Common Lab Errors, and Effect of various Anticoagulants on Tests
Common Lab Errors
Effect of Various Anticoagulants on Tests
- Handling the specimens is critical to decreasing the error in the lab results.
- There are the following areas where the mistake can lead to erroneous laboratory results.
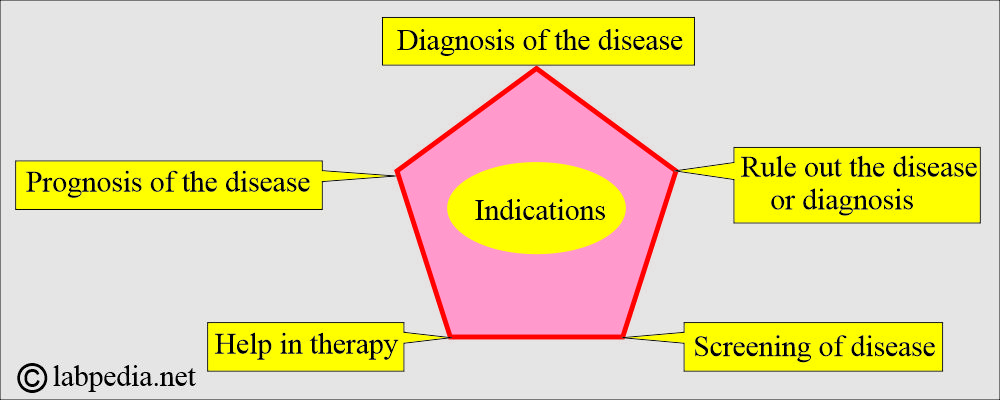
What are the indications for ordering laboratory tests?
- To confirm a clinical impression or to make a diagnosis.
- To rule out a diagnosis or disease.
- To follow the prognosis of the disease.
- To help in the therapy of various diseases.
- For the screening of the disease in the population.
What are the steps in the chemical analysis?
- Measurement of the analytes.
- Sample pretreatment.
- Measurement of the reagent.
- Reagent and sample test mixing.
- Incubation of the tests.
- Wait for the required time.
- Give time for the reaction.
- Calculation of the test results.
- The final end is the reporting and releasing of the results.
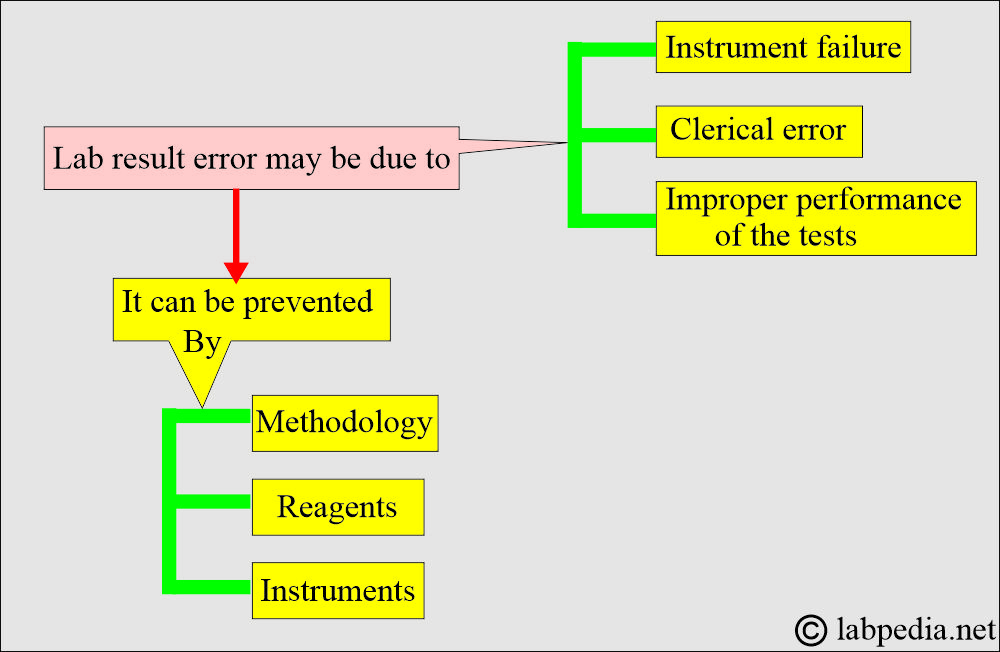
How will you maintain the accuracy and reproducibility of the analysis?
- Various steps in the procedure.
- Check and maintain the instruments.
- Maintain quality assurance with internal/external quality control.
- It may help to run quality control with the patient sample.
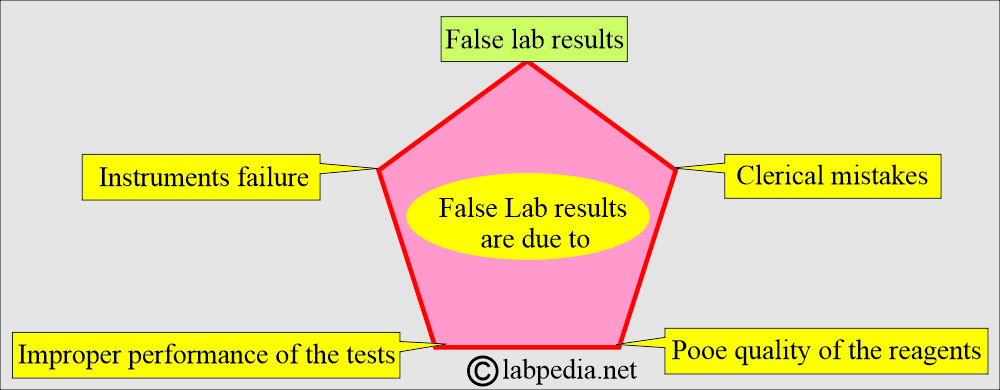
What are the causes of false lab results?
- Clerical mistakes.
- Improper performance of the tests.
- Instrument failure.
- Quality of the poor reagents.
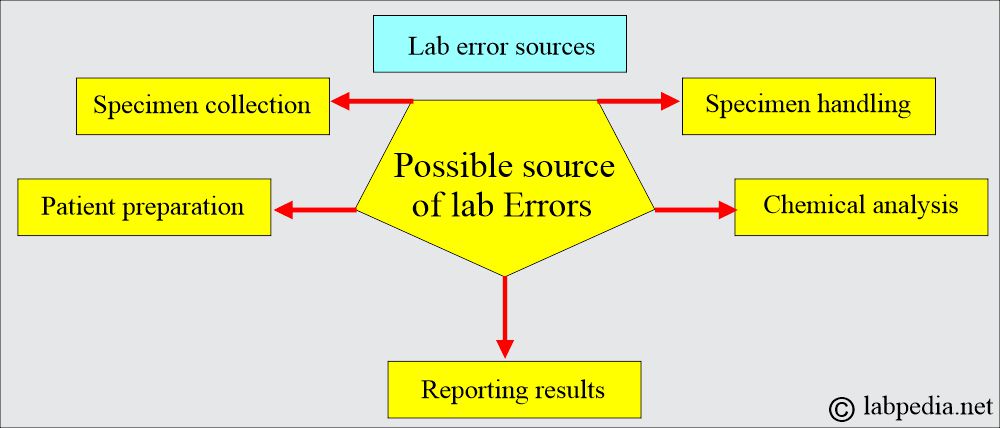
What are the factors leading to lab errors?
Preanalytical errors:
- Proper patient identification.
- Proper collection of the sample.
- Handling of the sample.
- Strict rejection policies.
- Exposure to heat, light, evaporation, and exposure to the atmosphere changes the result values.
- Light exposure to bilirubin causes photodegradation, and heat will change the enzyme activity.
- Exposure of plasma to a high temperature lowers the potassium value.
Specimen collection:
- Wrong blood collection techniques, such as too much pressure on the blood collection area.
- Blood is put into the wrong test tubes for serum in the test tube containing an anticoagulant.
- The blood sample was wrongly labeled.
Patient’s preparation:
- Blood was collected at the wrong time.
- If a blood sample is needed, a fasting sample is collected at a random time.
- There is a diurnal variation in the various blood samples. You may collect a sample at the peak level.
Specimen handling:
- If the blood sample is delayed in the transfer to the lab.
- A blood sample is stored at the wrong temperature.
- Did not process the blood sample correctly.
Chemical analysis:
- If technicians are not following quality control rules.
- If technicians are not following the protocol of the test procedure.
- There will be a difference between manual and automation.
Reporting of the result:
- Mistakes in the calculation of the result.
- The difference in reporting the result on the phone and on paper.
What is the most common lab error?
The most common lab errors are in the collection of the samples:
- Wrong labeling of the sample.
- The technique of the blood sample:
- It is very important to follow an excellent technique to collect good-quality blood.
- If you apply a tourniquet for an extended period, it will lead to acidosis and hemoconcentration.
- The wrong sample of the different patients or the improper identification of the patient.
- The wrong ratio of blood and anticoagulant.
- Improper mixing of the blood may lead to microclot formation.
- Keeping the sample at an extreme (hot) temperature.
- There may be hemolysis, which is not a good sample for electrolytes, and so many other tests.
- Try to collect an adequate blood sample and avoid microclots.
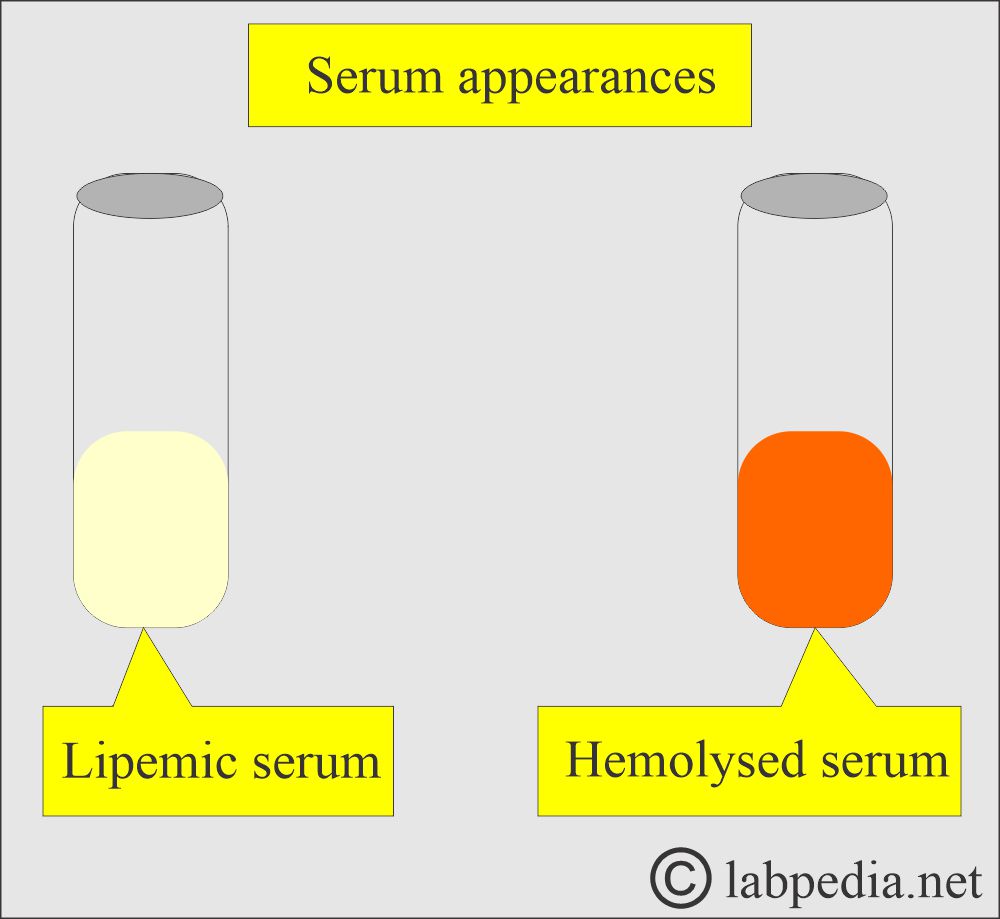
- If there is a lipemic serum that will interfere with biochemical reactions.
- Wrong timing of the sample for some special tests, like hormones, etc.
- If a blood sample is taken after the food ingestion, then:
- The glucose level will be high.
- Will raise triglyceride.
- Will raise lipid fractions.
- Improper centrifugation of the blood will not give a good, clear serum.
- If the sample is not stored at the appropriate temperature.
- Some tests are influenced by the light in the blood, like bilirubin.
- The delayed performance of the tests.
- Human errors can also account for laboratory variation. This depends upon the performance of the testing.
- This can be minimized by automation.
- There will be mistakes if:
- Selecting a specimen from the wrong patient to analyze.
- There are transcriptional errors.
- There are many mistakes along the whole chain of collecting, processing, analyzing, and reporting.
Which sample should be rejected?
Hemolysis:
- The sample showing hemolysis should be rejected.
- RBCs release analytes and enzymes into the blood/serum.
- It increases potassium, phosphate, and prostatic acid phosphatase.
- Cholesterol in case of severe hemolysis.
- SGOT, SGPT, creatine kinase, iron, and magnesium may also be affected.
Lipemia:
- The serum showing lipemia should be rejected. This may cause:
-
- Decrease in sodium, potassium, and anion gap.
- Turbidity of the lipemic serum interferes with photometry.
- Fat replaces the water, which will change the electrolytes’ distribution.
- Triglycerides >1500 mg/dL make the serum turbid and milky.
- Serum iron may also be decreased.
What are other factors for rejecting the blood sample?
- When there are microclots in the blood sample.
- When the sample is too small to perform the test.
- When too much force is applied to draw the blood.
- If the specimen is contaminated.
- If the container is leaking.
- Faulty transportation is like very hot or very cold weather.
- Unlabelled sample.
What are the effects of various anticoagulants on different tests?
| Anticoagulant | Inhibit the action | Decrease the value | Increase the value | Stimulator effect | Distort the morphology |
| Oxalate | Alkaline phosphatase | Calcium | Sodium | —- | Blood cells |
| Acid phosphatase | —- | Potassium | —- | — | |
| LDH | —- | —- | —- | — | |
| Amylase | — | —- | — | — | |
Citrate |
SGPT | Amylase | Sodium | Acid phosphatase | — |
| SGOT | Calcium | Potassium | —- | — | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | —- | —- | —- | — | |
EDTA |
Creatine Kinase | Calcium | PT | —- | — |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Iron | PTT | —- | — | |
| platelet aggregation | Sodium | —- | — | ||
| — | Potassium | —- | — | ||
|
Heparin
|
— | T 3 | —- | — | |
| — | Thyroxine | —- | — | ||
| — | PT and PTT | —- | — | ||
| — | Lithium | —- | — | ||
| — | Sodium | —- | — | ||
| Fluoride | Acid phosphatase | — | Cell morphology | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase | — | ||||
| SGPT | — | ||||
| SGOT | — | ||||
| Creatine kinase | — | ||||
| Amylase |
What are the precautions before performing the tests?
- It is best to perform all the tests within the first 45 minutes to one hour after collection.
- If delayed, then correctly store the sample at the appropriate temperature.
- The serum is needed for electrophoresis.
- For gases and ammonia, whole blood is needed.
- The serum is the best option for clinical chemistry, but plasma may be used.
- For plasma preparation, centrifuge the blood within one hour of sample collection for 10 minutes at 850 to 1000 x gravity.
- Cap the bottle to avoid evaporation.
- Keep the sample in the colored container for bilirubin estimation.
What should the lab workers know before performing the tests?
- Misidentification of the sample.
- Reject the hemolysed sample.
- Avoid exposure of the sample to light and heat.
- Avoid evaporation of the sample.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the effect of hemolysis on lab tests?
Question 2: What is the common cause of lab error?

Thank you very much for the explanation