Dubin-Johnson Syndrome, Diagnosis
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
What sample is needed for Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?
- Blood is needed to get the serum.
- A random sample can be taken.
How will you define Dubin-Johnson syndrome?
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJ) is a benign condition and looks like mild viral hepatitis.
- It is characterized by mild recurrent jaundice with hepatomegaly.
Pathophysiology of Dubin-johnson syndrome
- This is a rare genetic autosomal recessive disorder (chromosome 10q24).
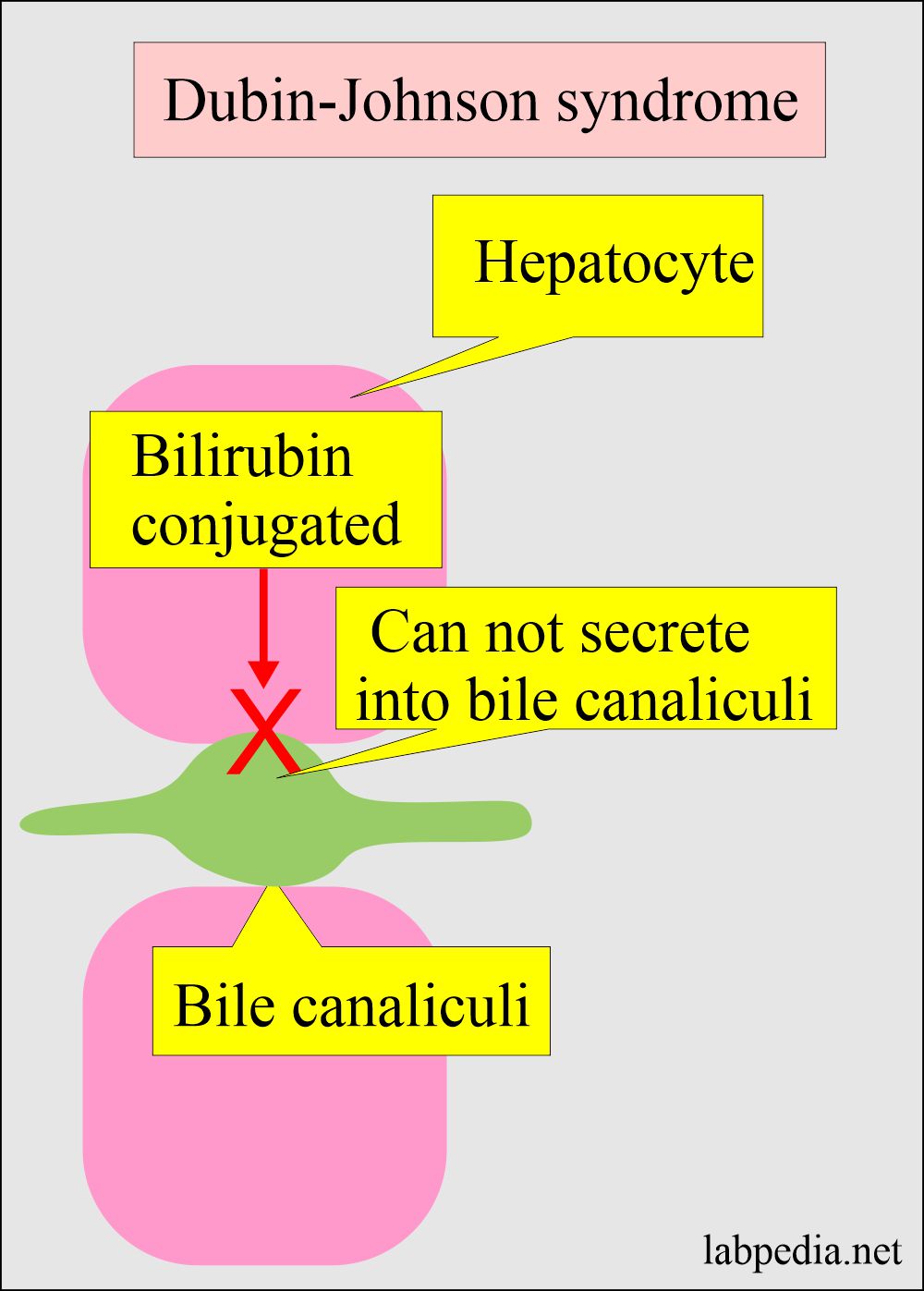
- This is due to the inability to transport bilirubin-diglucuronide through the parenchymal hepatic cells into bile canaliculi.
- This is a defect in the canalicular multispecific organic anion transport associated with increased plasma-conjugated bilirubin.
- There is mild jaundice with a total bilirubin of 2 to 5 mg/dL.
- The liver has intense dark pigmentation due to the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment.
- While the conjugation of bilirubin is regular.
What are the Signs and symptoms of Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?
- There is a yellowness of the eyes and skin due to hyperbilirubinemia.
- Mild jaundice, which may not appear until puberty or adulthood, is the only symptom of Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- The jaundice is nonpruritic.
- Most of the patients are asymptomatic.
What are the Risk factors that increase jaundice?
- Infection.
- Pregnancy.
- Birth control pills.
- Use of alcohol.
- Environmental factors that may affect the liver.
How will you Diagnose Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?
- Serum bilirubin is raised (maybe 3 to 10 mg/ 100 ml). Approximately 50% is indirect bilirubin.
- Serum SGOT and SGPT (ALT, AST) are normal.
- Urine contains bile and urobilinogen.
- A liver biopsy shows plenty of yellow or black pigments in the hepatocytes and gives the liver a black appearance.
- Cholecystography shows the absence of the gallbladder.
Summary of Dubin-Johnson syndrome
| Clinical features | Dubin-johnson syndrome features |
| Incidence | Uncommon |
| Inheritance method | Autosomal recessive (chromosome 10q24) |
| Pathogenesis | There is impaired biliary excretion of conjugated bilirubin |
| Clinical signs and symptoms |
|
| Serum bilirubin |
|
| Liver function tests | Normal except bilirubin |
| Age at the onset of jaundice | Childhood and adolescence |
| BSP test (Impaired excretion of the dye) |
|
| Orla cholecystography | The gallbladder is usually not visualized |
| Liver biopsy |
|
| Prognosis | Usually not bad (Not shorten the life) |
| Treatment | Not needed |
How will you Treat Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?
- This is a benign disease and does not need any specific treatment.
- This patient should be given a warning for follow-up in case of pregnancy, oral contraceptives, and any illness that leads to an increase in the bilirubin level.
- Phenobarbitone was used but is not now recommended.
What is the outcome of Dubon-Johson syndrome?
- The picture is not gloomy and does not shorten the patient’s lifespan.
How will you describe different types of inherited jaundice?
| Clinical parameters | Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia | Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia | |||
| Gilbert’s disease | Type 1 Criggler-Najjar | Type II Criggler-Najjar syndrome | Rotor’s syndrome | Dubon-Jhonson syndrome | |
| Inherited mode | Autosomal dominant | Autosomal recessive | Autosomal dominant | Autosomal recessive | Autosomal recessive |
| Incidence | <7% of the population | Very rare | Uncommon | Rare | Uncommon |
| Age at onset | In adolescence | In infancy |
|
Early adulthood |
|
| Pathogenesis | Glucoronyl transferase enzyme deficiency (GTE) | GTE decreased | Marked decrease | Impaired conj. bilirubin excretion | Impaired cong. bilirubin excretion |
| Bilirubin level |
|
Mainly indirect | Mainly indirect |
|
|
| Clinical signs/symptoms |
|
|
|
Asymptomatic jaundice in young adults | Asymptomatic jaundice |
| Effect of phenobarbitone | Decreased to normal | There is no effect | Marked decrease | —– | —– |
| BSP (Dye excretion) test | May be mildly impaired in <40% of cases | It is absent | _____ | Positive, Initial rapid fall and then rise in 40 to 90 minutes | Positive, Slow clearance and no rise |
| Oral cholecyctography | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | GB usually not visualized |
| Liver biopsy | Normal | —- | —- | No pigments | Characteristic pigments |
| Treatment | Not needed | There is no treatment | Not needed | ||
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the mechanism of Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?
Question 2: What is the color of the liver in Dubin-Johnson Syndrome?


hello,
Im vinoth kambli,
doctor was confirmed for me . i have a dubin johnson syndrome.
problems a matter is im not able to clear medical test for foreighn jobs in any country.
so,please reply….any solutions?
Please read my article.
Hello,
I am Muha,
I have liver function test. I have elevated direct bilirubin (5.9 umol/l) and ALP (311 U/l). All other parameters (ALT, AST, GGT, TP, Albumin and total bilirubin) are normal. Abdominal (liver) ultrasound reveals no abnormalities. I have mild intermittent colic. I am not sure what is going on. My doctor said nothing to worry about. I appreciate if you could help me. Thank you
Have you checked the viral profile (HBV, HCV)? If there is only raised direct bilirubin, then the possibilities are hereditary hyperbilirubinemia. Mostly these are benign conditions. You can try the tab. Phenobarbitone or consult a physician about this drug. It will lower the bilirubin level.
Thank you for your reply. Yes, I have checked for HCV in 2017 and it was negative. I have experienced an elevated ALP since I was 11 (16-year-old now). What is the tab?