Drabkin’s Solution for Hemoglobin, Preparation of Drabkin’s Solution
Drabkin’s Solution for Hemoglobin Estimation
- There are commercially available kits, which make it easy to make the solution.
- When blood runs in the hematology analyzer, these instruments also estimate hemoglobin.
What sample is needed for hemoglobin estimation?
- Whole blood is needed for hemoglobin estimation.
What precautions will you take to keep the Drabkin’s solution?
- Keep the solution in a dark-colored bottle and in the dark to protect it from the light.
- If the solution is cloudy after adding the blood, centrifuge before the reading; this may be due to nonhemolyzed RBCs or globulins.
- Spectrophotometer cells should be fingerprint-free; otherwise, the reading will be high.
- Drabkin’s solution is a pale yellow clear fluid; it should not be used when it is cloudy.
What is the principle of Drabkin’s solution?
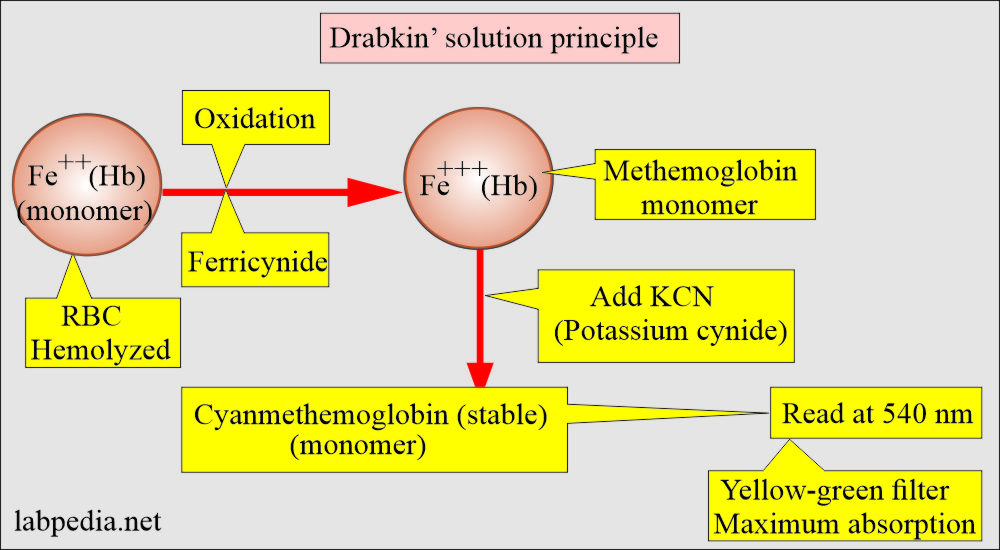
- Whole blood is diluted 1 into 200 dilutions with Drabkin’s solution, containing potassium ferricyanide and potassium cyanide.
- RBCs are hemolyzed by Drabkin’s solution.
- Now hemoglobin is oxidized, and its derivatives, except sulfhemoglobin, form methemoglobin in the presence of alkaline K-ferricyanide.
- The methemoglobin reacts with K-cyanide to form a very stable compound, cyanmethemoglobin, and this complex has maximum absorption at 540 nm.
How will you manually make Drabkin’s solution?
- Hemoglobin (Drabkin’s) solution can be prepared in the laboratory.
- Drabkin’s solution reagents needed are:
- Potassium ferricyanide = 200 mg
- Potassium cyanide = 50 mg
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate = 140 mg
- Non-ionic detergent = 1 ml
- Distal water = Make up to 1000 ml (1 L)
How to estimate hemoglobin by Drabkin’s solution (Procedure)?
- Take 20 microliter of blood + Drabkin 4 mL = 1: 200 dilution.
- OR take 20 microliter of blood + Drabkin 5 mL = 1: 250 dilution.
- Now mix well.
- Read within 6 hours of mixing the blood with Drabkin’s solution.
- Read on a spectrophotometer at filter 540.
- Read against the blank of Drabkin’s solution (Drabkin solution can be used as blank).
- Also, read the standard solution (12 G/dL) with the same dilution as the test sample.
- Read by the spectrophotometer; the reading is called optical density (OD).
Normal hemoglobin:
- Adult male = 14 to 18 g/dL
- Adult female = 12 to 16 g/dL
- 10 years old child = 12 to 14.5 g/dL
- 3 months old infants = 9 to 14 g/dL
- Newborn = 17 to 23 g/dL
Physiological variation of Hb:
- Strenuous physical exercise.
- There is a diurnal variation, with the highest level in the morning and low in the evening.
- High altitude increases the Hb concentration.
False causes of raised Hb:
- Hemoconcentration due to dehydration and burns.
- Immediately after hemorrhage.
- If taken during the I/V infusion, if it contains iron.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the end result of KCN reaction for hemoglobin?.
Question 2: What is the physiological variation in the hemoglobin?



You shows the principle of drabkin solution but not show how we are apply this solution
Dear
As I have understood from your question, that you want the procedure by Drabkin’s solution. It is already given there. Or please explain your question.
I got good news
ok Thanks.
Can we take 2ml reagent and multiple the reading with 20
You have to keep the same dilution, that is very important.
Sir how to measure bilirubin ??
Dear nowadays nobody make reagents themselves. Ready-made kits are available in the market. Definitely you need a lab facility.
what is the function of potassium dihydrogen phosphate in drabkin’s solution ?
This has the buffering action.
Can drabkins reaction work with freeze dried hemoglobin instead?
I think if you thaw the frozen Hb, then try with control. That may work.
What’s the quality control of drabkin solution?
You can run known control of hemoglobin. These known controls are available from various companies.
what is the function of the non-ionic detergent in the drabkins solution ?
Please see the following link for your question.
https://patents.google.com/patent/US4341527A/en
May i ask sir, i read that a source of error when using the Drabkin’s reagent was a possible increase of globulins which can then be fixed using the dihydrogen potassium phosphate – is this true? and if so, how come what’s the principle behind it? Thank you !!
I have given diagrammatically the principle of Drabkin’s solution.
https://labpedia.net/haemoglobin-part-3-hemoglobin-solution-drabkins-solution-preparation/
Can we prepare the standard solution of cyanmethemoglobin process in lab…if it is not available commercially?
You can prepare Drabkin’s solution. I have described the procedure.
sir, what is OD in formula?
OD is the reading by the spectrophotometer, called optical density. Read the article again.
https://labpedia.net/drabkins-solution-for-hemoglobin-estimation/
Sir is Hb levels of 17.4 normal according to Drabkins method sir?
This is a higher limit. Please keep on checking Hemoglobin to rule out the possibility of polycythemia. It would be better to consult a hematologist.
Sir
Can hemoglobin react with potassium thiocyanate? Please
You can use sodium cyanide instead of potassium cyanide.
The procedure for commercially available cyanmethemoglobin standard soln is differ from the above mentioned one…
because if we use commercially available std. soln we should use directly if the soln. is in RT.
You can use a ready-made solution.
Hi, thank you for this useful publication. If I want to measure hemoglobin from plasma that was mixed in Drabkin reagent, would it be suitable to produce a standard by mixing a known quantity of lyophilized hemoglobin in Drabkin reagent? This way, I could build a standard curve with increasing hemoglobin concentrations, am I right?
https://labpedia.net/laboratory-part-1-serum-plasma-preparation-specimen-storage-and-precautions/
Please see this topic and it will answer your question.
https://labpedia.net/laboratory-part-1-serum-plasma-preparation-specimen-storage-and-precautions/
Please see this topic, and it will answer your question.
How to discard Drabkin’s reagent after use
Section 13. Disposal Considerations
In the fume hood, add the Cyanide solution to a solution of 1% Sodium Hydroxide (about 50 mL/g of Cyanide). Household bleach (about 70 mL/g of Cyanide) is
slowly added to the basic Cyanide solution with stirring. When the addition of the bleach is complete, the solution can be tested for the presence of Cyanide
using the Prussian Blue test: to 1 mL of the solution to be tested add 2 drops of freshly prepared 5% aqueous Ferrous Sulfate solution. Boil this mixture for at
least 60 seconds, cool to room temperature, and then add 2 drops of 1% Ferric Chloride solution. The resulting mixture is made acid to litmus with 6 Molar
Hydrochloric Acid (prepared with equal amounts of concentrated Hydrochloric Acid and water ). If Cyanide is present, a deep blue precipitate will form.
(Concentrations of greater than 1 ppm Cyanide can be detected.) If the test is positive, more bleach is added to the Cyanide solution, and the test is repeated.
Continue until no Prussian Blue precipitate is formed. Wash the solution down the drain with excess water. Always dispose of in accordance with local, state
and federal regulations.
Section 14. Transport Information
https://us.vwr.com/assetsvc/asset/en_US/id/8452666/contents
Please read this article.
What can be used instead of potassium dihydrogen phosphate?
Please read this article, and it may help you.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC477205/pdf/jclinpath00098-0110b.pdf
I want to try using actual whole blood with the above method.
Do I need to process the blood in any way before using it?
Can I use chemistry analyser since we have blank, standard and test
Your question is not clear to me. Please explain your question.