 21 to 35 days and still will be normal.
- This bleeding phase lasts 3 to 7 days. But most ladies have three days of bleeding.
Follicular phase:
- A rapid rise in estrogen occurs immediately before ovulation and appears to stimulate LH secretion from the anterior pituitary glands.
- The ovarian follicle grows and produces estrogens.
Ovulatory phase:
- It is just before ovulation; there is a dramatic increase in estrogen.
- Ovulation is the beginning of the luteal or secretory phase.
- The ovarian follicle transforms into the corpus luteum.
- LH from the anterior pituitary glands stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone, which will lead to the secretory phase.
- If conception occurs, then nutrient-laden endometrium is ready for implantation.
- This increased estrogen will trigger the hypothalamus and give LH a surge.
- LH surge is a good indicator of ovulation. This occurs 24 to 36 hours before the ovulation and peaks 10 to 12 hours before the ovulation.
The luteal phase:
- It is the last half of the menstrual cycle when there is increased production of progesterone and estrogen from the corpus luteum.
The menstrual phase:
- It is without estrogen and progesterone, endometrium enters the ischemic phase of the menstrual phase.
- This makes the beginning of another cycle.
The menopausal phase:
- It is when the ovary cannot produce enough amount of estrogen.
- Estradiol is the most active of endogenous estrogens.
- This test is of value with an evaluation of other gonadotropins for evaluating menstrual and fertility problems in adult females.
- Measurement is also helpful in evaluating gynecomastia or feminization states in estrogen-producing tumors.
- This also helps in evaluating menstrual irregularities and sexual maturity in females.
What are the Normal values of various estrogen?
Source 2
Estradiol E2 (Unconjugated)
| Sex | Serum (Blood) pg/ mL | Urine mcg /24 hours |
| Adult male | 10 to 50 | 0 to 6 |
| Adult female | ||
| Early Follicular phase | 20 to 150 | |
| Late Follicular phase | 40 to 350 | 1 to 13 |
| Mid-cycle phase peak | 150 to 750 | 4 to 14 |
| Luteal phase | 30 to 450 | 1 to 17 |
| Postmenopausal | ≤20 | 0 to 4 |
| Children under 10 years | <15 | 0 to 6 |
Another source
Estriol E 3 (Free, unconjugated) |
ng/mL |
| Adult male | <2.0 |
| Nonpregnant female | <2.0 |
| 34 weeks of pregnancy | 5.3 to 18.3 |
| 36 weeks of pregnancy | 8.2 to 28.1 |
| 38 weeks of gestation | 8.6 to 38.0 |
| 39 weeks of pregnancy | 7.2 to 34.3 |
| 40 weeks of pregnancy | 9.6 to 28.9 |
Estriol E3 Total |
|
| 28 to 30 weeks of pregnancy | 38 to 140 |
| 34 weeks of pregnancy | 45 to 260 |
| 36 weeks of pregnancy | 48 to 350 |
| 38 weeks of pregnancy | 59 to 570 |
| 40 weeks of pregnancy | 95 to 460 |
Estrone E1 |
|
| Adult male | 1.5 to 6.5 |
| Early follicular phase | 1.5 to 15 |
| Late follicular phase | 10 to 20 |
| Luteal phase | 1.5 to 2 |
| Postmenopausal | 1.5 to 5.5 |
Estrogens Total |
pg/mL |
| Adult male | 20 to 80 |
| Follicular phase | 60 to 200 |
| Luteal phase | 160 to 400 |
| Postmenopausal | <130 |
Urinary E3
- 28 weeks of gestation in normal pregnancy = average 4 mg/day (range 2 to 7 mg/day).
- 32 weeks of gestation in normal pregnancy = 13 mg/day.
- 36 weeks of gestation in normal pregnancy = 18 mg/day.
- 40 weeks of gestation of normal pregnancy = 26 mg/day
Total estrogen serum = Estradiol + Estrone + Estriol.
What are the conditions where estrogens are increased?
- Estrogen-producing tumors.
- Gynecomastia.
- Hepatic cirrhosis.
- Liver necrosis.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Ovarian tumors.
- Precocious puberty.
- Testicular tumor.
- Adrenal tumors.
- Normal pregnancy ( E3 mainly ).
What are the contions where estrogens are decreased?
- Primary and secondary hypogonadism.
- Turner’s syndrome.
- Ovarian agenesis.
- Hypopituitarism.
- Primary and secondary hypogonadism.
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome.
- Menopause.
Question 1: Which estrogen is biologically inactive?
Question 2: Which estrogen is biologically active?


Excellent summary of Estrogen. Very Very useful.
Mehboob Fatteh
Thanks a lot for your encouraging remarks.
Thank you Doctor. The best respect
Thanks.