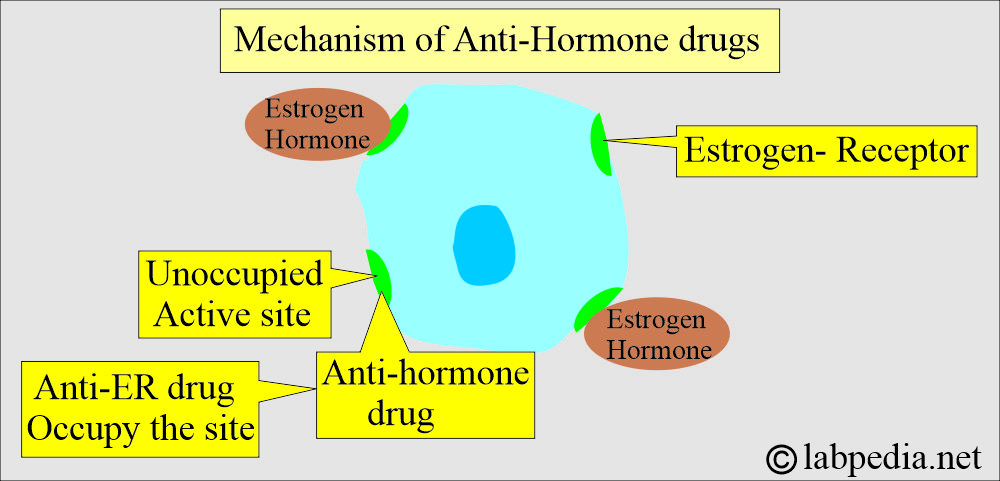
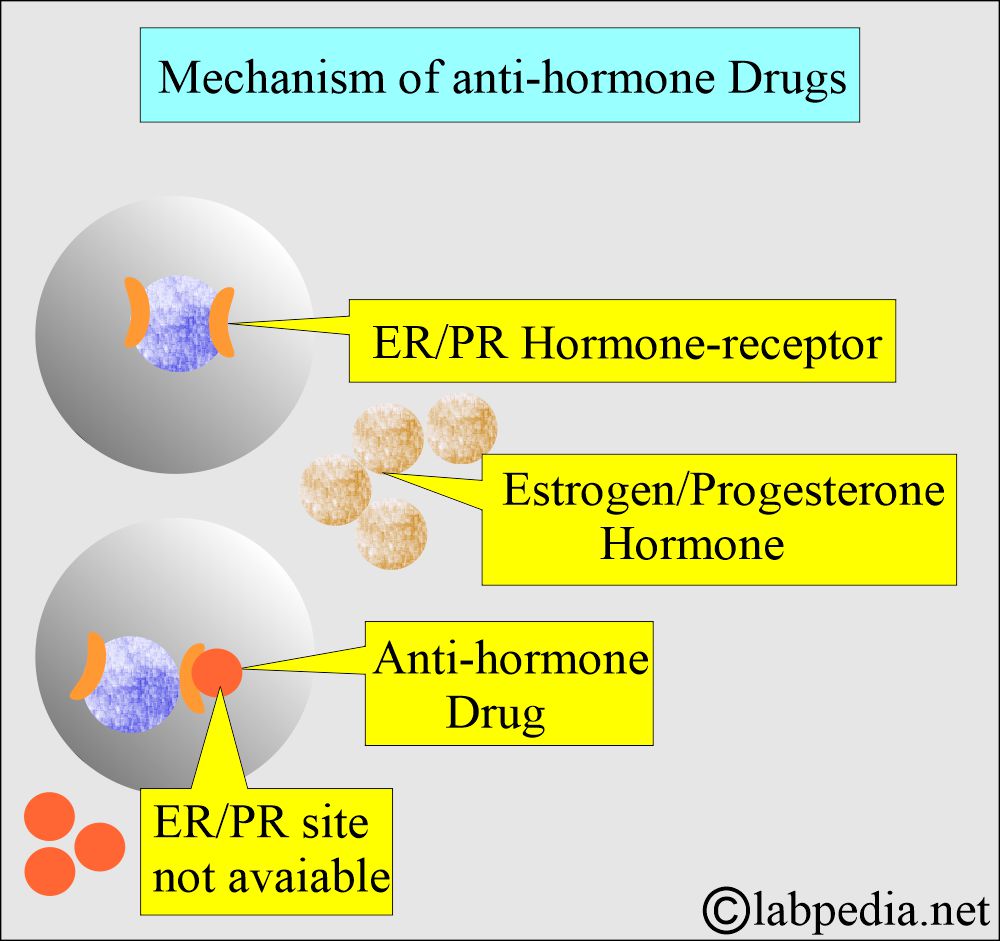
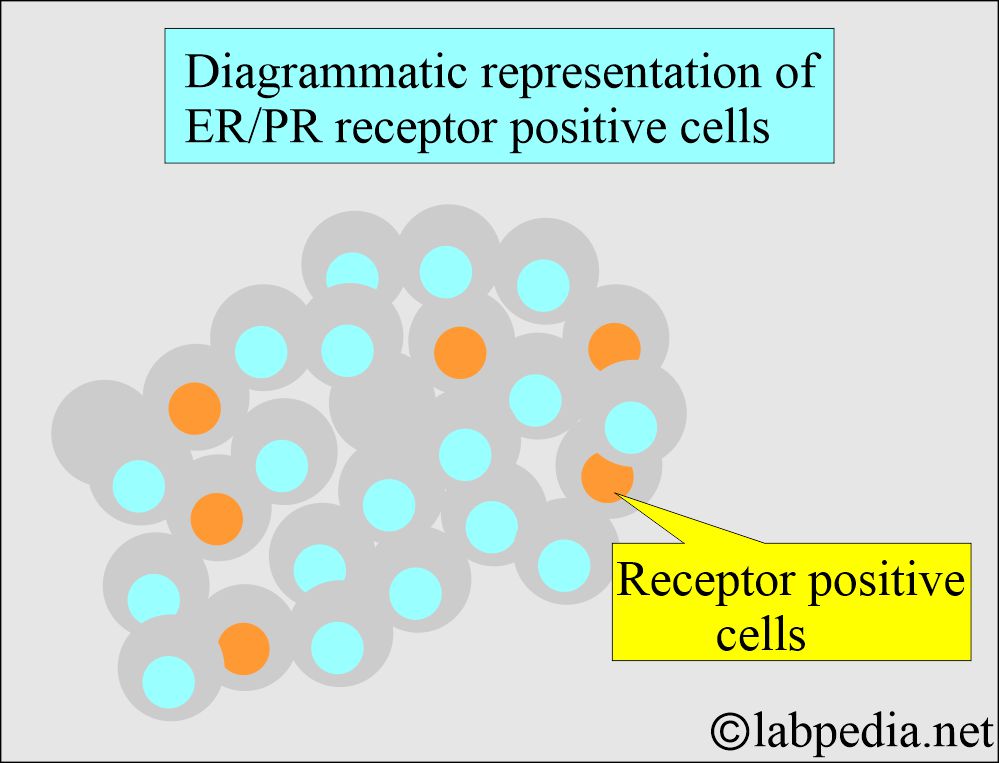
Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors (ER/PR Receptors)
Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors
What samples are needed for Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors?
- This procedure is done on the paraffin blocks of Breast cancer cases.
- This can also be done on fresh biopsy tissue. Place the tissue on ice or in formalin.
- Controls are required and must run.
What are the Indications for Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors?
- Estrogen/progesterone receptors are done on breast cancer to find hormone sensitivity and therapy.
- ER/PR is used as a prognostic factor.
What precautions are needed for Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors?
- Delayed fixation may cause receptor deterioration and yield lower results.
- Hormones should be discontinued before the biopsy.
- Tamoxifen therapy may cause a false-negative result.
- Contraceptives or menopausal estrogen, when given, lower the result.
How will you discuss the Pathophysiology of Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors?
- Biochemical concept:
- ER/PR receptors are cellular proteins with high affinity and great specificity for these hormones.
- These receptor proteins are present in other target organs, such as the uterus, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and breast.
- Estrogen stimulates biochemical processes in target cells that normally contain estrogen receptors; a reduction in blood estrogen levels is expected to reduce the biochemical activity of these cells.
- This is the accepted rationale for using endocrine therapy in females with breast carcinoma.
What is the ER/PR response to anti-hormone therapy?
- ER/PR are the biomarkers of breast cancer. These can be prognostic, predictive of treatment response, or both.
- The higher the ER content positivity, the higher the response rate to endocrine therapy.
- In carcinoma of the breast, 60% of the cases are estrogen receptor-positive.
- Roughly two-thirds of the cases of ER-positive respond to anti-hormone therapy.
- In 95% of the cases, negative ER-receptor fails to respond to anti-hormone therapy.
- Breast cancer ER-positive or PR-positive cells are twice as sensitive to anti-hormonal therapy (70 % response to anti-hormonal treatment).
- ER/PR-negative cases have a 10% response rate.
- ER/PR-positive cases have more disease-free survival.
- Hormone receptor testing should be performed in all cases of breast cancer.
- ER/PR is more favorable in a menopausal group than in younger patients.
How will you define PR- -receptor?
- It is useful for the assay of PR receptors.
- Metastatic cancer with ER and PR receptor-positive tumors has a response rate of 75% to endocrine therapy.
- If the ER-positive and PR-negative tumors have a 40% response rate.
- The only response rate to endocrine therapy and ER-negative, PR-positive patients is 25%.
- In cases with ER and PR negative, the response rate is only 5%.
- The percentage of positive cases among postmenopausal women is higher than among premenopausal women.
What is the Normal report of ER/PR?
- Negative case = <5 % cell stains for receptors.
- Positive case = >5% of the cells stain for receptors.
Another source
ER/PR receptors assay on tissue:
- Negative = <3 fmol/mg cytosol protein.
- Borderline = 3 to 9 fmol/mg cytosol protein.
- Positive = >10 fmol/mg cytosol protein.
How will you describe the positivity of Estrogen/Progesterone Receptors?
- This subjective interpretation depends on the staining intensity and the number of positive cell nuclei.
- Only the cell nuclei staining is considered positive.
- Favorable response >20% cell stain.
- The borderline response is 11% to 20 % of the cell stain.
- The unfavorable response is <10% cell staining.
- ASCO guidelines are:
- Positive for ER/PR if ≥1% of the tumor cell nuclei are immunoreactive.
- Negative ER/PR if <1% of tumor cell nuclei are immunoreactive.
- Allred scoring: This replaced the early scoring system.
- ER-positive tumor cells have >10% positive cells.
- ER-negative tumor cells are 1%-9% positive.
| Score | Positive cells % | Intensity | Intensity score |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
What is the hormone receptor positivity in different patients?
- ER+ = 80% of the cases.
- ER+ PR+ = 65% of the cases.
- ER+ PR– = 13% of the cases.
- ER– PR+ = 2% of the cases.
- ER– PR– = 25% of the cases.
What is the response to anti-hormone therapy?
| ER | PR | Response to hormone therapy |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- >50% of the ER-positive cases respond to chemotherapy like tamoxifen, estrogen, androgens, oophorectomy, and adrenalectomy.
- Positivity increases when PR is positive.
- The advantage is that endocrine (anti-hormonal) therapy with tamoxifen is highly effective and relatively nontoxic. It is more tolerable than other modalities like radiation and chemotherapy.
- The disadvantage is that ER/PR-negative breast cancer cases have no anti-hormone-positive role.
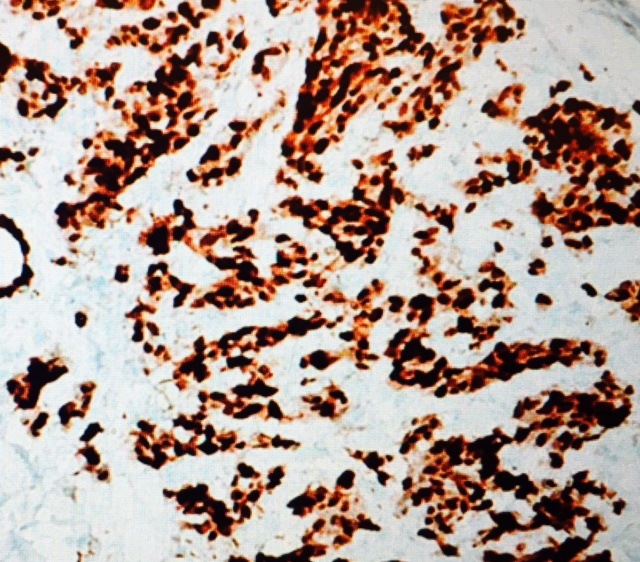
The brown color indicates a positive reaction (ER/PR+)
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the significance of ER/PR positivity?
Question 2: When will you say that ER/PR stain is negative?