Blood banking:- part 3 – Blood Donation Procedure, Blood Components and Their Indications
Blood Donation Procedure
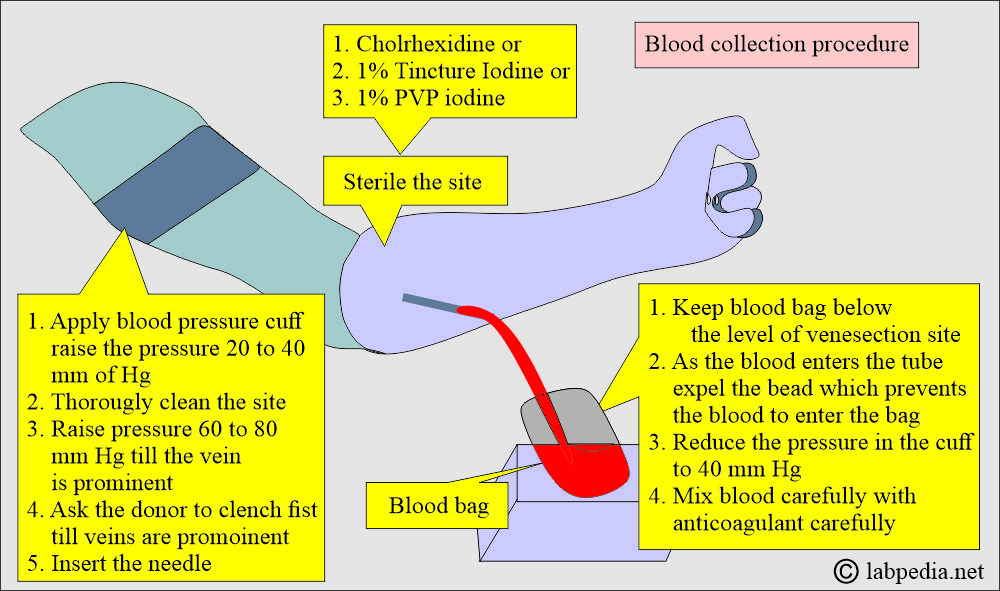
How to collect blood from the donor?
How will you give Donor assurance?
- Make the donor comfortable and assure him of safety.
- Give some time to the donor to acclimate to the atmosphere.
- Now, apply the blood pressure cuff above the elbow and apply a pressure of 20 to 40 mmHg.
How will you clean the site of blood collection?
- Now, thoroughly clean the site of venipuncture.
- Can use chlorhexidine, 1% tincture iodine, or 1% PVP iodine.
How will you collect the blood bag?
- Keep the blood pack below the level of the donor.
- Keep the pack in balance.
- Now, increase the blood pressure to 60 to 80 mmHg till the vein is prominent. Ask him to clench their fist.
- Insert the needle into the vein; as blood comes out, remove the bead, preventing blood from entering the pack.
- Now reduce the pressure in the cuff.
- Carefully and slowly mix the blood with the anticoagulants.
- When blood donation is complete, reduce the pressure in the cuff to 0.
- Clamp the blood pack (bag).
- Take out the needle and apply pressure on the venipuncture site.
What are the post-blood donation precautions?
- Please don’t allow the donor to sit immediately; ask him to lie down for at least 5 to 10 minutes.
- Sometimes the donor gets headaches, nausea, and dizziness.
- Donor blood pressure may become low.
- Label the pack and make at least 4 to 5 tubing segments for further testing.
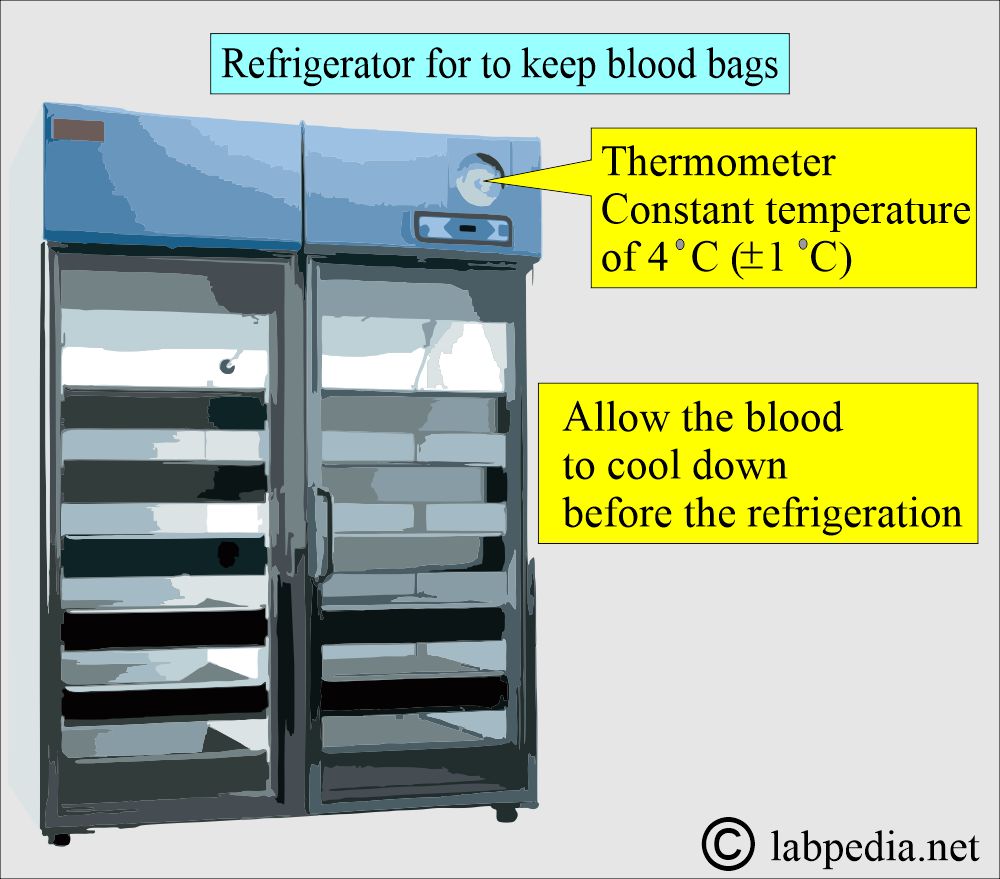
- Allow the blood to cool down before refrigeration is done. This period should not exceed one hour.
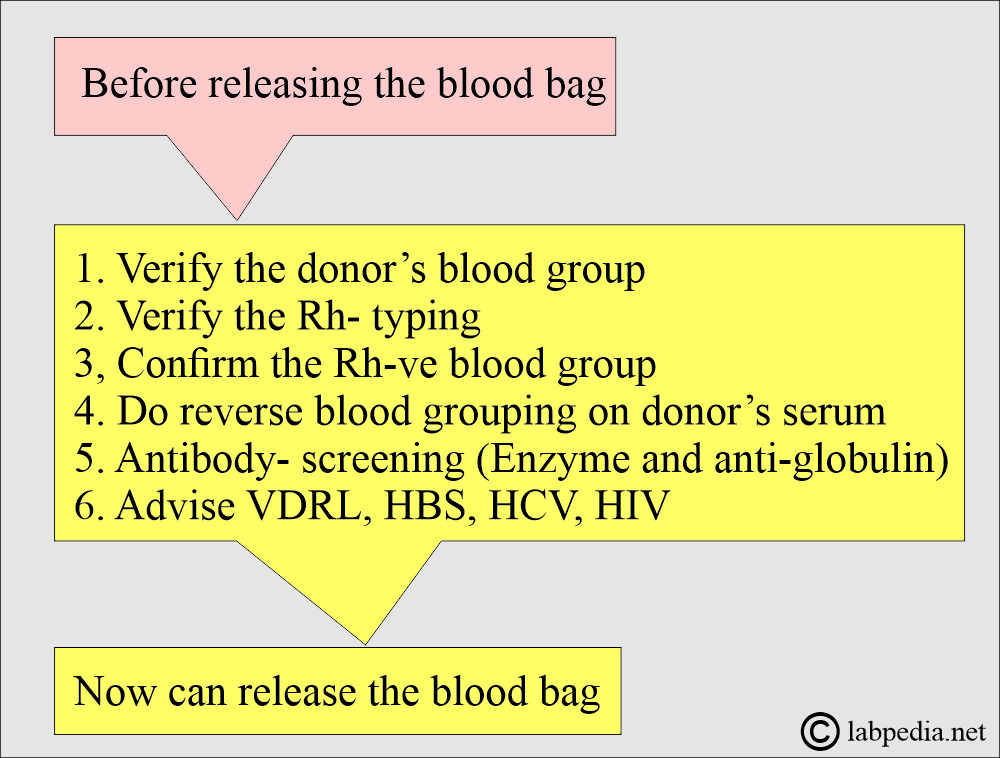
What tests are done before the donated blood is released?
- The following tests are performed on the donor’s blood and serum.
- The donor’s blood grouping ABO is verified.
- Verify the Rh typing. Rh-negative blood is reconfirmed.
- All Rh°(D) negative blood bags are confirmed.
- Now test for anti-CD and anti-DE.
- Perform Du tests on all r’ and r” blood bags.
- Reverse blood ABO grouping is done on the donor serum.
- Antibody screening is done by the enzyme and antiglobulin method.
- Perform the VDRL, HBS, HCV, and HIV.
- After doing all these tests, you can now release the blood pack for donation to the patient.
What are the criteria for blood donation?
- Donors can donate their blood at intervals of 8 weeks.
- Healthy individuals can donate blood every 5 to 7 days for a limited period, around 1 to 2 months.
- In the above donor, an iron supplement is needed.
What is Autotransfusion (autologous transfusion)?
- This is the blood collection and subsequent transfusion of the patient’s own blood.
- Can donate blood every 5 to 7 days before elective surgery.
- Advantages:
- This will prevent all transfusion reaction problems and transfusion-related infections, and avoid complications related to religious beliefs.
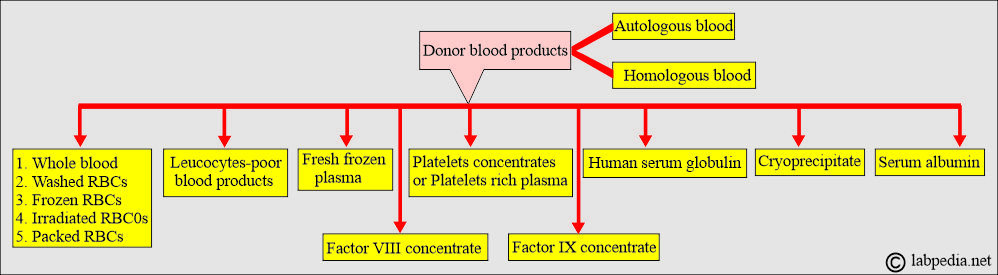
Blood products:
What are the blood components most commonly used?
- Whole blood.
- Fresh frozen plasma.
- Packed red blood cells.
- Frozen red blood cells.
- Human serum albumin.
- Human immune serum globulin.
- Antihemophilic factor concentrate (cryoprecipitate).
- Factor IX concentrate.
- Platelets concentrate or platelet-rich plasma.
- White blood cell-poor blood (where the white cells are removed).
What are the Blood components?
Whole blood:
- Proper storage of the blood is crucial:
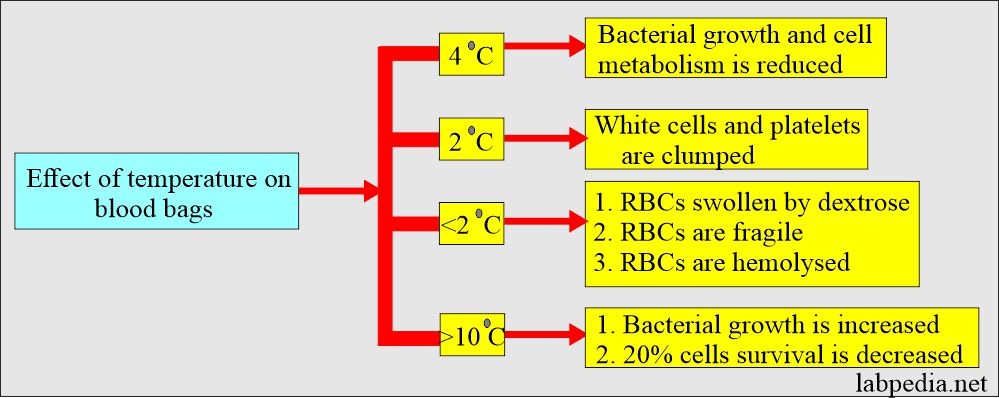
- Whole blood needs to be stored at a constant 4 °C (± 1 °C).
- At this temperature, bacterial growth and cell metabolism slow down.
- Some researchers say that a temperature of 2 °C is better, but the disadvantages are:
- White blood cells and platelets become irreversibly clumped at this temperature.
- Also, at 2 °C, RBCs are swollen due to the presence of dextrose, become fragile, and may be hemolyzed.
- At temperature >10 °C:
- Bacterial growth is enhanced.
- Cell survival is decreased by around 20%.
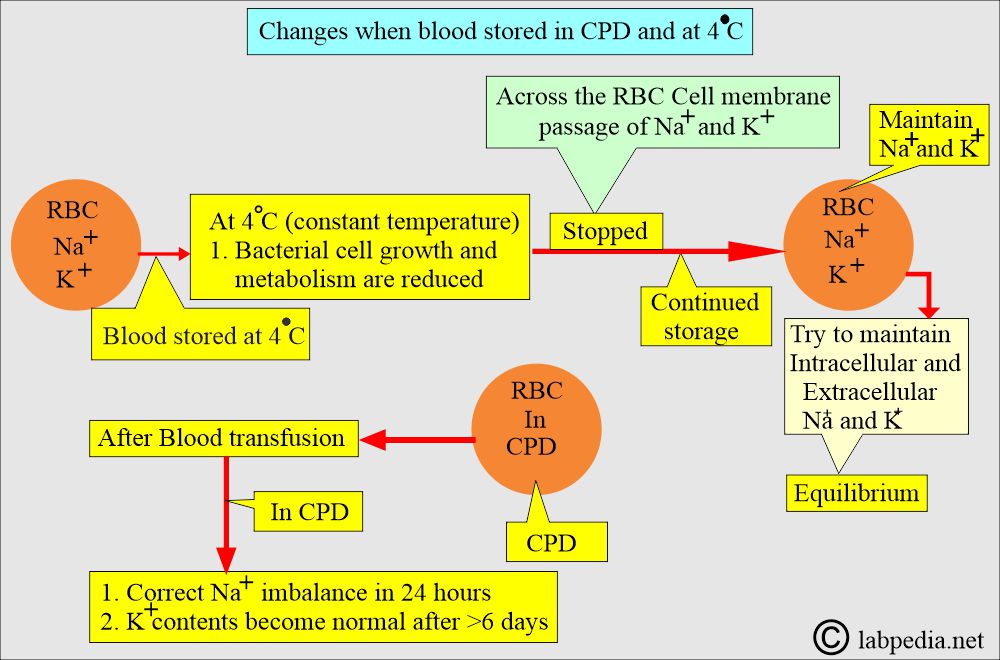
What are the changes in stored blood?
- Blood deterioration starts when stored in Citrate phosphate dextrose anticoagulant (CPD) or Acid Citrate Dextrose anticoagulant (ACD) within a few days of collection.
- RBCs will lose their ability to metabolize glucose.
- The cells lose K+ to the plasma.
- The osmotic and mechanical fragility is increased.
- There is a loss of membrane lipids.
- What is the survival of the RBCs in vivo?
- 5% after the first week.
- 10% to 15% after 2 weeks.
- 15% to 30% after 3 weeks.
- The addition of Adenine (Adenine + CPD) will prolong the shelf life of RBCs to 35 days.
- In storage, there is a decrease in the 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) and Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- The concentration of the 2,3-DPG is better maintained in the CPD than in the ACD.
- Blood stored at 4 °C stops the transport of Na+ and K+ across the red blood cell (RBC) membrane.
- If storage is continued, then:
- In that case, the intracellular and extracellular concentrations of Na+ and K+ are maintained.
- After a blood transfusion in CPD, sodium levels are corrected within 24 hours.
- However, the K+ level does not return to normal and takes more than 6 days.
- What are the uses of whole blood?
- It is advised for patients with enough acute blood loss leading to hypovolemia.
- This may be given to patients with severe anemia, preferably by giving packed RBCs.
Washed red blood cells:
- These packed red blood cells were washed several times with saline, followed by centrifugation.
- This will remove more than 90% of the white blood cells, as well as platelets and plasma.
- 10% to 20% of RBCs are also lost in washing.
- What are the indications of washed red blood cells?
- There are very few indications for washed red blood cells.
- Cell washing removes donor antibodies and is useful in IgA-mediated immune reactions.
- Washed RBCs are used for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Washed RBCs should be used within 24 hours after preparation (washing).
Fresh frozen plasma (Plasma):
- Plasma is separated from the RBCs by centrifugation at 4°C and is frozen as quickly as possible.
- This is stored at -30 °C for a maximum period of one year.
- At -20 °C, it can be stored for 3 months.
- In the storage of fresh frozen plasma, deterioration occurs for labile clotting factors.
- What is the use of the fresh frozen plasma?
- It is used for the deficiency of labile coagulation factors.
- With concentrated RBCs and frozen plasma.
- Stored plasma is useful in treating protein replacement or increasing blood volume.
- Stored plasma is also used in the treatment of burns, hypovolemic shock, coagulation factor deficiencies (except factors V and VIII), and for reversing anticoagulants.
Packed red blood cells:
- When Red blood cells are concentrated in a closed atmosphere, the sterility of the cells remains unaffected.
- In this way, you can avoid bacterial proliferation.
- These are used to avoid disturbing Hct and circulatory overload.
- This will also prevent the reaction caused by the donor antibodies.
- What are the uses of packed RBCs?
- This is indicated when the Hct needs to be increased without affecting blood volume, e.g., in anemia.
- What are the advantages of Packed cells over whole blood?
- This will minimize circulatory overload.
- This will reduce the reaction due to the donor antibodies.
- It will reduce the quality of anticoagulants and electrolytes transfused in whole blood.
- It will minimize the reaction due to plasma components.
What is the difference between whole blood and packed cells?
| Characteristic features | Packed cells | Whole blood |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cryoprecipitate:
- Cryoprecipitate is prepared from fresh frozen plasma; the material does not become liquid when fresh frozen plasma is slowly thawed, and the major part remains in a solid state.
- How is cryoprecipitate made?
- First, collect fresh frozen plasma.
- It is slowly thawed at 1 to 6 °C, allowing proteins to precipitate out.
- The precipitate is collected and frozen again for storage.
- What are the indications for cryoprecipitate?
- It is given in low fibrinogen (hypofibrinogenemia).
- It is given in DIC.
- In liver diseases with low clotting factors.
- Patients with massive bleeding or hemorrhage.
- What are the advantages of Cryoprecipitate?
- The significant advantage over fresh frozen plasma is the reduced volume of transfused fluid.
- Each unit contains around 150 mg of fibrinogen.
- Cryoprecipitate is suitable for treating von Willebrand’s disease and Hemophilia A.
- What are the contents of cryoprecipitate?
- Cryoprecipitate contains 50% of the factor VIII and von Willebrand factor activity.
- Fibrinogen and factor XIII are approximately 20% to 40% of the total.
Human serum albumin:
- This is prepared from normal human plasma.
- Human albumin is prepared by cold ethanol plasma fractionation and is available in concentrations of 5% or 25%.
- 25% albumin is stored at 2-8 °C and should not be frozen.
- 5% albumin is stored at room temperature, and the temperature should not exceed 37 °C and should not be frozen.
- The shelf life for both products is 3 years; expiry dates should not be ignored.
- Storage has no effect if it is stored at the proper temperature and used before the expiry dates.
- What are the uses of human albumin?
- It is used in the case of shock due to hemorrhage or surgery.
- This can be used as a fluid replacement during manual or automated therapeutic plasma exchange.
- In the case of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
- What are the complications of human albumin?
- The patient may have a pyogenic or allergic reaction.
- There may be a hypotensive reaction.
- The above S/S disappears when the infusion is slowed down or stopped.
- The patients may have dilutional anemia.
- It should not be given to patients with contraindications, such as a rapid increase in the volume, which can affect their health.
Gamma Globulin (Immune Serum Globulin):
- Immune serum globulins are stored at 2-8 °C for 2 years without any deterioration.
- What are the uses of immunoglobulins?
- These are given to boost passive immunity (passive antibody) and protect against exposure to some diseases.
- In congenital immune deficiency disorders.
- These immunoglobulins are effective in:
- Measles.
- Hepatitis A infection.
- Hypogammaglobulinemia.
Antihemophilic factor (Factor VIII concentrate):
- Factor VIII concentrate is obtained from the pooled fresh frozen plasma.
- This is available in lyophilized form and should be stored at 2-8 °C, avoiding freezing.
- This can be stored at room temperature for a short period.
- Cruprecipitate factor VIII is prepared from a single donation of fresh blood by cold precipitation.
- What are the uses of the antihemophilic factor VIII?
- This is used in the case of hemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency).
- In the cases of acquired factor VIII inhibitors.
Platelet-rich plasma or platelet concentrate:
- Platelet-rich plasma concentrate can be stored at room temperature for up to 72 hours with constant agitation.
- What is the Effect of storage?
- With time, there is a progressive decrease in hemostatic efficiency.
- After 72 hours, the pH falls to 6.0, at which point the platelets’ hemostatic activity is lost or decreased.
- Now, plastic bags (O2-diffusible) are available, allowing platelet activity to remain for 5 days.
- What are the uses of platelet concentrate?
- It is used to treat or prevent thrombocytopenia.
- These are used to treat bleeding disorders due to platelet functional disorders.
What are the Blood components and their indications?
| Components | Composition | Indications |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the effects of temperature on the storage of blood?
Questions and answers:
Question 1: What is the purpose of albumin transfusion?
Question 2: How much cryoprecipitate does one unit contain fibrinogen?

Sir please can u explain how to perform each of this test VDRL, HBS, HCV individually after blood donation