Electrolytes:- Part 3 – Electrolytes Panel
Electrolytes Panel
What sample is needed for the Electrolytes Panel?
- We need venous blood to prepare the serum.
- Also, arterial blood is used for some of the parameters.
How will you define electrolytes?
- These are the charged low-molecular-weight molecules present in the plasma and the cytosol.
- Electrolytes are substances that acquire a net positive or negative charge when dissolved in water.
- In an adult, about 60% of the body is water, which contains these electrolytes.
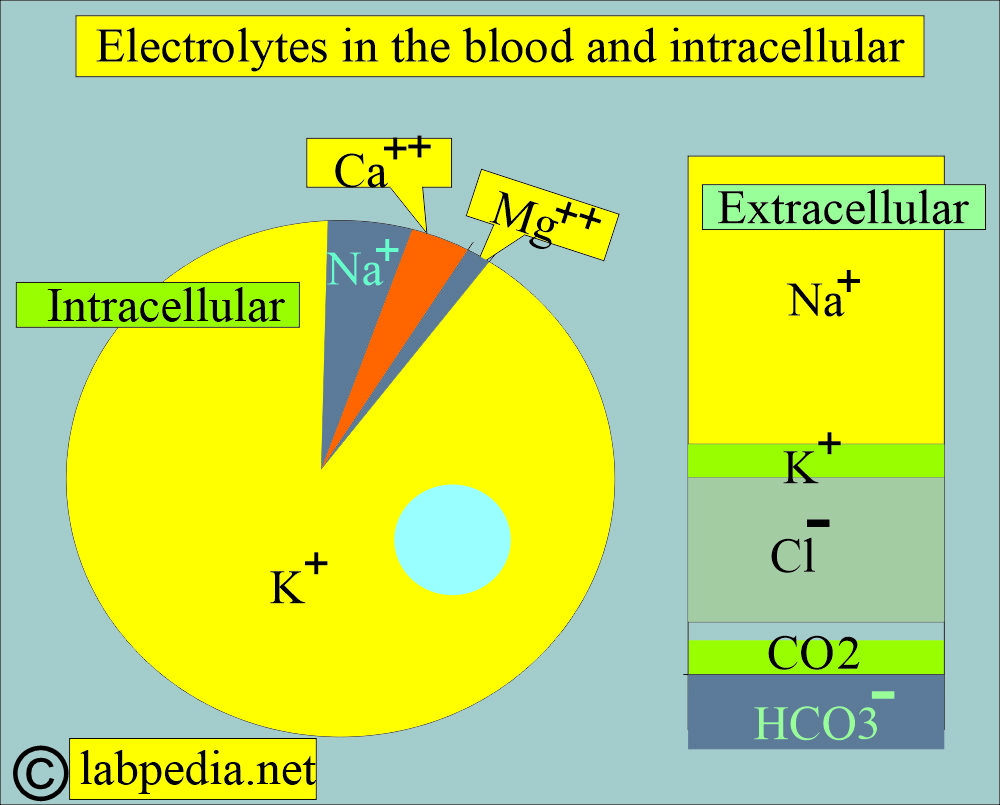
What are the electrolytes present in the blood?
- Sodium.
- Potassium.
- Calcium.
- Magnesium.
- Chloride.
- Bicarbonate.
- Phosphate.
- Lactate.
- Sulfate.
How will you divide Electrolytes?
- Anions are negatively charged ions that move toward the anode.
- Cations are positively charged ions that move toward the cathode.
What are Physiological electrolytes?
- Na+, K+, Ca+, Mg+.
- HCO3–, H2PO3–, HPO42-, SO4–.
- Organic anions are lactate and trace elements.
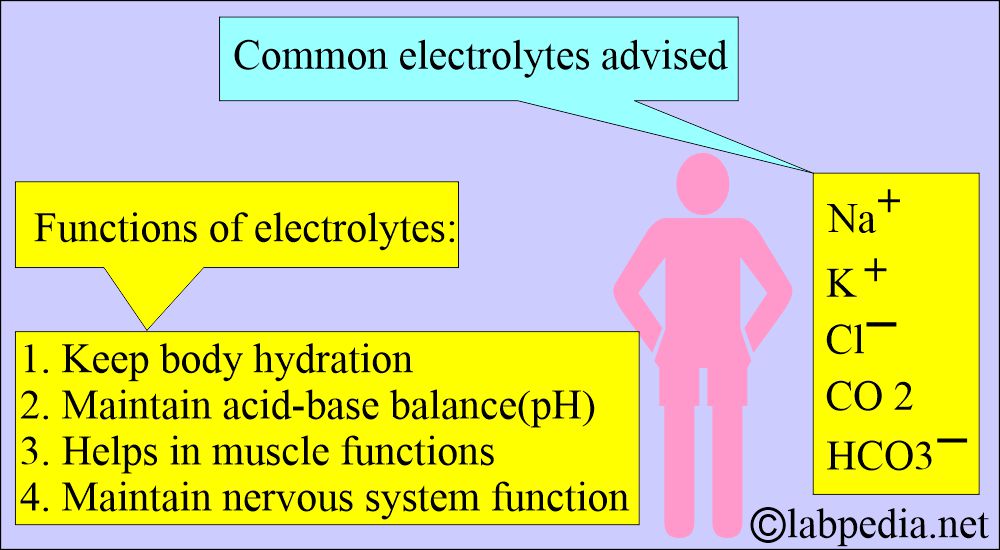
How will you evaluate the electrolyte balance?
- Sodium (Na+).
- Potassium (K+).
- Chloride (Cl–).
- Carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Bicarbonate level (HCO3–).
What are electrolytes’ functions?
- Maintain the osmotic pressure.
- The body is working normally.
- It regulates the heart rhythm.
- Regulate muscle contractions.
- Help the brain function.
- Cells can generate energy.
- Cells can maintain the stability of the cell walls.
- Carbon dioxide and Bicarbonate keep the body’s pH normal.
- It will prevent dehydration.
- Maintain the acid-base balance (body pH).
What are the Panic or critical values of electrolytes?
| Electrolyte | Low value (Signs/Symptoms) | High value (Signs/Symptoms) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the main function of electrolytes?
Question 2: How will you divide electrolytes?