Ceruloplasmin, Acute Phase Protein
Ceruloplasmin, Acute Phase Protein
What sample is needed for Ceruloplasmin?
- This test is done in the serum.
- The test is done with a fresh sample.
- The sample can be stored for 3 days at 4 °C.
- For 4 weeks, it can be stored at -20 °C.
What are the precautions for Ceruloplasmin?
- Avoid hemolyzed or lipemic serum.
- Ceruloplasmin is affected by infection and liver function.
- Birth control pills increase ceruloplasmin and pregnancy.
What are the indications for Ceruloplasmin?
- Advised on chronic inflammations.
- This is done to diagnose Wilson’s disease.
- To diagnose an accumulation of copper in the liver, eyes, and other organs.
How will you discuss the Pathophysiology of Ceruloplasmin?
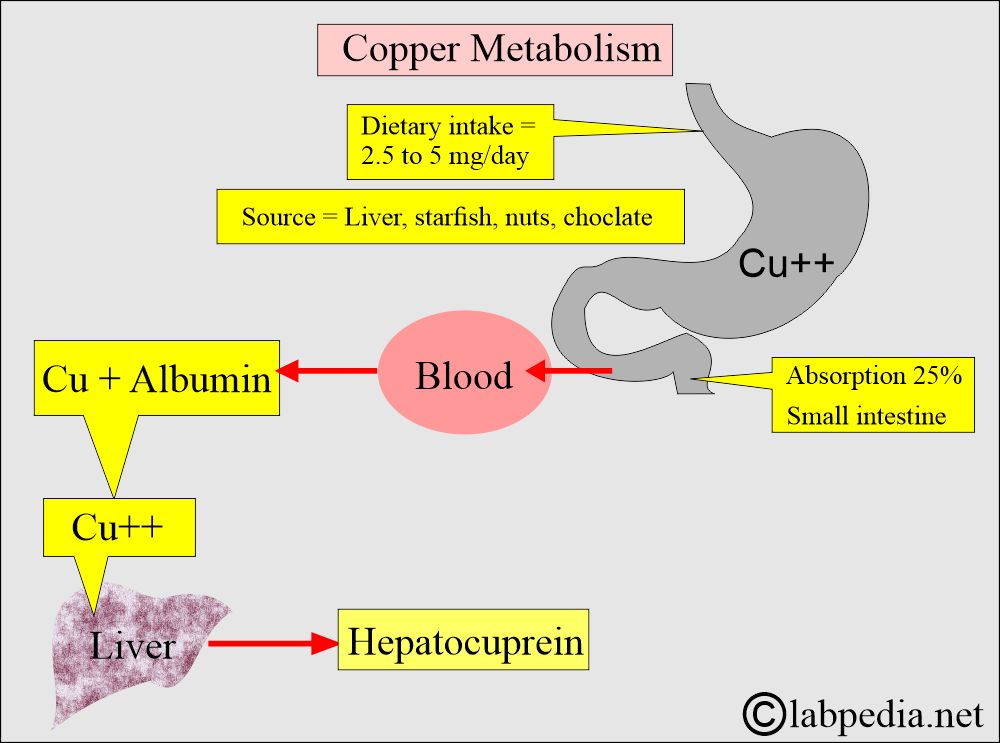
- Ceruloplasmin is a major copper-carrying protein in the blood.
- Ceruloplasmin is an α2-globulin and glycoprotein (7.5% carbohydrate) made by the liver.
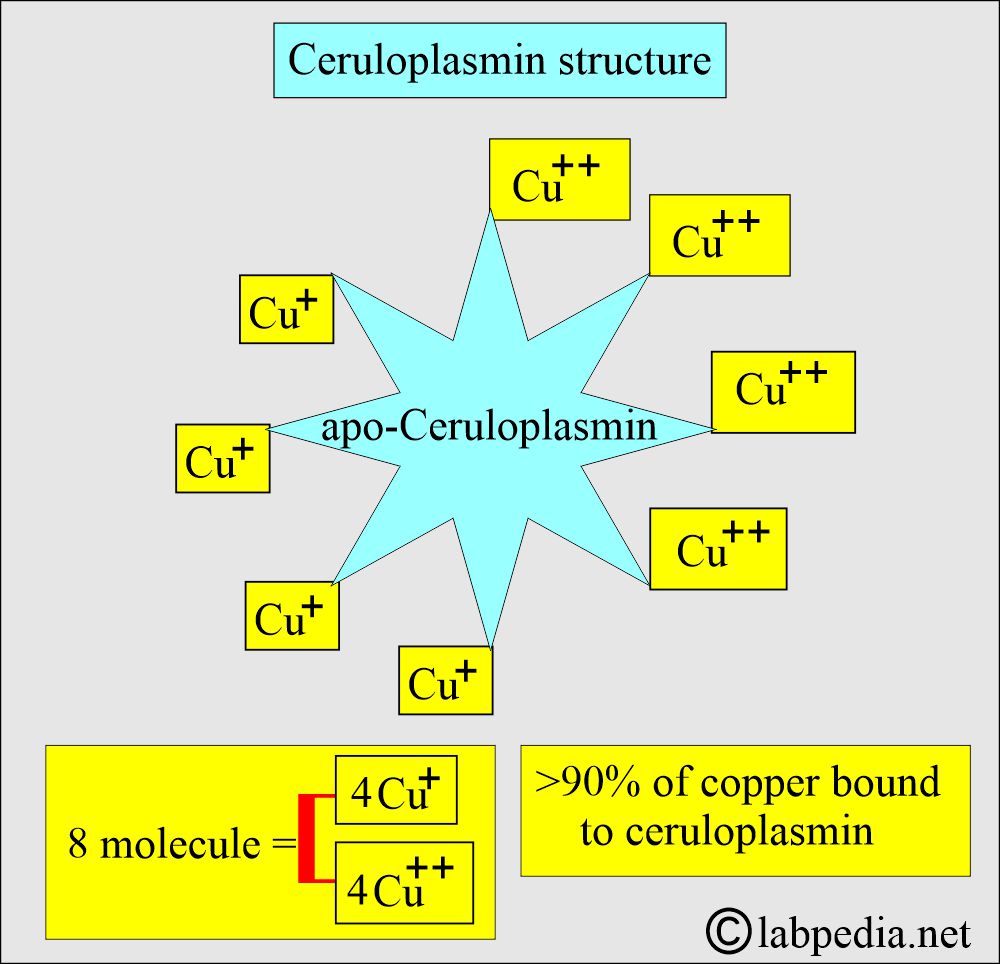
- Ceruloplasmin contains approximately 95% of the total copper and gives it a blue color.
- 95% of the copper is bound to Ceruloplasmin.
- Its molecular mass is 134,000.
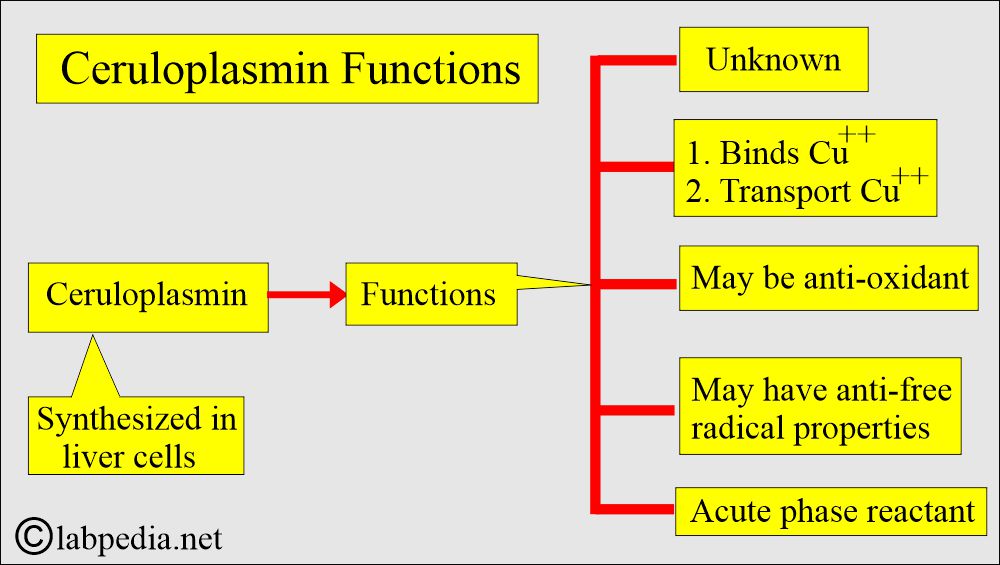
- This is an acute-phase protein with enzymatic activity (peroxidase activity).
What is the role of Ceruloplasmin as an acute-phase protein?
- Ceruloplasmin reduces the number of WBCs attached to the endothelium.
- In one experiment, it was found that ceruloplasmin may act as an anti-inflammatory agent by reducing the number of PMNs attaching to the endothelium and by serving as an extracellular scavenger of superoxide.
- Elevated levels of minor acute phase reactants, such as ceruloplasmin, have been related to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Ceruloplasmin helps monitor chronic inflammation in patients, and in these patients, there is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly among those undergoing dialysis.
- This is a decrease in Wilson’s disease.
- The decreased ceruloplasmin and blood copper concentrations, along with an increased urine copper level, indicate Wilson’s disease.
- This is an increase in acute and chronic inflammation.
What is the normal ceruloplasmin (source 1)?
| Age of the person | Normal level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Another source gives this normal value:
- Male = 36.0 ± 5.6 mg/dL (2.38 ± 0.37 µmol/L).
- Female = 40.9 ± 6.8 mg/dL (2.71 ± o.45 µmol/L).
- Source 4
- 25 to 63 mg/dL (250 to 630 mg/L) by nephelometry.
What is the Critical value of Ceruloplasmin? = <20mg/dL is abnormal.
What are the causes of an increased level of ceruloplasmin?
- The latter half of the pregnancy.
- Acute and chronic infections.
- In myocardial infarction.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Leukemia and cancers.
- In liver cirrhosis.
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the picture in Wilson's disease?
Question 2: What is the role of Ceruloplasmin in inflammation?