Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)
Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)
What sample is needed for Erythropoietin Hormone?
- Take the venous blood.
- Separate the serum as early as possible.
- The serum is stable at room temperature.
What are the Indications for erythropoietin (EP)?
- This test helps to diagnose the cause of anemia.
- This test also helps to differentiate primary from secondary polycythemia.
- It detects the recurrence of EP-producing tumors.
- This can be an indicator for the therapy of EP in patients with renal failure.
What precautions will you take for Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Pregnancy is associated with a raised level.
- Steroids and birth control pills can increase the level.
- Blood transfusion gives reduced EP levels.
- Drugs like ACTH, contraceptive pills, and steroids increase the level.
How will you define Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
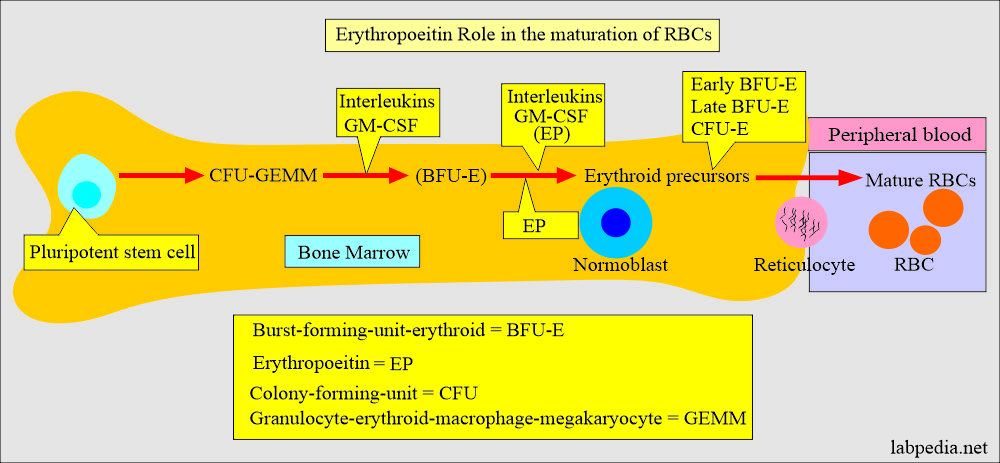
- Erythropoietin (EP) is a glycoprotein hormone that regulates erythropoiesis.
- This is a glycosylated polypeptide of 165 amino acids with a molecular weight of 34 kDa (31,000 daltons; another source says 45).
- It is the major regulator of erythropoiesis.
- It has a plasma half-life of 6 to 9 hours.
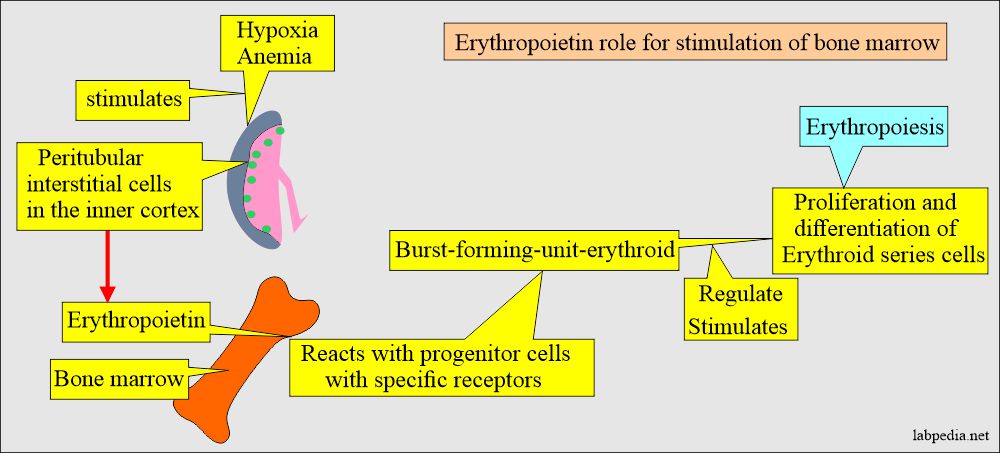
Discuss the Pathophysiology of Erythropoietin Hormone (EP) and production?
- EP is produced in:
- 90% is made in the peritubular interstitial cells in the inner cortex of the kidneys.
- 10% is produced in the liver.
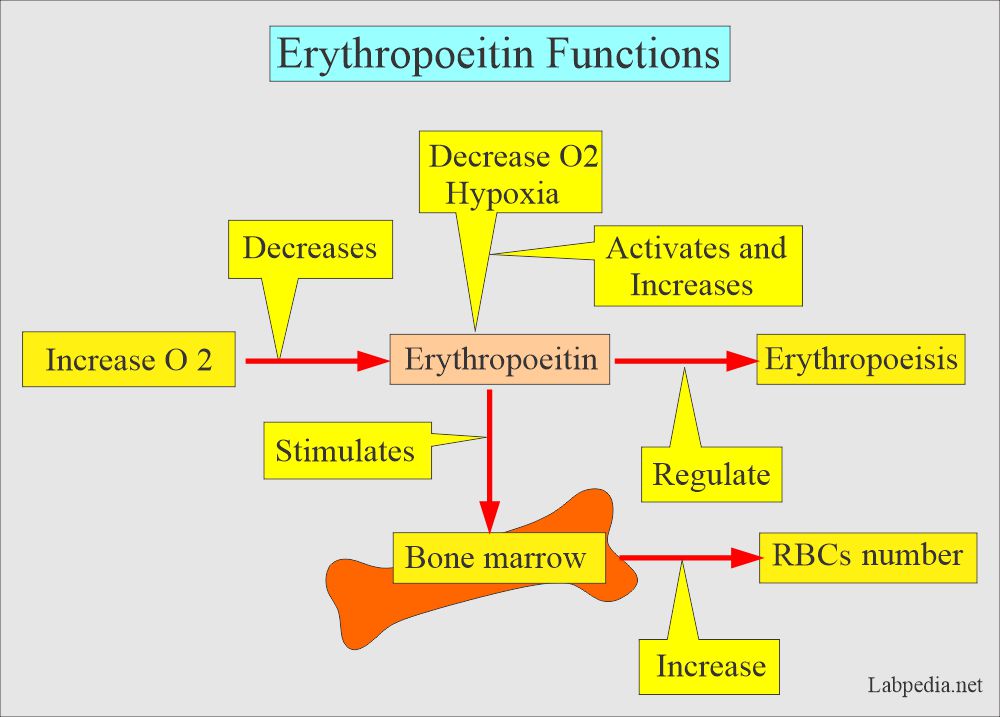
- EP is the stimulus for the bone marrow to increase RBC cell numbers.
- The increased RBC number increases the oxygenation in the kidneys.
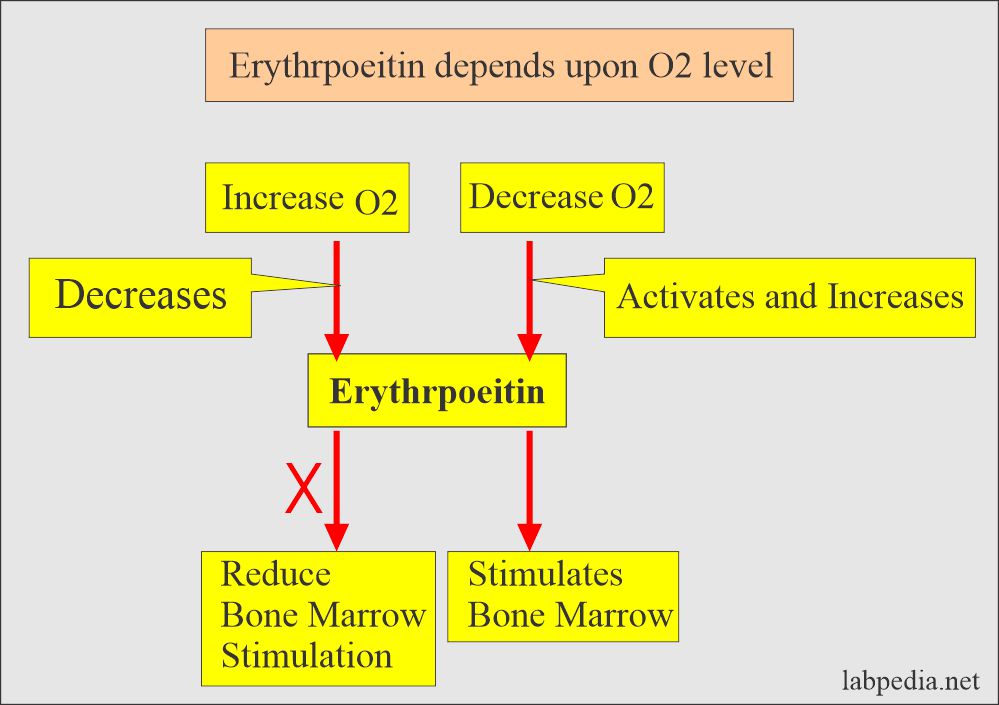
- So, the stimulus for the EP is reduced.
- This feedback mechanism is very sensitive to the oxygen level.
- The stimulus for the activation of the above cells is decreased oxygen, the stimulus for Increased EP production.
- There is a feedback mechanism that increases oxygen and reduces EP production.
- EP is inversely related to red blood cell volume and hematocrit.
What is the significance of Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- EP is given under the following conditions:
- Anemia in the case of chemotherapy patients.
- Athletes abuse this hormone to improve their oxygen-carrying capacity and improve their performance.
What are the stimuli for Erythropoietin Hormone (EP) production?
- Low hemoglobin due to bone marrow failure due to Iron deficiency anemia.
- Or low Hb due to increased destruction of RBCs in case of hemolytic anemia.
- Defective cardiac or pulmonary function.
- Damage to renal circulation affects O2 delivery to the kidney.
- EP is high in EP-producing tumors, like renal cell carcinoma and adrenal gland carcinoma.
- Increased EP level in patients with polycythemia is due to decreased O2 (hypoxemia).
What are the stimuli for low Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Patient with renal diseases or nephrectomy (bilateral) has low EP levels.
- Decreased EP level is seen in a patient with Malignant polycythemia vera.
What is the role of Erythropoietin (EP) in renal failure?
- EP, as recombinant human erythropoietin, is very effective in treating anemia due to chronic renal failure in patients who are on dialysis.
- Polycythemia has elevated EP levels.
- While malignant polycythemia vera has reduced EP levels.
What is the Normal value of Erythropoietin?
Source 1
- Serum = 5 to 36 mU/L
- To convert into SI units x 1.0 = U/L
Source 2
- 5 to 35 IU/L.
Another source
- 3 to 20 mIU/L
What are the conditions leading to Increased levels of Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Megaloblastic anemia.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Myelodysplasia.
- Chemotherapy.
- Pregnancy.
- Secondary polycythemia due to high altitude and COPD.
- AIDs.
- Renal cell carcinoma.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Adrenal carcinoma.
What are the conditions leading to markedly increased levels of Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Erythropoietin-producing tumors:
- Renal adenocarcinoma.
- Renal Cyst.
- Renal transplant rejection.
- Pheochromocytomas.
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Sometimes seen in the ovary, adrenal, testicular, breast, and liver carcinoma.
What are the conditions leading to Decreased Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Multiple myelomas.
- Malignancies.
What are the conditions leading to markedly decreased Erythropoietin Hormone (EP)?
- Polycythemia Vera (primary).
- Autoimmune nephropathy.
- Renal failure and renal diseases.
- After bone marrow transplantation.
What are the conditions for Erythropoietin Hormone (EP) therapy?
- EP is the best drug for treating anemia due to renal diseases.
- This can be given in end-stage kidney disease.
- Anemia of chronic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or malignancies.
- It is given I/V or subcutaneously 3 to 7 times per week.
- Or once every 1 to 2 weeks, depending upon the indication of the patient.
What are the complications of Erythropoietin Hormone (EP) therapy?
- Increased blood pressure.
- Local site injection.
- Increased platelet count.
Question 1: In which condition is erythropoietin given?
Question 2: What is the site of production of the erythropoietin?