Creatinine (Serum Creatinine)
Serum Creatinine
What Sample is needed for serum creatinine?
- This test is done on serum(clotted blood 3-5 ml) or plasma.
- The plasma may be prepared in fluoride or heparin.
- Flouride or heparin are not suitable for the enzymatic methods of creatinine.
- The sample is stable for 24 hours when kept at 4 °C.
- The non-fasting sample is acceptable.
What precautions for serum creatinine are important?
- No preparation is needed, and a random sample can be taken.
- Lipemic and hemolyzed samples give a falsely high level.
- Heparin and fluoride are not good for the enzymatic procedure.
- Excessive exercise and a high meat diet increase the level.
- Drugs may increase the level like gentamicin, cimetidine, chemotherapy (cisplatin),
What is the purpose of the test (Indications) for estimating serum creatinine?
- Creatinine level is done to assess kidney function.
- Creatinine can be advised to see any blood pressure or diabetes effect on the kidney.
- Creatinine is advised to monitor renal diseases.
- Creatinine may be measured in amniotic fluid to assess the gestational (fetal) age and (fetal-maturity index) and cephalosporins.
Definition of creatinine:
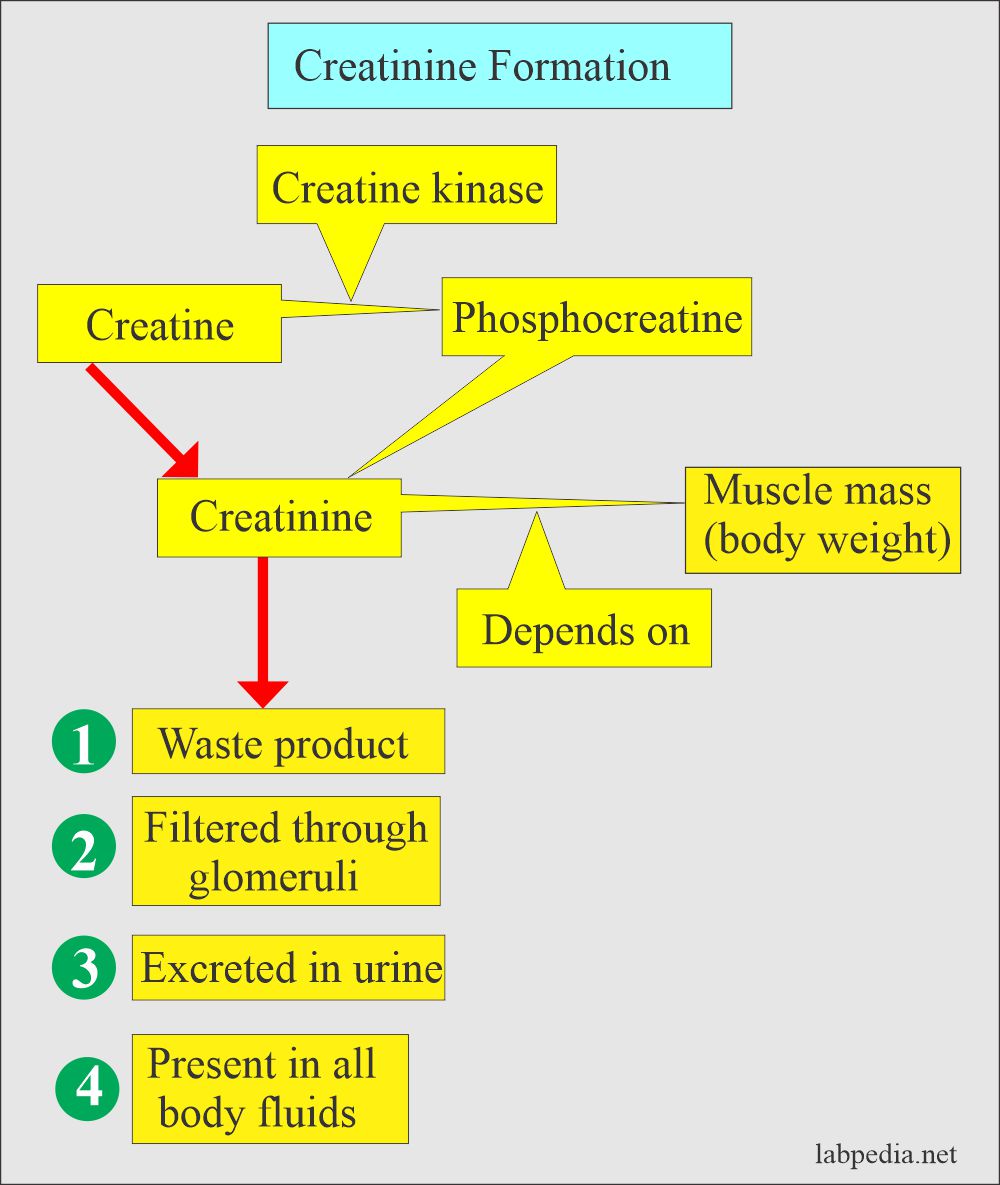
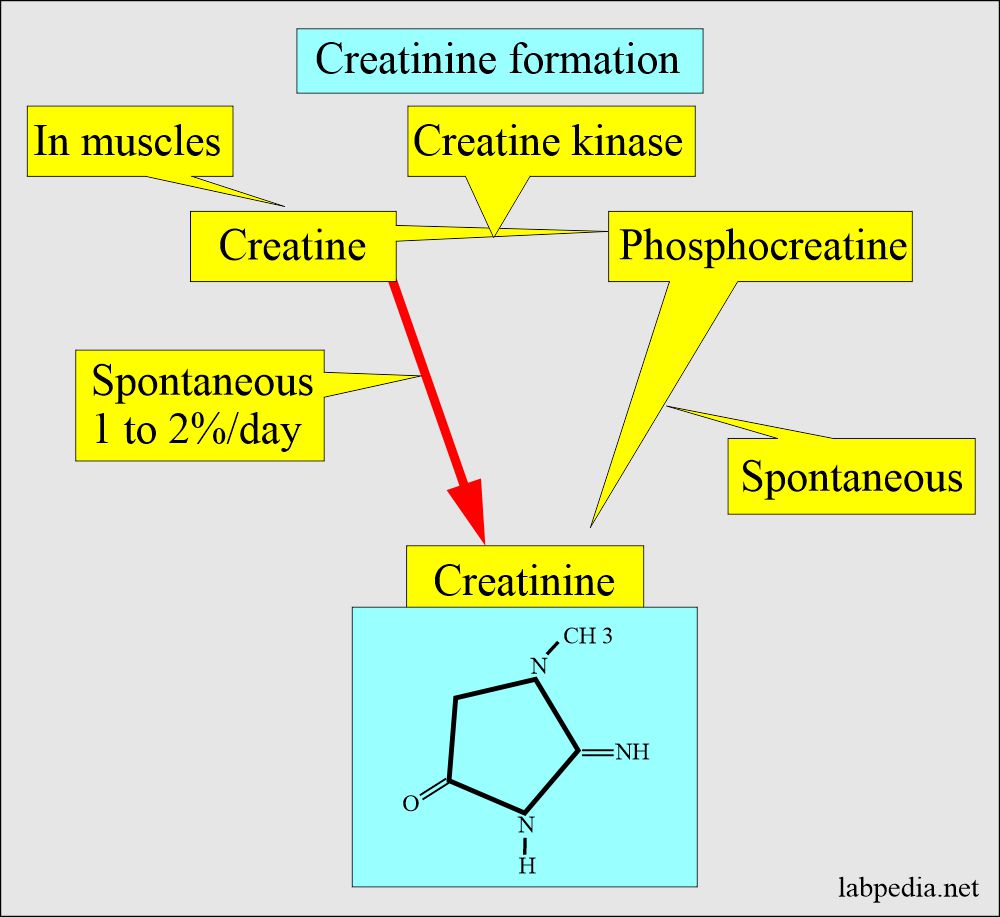
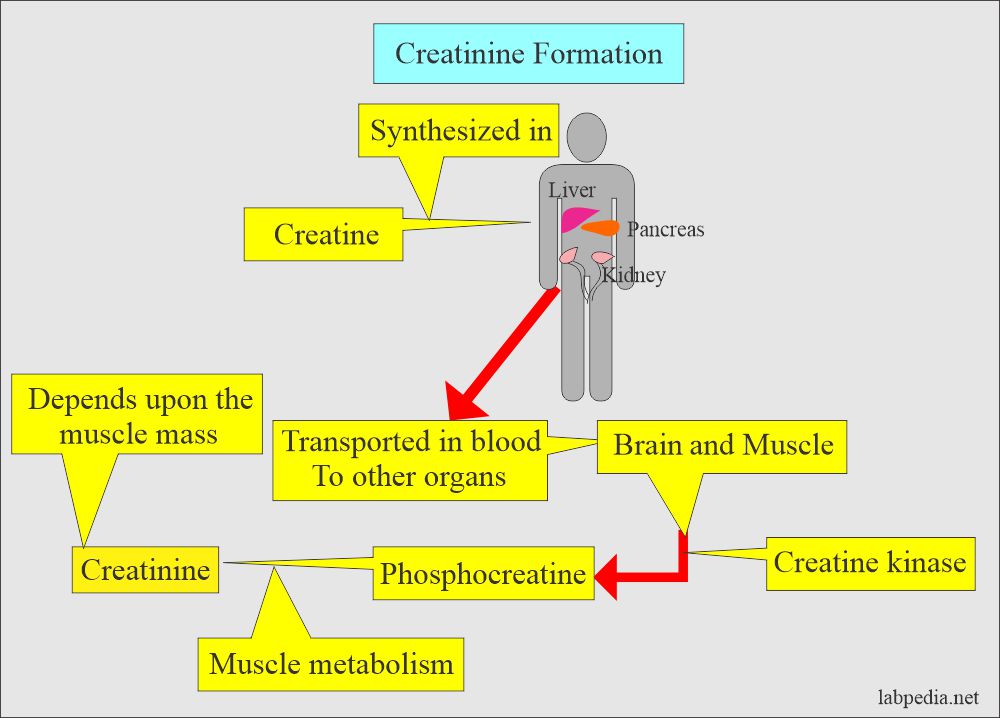
- Creatinine is a waste product formed in the muscles.
- Creatinine in the muscles is formed by the high-energy storage compound creatine phosphate, also called phosphocreatine.
- The above reaction is not reversible, and the creatinine is excreted in the urine.
Pathophysiology of creatinine
- Creatinine is produced by muscle metabolism. It depends upon the body’s muscle mass; the greater the muscle mass, the higher the creatinine in serum and urine.
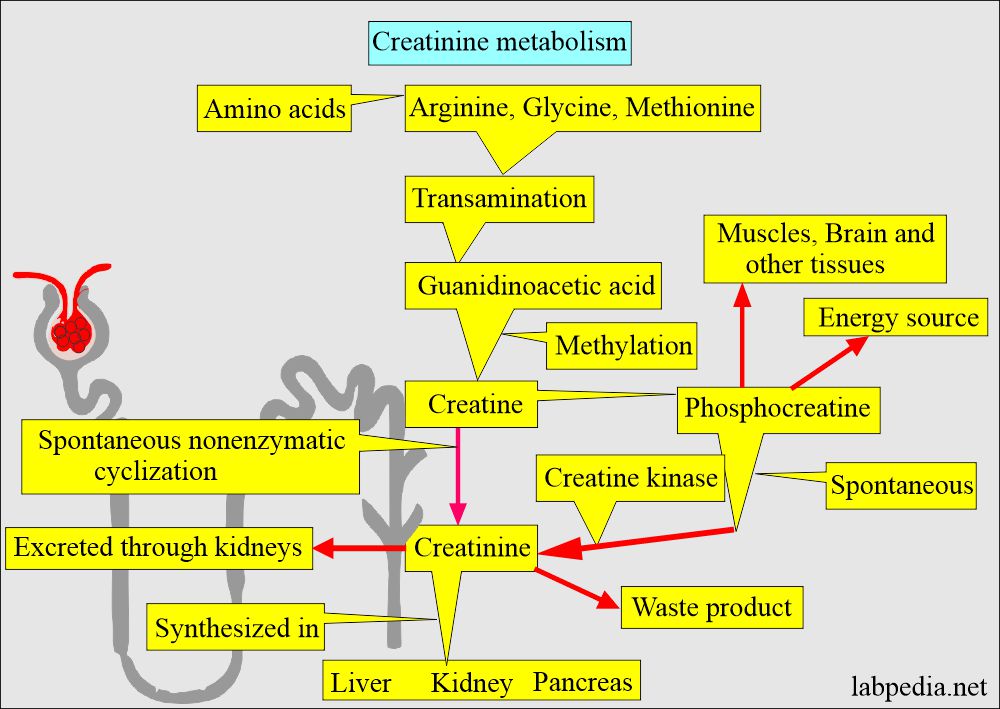
- Creatinine is the end product of the catabolism of creatine phosphate.
- Free creatinine, a waste product of creatine metabolism, is present in all body fluids and secretions.
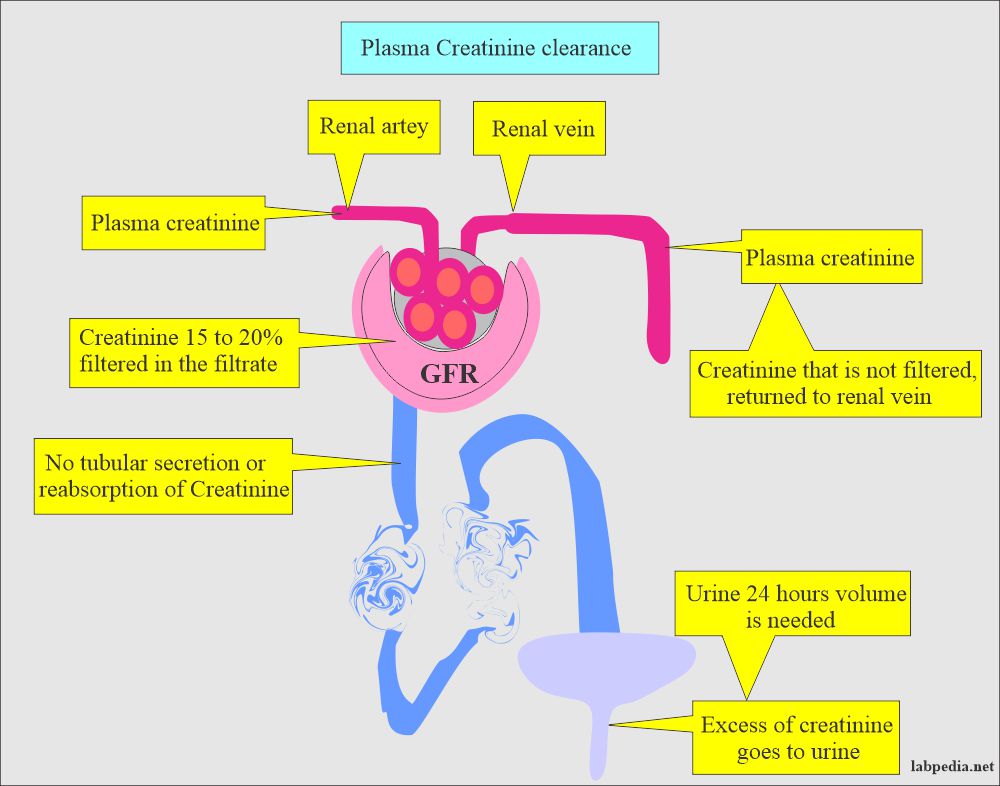
- The glomerulus freely filters it.
- There is diurnal variation when low at 7 AM and high at 7 PM.
- There is a slight increase after the meal and especially after the meat in the diet (20% to 25%) because a small amount is present in the meat.
- There is very little effect on liver function.
- Creatine phosphate is used in the contraction of skeletal muscles by providing energy.
- Creatinine is the waste product formed in the muscles from the high-energy compound creatine phosphate.
- The daily production of creatine and creatinine is dependent upon muscle mass.
- A small amount of creatinine is ingested as a meat component, but this does not affect the serum creatinine level. There is raised level of creatinine only seen in the case of kidney disease.
- Creatinine in the blood has a stable amount of concentration, and variation is <10% in 24 hours.
Creatinine excretion:
- It is the metabolism of muscle mass and is not dependent upon the following:
- Age.
- Sex.
- Diet.
- Exercise.
- Women excrete less creatinine than men because of less muscle mass.
- The daily creatinine excretion is relatively constant and is ±15% per person per day, and its production is not dependent upon protein catabolism or other external factors.
- Creatinine excretion is not affected by protein metabolism or other external factors.
- So serum creatinine is the best measure of glomerular function (filtration).
- Creatinine is raised only when 50% function of the kidney is lost.
- There is a minimal amount of creatinine in the urine from tubular secretion.
- Creatinine in the urine increases as the creatinine concentration rises in the blood.
- The kidneys entirely excrete creatinine, so directly proportional to kidney function.
Creatinine and the role of kidneys:
- Creatinine level remains normal with the normal excretory function of kidneys.
- The glomeruli excrete creatinine as the filtrate (15% to 20% of the plasma creatinine), which is not absorbed by the tubules.
- If there is any problem with glomerular filtration function, its level will increase in the blood.
- Creatinine is a by-product of skeletal muscle creatine phosphate metabolism.
- Creatinine is filtered across the glomerular filtration barrier and enters the bowman space. It is not reabsorbed, secreted, or metabolized by the tubular cells. So creatinine excreted in the urine per minute equals the amount of creatinine filtered in the bowman space.
- So renal disorders of kidneys give rise to an increase in creatinine levels like:
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Acute tubular necrosis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urinary obstruction.
- Creatinine is a more specific and sensitive parameter of renal function and renal disease than blood urea nitrogen.
- This is specific to renal function and gives an idea about renal dysfunction.
- This is not a sensitive indicator of early renal disease.
- For a 50% reduction in GFR, serum creatinine level will be double.
- The serum creatinine concentration is a better indicator of renal function than uric acid and BUN.
Kidney’s role in excretion, reabsorption, and filtration:
| Chemical analytes | The amount excreted/per day | Reabsorption in % | Filtration per day amount |
| Water | 1.5 Liters | 99.2 | 180 Liters |
| Albumin | 18 mg | 95 | 360 mg |
| Glucose | Zero | 100 | 180 gram |
| Sodium (Na+) | 100 meq | 99.6 | 24,000 meq |
| Potassium (K+) | 50 meq | 92.5 | 700 meq |
| Bicarbonate (HCO3–) | 2 meq | 99.9 | 5000 meq |
| Chloride | 100 meq | 99.5 | 20,000 meq |
The BUN/creatinine ratio:
It is important to evaluate renal function.
- Normally BUN/creatinine ratio is 10:1.
- Under standard conditions, a 50% decrease in the GFR will roughly double the BUN or creatinine level.
-
- Normal in adults = 6 to 25
- Optimum level = 15.5
What are the Normal values of serum creatinine?
Source 1
| Age | mg/dL | ||
| Cord blood | 0.6 to 1.2 | ||
| Newborn 1 to 4 day | 0.3 to 1.0 | ||
| Infants | 0.2 to 0.4 | ||
| Child | 0.3 to 0.7 | ||
| Adolescent | 0.5 to 1.0 | Male | Female |
| 18 to 60 year | 0.9 to 1.3 | 0.6 to 1.1 | |
| >90 year | 1.0 to 1.7 | 0.6 to 1.3 |
- To convert to SI unit x 88.4 = µmol/L
Source 5
- Child = 0.3 to 0.7 mg/dl
- Adult = 0.5 to 1.0 mg/dl
- 18-60 years :
- male = 0.9 to 1.3 mg/d
- Female = 0.6 to 1.2 mg/dl
- Above 90 years
- Male =1.0 to 1.7 mg/dl
- Female = 0.6 to 1.3 mg/dl
Source 6
- Adult
- Malle = 0.6 to 1.0 mg/dL (53 to 106 µmol/L)
- Female = 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL (44 to 97 µmol/L)
- Elderly = Decrease in muscle masses causing the decreased value
- Adolescent = 0.5 to 1.0 mg/dL
- Child = 0.3 to 0.7 mg/dL
- Infants = 0.2 to 0.4 mg/dL
- Newborn = 0.3 to 1.2 mg/dL
Another source
What is normal Urinary creatinine?
- Male = 14 to 26 mg/Kg/day (124 to 230 µmol/Kg/day).
- Female = 11 to 20 mg/Kg/day (97 to 177 µmol/Kg/day).
- Creatinine excretion in the urine decreases with age.
Serum creatinine and creatinine clearance with the condition of the patient:
| Serum creatinine mg/dL | Creatinine clearance mL/minute | The condition of the patient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
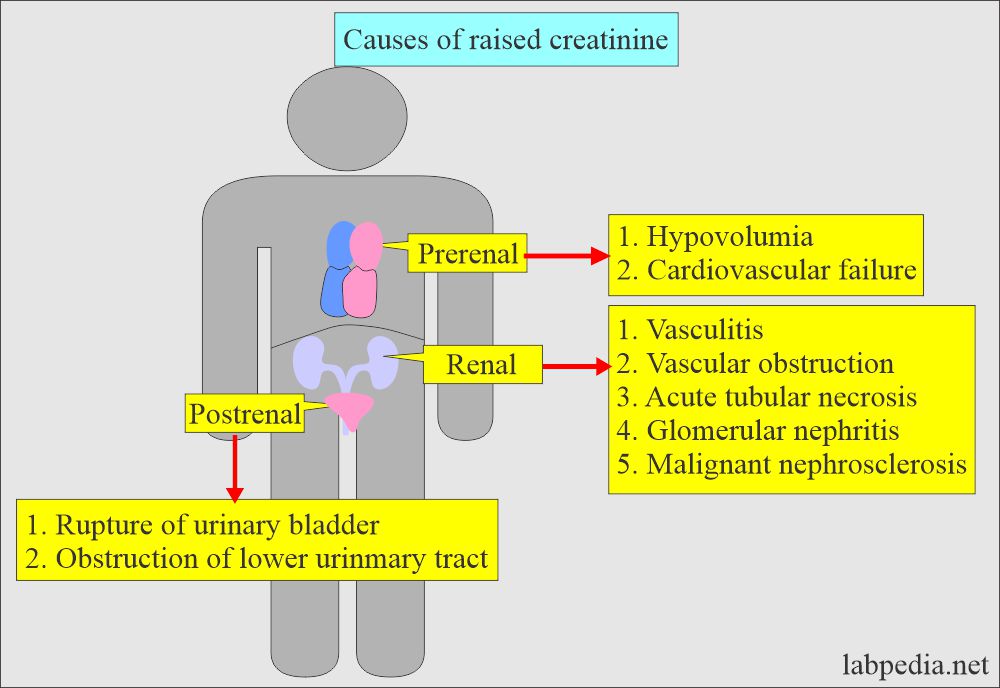
What is the classification of Increased creatinine?
- Pre-renal.
- Renal.
- Post-renal.
Pre-renal factors for raised serum creatinine are:
- Congestive heart failure.
- Shock.
- Salt and water depletion due to:
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- GIT fistulas.
- Increased use of diuretics.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
- Diabetes insipidus.
- Excessive sweating (decreased salt intake).
Renal factors for raised serum creatinine are:
- Damage to:
- Glomerulus.
- Tubules.
- Interstitial tissue.
- Blood vessels.
Post-renal factors for raised serum creatinine are:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Neoplasia compresses the ureter.
- Calculi obstructing the ureter.
- Congenital abnormalities obstruct or compress the ureter.
The increased creatinine level is seen in the following conditions:
- Renal function impairment is both an acute and chronic disease.
- Postrenal obstruction of urine.
- Decrease in blood perfusion because of any reason.
- Gigantism and Acromegaly.
- Injury to the muscles (Rhabdomyolysis).
- Myasthenia gravis.
- Poliomyelitis.
- Muscular dystrophy.
- Dehydration due to loss of body fluids.
- It may be seen in pregnancy during eclampsia and preeclampsia.
The decreased creatinine level is seen in the following conditions:
- Old-age.
- Decreased muscle mass.
- Pregnancy, especially in the first and second trimesters.
- Advanced and severe liver disease.
- Inadequate dietary intake.
Drugs leading to an increased level of creatinine:
- Gentamicin.
- Cimetidine.
- Heavy metals chemotherapy, e.g., Cisplatin.
- Nephrotoxic drugs like Cephalosporin, e.g., Cefoxitin.
Interfering factors:
- Ascorbic acid can increase creatinine levels.
- A diet high in protein, like meat, can increase the level.
- The critical value is >4 mg/dL, suggesting severe renal disease.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the source of creatinine?
Question 2: What is the value of creatinine as a renal function?

What the nomal creatinine for someone to undergo a surgery?
Normal creatine is needed and better to have <1.0 mg/dL.
HOW TO DITULE SERUM SAMPLE WITH NORMA; SALI NE FOR CREATININE TEST?
You can dilute serum with saline for any test. This depends upon the dilution you want to do. If you’re going to dilute 1:2, then take the equal volume of the serum and saline.
i need citation pleas
Diagrams are made by myself. Subject collected from different books and then compiled according to my idea.
It’s a very brief and good article. Thank you for your hard work.
Thanks for the comments.