Creatinine Clearance (CrC), and Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Creatinine Clearance (CrC)
Sample
What should be the sample for Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
- 24 hours of urine and serum (clotted blood 3 to 5 ml) are collected.
- When starting urine collection, note the time and discard the first urine sample. When 24 hours are completed, empty the bladder’s last urine sample in the same container.
- Refrigerate the urine during collection or keep it on ice.
- Collect the blood in the mid of urine collection.
- A 2-hour collection of urine also correlates with 24 hours of urine.
- The 2-hour collection should preferably be done in the early morning fasting patient because, in the postprandial state, there is an increase in the blood creatinine and urine level (10% to 40%).
What are the precautions for Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
- The patient should be hydrated, so there is >2 mL urine output per minute.
- Avoid coffee, tea, and drugs during the test.
- Stop the medication (Drugs) like cortisone or ACTH treatment.
- Exercise increases creatinine levels.
- An incomplete collection of urine gives a false value.
- A meat-rich diet increases creatinine.
- Drugs. Like aminoglycosides, e.g., gentamicin, heavy metals, and nephrotoxic drugs increase the creatinine level.
- The test becomes less accurate when GFR falls below 10 mL/min.
- In the case of high plasma protein, creatinine secretion is increased, leading to a marked overestimation of GFR.
Indications:
What are the Indications for Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
- Creatinine clearance reflects the Kidney’s ability to excrete creatinine.
- Creatinine clearance is used to measure the kidney’s glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- This test will give information on renal functions like:
- Obstruction of the kidney.
- Acute or chronic renal failure.
- Dysfunction due to other causes like heart failure.
- In acute glomerulonephritis, it is used to follow the therapeutic response to the treatment.
- Creatinine clearance can be used to differentiate between glomerular disease and diffuse chronic structural changes.
- This is a good test to assess the overall renal functional damage.
What is the definition of Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
- It is defined as the quantity of blood cleared of a substance per unit of time and depends on the substance’s plasma concentration and the kidney’s excretion rate, which reflects GFR and renal plasma flow.
- Creatinine clearance is a measure of the glomerular filtration rate.
- Urine and serum creatinine levels are measured, and the creatinine clearance rate is calculated.
- Creatinine clearance is defined. as the volume of blood plasma cleared of creatinine per unit time.
- It is a rapid and cost-effective method to assess the renal function.
Pathophysiology of Creatinine Clearance (CrC):
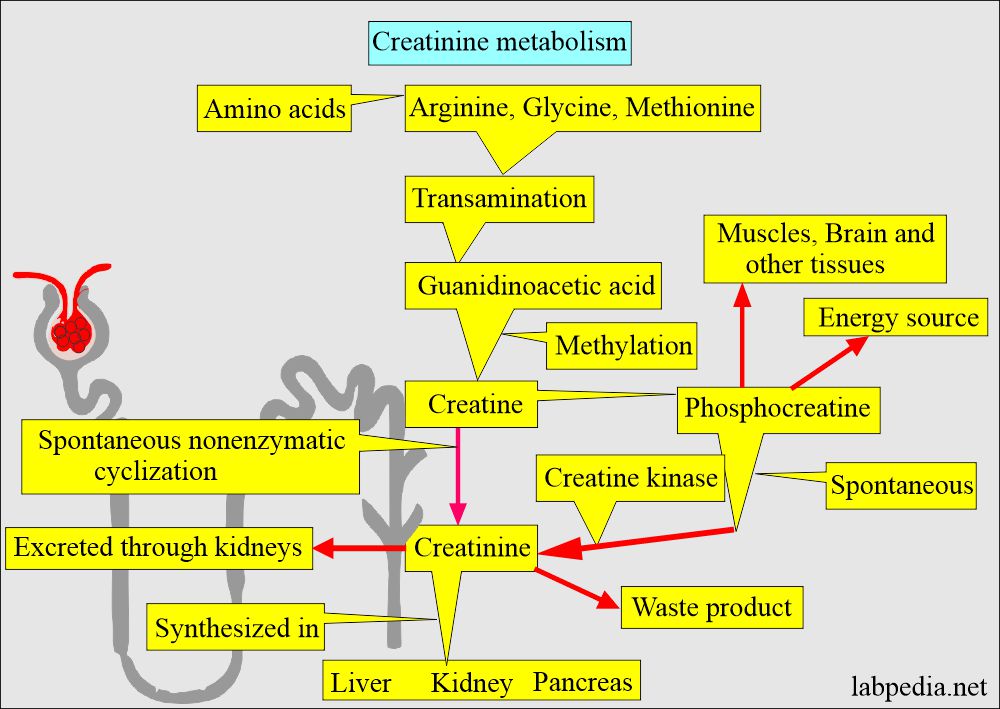
- Creatinine is a metabolic product of creatine-phosphate dephosphorylation in the muscles.
- Creatinine is a breakdown of creatine phosphate, which has an important role in the contraction of muscles.
- Daily creatine and creatinine production depend upon muscle mass, which fluctuates very little. Most of the creatinine production is stable throughout the day.
- Creatinine is freely and mainly excreted by the kidney, so this will reflect the filtration power of the kidney.
- Excretion of creatinine by the kidney is a combination of glomerular filtration, which is 70% to 80%, and another fraction is by tubular secretion.
- Creatinine excretion by the kidney will depend upon the number of a millimeter of filtrate (urine) per minute, called the glomerular filtration rate (GFR ).
- The filtrate will depend upon the amount of blood to be filtered.
- Further filtration will depend upon the ability of the glomeruli to act as a filter.
Creatinine clearance is a measure of GFR:
- Creatinine clearance is roughly equal to the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- Plasma creatinine of 15% to 20% is filtered, and the rest goes back to the systemic circulation and renal vein.
- Amount filtered = Amount excreted.
- GFR x Plasma creatinine = Urine creatinine x Urine volume
- The amount of blood to be filtered decreases in renal artery atherosclerosis, dehydration, and shock.
- The ability of filtration by glomeruli will be decreased in glomerulonephritis, acute tubular necrosis, and other primary renal diseases.
- If one kidney is knocked out, then another kidney is normal, can compensate for the filtration, and GFR will be within the normal limit.
- Creatinine clearance depends upon the following:
- Creatinine Clearance (CrC) decreases by 6.5 mL/min each decade because of a decrease in GFR.
- Urine collection is for 24 hours, so any error in the collection will give false results.
- Muscle mass varies among people and will also affect the CrC.
- Decreasing muscle mass will give decreased values.
- Ingestion of a large amount of meat for a time will increase the CrC.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
What is the definition of GFR?
- GFR is defined as the number of millimeters of urine filtrate the kidneys make per minute.
- Normally, this amount is around 130 mL/minute and 180 liters per 24 hours.
- GFR depends upon the effective filtration pressure in the glomeruli and the renal blood flow rate.
- GFR is described as = mL/min/1.73 m2.
Average or estimated GFR:
| Age of the person in years | Average GFR = mL/min/1.73 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is the Formula to calculate Creatinine clearance (CrC)?
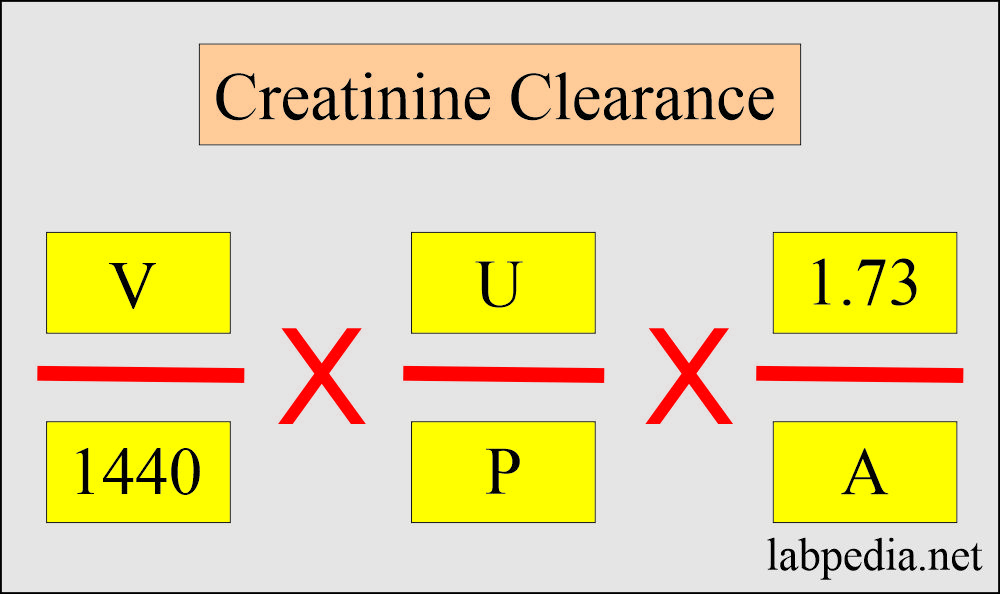
- Urine volume X urine creatinine/plasma creatinine.
- Creatinine clearance = UV/P
- P = Serum creatinine in mg/dL
- V = Volume of urine in mL/minute.
- U = Number of mg/dL of creatinine excreted in the urine in 24 hours (reference Mosby’s manual of diagnostic and laboratory tests).
- Creatinine clearance = UV/P
- Creatine clearance uncorrected formula:
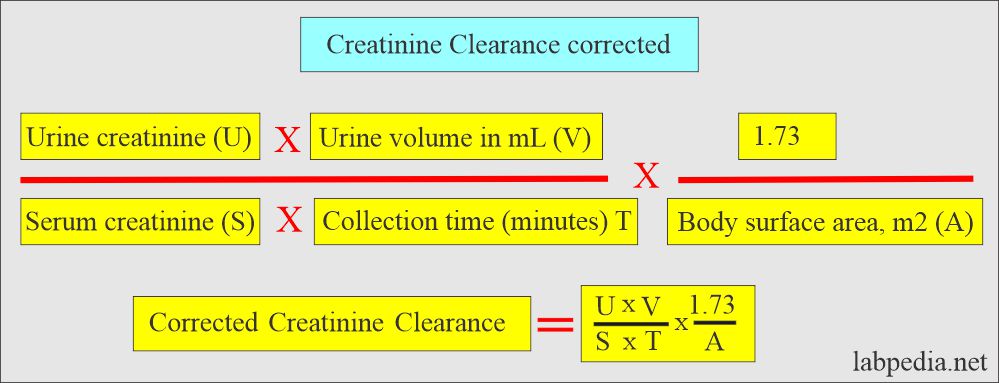
Creatinine clearance corrected formula:
The corrected creatinine clearance formula may be simplified = Measured creatinine clearance x 1.73 / Patient’s surface area (sq m).
Example:
U = Urine creatinine in mg/dL (number of mg/dL of creatinine excreted in the urine in 24 hours).
V = Urine output in 24 hours (1440 minutes) (volume of urine in mL/minute).
P = Plasma or serum creatinine in mg/dL
A = Body surface area in square meters (1.73/A is a body surface area).
- There are various simplified formulas for the calculation of creatinine clearance.
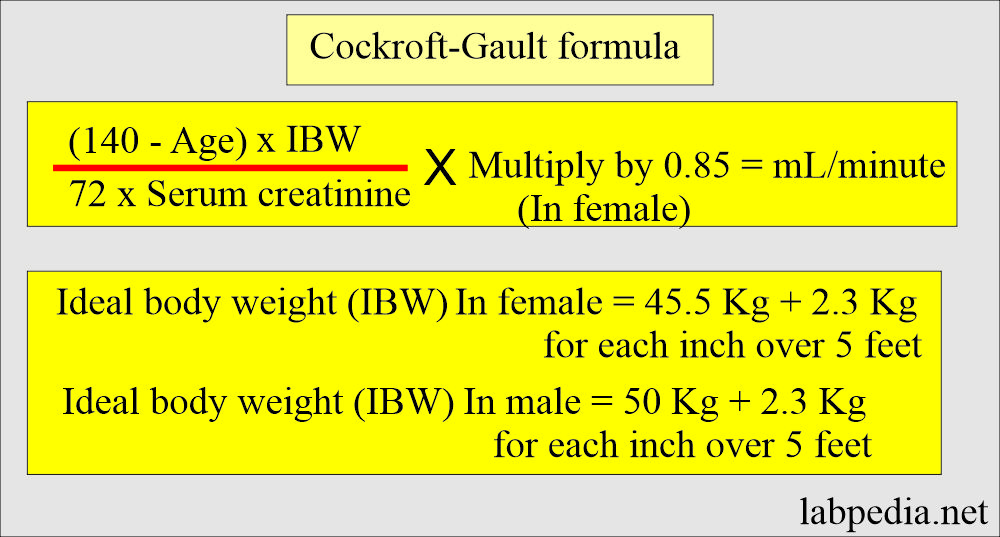
The Cockcroft-Gault formula is simple and reliable:
What are the advantages of the Cockcroft-Gault formula?
- This formula reduces the variability of serum creatinine estimates of GFR due to increased muscle mass based on age and sex.
- It does not consider variations caused by extrarenal elimination and tubular secretions.
- It does not consider creatinine production by the muscle mass caused by disease.
- GFR in a person with relatively low muscle mass in relation to their body weight (obese, edema, or chronically debilitated person).
- (Reference of Henery’s Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory method).
What is the Procedure for creatinine clearance?
2-Hours collection method:
- Can collect 2 hours sample of urine because the 24-hour collection is not as accurate as 2 hours.
- For good urine outflow, give 500 ml of water 10 to 15 minutes before the start of the collection.
- Completely empty the bladder and discard this urine.
- When the patient feels full bladder, start a collection of urine for exactly 2 hours and empty the last sample into the container at the end of 2 hours.
- Also, check the serum creatinine level.
Interfering factors for Creatinine Clearance (CrC):
- With increasing age, creatinine clearance also decreases because of a decrease in GFR.
- An incomplete collection of urine will give false values.
- Decreased muscle mass gives decreased values.
- Increased ingestion of meat will increase Creatinine clearance.
- Exercise may increase creatinine.
- Drugs like gentamicin, cimetidine, and cephalosporin may give rise to an increase in the level.
What is the normal value of Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
Source 1
| Age | mL /min / 1.73 m2 | ||
| 0 to 1 year | 72 | ||
| one year | 45 | ||
| 2 year | 55 | ||
| 4 year | 71 | ||
| 5 year | 73 | ||
| 6 year | 64 | ||
| 7 year | 67 | ||
| 8 year | 72 | ||
| 9 year | 83 | ||
| 10 year | 89 | ||
| 11 year | 92 | ||
| 12 year | 109 | ||
| 13 to 14 year | 86 | ||
| Male | Female | ||
| 20 to 29 year | 94 to 140 | 72 to 110 | |
| 30 to 39 year | 59 to 137 | 71 to 121 | |
| After this age, with each decade, the Value Decreases ∼by 6.5 mL/min. |
- To convert to SI units x 0.00963 = Mean creatinine Clearance mL/s/m2.
Source 2
- Male = 97 to 137 ml/min.
- Female = 88 to 128 ml/min.
- Children =70 to 140 ml/ min.
- Newborn = 40 to 65 ml/min.
Source 6
Adult <40 years of age
- Male = 107 to 139 mL/min (1.78 to 2.32 ml/sec)
- Female = 87 to 107 mL/min (1.45 to 1.78 mL/sec)
- value decreases by 6.5 mL/min/decade of life after the age of 20 years with a decline in GFR.
Newborn = 40 to 65 mL/min
Another source
- Male = 85 to 125 mL/min
- Females = 75 to 115 mL/min
- Effect of the age:
- 50 to 75 years = subtract 5 mL for each 5-year interval.
- Over 75 years = subtract 8 mL for each 5-year interval.
Artifacts that lower the value are:
- Incomplete urine collection.
- Presence of Ketones, Barbiturates.
- BSP, PSP, when the level is higher in the urine than in the plasma.
What are the causes of Increased values of creatinine clearance (CrC)?:
- This has no clinical significance; we suspect some errors in the collection procedure.
- Pregnancy
- Exercise.
- High cardiac output syndrome.
What are the causes of Decreased values of creatinine clearance (CrC)?:
- It is a very sensitive indicator of decreased glomerular filtration rate when done with all precautions.
- Diseases of the kidney with impaired renal function.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Cirrhosis with ascites.
- Shock.
- Dehydration (loss of body fluids).
- Bladder outlet obstruction.
Drawbacks of creatinine clearance (CrC):
- There are certain drawbacks of creatinine clearance.
- The reference limit is established for young adults, which is 90 to 120 mL/minute.
- GFR is found to decrease with age. There are references that 4 ml/minute decreases for each decade after the age of 20 years.
- Some studies found that creatinine clearance is as low as 50 mL/minute in clinically healthy elderly persons.
- Creatinine production and excretion also decrease with age, although serum creatinine is normal.
- There are several nonrenal factors affecting creatinine clearance.
- An accurate collection of urine is needed.
- Creatinine clearance is better than urea clearance and has replaced urea clearance.
- Creatinine comes from the muscles, so the individual’s muscle mass also affects the test.
- An old person with decreased muscle mass with chronic renal failure or malnourished persons can produce decreased creatinine clearance values.
- Dietary meat in abundant quantity may increase serum creatinine, decreasing creatinine clearance.
- Ketones in the blood may interfere with Jaffe’s biochemical estimation of creatinine.
- The major drawback is its nonspecificity when creatinine clearance decreases, which can not be used to differentiate the etiology of the abnormality.
What are the advantages of the creatinine clearance test (CrC)?:
- Creatinine clearance is still a better test than urea clearance.
- Creatinine clearance is reported as one of the most sensitive tests to find a renal failure warning.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the alternative to 24 hours urine collection for Creatinine Clearance (CrC)?
Question 2: What is the difference between CrC and GFR?



thankyou
welcome.
Thank for the knowledgeable study I’m interested in this page
Thanks.