Cerebrospinal fluid Xanthochromia (CSF)
Cerebrospinal fluid Xanthochromia
Specimen for Cerebrospinal fluid Xanthochromia
- Cerebrospinal fluid is needed.
Indication
- To assess the presence of increased protein in the CSF.
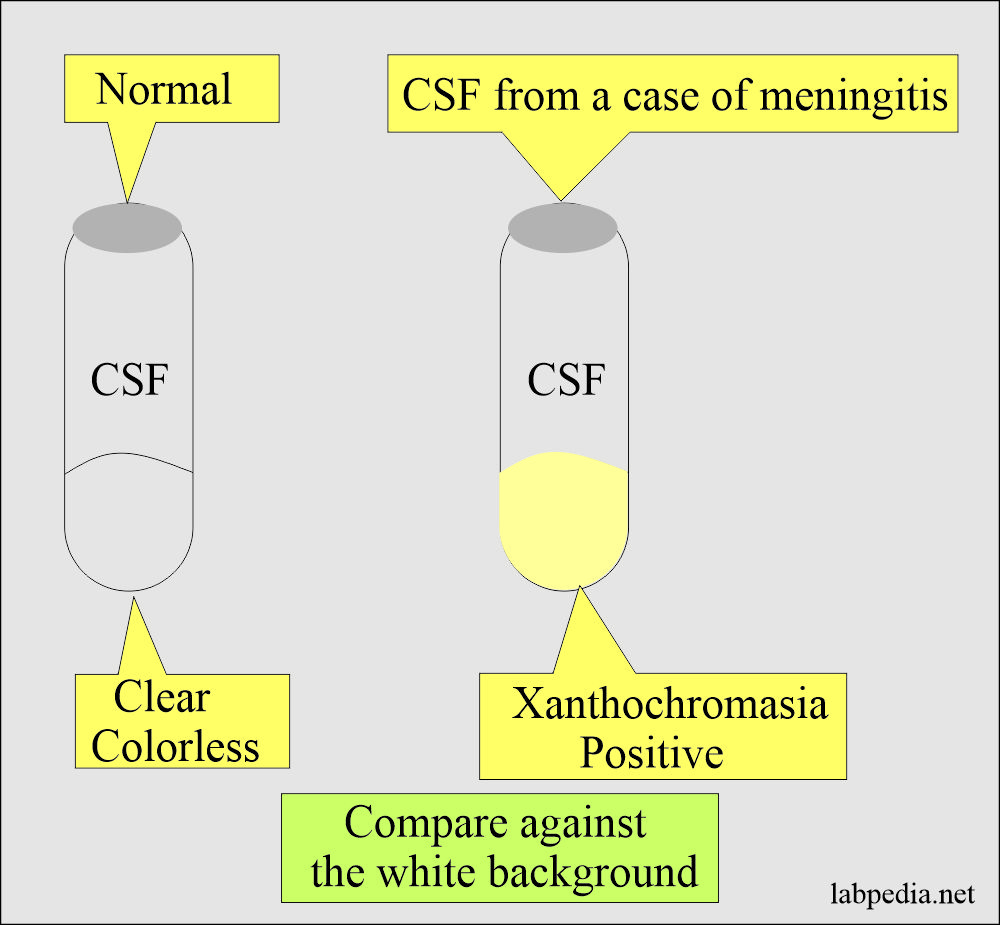
Xanthochromia:
Definition of Xanthochromasia:
- Xanthochromia is a yellow color, and it may occur due to hemoglobin pigments from lysed RBCs, or it appears when CSF proteins are >150 mg/dL and produce a faint yellow color.
- Severe jaundice may produce discoloration that may simulate xanthochromasia.
Pathophysiology of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):
- The normal color of the CSF is clear and colorless.
- The color appearance depends upon the presence of hyperbilirubinemia, hypercarotenemia, melanoma, and elevated protein levels.
- A cloudy appearance indicates an increased number of WBCs or increased proteins.
- A red tinge indicates blood that may be due to hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space or due to a traumatic tap.
- Due to traumatic tap, blood may form clots, which will not occur in the subarachnoid bleeding.
- In traumatic tap, successive tubes become clear of blood.
- Xanthochromia is usually referred to as a yellow tinge.
How to check xanthochromia:
- The easiest way is to centrifuge the CSF and see it against the white background.
- Result
Xanthochromia, when positive in the CSF, indicates a raised protein level. - Please see more details in the CSF fluid analysis.