Ceruloplasmin, Acute Phase Protein
Acute-phase protein (Acute Phase Reactants)
- Acute-phase protein is raised in inflammatory conditions.
- When there is an increase in a protein called positive acute-phase protein.
- In the case of a decrease in the acute phase protein, it is called the negative phase protein.
- The acute phase proteins (positive) are proteins whose concentration increases in the plasma, and after the disease episode is over, then it decreases and may become normal.
Ceruloplasmin, Acute Phase Protein
Sample
- This test is done in the serum.
- The test is done with a fresh sample.
- Can store the sample for 3 days at 4 °C.
- For 4 weeks can store at -20 °C.
Precautions
- Avoid hemolyzed or lipemic serum.
- Ceruloplasmin is affected by infection and liver function.
- Birth control pills increase ceruloplasmin and pregnancy.
Indications
- Advised in chronic inflammations.
- This is done to diagnose Willson’s disease.
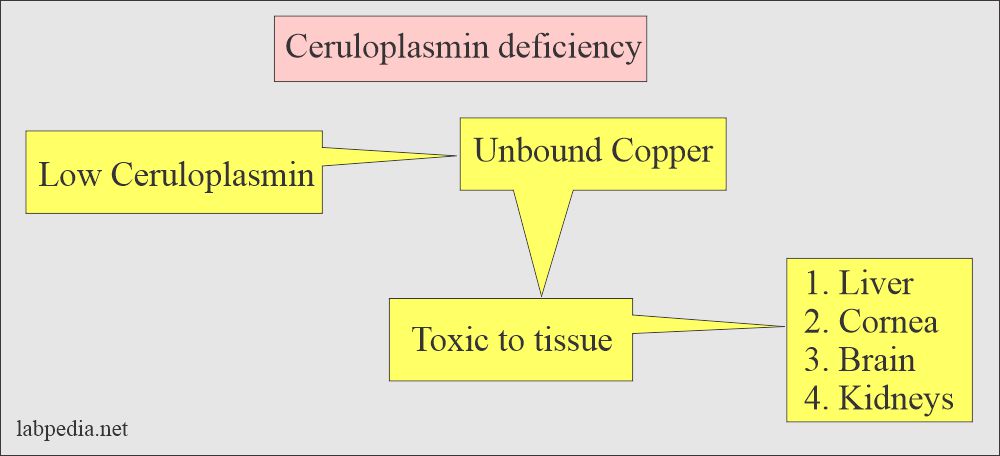
- To diagnose an accumulation of copper in the liver, eye, and other organs.
Pathophysiology of ceruloplasmin
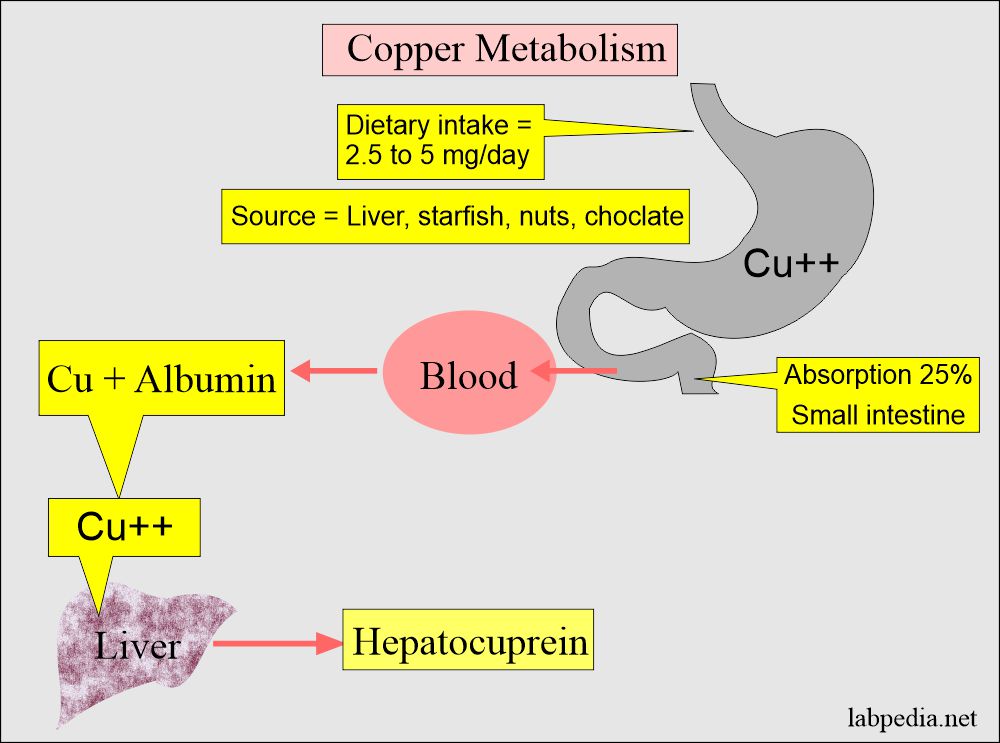
- Ceruloplasmin is a major copper-carrying protein in the blood.
- Ceruloplasmin is α2- globulin and glycoprotein (7.5% carbohydrate) made by the liver.
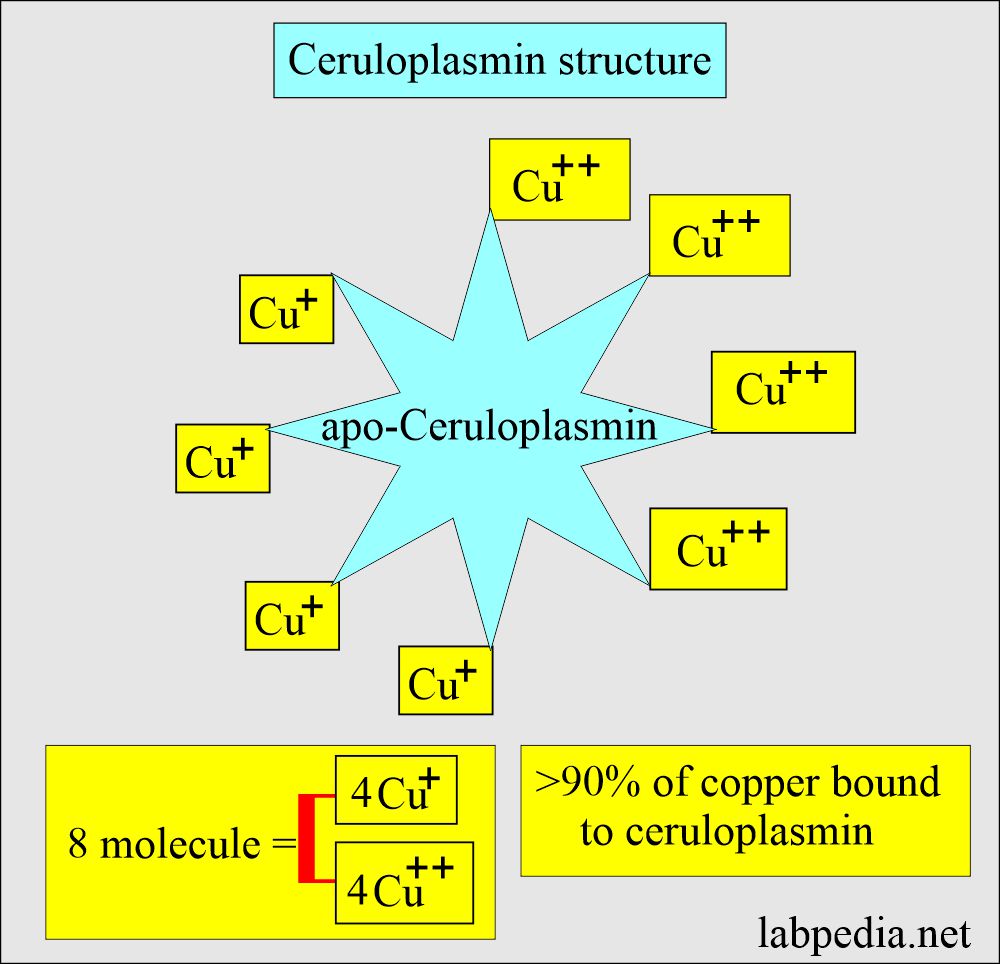
- Ceruloplasmin contains 95%of the total copper and gives it a blue color.
- 95% of the copper is bound to Ceruloplasmin.
- Its molecular mass is 134,000.
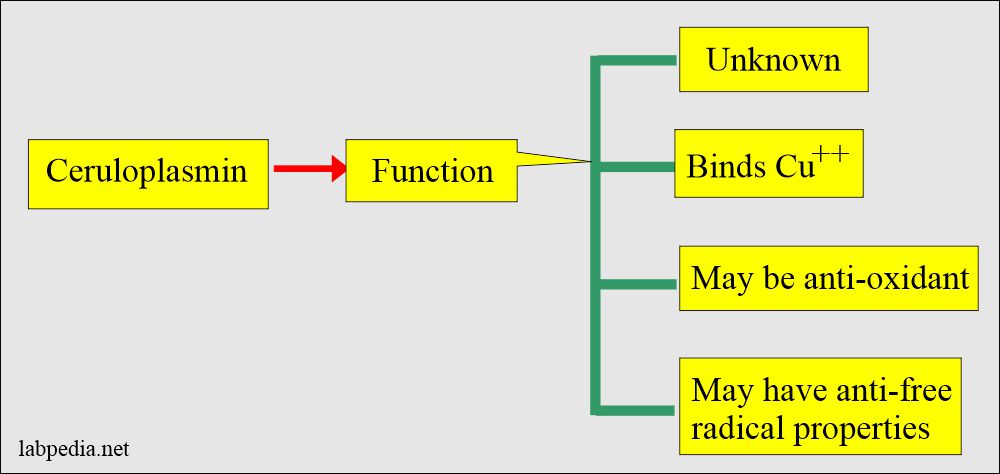
- This is an acute-phase protein with enzymatic activity (peroxidase activity).
Ceruloplasmin as a role of acute phase protein:
- Ceruloplasmin reduces the number of WBCs attached to the endothelium.
- In one of the experiments, it was found that ceruloplasmin may act as an anti-inflammatory agent by reducing the number of PMNs attaching to endothelium and by acting as an extracellular scavenger of superoxide.
- Elevated levels of minor acute phase reactants, such as ceruloplasmin, have been related to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Ceruloplasmin is useful in monitoring chronic inflammation in the patient, and in these patients, there is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in patients on dialysis.
- This is a decrease in Wilson’s disease.
- The decreased ceruloplasmin and blood copper concentration, with increased urine copper level, indicate Wilson’s disease.
- This is an increase in acute and chronic inflammation.
Normal ceruloplasmin source 1
| Age of the person | Normal level |
| one day to 3 months |
|
| 6 months to one year |
|
| 13 months to 3 years |
|
| 4 to 5 years |
|
| 6 to 7 years |
|
| >7 years |
|
| Adult |
|
- Another source gives this normal value:
- Male = 36.0 ± 5.6 mg/dL (2.38 ± 0.37 µmol/L).
- Female = 40.9 ± 6.8 mg/dL (2.71 ± o.45 µmol/L).
- Source 4
- 25 to 63 mg/dL (250 to 630 mg/L) by nephelometry.
- Critical value = <20mg/dL is abnormal.
Increased level of ceruloplasmin is seen in:
- The latter half of the pregnancy.
- Acute and chronic infections.
- In myocardial infarction.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Leukemia and cancers.
- In liver cirrhosis.