Coombs’ Test:- Part 1- Coombs’ Direct, Direct-Anti-globulin test
Coombs’ Direct
What will be the sample for Coombs’ Direct test
- The blood is collected in EDTA.
- Separate RBC immediately to prevent the absorption of the complement to RBC.
- Avoid clotted blood if possible. In the case of clotted blood, keep the blood at room temp. 37 °C until the cells are separated.
- Can store samples at 4 °C for one week.
Purpose of the Coombs’ Direct (Indications)
- To diagnose the hemolytic anemia of the newborn.
- This test is done on the cells (RBC), especially in the case of a newborn in an Rh-negative mother when the baby is Rh-positive and in the case of erythroblastosis fetalis.
- T0 diagnoses autoimmune hemolytic anemias.
- To diagnose blood transfusion reactions.
- To diagnose drug-induced hemolytic anemia.
- It also detects C3 on patients’ RBCs.
Precautions for Coomb’s test (Coombs’ Direct):
- Remember that some drugs give false positive coombs direct tests, like cephalosporin, chlorpromazine, ampicillin, captopril, indomethacin, isoniazid (INH), streptomycin, tetracycline, sulphonamide, penicillin.
What is the definition of Direct Coomb’s test:
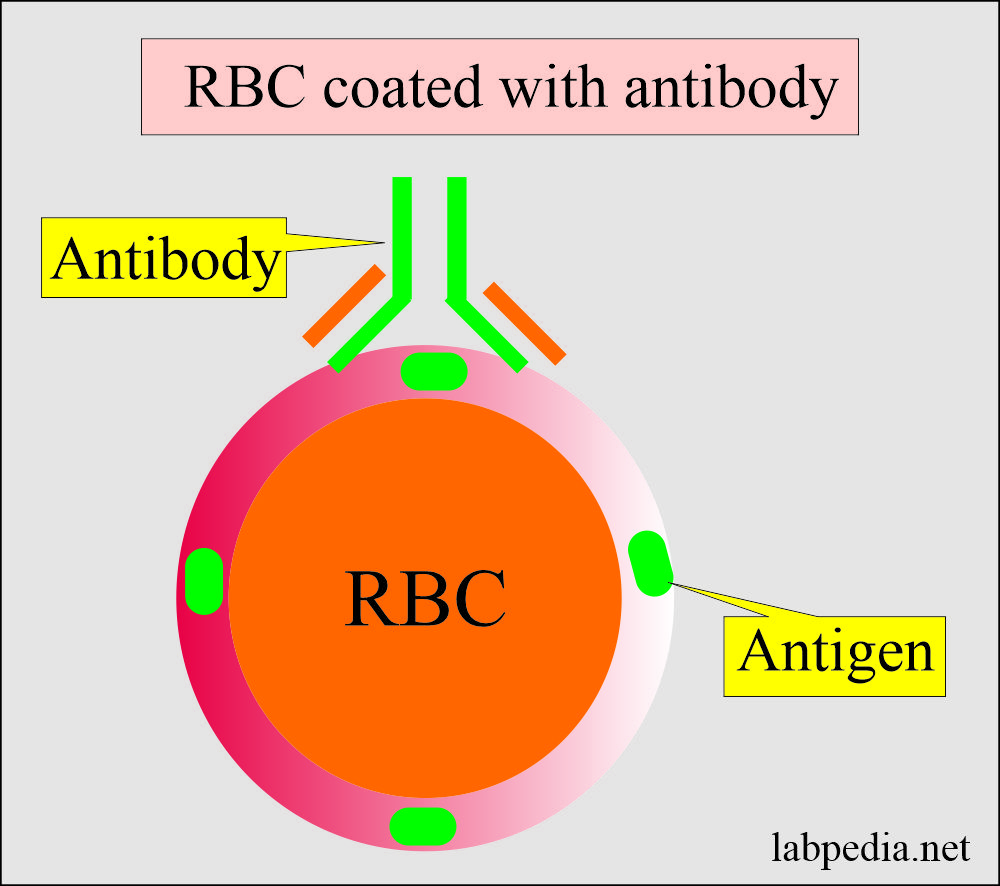
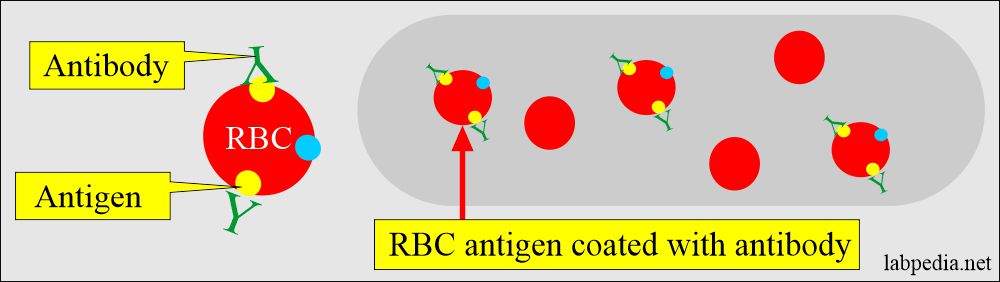
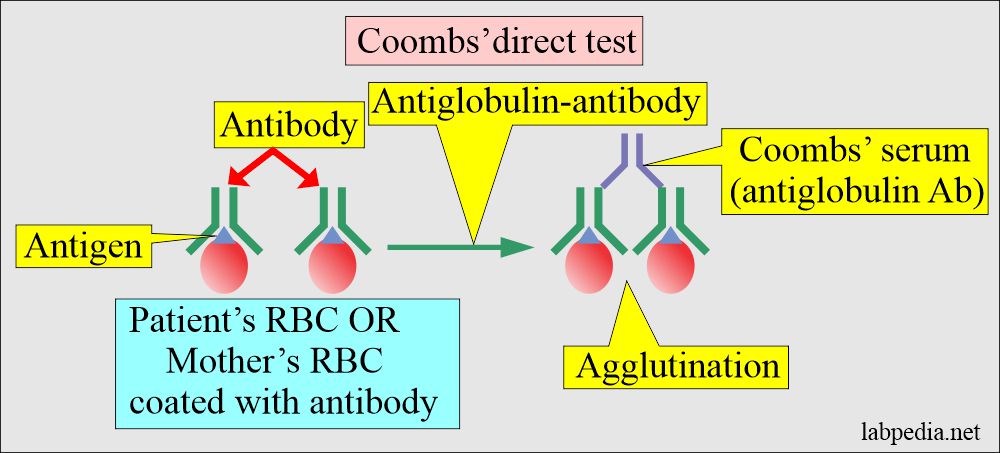
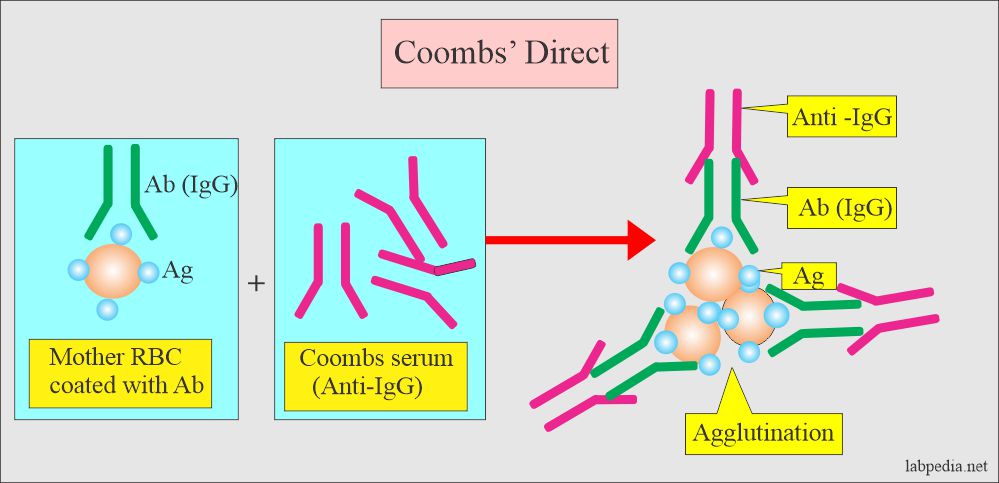
- Direct Coomb’s test detects antibodies that have coated the RBCs.
Pathophysiology of the Coombs’ Direct test:
- Coombs’ direct test will detect coated RBCs with antibodies.
- Most of the antibodies are due to ABO and Rh antigens.
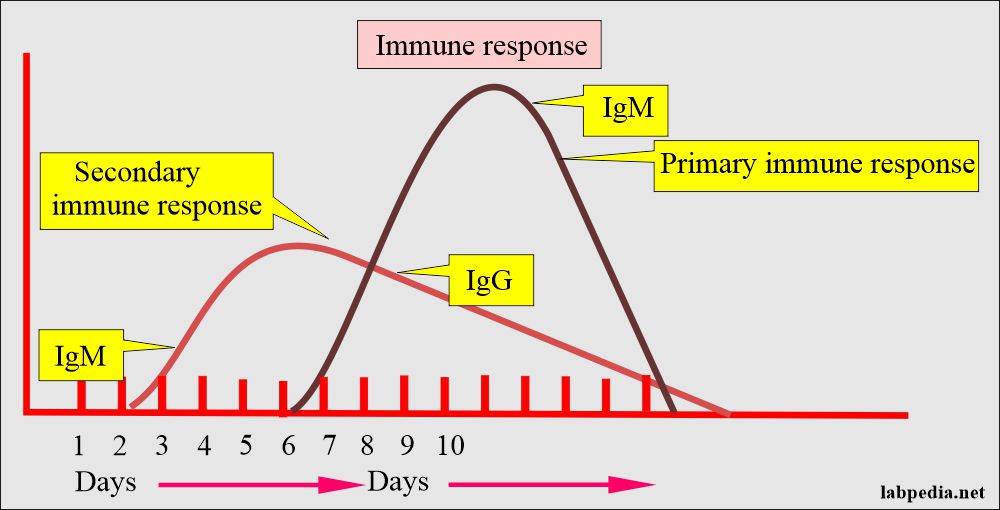
- Antibodies appear within 7 to 10 days of primary exposure (Primary immune response) and 1 to 2 days in the second exposure (Secondary immune response).
- Once there is a reaction, then these antibodies are coated to RBC (RBC coated-antibodies).
- Such antibodies can also develop due to drugs like methyldopa and penicillins (Non-blood grouping antigens).
- Also, autoantibodies can attach to RBC.
Signs and symptoms of blood transfusion reaction are:
- Fainting and dizziness.
- Fever and chills.
- Rash.
- Back pain and pain in the flanks.
- Hematuria (blood in the urine).
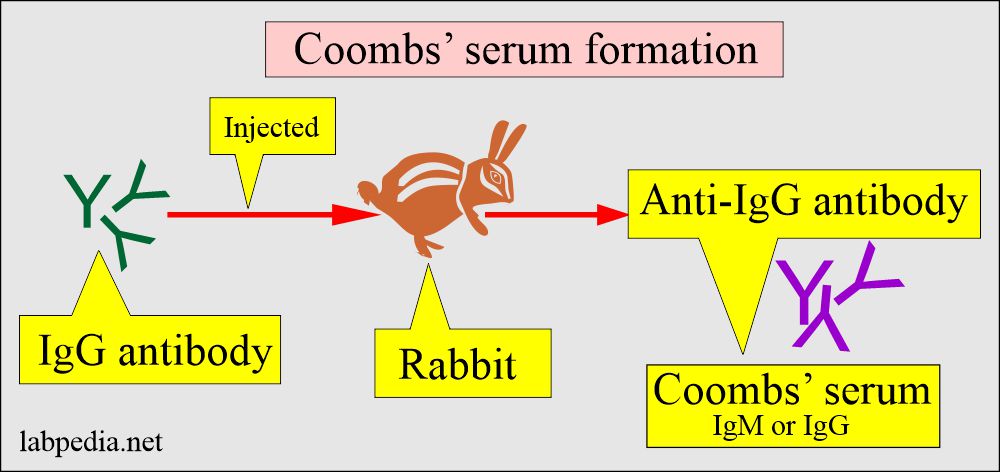
Coombs’ serum (Antibody):
- It is prepared in the rabbit against the human antibodies IgM and IgG.
- Rabbit produces anti-human (IgM and IgG) antibodies called Coombs’ serum.
What is the procedure for Coomb’s direct test:
- Wash the patient’s RBC three times with saline.
- Decant the supernatant saline.
- Now, make 2% to 5% of these RBCs suspended in saline.
- Add Coombs’ serum and centrifuge.
- Look for agglutination (clumping of RBC).
How you will read Coomb’s direct test:
- It is normally negative; there is no agglutination.
- Positive direct Coomb’s show agglutination immediately after centrifugation, indicating that RBCs are coated with antibodies.
- This test is read positive when the clumping is on a trace scale, trace to 4+.
How Coomb’s direct test is reported:
| Grade of the reaction | Degree of agglutination |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When False-positive results are seen:
- Insufficient washing of the RBCs.
- Over Centrifugation of the test.
- Contaminated reagents.
- If the washed RBCs are left for a longer period.
- It may be seen in m multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia.
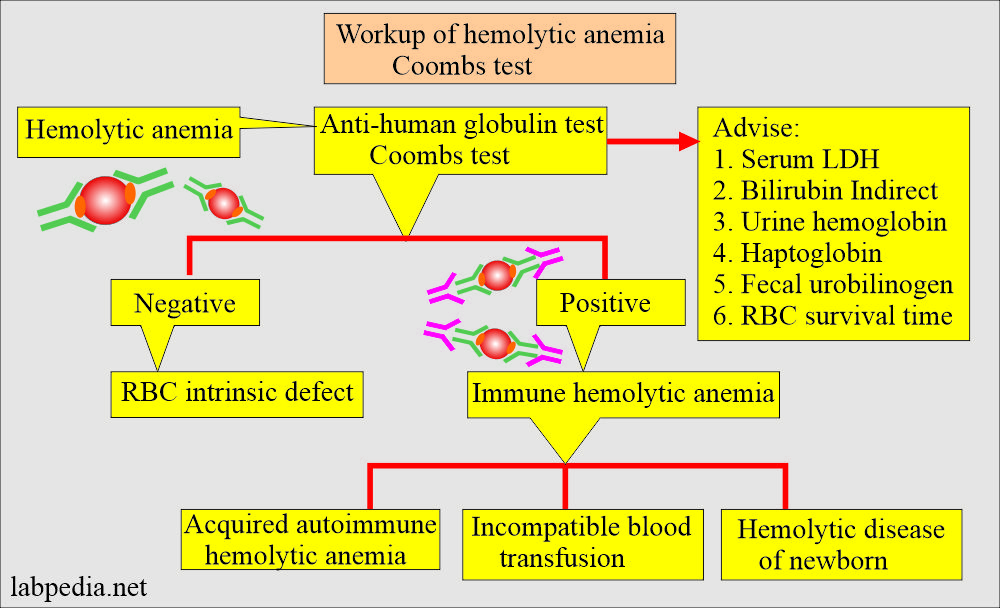
What are the conditions showing positive Coomb’s direct test:
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- Warm reactive autoantibody.
- Cold reactive autoantibody.
- Cold haemagglutinin disease is seen in Lymphoma and pneumonia.
- Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Drug-induced hemolytic anemia, e.g., penicillin, quinidine, Cephalosporin, and α-methyldopa.
- α-methyldopa hemolytic reaction occurs in <30% of the patient with therapy, but only <1% shows hemolysis; rarely in the first 6 months of the treatment.
- If it is not found within 12 months of the treatment, then less likely to see the reaction.
- A reversal takes place from weeks to months after stopping the drugs.
- Hemolytic anemia: Transfusion reaction to incompatible RBC and hemolytic anemia of the newborn.
- Erythroblastosis fetalis.
- Incompatible blood transfusion.
- Delayed hemolytic blood transfusion reaction.
- Malignant diseases:
- Lymphoma.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
- Acute and chronic leukemias.
- Infections :
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Weak positive tests are seen in:
- Renal diseases.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Epithelial malignancy.
- Weak positive tests usually have no clinical significance.
When you will see Coomb’s direct negative results:
- Hemolytic anemia is caused by the intrinsic defect in the RBC, e.g., G6PD deficiency hemoglobinopathies.
- Hemolytic anemias due to weak or smaller amounts of IgG bound to RBCs.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What sample you need for Coombs direct test?
Question 2: What type of antibody gives positive Coombs direct test?
Question 3: What is Coombs serum?